Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
AI Paper Weekly Report | Cutting-Edge OCR Technology Interpretation: DeepSeek, Tencent, and Baidu Compete on the Same Stage, From Character Recognition to Structured Document Parsing

Over the past few years, OCR (Optical Character Recognition) has been rapidly evolving from a "character recognition tool" to...A general document understanding system based on a vision-language modelWhile global companies like Microsoft and Google continue to invest, leading Chinese vendors such as Baidu, Tencent, and Alibaba Cloud are also making intensive deployments, driving the market to rapidly upgrade from rule-driven OCR to intelligent document processing (IDP) that integrates artificial intelligence and natural language processing, and continuously deepening its application in real business scenarios such as finance, government affairs, and healthcare.
Driven by continued industry demand, the focus of OCR research has also changed significantly:The model no longer only pursues "recognition accuracy", but has begun to systematically solve more challenging problems such as complex layouts, multimodal symbols, long context modeling, and end-to-end semantic understanding.How to efficiently encode two-dimensional visual information, more efficiently parse text information, and how to make the reading order of the model closer to human cognitive logic are becoming core issues of common concern to academia and industry.
Against this backdrop of high interaction, continuously tracking and analyzing the latest OCR academic papers is particularly crucial for grasping the cutting-edge direction of technology, understanding the real challenges of the industry, and even finding the next stage of paradigm breakthroughs.
This week, we recommend 5 popular AI papers on OCR.It includes teams from DeepSeek, Tencent, Tsinghua University, and others. Let's learn together! ⬇️
In addition, to allow more users to understand the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence in academia, the HyperAI website (hyper.ai) has launched a "Latest Papers" section, which is updated daily with cutting-edge AI research papers.
Latest AI Papers:https://go.hyper.ai/hzChC
This week's paper recommendation
- DeepSeek-OCR 2: Visual Causal Flow
Building upon DeepSeek-OCR, DeepSeek-AI researchers have proposed DeepSeek-OCR 2. If DeepSeek-OCR was a preliminary exploration of the feasibility of compressing long contexts through two-dimensional optical mapping, then DeepSeek-OCR 2 aims to explore the feasibility of a novel encoder—DeepEncoderV2—dynamically rearranging visual tokens driven by image semantics. DeepEncoder V2 is designed to endow the encoder with causal reasoning capabilities, enabling it to intelligently rearrange visual tokens before LLM-based content understanding, replacing rigid raster scanning processing. This achieves more human-like, semantically coherent image understanding, enhancing OCR and document analysis capabilities.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/ChW45
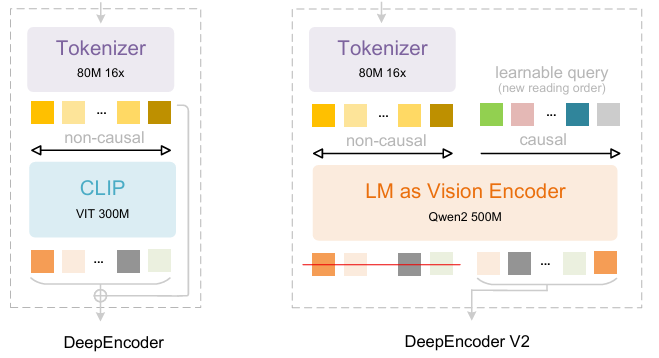
The training dataset consists of OCR 1.0, OCR 2.0, and general vision data, with OCR data accounting for 80% of the mixed training data. For evaluation, OmniDocBench v1.5 was used, a benchmark containing 1,355 pages of Chinese and English documents, covering journals, academic papers, and research reports across nine categories.
2. LightOnOCR: A 1B End-to-End Multilingual Vision-Language Model for State-of-the-Art OCR
LightOn researchers have released LightOnOCR-2-1B, a compact 1 billion-parameter multilingual visual-language model that extracts clean, ordered text directly from document images, outperforming larger models. It also enhances image localization capabilities through RLVR and improves robustness through checkpoint merging. The model and benchmarks are open source.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/zXFQs
One-click deployment tutorial link:https://go.hyper.ai/vXC4o
The LightOnOCR-2-1B dataset combines teacher-annotated pages from multiple sources, including scanned documents to enhance robustness and supplementary data for layout diversity. It includes cropped regions (paragraphs, headings, abstracts) annotated with GPT-4o, blank page examples to suppress illusions, and TeX-derived supervision obtained from arXiv via the nvpdftex pipeline. Public OCR datasets have been added to increase diversity.
3. HunyuanOCR Technical Report
This paper proposes HunyuanOCR, an open-source vision-language model with 1 billion parameters developed by Tencent and its collaborators. Through data-driven training and a novel reinforcement learning strategy, it adopts a lightweight architecture (ViT-LLM MLP adapter) to unify end-to-end OCR capabilities, including text localization, document parsing, information extraction, and translation. Its performance surpasses that of larger models and commercial APIs, enabling efficient deployment in industrial and scientific research applications.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/F9fni
One-click deployment tutorial link:https://go.hyper.ai/C4srs

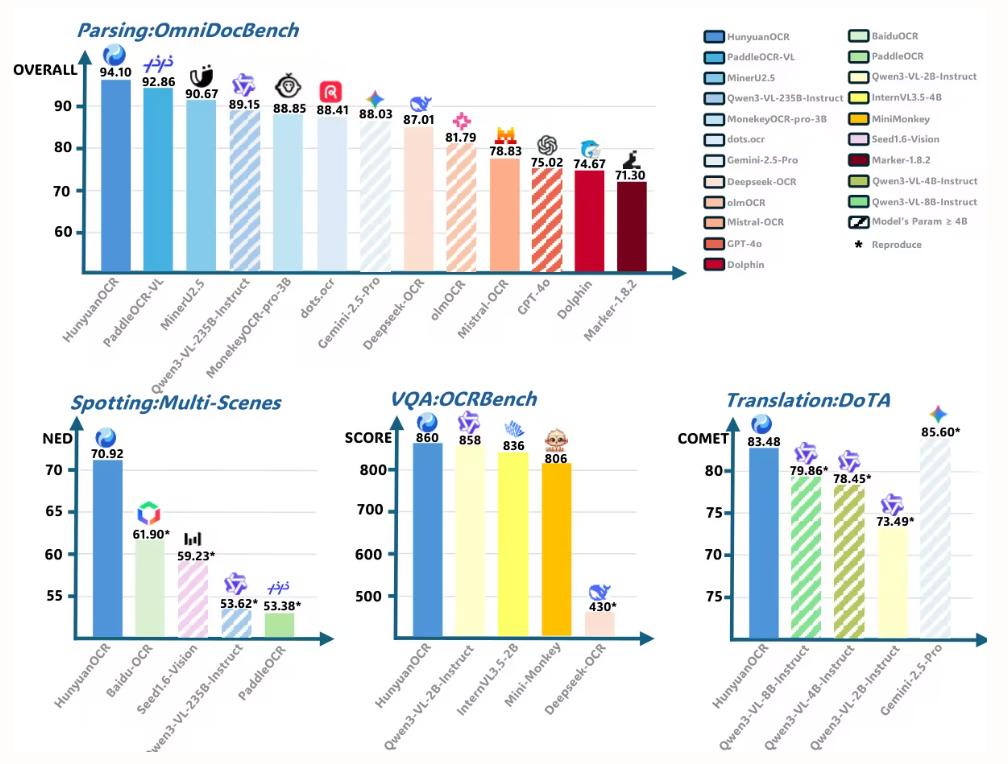
This paper uses HunyuanOCR to evaluate document parsing performance on OmniDocBench. It achieves the highest total score of 94.10, surpassing all other models (including larger ones).
4 .PaddleOCR-VL: Boosting Multilingual Document Parsing via a 0.9B Ultra-Compact Vision-Language Model
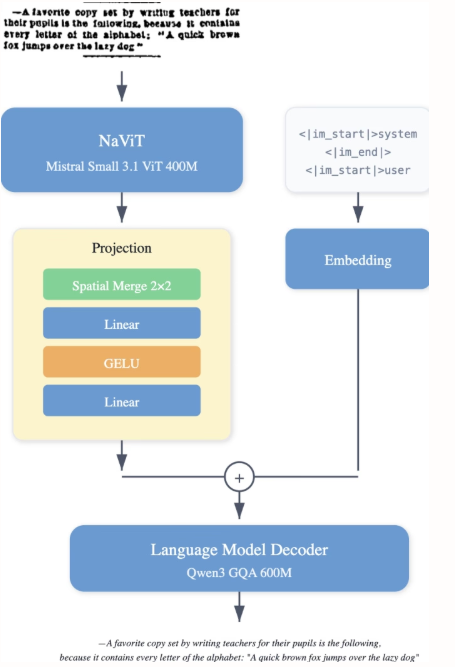
Baidu's team proposed PaddleOCR-VL, a resource-efficient vision-language model that integrates a NaViT-style dynamic resolution encoder with the ERNIE-4.5-0.3B model. It achieves state-of-the-art performance in multilingual document parsing, accurately recognizing complex elements such as tables and formulas. While maintaining fast reasoning capabilities, it outperforms existing solutions and is suitable for deployment in real-world scenarios.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/Rw3ur
One-click deployment tutorial link:https://go.hyper.ai/5D8oo
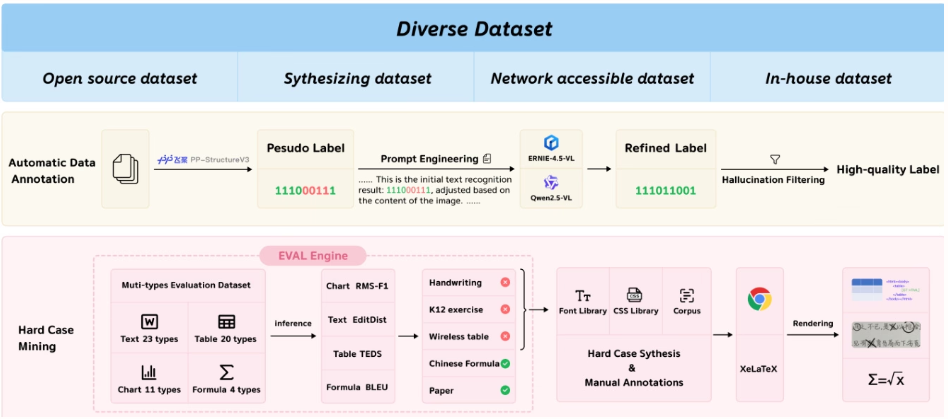
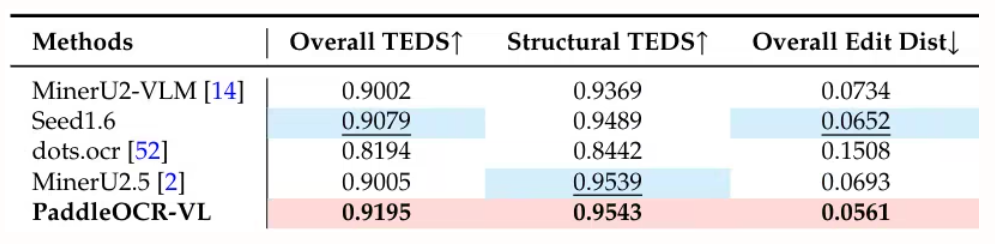
This study evaluated page-level document parsing on OmniDocBench v1.5, olmOCR-Bench, and OmniDocBench v1.0. It achieved a state-of-the-art overall score of 92.86 on OmniDocBench v1.5, which is better than MinerU2.5-1.2B (90.67). It also led in text (edit distance 0.035), formulas (CDM 91.22), tables (TEDS 90.89 and TEDS-S 94.76) and reading order (0.043).
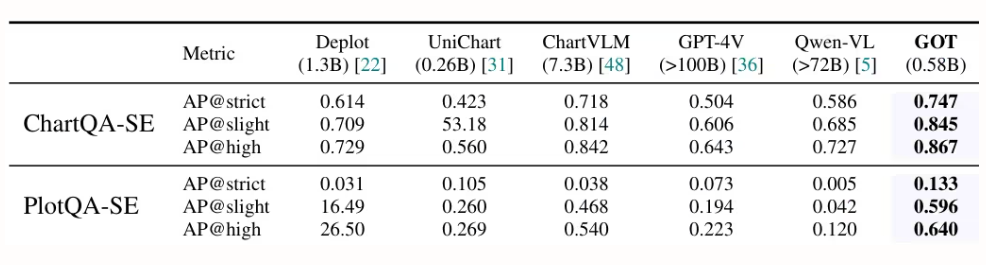
5. General OCR Theory: Towards OCR-2.0 via a Unified End-to-end Model
Researchers from StepFun, Megvii Technology, the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Tsinghua University proposed GOT, a unified end-to-end OCR-2.0 model with 580 million parameters. Through a high-compression encoder and a long context decoder, it extends recognition capabilities from text to a variety of artificial optical signals—such as mathematical formulas, tables, charts, and geometric figures. It supports slice/full-page input, formatted output (Markdown/TikZ/SMILES), interactive region-level recognition, dynamic resolution, and multi-page processing, significantly advancing the development of intelligent document understanding.
Paper and detailed interpretation:https://go.hyper.ai/9E6Ra
One-click deployment tutorial link:https://go.hyper.ai/HInRr
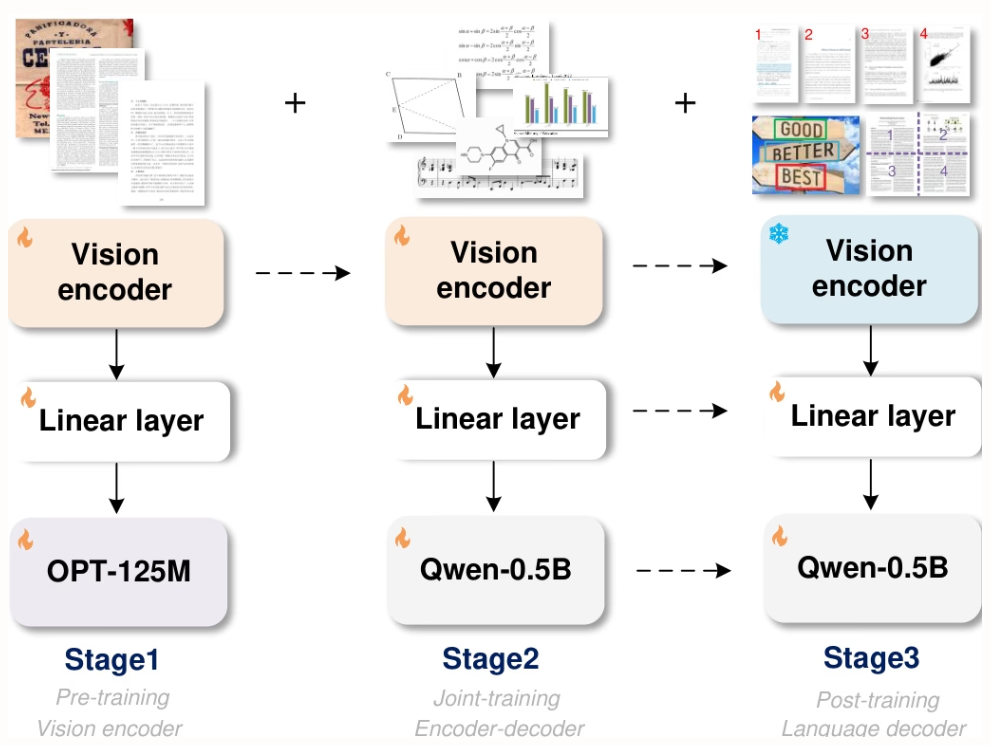
The experiments in this paper were conducted on an 8×8 L40s GPU and three stages of training were performed: pre-training (3 rounds, batch size 128, learning rate 1e-4), joint training (1 round, maximum token length 6000), and post-training (1 round, maximum token length 8192, learning rate 2e-5). The first stage retained 80% of data to maintain performance.
The above is all the content of this week’s paper recommendation. For more cutting-edge AI research papers, please visit the “Latest Papers” section of hyper.ai’s official website.
We also welcome research teams to submit high-quality results and papers to us. Those interested can add the NeuroStar WeChat (WeChat ID: Hyperai01).
See you next week!