Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
AI Paper Weekly Report: 100 Million Cell Data modeling/efficient Prediction of Genetic trajectories/command Ambiguity cracking/verifiable rewards/highly Dynamic Game Generation, a Quick Overview of 5 Major Breakthroughs

The response of cells to perturbations is the cornerstone for understanding biological mechanisms and selecting potential drug targets. Compared with experimental methods, computational models have great potential in predicting the effects of perturbations, but their practical applications are limited by their difficulty in generalizing the effects of experimentally observed cellular environments to unobserved environments.
Based on this, Arc Institute, together with the University of California and other universities, introduced a machine learning architecture State, which can take into account the cellular heterogeneity within and between perturbation experiments while predicting the perturbation effect. On multiple large data sets, State's ability to distinguish perturbation effects has increased by more than 50%, and the accuracy of identifying truly differentially expressed genes in genetic, signal, and chemical perturbations is more than twice that of existing models.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/xkBgn
Latest AI Papers:https://go.hyper.ai/hzChC
In order to let more users know the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence in academia, HyperAI's official website (hyper.ai) has now launched a "Latest Papers" section, which updates cutting-edge AI research papers every day.Here are 5 popular AI papers we recommend, including gene expression, game video generation, and in-depth research benchmark datasets and their download links. Let's take a quick look at this week's AI cutting-edge achievements⬇️
This week's paper recommendation
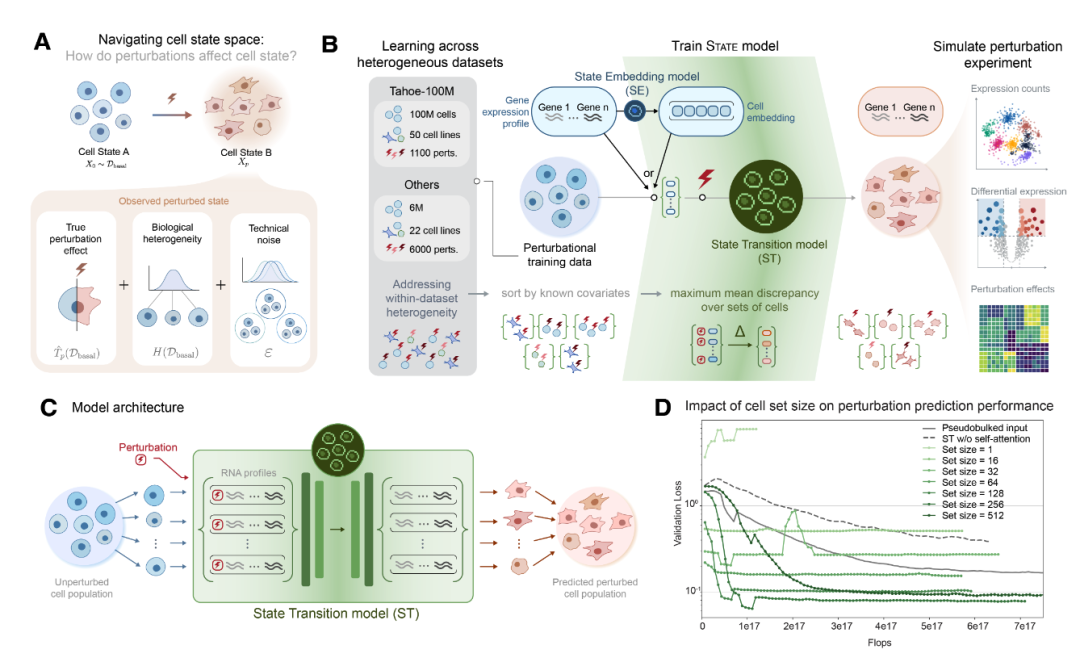
1 Predicting cellular responses to perturbation across diverse contexts with State
This paper introduces a machine learning architecture called State, which is used to predict the response of cells to different types of interference (such as genetic, chemical or signaling intervention). By combining the state transition model and the cell embedding model, the State model can effectively process and simulate more than 100 million disturbed cell data across 70 different cell environments. Compared with existing models, State performs significantly better than 50% on multiple large data sets, especially in identifying differential gene expression, with an accuracy of more than twice.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/xkBgn
* Tahoe-100M single cell dataset:
* Parse-PBMC single-cell RNA sequencing dataset:
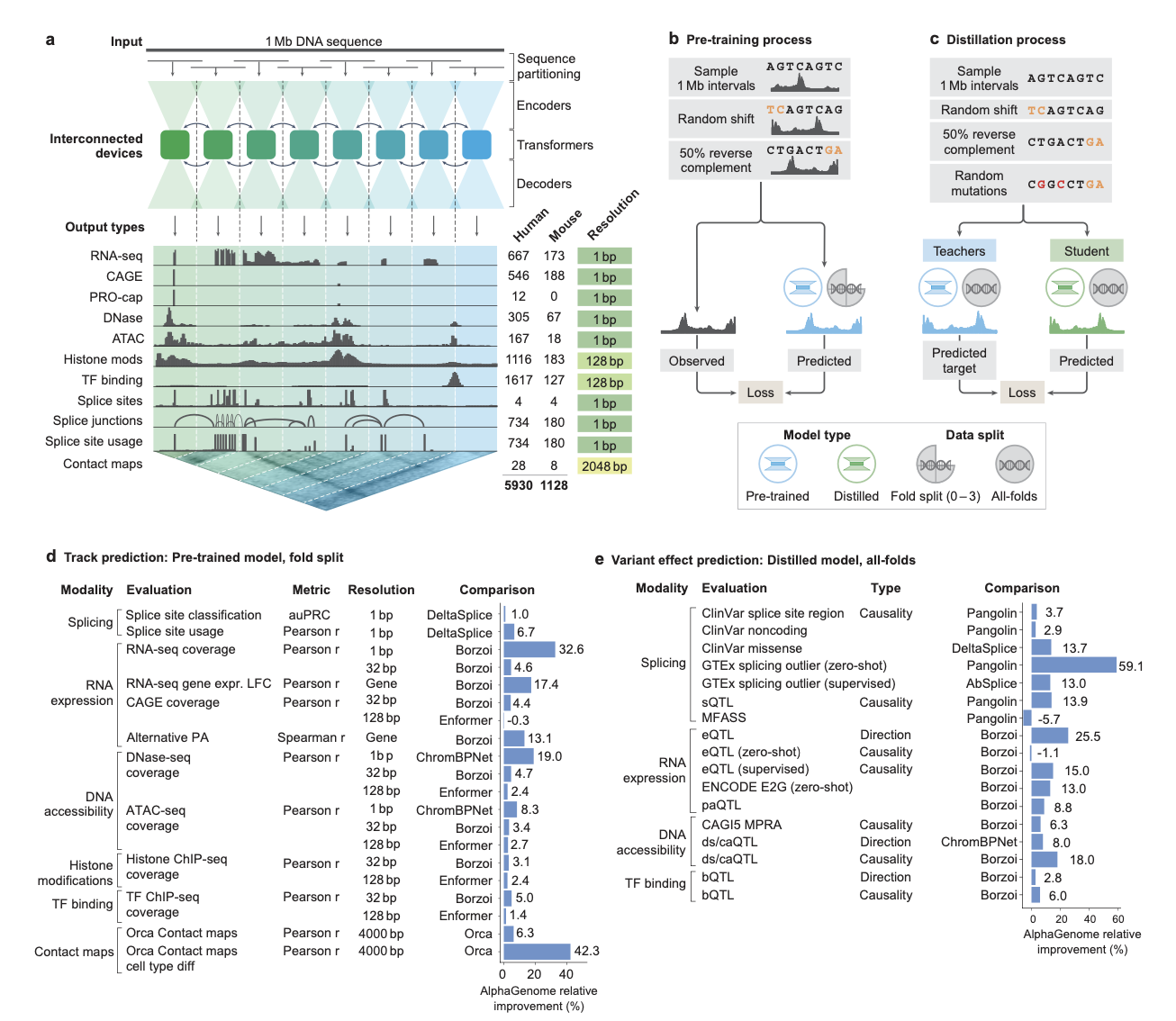
2 AlphaGenome: advancing regulatory variant effect prediction with a unified DNA sequence model
This paper introduces a deep learning model called AlphaGenome, which can predict a variety of functional genetic tracks such as gene expression, transcription initiation, chromatin accessibility, histone modifications, transcription factor binding sites, chromatin contact maps, etc. from DNA sequences, and can predict a large number of variant effects in a single device call, which is extremely fast. AlphaGenome solves two major problems faced by current deep learning models: the trade-off between input sequence length and prediction resolution, and the balance between multimodal and single-modal prediction capabilities.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/D4sjw
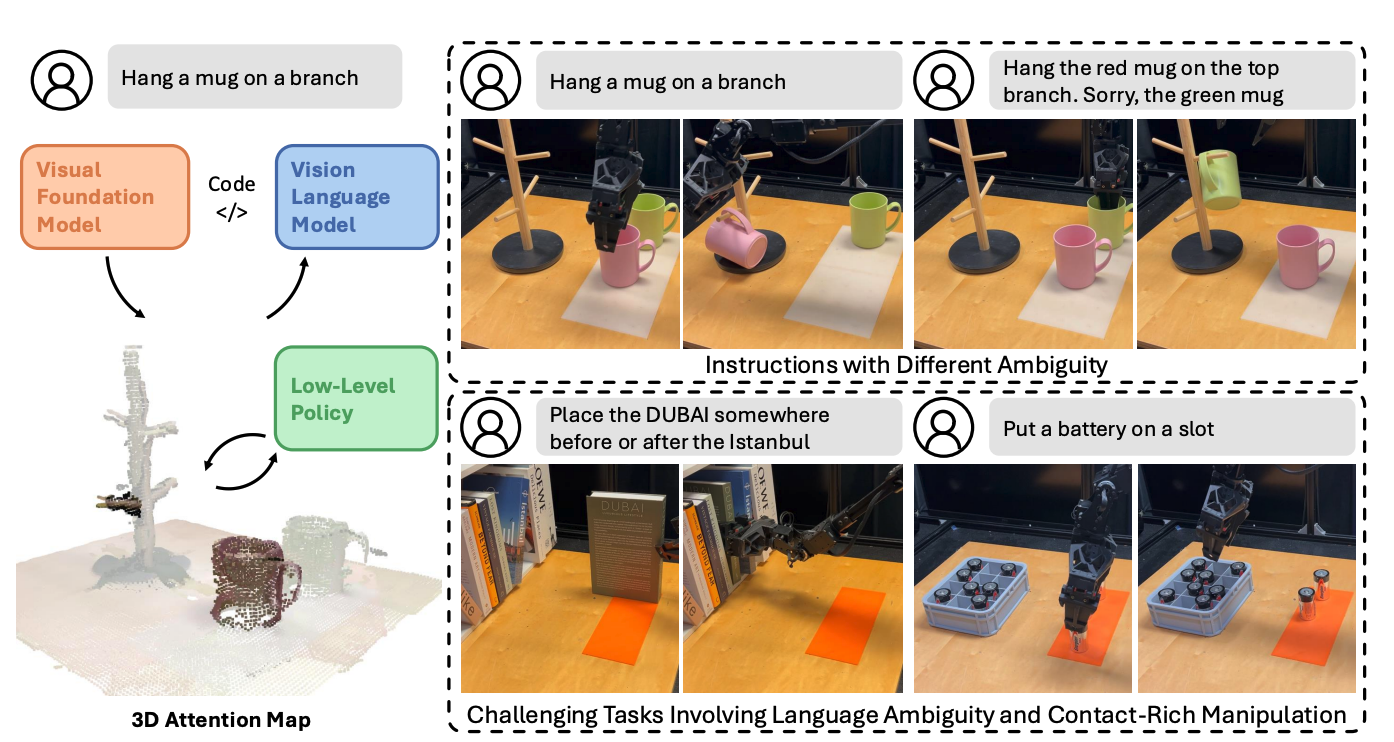
3 CodeDiffuser: Attention-Enhanced Diffusion Policy via VLM-Generated Code for Instruction Ambiguity
This paper introduces a robot task execution framework for language ambiguity and polysemy, CodeDiffuser. The framework parses natural language instructions by using the code generated by the visual language model, and calculates the three-dimensional attention map through the visual base model as an intermediate representation to solve the problem of abstract and ambiguous language instructions. Experimental results show that after the introduction of CodeDiffuser, the performance of the system has been significantly improved, and it has successfully completed complex tasks involving language ambiguity, intensive operations, and multi-object interactions.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/Y6M3P
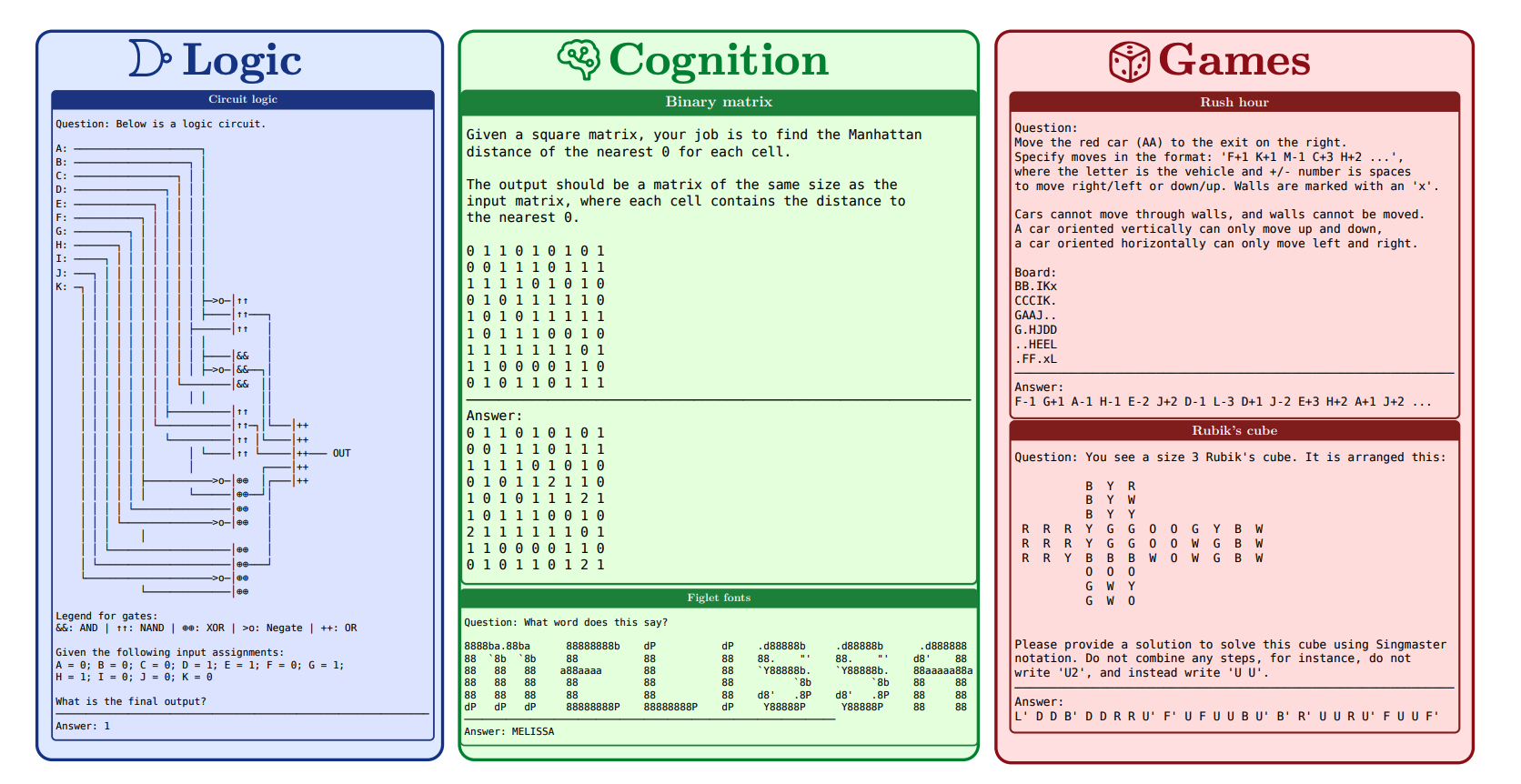
4 REASONING GYM: Reasoning Environments for Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards
This paper introduces REASONING GYM (RG), a library of reasoning environments designed for reinforcement learning, which features the ability to generate unlimited training data with verifiable rewards and supports a variety of reasoning tasks, including algebra, arithmetic, logic, graph theory, etc. The tasks automatically generated by the algorithm can adjust the difficulty level, thereby enabling dynamic evaluation and training. Through testing on external benchmarks, it is confirmed that the knowledge gained from RG training can be effectively transferred to real-world problem-solving tasks. REASONING GYM provides a powerful tool for systematically exploring and enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/JvIlr
5 Hunyuan-GameCraft: High-dynamic Interactive Game Video Generation with Hybrid History Condition
This paper introduces a new interactive game video generation framework, Hunyuan-GameCraft, which achieves high-quality and dynamic game video generation by combining diffusion models and conditional control. This method supports complex interactive input by unifying keyboard and mouse input into a shared camera representation space, and proposes a hybrid history conditional training strategy to maintain long-term spatial and temporal consistency. Experimental results show that compared with existing models, Hunyuan-GameCraft performs significantly better in dynamic performance, interaction accuracy, temporal and spatial consistency, indicating that it has great potential in real-time interactive and high-dynamic game video generation.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/kVEMV

The above is all the content of this week’s paper recommendation. For more cutting-edge AI research papers, please visit the “Latest Papers” section of hyper.ai’s official website.
We also welcome research teams to submit high-quality results and papers to us. Those interested can add the NeuroStar WeChat (WeChat ID: Hyperai01).
See you next week!








