Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
AI Paper Weekly Roundup | Attention Mechanism / NVIDIA VLA Model / TTS Model / Graph Neural Networks... A Comprehensive Overview of the Latest AI Developments

Visual language models (VLMs) and visual language architectures (VLAs) have been widely used in the field of autonomous driving. However, most existing methods have obvious limitations: they either lack explicit reasoning mechanisms or perform reasoning in a free and unstructured manner, making it difficult for the models to generalize beyond the training data distribution.
Nvidia has introduced Alpamayo-R1 (AR1), a vision-action (VA) model with structured reasoning capabilities. Extending the previously proposed Alpamayo-VA model, AR1 enhances decision-making in complex driving scenarios by connecting reasoning and action prediction, thus supporting general autonomous driving. By combining interpretable reasoning with precise control, AR1 demonstrates a practical path towards Level 4 autonomous driving.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/Q15y9
Latest AI Papers:https://go.hyper.ai/hzChC
In order to let more users know the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence in academia, HyperAI's official website (hyper.ai) has now launched a "Latest Papers" section, which updates cutting-edge AI research papers every day.Here are 5 popular AI papers we recommend, let’s take a quick look at this week’s cutting-edge AI achievements⬇️
This week's paper recommendation
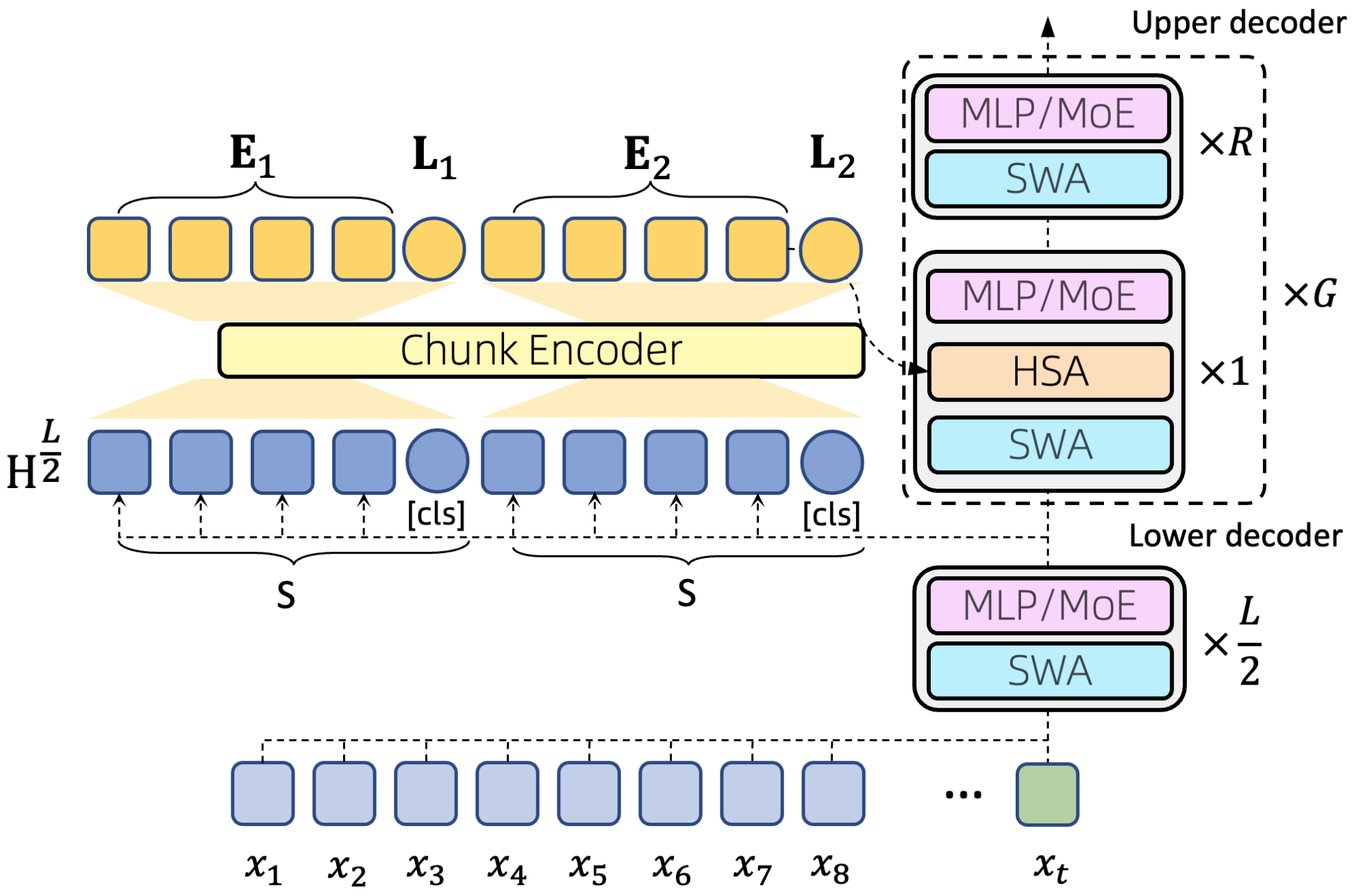
1. Every Token Counts: Generalizing 16M Ultra-Long Context in Large Languag Models
This paper explores the challenge of building "machines that can remember," defining the long-term memory problem as the problem of efficiently modeling ultra-long contexts. Researchers argue that achieving this goal requires three key properties: sparsity, flexibility in random access, and length generalization ability. To address the challenge of modeling ultra-long contexts, this paper introduces a novel attention mechanism—Hierarchical Sparse Attention (HSA)—which simultaneously satisfies the above three properties. Integrating HSA into the Transformer architecture, researchers constructed a hybrid expert (MoE) model, HSA-UltraLong, with 8 billion parameters.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/axKy6
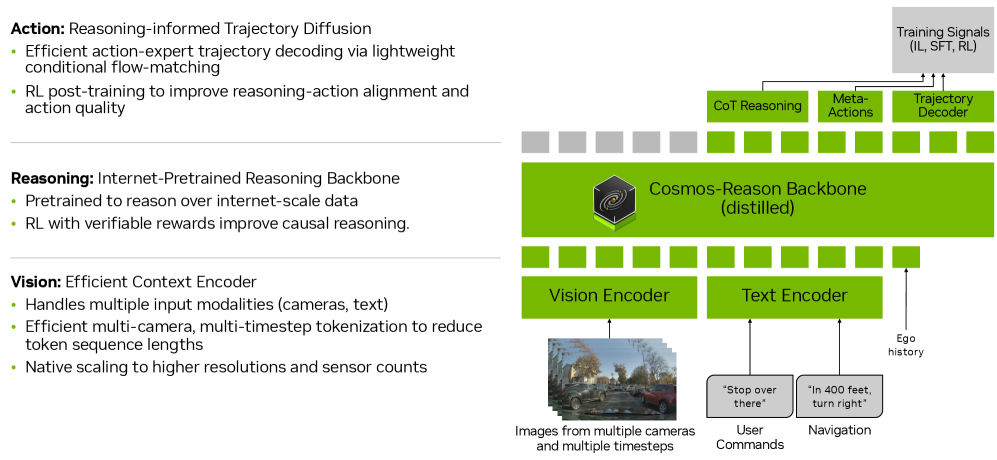
2. Alpamayo-R1
Title: Alpamayo-R1: Bridging Reasoning and Action Prediction for Generalizable Autonomous Driving in the Long Tail
This paper proposes Alpamayo-R1 (AR1), a vision-language-action (VLA) model that integrates causal reasoning and trajectory planning to improve decision-making capabilities in complex driving scenarios. Evaluation results show that, compared to a baseline model that relies solely on trajectory, this model achieves a planning accuracy improvement of up to 121 TP3T in complex scenarios; in closed-loop simulations, the vehicle deviates from the road by 351 TP3T and the close encounter rate decreases by 251 TP3T. By fusing interpretable reasoning with precise control, AR1 provides a feasible technical path to achieving Level 4 autonomous driving.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/Q15y9
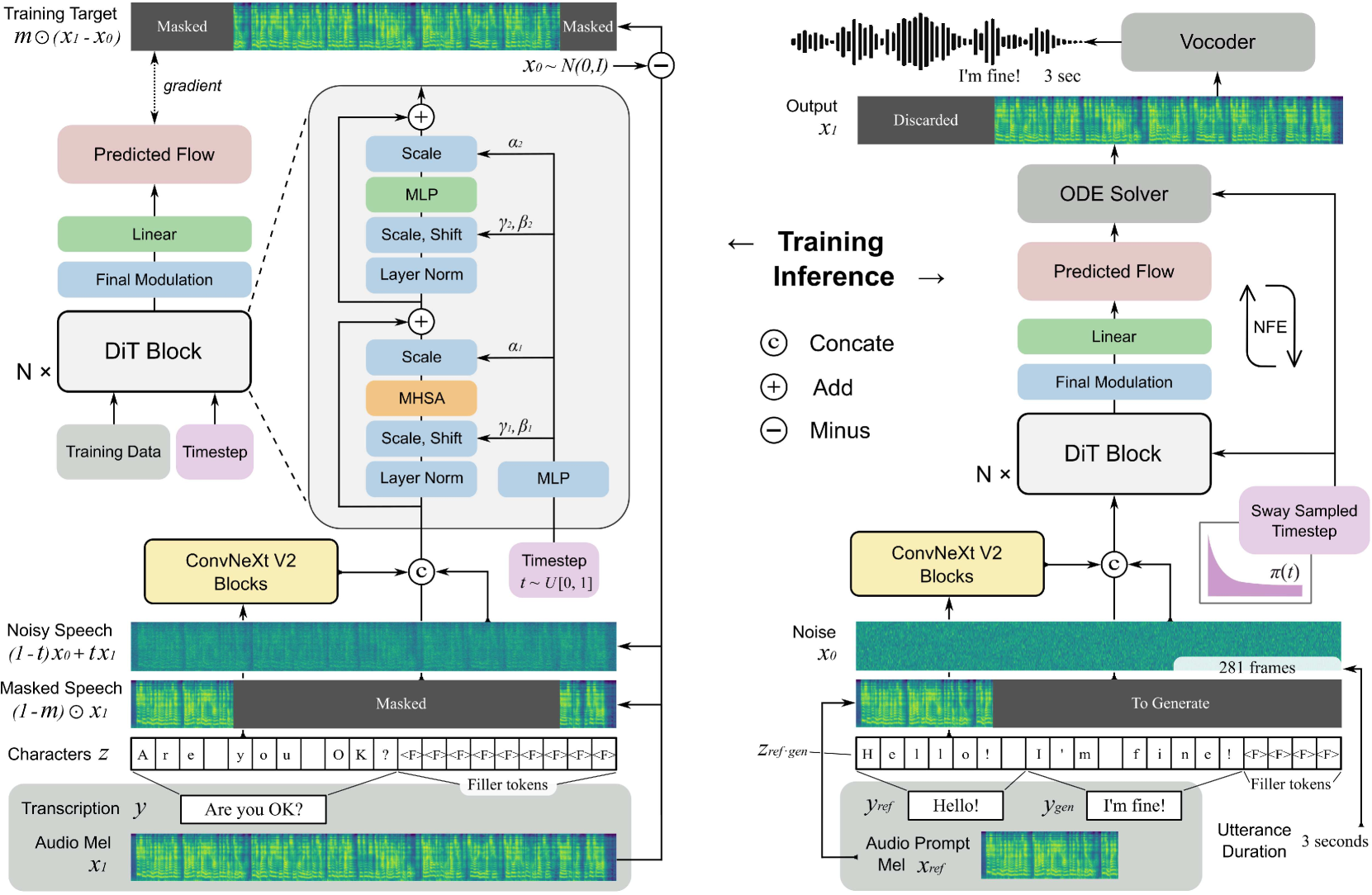
3. F5-TTS: A Fairytaler that Fakes Fluent and Faithful Speech with Flow Matching
This paper proposes F5-TTS, a fully non-autoregressive text-to-speech (TTS) system based on flow matching and Diffusion Transformer (DiT). After training on a publicly available 100,000-hour multilingual dataset, F5-TTS demonstrates highly natural and expressive zero-shot generation capabilities, supports seamless code-switching, and exhibits efficient speech rate control performance.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/Q15y9
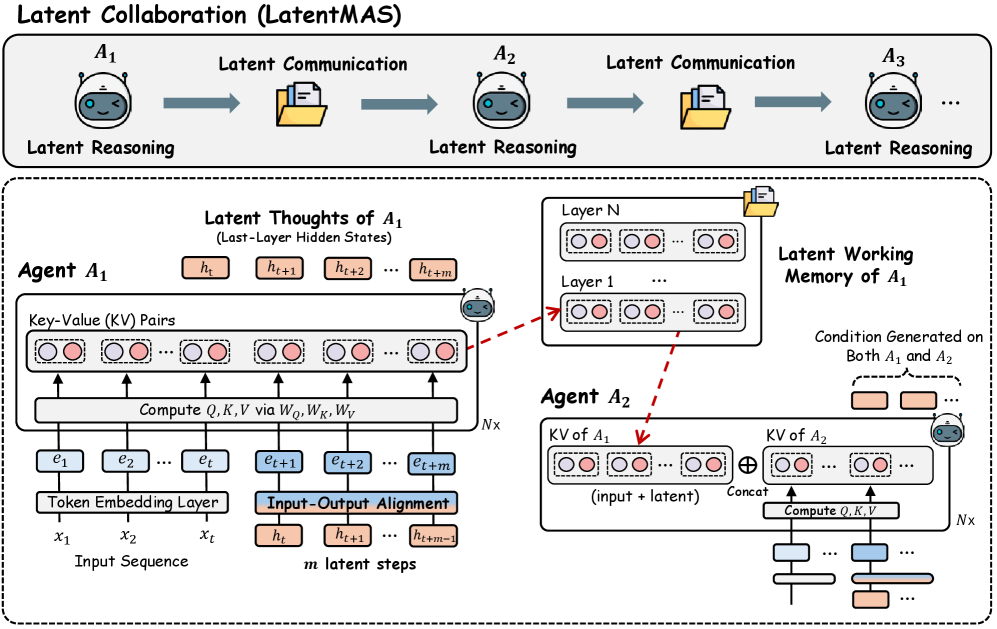
4. Latent Collaboration in Multi-Agent Systems
This paper proposes LatentMAS—an end-to-end, training-free framework that supports pure latent space collaboration between LLM agents. In LatentMAS, each agent first generates latent space thought representations autoregressively through the embedding of the last layer of hidden states; subsequently, the shared latent space working memory stores and transmits the internal representations of each agent, ensuring lossless information exchange.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/M587U
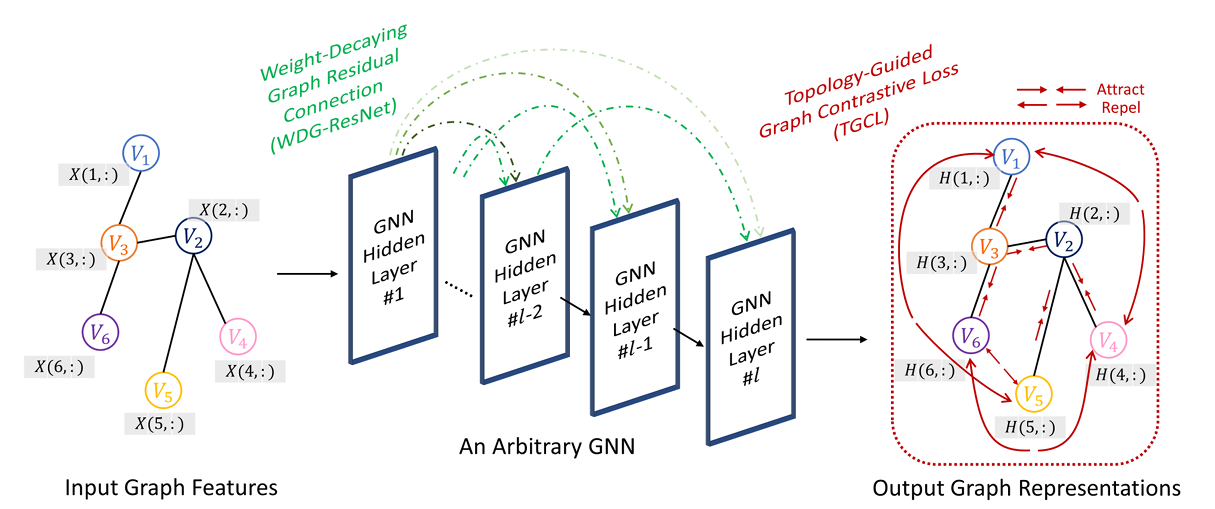
5. Deeper-GXX: Deepening Arbitrary GNNs
This paper proposes a novel graph neural network (GNN) method called Deeper-GXX. This method consists of two core modules: a weight-decaying graph residual connection (WDG-ResNet) module and a topology-guided graph contrastive loss (TGCL) function. WDG-ResNet effectively alleviates the vanishing gradient problem by introducing a dynamic weight decay mechanism, while suppressing the shadow neighbor effect; TGCL utilizes the graph's topological structure to guide contrastive learning, enhancing the discriminative power of node representations and suppressing oversmoothing.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/gwM7J