Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Unveiling AI Inference: OpenAI's Sparse Model Makes Neural Networks Transparent for the First Time; Calories Burnt Prediction: Injecting Precise Energy Data Into Fitness Models

Original article by Lin Jiamin HyperAIJanuary 14, 2026, 17:06Beijing
In recent years, large language models have made rapid progress in their capabilities, but their internal decision-making processes remain a deeply entangled "black box," difficult to trace and understand. This fundamental problem seriously hinders the reliable application of AI in high-risk fields such as healthcare and finance.How to make the thought process of a model transparent and traceable remains a key unresolved issue.
Based on this,OpenAI released Circuit Sparsity, a 0.4B parameter large language model, in December 2025. It uses circuit sparsity technology to reset 99.9% weights to zero, constructing an interpretable sparse computation architecture.Breaking through the "black box" decision-making limitations of traditional Transformers, this model enables the AI inference process to be analyzed layer by layer. At its core, it transforms traditional dense neural networks into structured sparse "circuits" through a unique training method.
*Dynamic forced sparsityUnlike traditional methods, it performs "dynamic pruning" at every step of training, retaining only a very small number of weights with the largest absolute value (such as 0.1%) in each round, and forcing the rest to be zero, thus forcing the model to learn to work under minimal connectivity from the beginning.
*Activate sparsityBy introducing activation functions at key locations such as attention mechanisms, the output of neurons tends to a discrete state of "either/or", thereby forming clear information channels in sparse networks.
*Customized componentsRMSnorm is used instead of LayerNorm to prevent the destruction of sparsity; and a Bigram lookup table is introduced to handle simple word prediction, allowing the main network to focus more on complex logic.
The model trained using the above method spontaneously forms functionally defined and resolvable "circuits." Each circuit is responsible for a specific subtask. Researchers can clearly identify that some neurons are specifically used to detect "single quotes," while others act as logical "counters." Compared to traditional dense models, the number of active nodes required to complete the same task is significantly reduced.Its accompanying "bridge network" technology attempts to map the interpretations obtained from sparse circuits back to high-performance dense models such as GPT-4, and also provides a potential tool for analyzing existing large models.
The HyperAI website now features "Circuit Sparsity: OpenAI's New Open Source Sparse Model," so come and try it out!
Online use:https://go.hyper.ai/WgLQc
A quick overview of hyper.ai's official website updates from January 5th to January 9th:
* High-quality public datasets: 8
* A selection of high-quality tutorials: 4
* This week's recommended papers: 5
* Community article interpretation: 5 articles
* Popular encyclopedia entries: 5
* Top conferences with deadlines in January: 9
Visit the official website:hyper.ai
Selected public datasets
1. MCIF Multimodal Cross-Language Instruction Following Dataset
MCIF is a multilingual, multimodal, manually annotated evaluation dataset based on scientific speeches, released in 2025 by Fondazione Bruno Kessler in collaboration with the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology and Translated. It aims to evaluate the ability of multimodal large language models to understand and execute instructions in cross-linguistic scenarios, as well as their ability to integrate speech, visual, and textual information for reasoning.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/SyUiL
2. TxT360-3efforts Multi-Task Inference Dataset
TxT360-3efforts is a massively large-scale language model training dataset for supervised fine-tuning (SFT), released by Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence in 2025. It is designed to control three inference strengths of the model through chat templates.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/fMEbf
3. X-ray Contraband Detection Dataset
The X-ray Contraband Detection Dataset is a dataset released in 2025 by South China Normal University in collaboration with Hong Kong Polytechnic University and the University of Saskatchewan. It is designed to improve the detection capabilities of detection models in complex and crowded security images, especially addressing real-world problems such as class imbalance and sample scarcity.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/ppXub
4. MCD-rPPG Multi-camera Remote Photoplethysmography Dataset
MCD-rPPG is a multi-camera video dataset released by Sber AI Lab in 2025. The dataset consists of synchronized videos and biosignal data taken by 600 subjects in different states, and is designed to perform remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) and health biomarker estimation.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/6KY40
5. LongBench-Pro Long Context Comprehensive Evaluation Dataset
LongBench-Pro is a dataset for evaluating long-context language models, designed to systematically assess a model's ability to understand and process long texts under different context lengths, task types, and runtime conditions.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/7esQI
6. Human Faces dataset
Human Faces is a dataset released in 2025 for computer vision tasks related to faces. It aims to provide high-quality, well-structured image data support for applications such as face recognition, detection, expression analysis, and generative modeling.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/9WlDl

7. Calories Burnt Prediction Dataset
Calories Burnt Prediction is a supervised learning dataset for predicting exercise energy expenditure. It aims to use an individual's physiological characteristics and exercise status information to predict the number of calories burned during a workout.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/o6X59
8. MapTrace Path Tracing Dataset
MapTrace is a large-scale synthetic map path tracing dataset released by Google in collaboration with the University of Pennsylvania in 2025. The dataset aims to improve the fine-grained spatial reasoning and path planning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in map scenes. The core objective is to train models to generate pixel-accurate, continuous, and walkable paths from the origin to the destination.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/BGHUu
Selected Public Tutorials
1. Circuit Sparsity: OpenAI's New Open Source Sparse Model
Circuit-sparsity is a 0.4B parameter large language model released by OpenAI. It employs circuit sparsity technology, resetting 99.9% weights to zero to construct an interpretable sparse computational architecture. This breaks through the "black box" decision-making limitations of traditional Transformers, allowing AI inference to be analyzed layer by layer. The Streamlit toolkit released with the model provides "activation bridge" technology, enabling researchers to trace internal signal paths, analyze the corresponding circuits, and compare the performance differences between sparse and dense models.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/zui8w
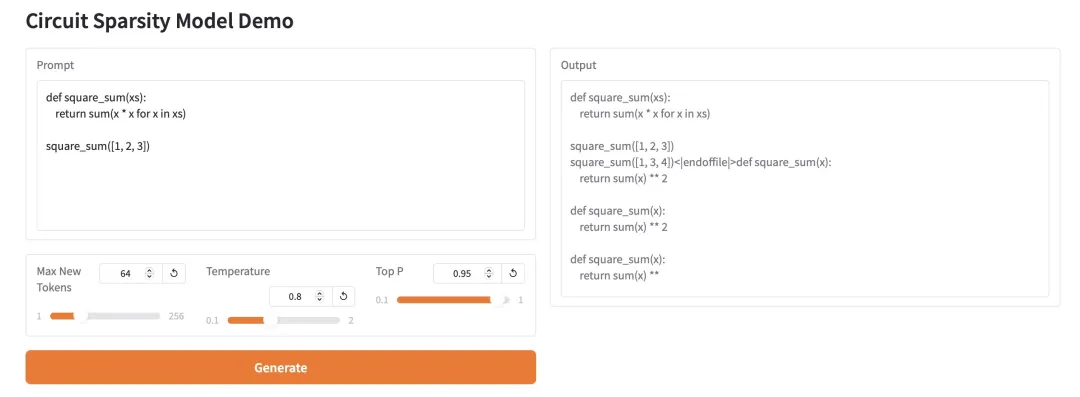
2. HY-MT1.5-1.8B: Multilingual Neural Machine Translation Model
HY-MT1.5-1.8B is a multilingual machine translation model with 1.8 billion parameters released by Tencent's Hunyuan team. Based on the unified Transformer architecture, it supports mutual translation between 33 languages and 5 ethnic languages/dialects, and is optimized for real-world scenarios such as mixed languages and terminology control. While achieving translation quality close to that of the 7B model, this model has only one-third the number of parameters, supports quantitative deployment and integration with the HuggingFace ecosystem, and is suitable for efficient and low-cost online multilingual translation services.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/I0pdR
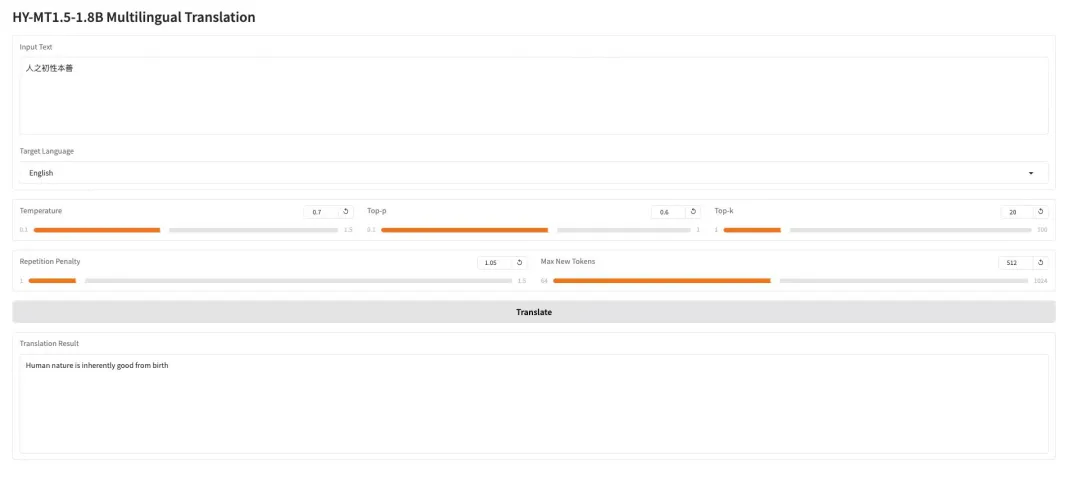
3. AWPortrait-Z Portrait Art LoRA
AWPortrait-Z is a portrait enhancement model based on LoRA technology. As a plugin, it integrates with mainstream text-based image diffusion models, significantly improving the realism and photographic quality of generated portraits without requiring retraining of the base model. This model specifically optimizes the rendering of facial structure, skin texture, and lighting, resulting in more natural and refined effects, suitable for portrait creation and image compositing that require photographic realism.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/wRjIp
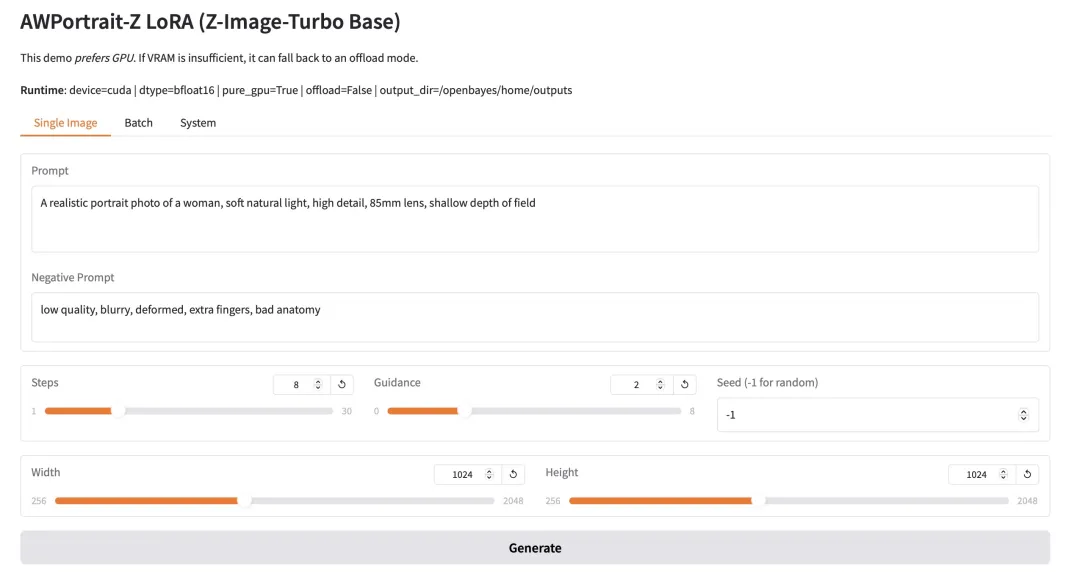
4. Granite-4.0-h-small: A one-stop platform for multilingual dialogue and coding tasks.
Granite-4.0-h-small is a 3.2 billion parameter long context instruction fine-tuning model released by IBM. It is based on a base model, integrates open-source and synthetic data, and employs supervised fine-tuning, reinforcement learning alignment, and model merging techniques. This model boasts excellent instruction compliance and tool invocation capabilities, uses a structured dialogue format, and is optimized for high-efficiency enterprise-level applications.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/1HhB9
This week's paper recommendation
1. mHC: Manifold-constrained hyperconnection
This paper proposes Manifold-Constrained Hyper-Connections (mHC), a general framework that restores the identity mapping property of HC by projecting the residual connection space of HC onto a specific manifold, while ensuring computational efficiency through rigorous infrastructure optimization. Experimental results demonstrate that mHC performs exceptionally well in large-scale training, delivering not only tangible performance improvements but also exhibiting remarkable scalability. We anticipate that, as a flexible and practical extension of HC, mHC will contribute to a deeper understanding of topology design and provide promising new directions for the evolution of basic models.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/ZePnH
2. Youtu-LLM: Unleashing the potential of native intelligent agents in lightweight large language models
The authors propose Youtu-LLM, a lightweight language model with 1.96 billion parameters developed by the Youtu-LLM team. By pre-training from scratch using a "common sense-STEM-agent" principle curriculum, it achieves state-of-the-art performance among sub-2 billion parameter models. This model integrates a compact multi-latency attention architecture, a STEM-oriented tokenizer, and a scalable pipeline to generate high-quality agent trajectory data in fields such as mathematics, programming, deep research, and tool use. This enables the model to internalize native planning, reflection, and action capabilities, significantly outperforming larger models in agent benchmarks while maintaining strong general reasoning and long-contextuality capabilities.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/gitUc
3. Youtu-LLM: Unleashing the potential of native intelligent agents in lightweight large language models
This paper first elucidates the definition and function of memory by tracing its evolution from cognitive neuroscience to large language models and then to intelligent agents. Subsequently, it compares and analyzes the classification system, storage mechanism, and complete management lifecycle of memory from both biological and artificial perspectives. Based on this, it systematically reviews current mainstream intelligent agent memory evaluation benchmarks. Furthermore, this paper explores the security issues of memory systems from both attack and defense perspectives. Finally, it looks forward to future research directions, focusing on the construction of multimodal memory systems and skill acquisition mechanisms.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/01H6H
4. Let Thought Flow: Building Intelligent Agents in the Context of Rock Music, and Creating the ROME Model within an Open Intelligent Agent Learning Ecosystem.
The authors propose ROME, an open-source agent model based on the Agenetic Learning Ecosystem (ALE). This framework integrates ROCK's sandbox orchestration, ROLL's post-training optimization, and iFlow CLI's context-aware agent execution. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on Terminal-Bench 2.0 and SWE-bench Verified by assigning credits to semantic interaction blocks through a novel policy optimization algorithm (IPA), and supports real-world deployment, thereby building scalable, secure, and production-ready agent workflows.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/UaAXZ
5. IQuest-Coder-V1 Technical Report
This paper proposes a novel family of Large Language Models (LLMs), the IQuest-Coder-V1 series (7B/14B/40B/40B-Loop). Unlike traditional static code representations, the authors propose a multi-stage training paradigm based on code flow, dynamically capturing the evolution of software logic at different stages of the pipeline. The model is constructed through an evolutionary training pipeline. The release of the IQuest-Coder-V1 series will significantly advance research progress in autonomous code intelligence and real-world intelligent agent systems.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/DBYN7
More AI frontier papers:https://go.hyper.ai/iSYSZ
Community article interpretation
1. Generating 18,000 years of climate data, NVIDIA and others proposed long-distance distillation, enabling long-term weather forecasting with only a single-step calculation.
A research team from NVIDIA Research, in collaboration with the University of Washington, has introduced a new method for long-range distillation. The core idea is to use an autoregressive model, adept at generating realistic atmospheric variability, as a "teacher" to generate massive amounts of synthetic meteorological data through low-cost, rapid simulation. This data is then used to train a probabilistic "student" model. The student model generates long-term forecasts with a single-step computation, avoiding the accumulation of iterative errors and bypassing the complex data calibration challenges. Preliminary experiments show that the student model trained in this way performs comparably to the ECMWF integrated forecast system in S2S forecasting, and its performance continues to improve with increasing synthetic data volume, promising more reliable and economical climate-scale predictions in the future.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/Ljebq
2. Jensen Huang's latest speech: 5 innovations, Rubin performance data revealed for the first time; diversified open source, covering Agent/Robot/Autonomous Driving/AI4S
At the start of the new year, CES 2026 (Consumer Electronics Show), often referred to as the "Tech Spring Festival Gala," kicked off in Las Vegas, USA. Although Jensen Huang was not on the official CES keynote list, he was still busy making appearances at various events. Of particular note was his personal presentation at NVIDIA LIVE. In his recently concluded presentation, Huang, dressed in his signature black leather jacket, further introduced the Rubin platform, which incorporates five innovations, and released several open-source achievements. Specifically: the NVIDIA Nemotron series for Agentic AI; the NVIDIA Cosmos platform for Physical AI; the NVIDIA Alpamayo series for autonomous driving research; the NVIDIA Isaac GR00T for robotics; and NVIDIA Clara for the biomedical field.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/YMK1J
3. Bezos, Bill Gates, Nvidia, Intel, and others have made bets; NASA engineers are leading a team to create a general-purpose robotic brain, and the company is valued at $2 billion.
While large models can "grow infinitely" from the internet, image libraries, and massive amounts of text, robots are trapped in another world—real-world data is extremely scarce, expensive, and non-reusable. Addressing the constraints of insufficient data scale and limited structure in the physical world, FieldAI has chosen a different approach than the mainstream perception-first strategy. It builds a general-purpose robot intelligence system centered on physical constraints from the ground up, aiming to enhance robots' generalization and autonomy in real-world environments.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/9T1rE
4. Full Replay | Shanghai Chuangzhi/TileAI/Huawei/Advanced Compiler Lab/AI9Stars Deep Dive into AI Compiler Technology Practice
Amidst the ever-evolving wave of AI compiler technology, numerous explorations are taking place, accumulating insights, and converging. The eighth session of Meet AI Compiler was held on December 27th against this backdrop. This session invited five experts from Shanghai Innovation Academy, TileAI Community, Huawei HiSilicon, Advanced Compiler Lab, and AI9Stars to share their insights across the entire technology chain, from software stack design and operator development to performance optimization. The speakers, drawing on their teams' long-term research, demonstrated the implementation methods and trade-offs of different technical approaches in real-world scenarios, giving abstract concepts a more concrete foundation.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/8ytqF
5. Achieving highly selective substrate design: MIT and Harvard discover novel protease cleavage patterns using generative AI.
MIT and Harvard University have jointly proposed CleaveNet, an AI-based end-to-end design process that aims to revolutionize the existing paradigm of protease substrate design by working in tandem with predictive and generative models, providing entirely new solutions for related basic research and biomedical development.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/tcYYZ
Popular Encyclopedia Articles
1. Human-machine loop (HITL)
2. Super-reciprocal sorting fusion RRF
3. Embodied Navigation
4. Multilayer Perceptron
5. Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Here are hundreds of AI-related terms compiled to help you understand "artificial intelligence" here:
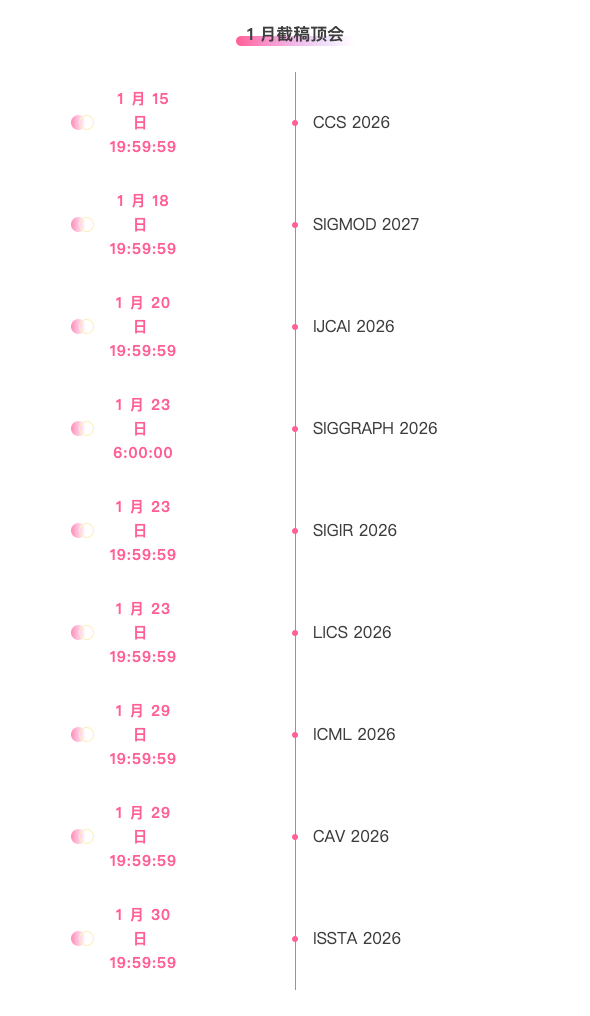
One-stop tracking of top AI academic conferences:https://go.hyper.ai/event
The above is all the content of this week’s editor’s selection. If you have resources that you want to include on the hyper.ai official website, you are also welcome to leave a message or submit an article to tell us!
See you next week!








