Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
AI Paper Weekly Report | A Special Report on cutting-edge Transformer Research, Analyzing the Latest Advances in Structural Sparsity, Memory Mechanisms, and Reasoning organization.

Over the past eight years, Transformer has almost reshaped the entire landscape of artificial intelligence research. Since Google proposed this architecture in "Attention Is All You Need" in 2017, the "attention mechanism" has gradually evolved from an engineering technique into a general paradigm for deep learning—from natural language processing to computer vision, from speech and multimodal computing to scientific computing, Transformer is becoming the de facto foundational model framework.
Industry players, represented by Google, OpenAI, Meta, and Microsoft, are constantly pushing the limits of scale and engineering, while universities such as Stanford, MIT, and Berkeley are consistently producing key results in theoretical analysis, structural improvements, and the exploration of new paradigms. As model size, training paradigms, and application boundaries continue to expand, research in the Transformer field is also showing a trend of high differentiation and rapid evolution—making a systematic review and selection of representative papers particularly necessary.
In order to let more users know the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence in academia, HyperAI's official website (hyper.ai) has now launched a "Latest Papers" section, which updates cutting-edge AI research papers every day.
* Latest AI Papers:https://go.hyper.ai/hzChCThis week, we've carefully selected 5 popular papers on Transformers for you.Teams from Peking University, DeepSeek, ByteDance Seed, Meta AI, and others are included. Let's learn together! ⬇️
This week's paper recommendation
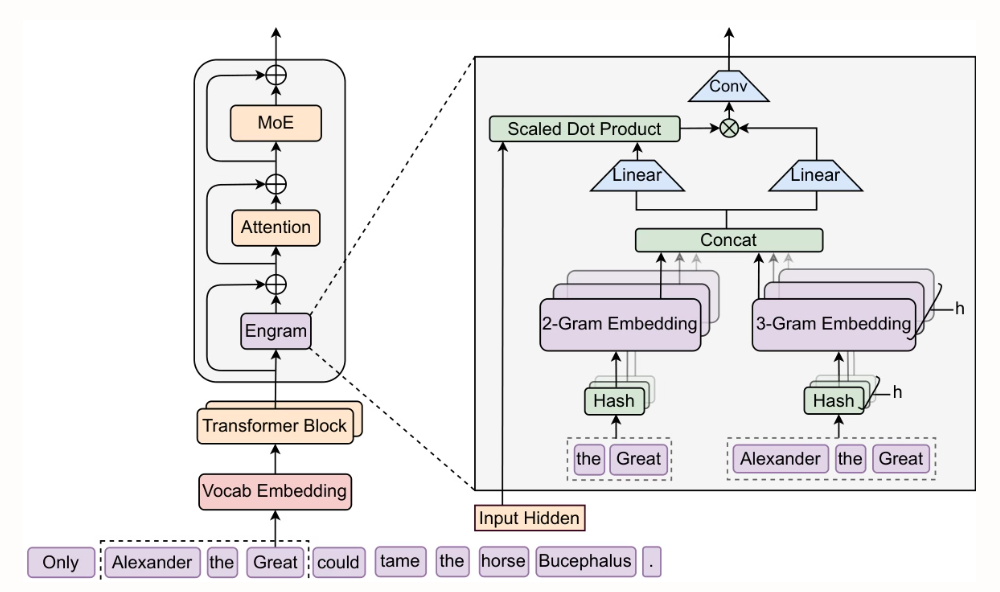
- Conditional Memory via Scalable Lookup: A New Axis of Sparsity for Large Language Models
Researchers from Peking University and DeepSeek-AI proposed Engram, a scalable conditional memory module with O(1) lookup complexity. By extracting it from the early layers of the static knowledge retrieval Transformer and complementing it with MoE, the early layers are freed up for deeper inference computation. Significant improvements are achieved on inference tasks (BBH +5.0, ARC-Challenge +3.7), code and math tasks (HumanEval +3.0, MATH +2.4), and long-context tasks (Multi-Query NIAH: 84.2 → 97.0), while maintaining the same number of parameters and the same number of FLOPs.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/SlcId
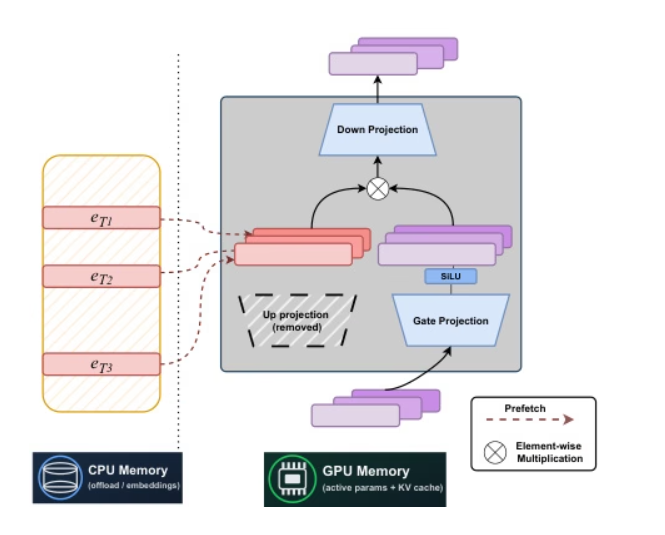
2. STEM: Scaling Transformers with Embedding Modules
Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and Meta AI have jointly proposed a static, label-index-based sparse architecture—STEM. By replacing the upprojection of FFN with intra-layer embedding lookup, stable training is achieved, reducing per-label FLOPs and parameter accesses by approximately one-third, and long-context performance is improved through scalable parameter activation. By decoupling capacity from computation and communication, STEM supports asynchronous prefetching for CPU offloading, leverages embeddings with large angular distributions to achieve higher knowledge storage capacity, and enables interpretable and editable knowledge injection without modifying the input text. In knowledge and reasoning benchmarks, it achieves performance improvements of up to approximately 3–41 TP3T compared to dense baselines.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/NPuoj
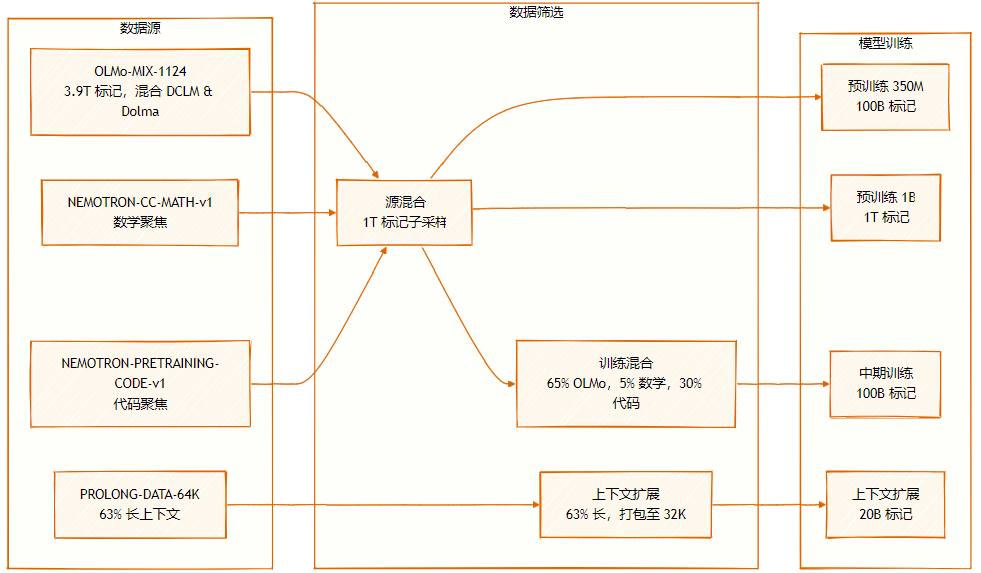
The dataset consists of multiple sources: OLMo-MIX-1124 (3.9T labeled), a mixture of DCLM and Dolma1.7; NEMOTRON-CC-MATH-v1 (mathematics-oriented); and NEMOTRON-PRETRAINING-CODE-v1 (code-oriented).
3. SeedFold: Scaling Biomolecular Structure Prediction
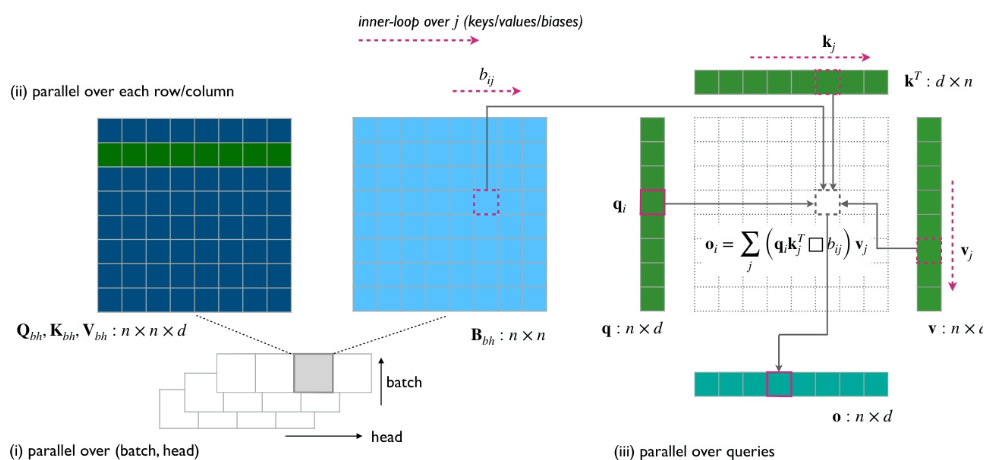
ByteDance's Seed team proposed SeedFold, a scalable biomolecular structure prediction model. It increases model capacity by expanding the width of the Pairformer, reduces computational complexity by using a linear triangular attention mechanism, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on FoldBench using a distillation dataset containing 26.5 million samples, while also surpassing AlphaFold3 on protein-related tasks.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/9zAID
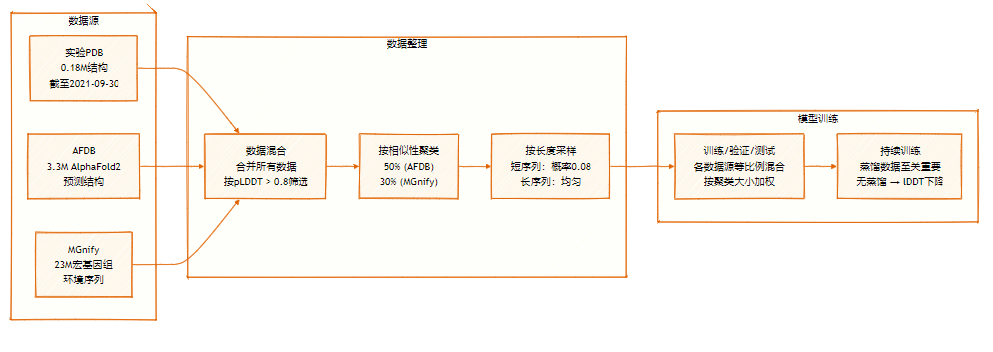
The SeedFold dataset contains 26.5 million samples, expanded by large-scale data distillation from two main sources: the experimental dataset (0.18M) and the distilled dataset from AFDB and MGnify.
4. Are Transformers Effective for Time Series Forecasting?
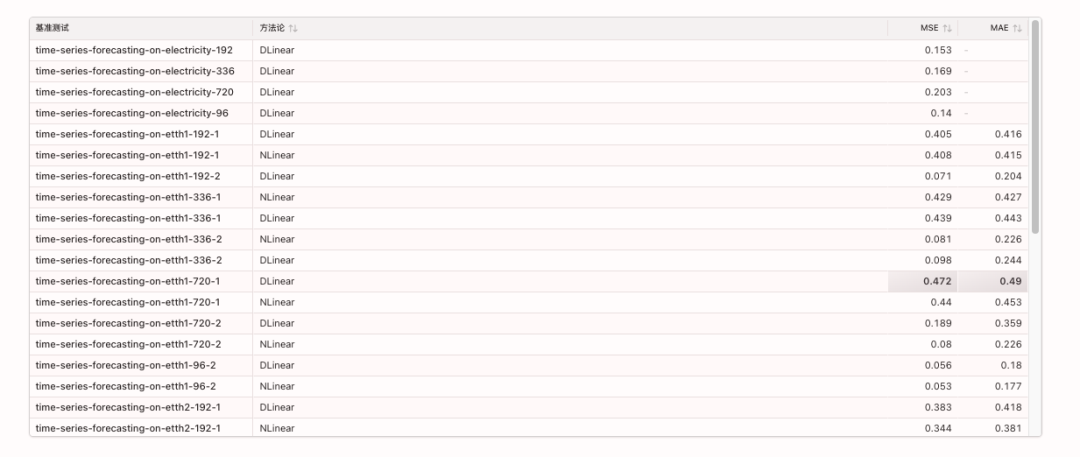
This paper finds that despite the rapid rise in popularity of Transformers in time series prediction, the permutation invariance of its self-attention mechanism leads to the loss of crucial temporal information. Through comparative experiments, simple single-layer linear models significantly outperform complex Transformer models on multiple real-world datasets. This finding challenges existing research directions and calls for a reassessment of the effectiveness of Transformers in time series tasks.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/Hk05h
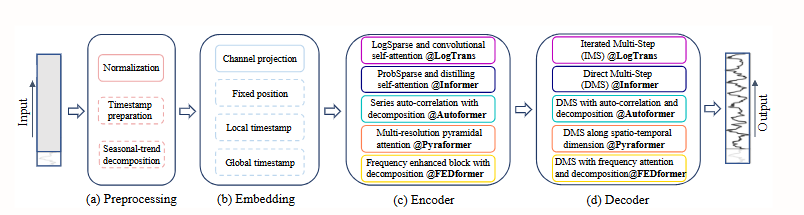
The relevant benchmarks are as follows:
5. Reasoning Models Generate Societies of Thought
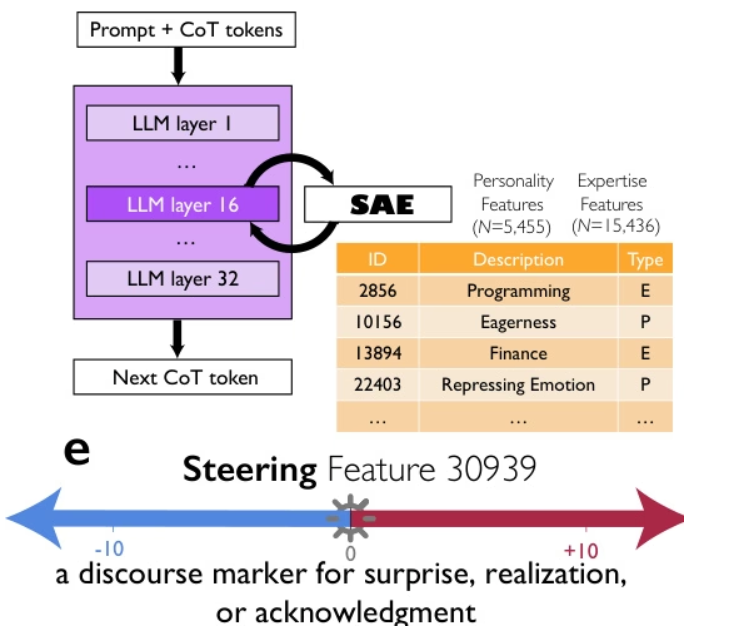
Researchers from Google, the University of Chicago, and the Santa Fe Institute propose that the superior performance of advanced reasoning models like DeepSeek-R1 and QwQ-32B is not merely due to longer thought chains, but rather through implicitly simulating a "society of thoughts"—a multi-agent-like dialogue between diverse perspectives with different personalities and expertise within the model. Through mechanistic interpretability and controlled reinforcement learning, they demonstrate a causal relationship between conversational behaviors (such as questioning, conflict, and reconciliation) and perspective diversity with accuracy, where guiding the utterance marker of "surprise" can double reasoning performance. This social organization of thoughts enables systematic exploration of the solution space, suggesting that the principles of collective intelligence—diversity, debate, and role coordination—are a core foundation for effective artificial reasoning.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/0oXCC
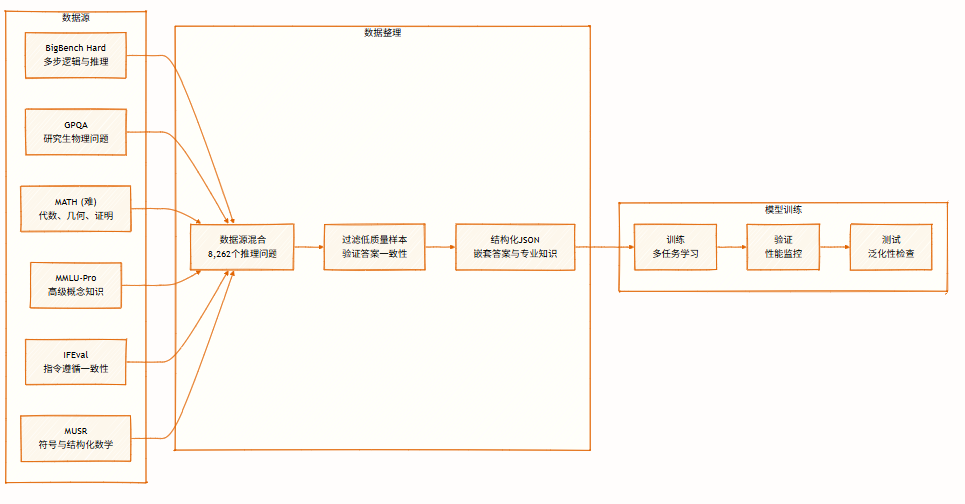
The dataset contains 8,262 reasoning problems from multiple domains, covering symbolic logic, mathematical solving, scientific reasoning, instruction following, and multi-agent reasoning. It supports multi-perspective reasoning and is used for training and evaluating models.
The above is all the content of this week’s paper recommendation. For more cutting-edge AI research papers, please visit the “Latest Papers” section of hyper.ai’s official website.
We also welcome research teams to submit high-quality results and papers to us. Those interested can add the NeuroStar WeChat (WeChat ID: Hyperai01).
See you next week!