Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
FLUX.2-klein-4B: Achieves 4-step sub-second Image Generation via Distillation, Enabling real-time Interaction on consumer-grade GPUs; Vehicles OpenImages Dataset: Focuses on Vehicle Detection and localization.

Currently, while mainstream image generation models can produce high-quality results, they suffer from slow inference speeds, high memory requirements, and an interaction mode that remains stuck in the era of "offline tools." Users can only passively wait after inputting prompts, and cannot achieve real-time response and interaction.This limits the application of AI in scenarios such as real-time design and rapid prototyping.
In this context,Black Forest Labs has released the open-source FLUX.2-klein-4B model, which compresses the inference steps to 4 steps through step distillation, achieving sub-second (≤0.5 s) end-to-end inference.Its unified architecture supports text-to-image, image-to-image, and multi-reference generation, eliminating the hassle of switching between multiple models. It only requires about 13 GB of video memory to run efficiently on consumer-grade GPUs and supports FP8/NVFP4 quantization, further increasing the speed by up to 2.7 times. It transforms AI image generation from a "cumbersome offline tool" into a responsive real-time collaborator, providing a lightweight and efficient solution for scenarios such as real-time design and interactive editing.
The HyperAI website now features "FLUX.2-klein-4B: A High-Speed Image Generation Model," so give it a try!
Online use:https://go.hyper.ai/N7D6c
A quick overview of hyper.ai's official website updates from January 26th to January 30th:
* High-quality public datasets: 7
* A selection of high-quality tutorials: 6
* This week's recommended papers: 5
* Community article interpretation: 5 articles
* Popular encyclopedia entries: 5
Top conferences with February deadlines: 6
Visit the official website:hyper.ai
Selected public datasets
1. Vehicles OpenImages vehicle image dataset
Vehicles OpenImages originates from Google's large-scale public OpenImages dataset and focuses on vehicle detection and localization, aiming to support the rapid and efficient training of vehicle detection models.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/Y8nUj

2. Chest X-ray Pneumonia Dataset
Chest X-ray Pneumonia is a dataset of numerical features extracted from chest X-ray images. This dataset supports statistical analysis and classical machine learning by transforming each image into structured numerical features, including global intensity statistics, texture descriptors (GLCM), frequency domain features (FFT), edge-based metrics, and local binary pattern (LBP) features.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/RNgZD
3. Diabetes Mexico (Mexico Diabetes Dataset)
Diabetes Mexico is a diabetes dataset released by the National Institute of Public Health (INSP) of Mexico. It is based on data from the 2024 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (ENSANUT) and aims to assess the metabolic risk characteristics associated with diabetes in the Mexican population.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/2L4uw
4. Delhi Pollution AQI (Delhi Air Quality Dataset)
Delhi Pollution AQI is an environmental dataset for air quality analysis and forecasting. This dataset provides hourly air quality and environmental data for major cities in the Delhi NCR region, suitable for pollution analysis, time series forecasting, and machine learning applications.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/cNuok
5. LightOnOCR-mix-0126 Text Transcription Dataset
LightOnOCR-mix-0126 is a large-scale OCR text transcription dataset released by LightOn, designed to provide supervision for end-to-end OCR and document understanding models, outputting naturally ordered full-page transcribed text.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/tZRlI
6. Sonar Signal (Underwater Sonar Signal Dataset)
Sonar Signal is a dataset of sonar signals used for underwater object classification. This dataset is suitable for binary classification tasks, aiming to distinguish whether a sonar signal originates from rocks or a mine shaft.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/uXIom
7. Hand Gestures Labbled Dataset for a Car Game
Hand Gestures Labbled is a gesture-based car game image dataset designed to train machine learning models for gesture-based car game controls. The dataset contains a total of 330 images across four gesture categories: left, mvefrd, right, and stop.
Direct use:https://go.hyper.ai/sZmIc
Selected Public Tutorials
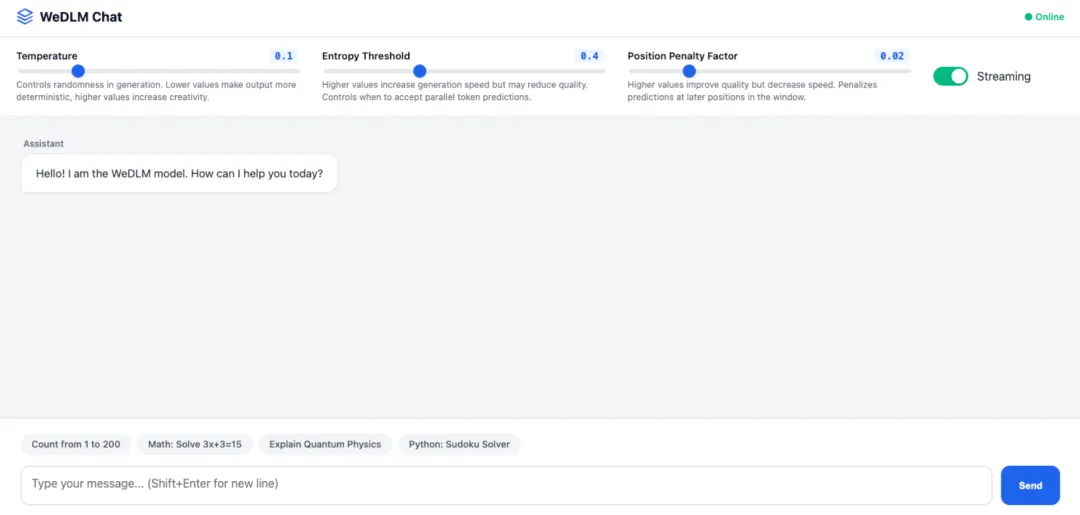
1. WeDLM: A high-efficiency large language model decoding framework
WeDLM (Window-based Efficient Decoding for Large Models) is a high-efficiency large language model decoding framework launched by Tencent, designed to provide next-generation AI dialogue systems with ultra-fast, intelligent, and highly adaptive language generation capabilities. This framework employs an innovative window-based parallel decoding architecture, achieving a significant improvement in decoding speed while maintaining high-quality text generation. Its core technological breakthrough lies in the integration of entropy threshold decision-making and positional penalty mechanisms, effectively solving the speed bottleneck problem of traditional autoregressive decoding when generating long sequences.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/Cfahp
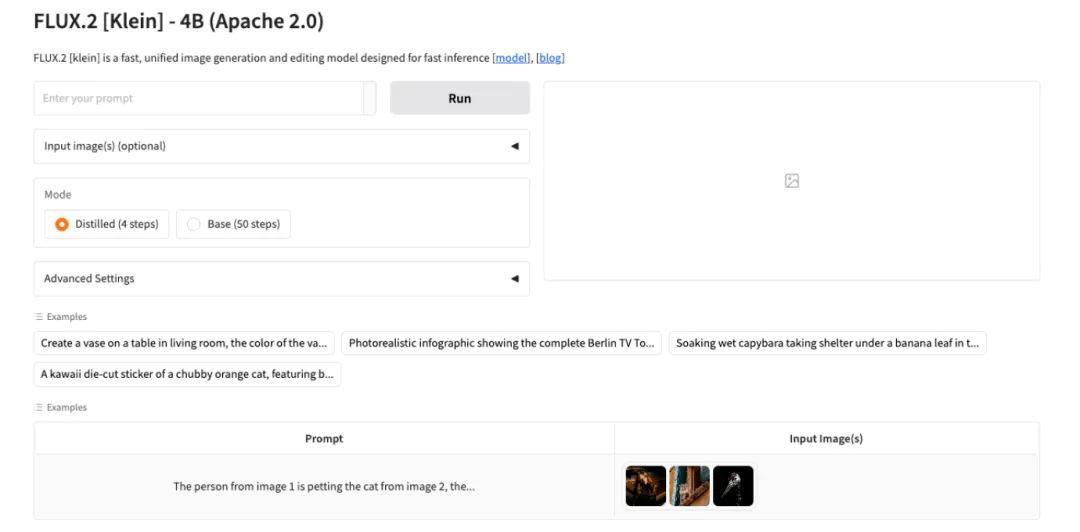
2. FLUX.2-klein-4B: Ultra-fast image generation model
FLUX.2-klein-4B is Black-Forest-Labs' latest ultrafast image generation model. Based on the Rectified-Flow architecture, it employs a 4 billion-parameter distilled Transformer design, unifying text-based image and multi-reference image editing capabilities within a compact model weight. It requires only about 13 GB of GPU memory and can achieve end-to-end inference speeds of less than 1 second on consumer-grade GPUs.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/N7D6c
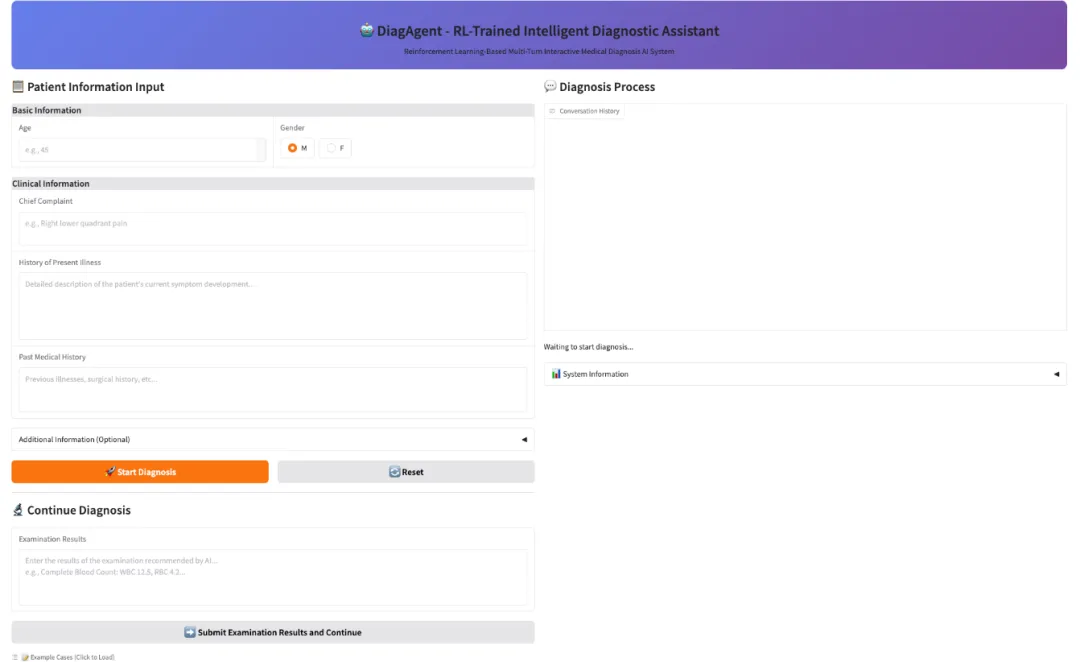
3. DiagGym Diagnostic Agent
DiagAgent, a diagnostic agent (7B, 8B, 14B) released by the AI4Med team at Shanghai Jiao Tong University and the Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, proactively manages the diagnostic trajectory, selecting the most informative examinations, deciding when to stop examinations, and providing an accurate final diagnosis. Unlike traditional large medical models that only provide a one-time answer, DiagAgent can recommend relevant examinations and adaptively update the diagnosis in multi-turn dialogues, only providing a final diagnosis when sufficient information is obtained. DiagAgent is optimized in the DiagGym environment through end-to-end multi-turn reinforcement learning (GRPO). In each interaction, the agent starts with an initial consultation, interacts with DiagGym by recommending examinations and receiving simulation results, and decides when to make a final diagnosis.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/FzOau
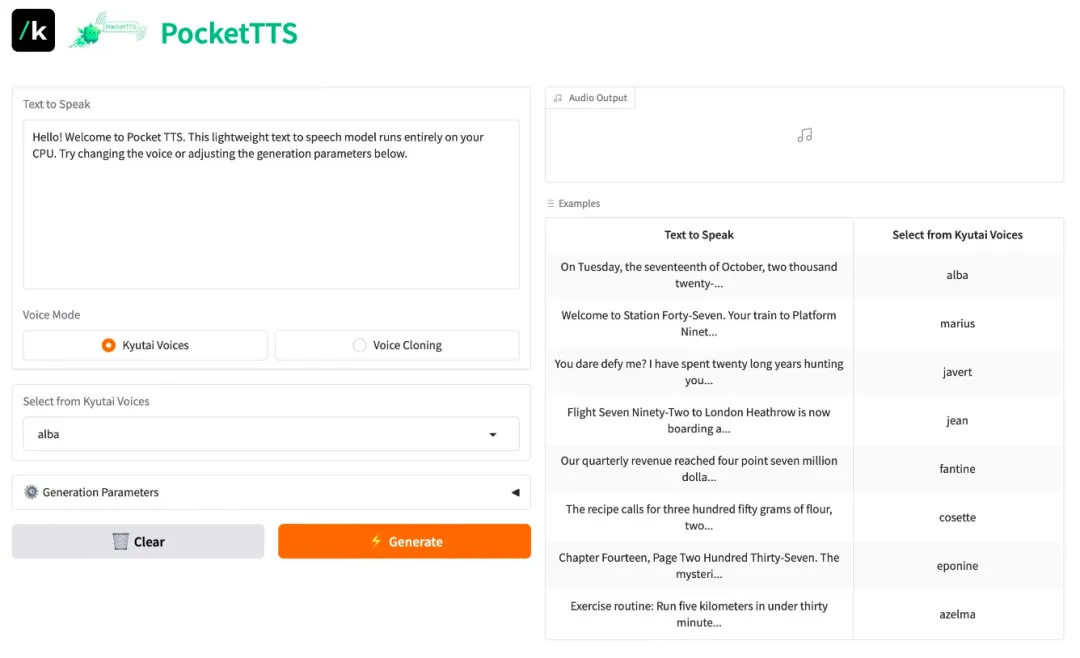
4. Pocket-TTS: A high-quality, lightweight streaming TTS system
Pocket-TTS is an ultra-lightweight speech synthesis model released by Kyutai Labs. This model focuses on low latency and streaming output, aiming to provide high-quality speech generation capabilities for resource-constrained environments or scenarios requiring real-time interaction (such as AI assistants).
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/CwgHo
5. Triton Compiler Tutorial
Triton is a language and compiler for parallel programming, designed to provide a Python-based programming environment for efficiently writing custom DNN computation kernels that can run at maximum throughput on GPU hardware.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/Xqd8j
6. TVM Tutorial 0.22.0
Apache TVM is an open-source machine learning compiler framework for CPUs, GPUs, and machine learning accelerators, designed to enable machine learning engineers to efficiently optimize and run computations on any hardware backend.
Run online:https://go.hyper.ai/s3yot
This week's paper recommendation
1. Rewarding the Rare: Uniqueness-Aware RL for Creative Problem Solving in LLMs
This paper proposes a uniqueness-aware reinforcement learning method. The method designs an objective function at the rollout level and rewards rare high-level reasoning strategies by reweighting the size of clustering and inverse clustering based on large language model (LLM). This significantly improves the solution diversity and pass@k performance on mathematical, physical and medical reasoning benchmarks without sacrificing pass@1.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/k5A3R
2. DeepResearchEval: An Automated Framework for Deep Research Task Construction and Agentic Evaluation
This paper proposes DeepResearchEval, an automated framework that generates realistic and complex deep research tasks through role-driven approaches and employs adaptive, task-specific quality assessment and proactive fact-checking mechanisms to evaluate agents based on large language models. This allows for the verification of claims without citations, thereby enabling reliable evaluation of multi-step network research systems.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/b92V4
3. Controlled Self-Evolution for Algorithmic Code Optimization
This paper proposes a controlled self-evolution (CSE) method, which improves code generation efficiency by enabling experience reuse through diversified initialization, feedback-guided genetic operations, and hierarchical memory. It achieves efficient exploration and continuous optimization of various LLM backbone networks on the EffiBench-X benchmark.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/RJHUC
4. MMFormalizer: Multimodal Autoformalization in the Wild
This paper proposes MMFORMALIZER, a novel multimodal automatic formalization framework that combines adaptive localization with perceptual primitives to recursively construct propositions with formal foundations in mathematical and physical axioms, enabling machine reasoning in fields such as classical mechanics, relativity, quantum mechanics, and thermodynamics, and demonstrating scalability on the PHYX-AF benchmark.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/mC7NC
5. MAXS: Meta-Adaptive Exploration with LLM Agents
This paper proposes MAXS, a meta-adaptive reasoning framework for large language model (LLM) agents. By introducing look-ahead planning and trajectory convergence mechanisms, it alleviates the problems of local shortsightedness and reasoning instability. Combined with advantage estimation and consistency-driven step size selection, it achieves efficient, stable and high-performance multi-tool reasoning.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/Wrhke
Community article interpretation
1. From Moltrbot to policy dividends, can an "AI one-person company" standing at the forefront of the trend grow into a big and strong enterprise?
As technological tools such as ChatGPT, AI design tools, and intelligent data analysis systems become increasingly widespread, the startup world is witnessing an unprecedented efficiency revolution. Clawdbot (now renamed Moltrbot), which recently went viral, is seen as an open-source personal assistant poised to revolutionize productivity by 2026. This AI agent, touted as a "top-tier LLM with hands," has become a sensation in Silicon Valley, with its GitHub stars soaring to 57.5k in just three days after its release. More importantly, this new form of startup has received positive policy support. As early as 2016, the "Opinions of the State Council on Promoting the Sustained and Healthy Development of Venture Capital" explicitly encouraged individuals with capital strength and management experience to engage in venture capital activities by legally establishing one-person companies.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/2hKRe
2. Skild AI, a robotics startup, raises $1.4 billion with participation from SoftBank, Nvidia, Sequoia Capital, and Bezos, among others, to develop general-purpose basic models.
In mid-January 2026, robotics startup Skild AI announced the completion of a Series C funding round of approximately $1.4 billion, valuing the company at over $14 billion. This round was led by Japan's SoftBank Group, with strategic investors including Nvidia's NVentures, Macquarie Capital, and Bezos Expeditions (founded by Amazon founder Jeff Bezos). Samsung, LG, Schneider Electric, and Salesforce Ventures also participated. At a time when robot hardware is still evolving and application scenarios remain highly fragmented, capital has repeatedly and almost simultaneously flocked to a few companies that don't only manufacture robots. This, to some extent, reflects the profit-driven nature of capital and confirms that this startup, less than three years old, has chosen a promising path.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/iYHbK
3. AlphaGenome graces the cover of Nature! Predicts variation effects across all modalities and cell types in under 1 second.
In June 2025, Google DeepMind released AlphaGenome. The AlphaGenome model takes DNA sequences of up to one million base pairs as input and predicts thousands of molecular properties related to their regulatory activities. It can also assess the impact of gene variations or mutations by comparing predictions of mutated and unmutated sequences. One of AlphaGenome's key breakthroughs is its ability to "directly predict splice junctions from sequences and use them for variation effect prediction." Dr. Caleb Lareau of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center commented, "This is a milestone in the field. For the first time, we have a model that simultaneously possesses long context, single-base accuracy, and top-tier performance, covering a wide range of genomic tasks."
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/jgO8K
4. Based on billions of genes from one million species, NVIDIA and others have built the EDEN series of models, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) genome and protein prediction capabilities.
The fundamental goal of programmable biology is to achieve rational design and precise regulation of living systems, thereby bringing revolutionary therapies to complex diseases. However, this process has long been limited by the inherent complexity of biological systems. Its generalization ability is severely insufficient when facing multimodal, cross-scale innovative therapy design. To overcome this fundamental limitation, Basecamp Research, NVIDIA, and several leading academic institutions have jointly developed the EDEN series of metagenomic basic models.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/jPS42
5. The University of California has built an on-chip spectrometer based on a fully connected neural network, achieving spectral resolution of 8 nanometers at a chip-scale.
Today, smartphone cameras have entered the era of megapixel counts, yet they still cannot analyze the chemical composition of substances like professional spectrometers. The key to this gap lies in the lack of a core component in smartphones and other devices—a spectrometer—that can accurately read the unique "spectral fingerprint" of a substance. Traditional spectrometers, as important tools for substance analysis, work by separating composite light into spectra of different wavelengths, and then identifying the substance's composition through characteristic spectral lines. However, they face a major challenge: miniaturization necessitates abandoning traditional dispersive structures; but without dispersive structures, how can spectral information be obtained? To address this challenge, a research team at the University of California proposed an innovative solution: designing a special photon trapping texture structure (PTST) on the surface of a standard silicon photodiode and introducing a highly noise-resistant fully connected neural network.
View the full report:https://go.hyper.ai/bYwq8
Popular Encyclopedia Articles
1. Frames per second (FPS)
2. Reverse sort fusion RRF
3. Visual Language Model (VLM)
4. HyperNetworks
5. Gated Attention
Here are hundreds of AI-related terms compiled to help you understand "artificial intelligence" here:
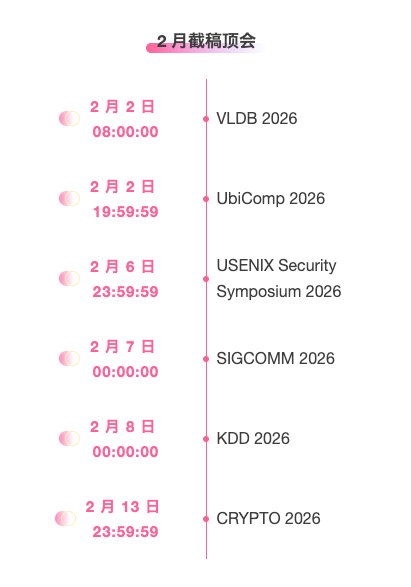
One-stop tracking of top AI academic conferences:https://go.hyper.ai/event
The above is all the content of this week’s editor’s selection. If you have resources that you want to include on the hyper.ai official website, you are also welcome to leave a message or submit an article to tell us!
See you next week!








