Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Doctor Training Welcomes DeepSeek Plug-in! Shanghai Institute of Physical Education/Shanghai Jiaotong University/Tsinghua University Collaborative Research Proves That Large Models Can Become the "golden Partner" for Primary Care Doctor Training

In the global health landscape, diabetes is attacking the health defenses of human beings with a "tsunami-level" ferocious momentum. In the past 30 years, this silent but extremely cruel health battle has caused 840 million people to become ill, which means that on average, one in every nine people is unfortunately diagnosed with diabetes. The latest warning issued by "The Lancet" has sounded the alarm: it is estimated that by 2050, the number of diabetes patients in the world will exceed 1.31 billion, which means that on average, one person will join the huge team of diabetes every 2.3 seconds.
Diabetes, a chronic disease, is like a ruthless "health harvester". It not only consumes precious medical resources at a rate of 10% per year, but also ruthlessly takes the lives of 4 million people every year. The serious complications caused by it, such as blindness, kidney failure, and amputation, have plunged countless patients into endless darkness and families into the abyss of pain.
In this severe health crisis, the "broken path" exposed by the primary medical system is heartbreaking. Take my country as an example, there are only 0.3 endocrinologists per 100,000 people, which shows how scarce they are. Even more serious is that the primary care physicians (PCPs) in 70% lack the ability to independently complete the risk assessment of diabetes complications.The traditional specialized training model is undoubtedly making matters worse, and is caught in a "triple dilemma":The training cycle is often as long as 3-5 years, which is too long to keep up with the rapid iteration of medical knowledge. There is a huge difference in training resources between the eastern and western regions, with a gap of more than 40 times, and serious uneven resource allocation. The training courses are highly homogenized, resulting in 73% grassroots doctors still having cognitive blind spots after completing the training..
With the rapid development of science and technology, large models such as DeepSeek and ChatGPT have strongly intervened in the global medical field, bringing new hope to medical education and gradually reconstructing the paradigm of medical education. With strong knowledge reserves and excellent reasoning ability, these large models are expected to fill many blind spots in the knowledge level of primary care doctors. However, this revolution in the medical field is not smooth sailing and is facing dual severe challenges.on the one hand,The "hallucination" problem of large models is still serious, which poses a great risk to medical safety;on the other hand,About 30% of AI misdiagnosis cases were caused by incorrect labeling of training data. In addition, there is a huge gap between fragmented clinical practice and the continuously updated guideline library, which seriously restricts the full realization of the value of AI.
When the diagnostic recommendations given by AI conflict with the doctor's clinical experience,How to build a new paradigm of "human-machine collaborative decision-making" has become a key issue concerning medical equity and efficiency. Only by making the big model an effective "smart external brain" for primary care doctors, rather than a "terminator" that replaces them, can the future AI revolution in diabetes management truly benefit hundreds of millions of patients. This is also highly consistent with the needs of the Healthy China strategy.
Recently, Professor Sheng Bin's team from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Professor Mao Lijuan's team from Shanghai University of Sport, Professor Huang Tianyin's team from Tsinghua University, and Professor Jia Weiping's team from Shanghai Institute of Diabetes have joined hands with other multidisciplinary forces to carry out in-depth cooperation with top international universities and research institutions such as Duke University, Johns Hopkins University in the United States, and the University of Melbourne in Australia.With the help of the authoritative bilingual examination system in Chinese and English, they jointly built a new evaluation scheme and conducted systematic tests on 10 mainstream large language models (LLMs) at home and abroad, including ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4.0, and Tongyi Qianwen.
at the same time,The team also evaluated DeepSeek's effectiveness in assisting physician training. Through this series of studies, the team provided the world's first prospective real-world evidence on the actual effectiveness of big models in assisting primary care physician training. It opened up new research directions for the application of big models in the medical field and provided a valuable reference for improving primary care levels.
The related results were published in Science Bulletin under the title "Large language models for diabetes training: a prospective study".

Paper address:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2095927325000891
The open source project "awesome-ai4s" brings together more than 200 AI4S paper interpretations and provides massive data sets and tools:
https://github.com/hyperai/awesome-ai4s
Test LLM's knowledge of diabetes
The team selected 10 mainstream LLMs at home and abroad.Including ChatGPT-3.5, ChatGPT-4.0, Google Bard, LlaMA-7B, LlaMA2-7B, Baidu ERNIE Bot, Tongyi Qianwen, Yilian MedGPT, Huatuo GPT, and Chinese LlaMA2-7B.
The test content covers two parts, Chinese and English.They correspond to the National Primary Diabetes Care Examination (NCE-CPDC) of China and the Specialty Certificate Examination (SCE) of Endocrinology and Diabetes of the Royal College of Physicians (MRCP (UK)) of the United Kingdom. The study requires each LLM to answer the questions according to the input questions and provide corresponding explanations. Subsequently, the research team compared the answers generated by the model with the official standard answers and cross-checked them to evaluate their accuracy, thereby comprehensively measuring the performance and application potential of each model in the field of diabetes medical knowledge.
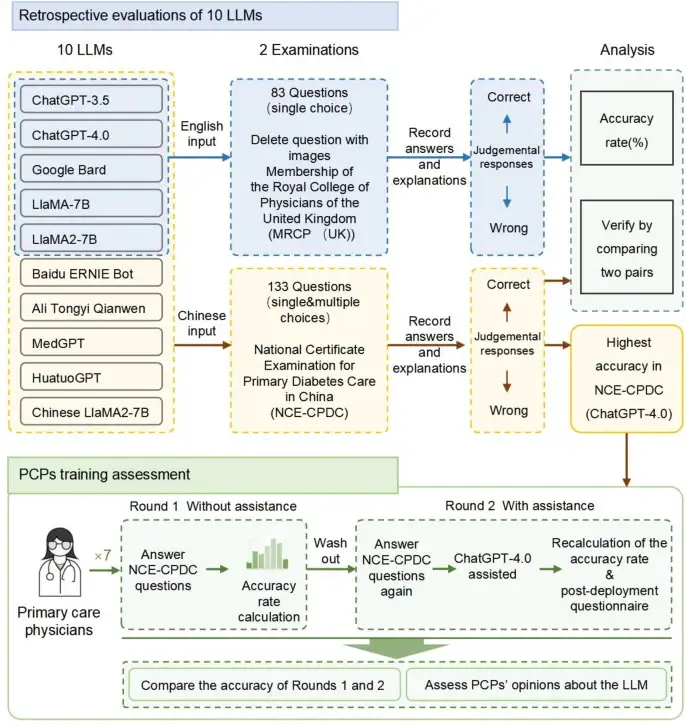
Chinese Test - NCE-CPDC:
* NCE-CPDC: China National Primary Diabetes Care Certificate Examination is a professional examination designed for PCPs, which is organized by the China National Primary Diabetes Care Office.
Based on the "National Primary Diabetes Prevention and Management Guidelines", it covers diabetes definition, screening, diagnosis, referral, lifestyle intervention, drug therapy, and acute and chronic complications management. NCE-CPDC certification is widely recognized in China, especially by healthcare professionals and those involved in diabetes care.Results with an accuracy rate exceeding 60% are considered passed.Any score below this is considered a failure.
In this test,ChatGPT-4.0 performed outstandingly with a high accuracy of 90.98%, significantly ahead of other models.Alitong YiQianwen also showed strong competitiveness, with an accuracy of 81.20%, significantly better than ChatGPT-3.5. Although some other models failed to meet the passing criteria, they provided valuable data and direction for subsequent technical improvement and optimization.
English Test - SCE:
* SCE: Professional Certificate Examination of the Royal College of Physicians (MRCP (UK)). This exam is highly professional and challenging, with a pass rate of only 28.6% for UK candidates in 2023.
The SCE exam questions are designed for endocrinologists and diabetes care specialists and cover difficult content such as diabetes pathophysiology, diagnosis, drug therapy, and management of acute and chronic complications. ChatGPT-4.0 successfully passed the passing line with an accuracy of 62.50%.The performance far exceeds that of other mainstream LLMs (such as Google Bard, LlaMA-7B, LlaMA2-7B, etc., which all failed to meet the qualification standards). This achievement not only proves the potential of ChatGPT-4.0 in handling highly difficult professional content, but also provides a solid basis for the subsequent application of LLM in medical training.
LLM assists primary care physician training
After completing a simple quiz test, the research team did not stop there.Instead, we further explore the application effect of large language model (LLM) in actual training scenarios. This time, the team carefully selected 7 primary care physicians (PCPs) as research subjects and asked them to take the National Examination for Primary Diabetes Care Certificate (NCE-CPDC) of China with or without the assistance of ChatGPT-4.0.
The test results are impressive: in the first test, ChatGPT-4.0 led the other large models with an accuracy rate of 84.82%, leaving all the doctors who participated in the test far behind. When assisted by ChatGPT-4.0, the performance of most doctors was even more remarkable.The average accuracy has steadily increased from 74.72% to 75.81%.
Although some doctors had difficulty identifying possible misleading explanations in the model during the test, which led to a decline in their performance, the overall data shows that As an auxiliary tool, LLM can undoubtedly effectively help doctors improve their mastery and application of diabetes care knowledge. It is worth noting thatAlmost all the PCPs who participated in the test praised this new training model.They believe that LLM performs excellently in terms of internal consistency, professional advice and practicality, injecting new vitality into traditional training methods and bringing surprising changes.
It is particularly worth mentioning that this research work was carried out as early as 2023. In recent years, domestic large language models have sprung up like mushrooms after rain, and have made great progress in the medical field. Among them, DeepSeek, as a domestic general large language model that has attracted much attention, has performed particularly well.The research team conducted rigorous tests on the accuracy of DeepSeek's answers to NCE-CPDC test questions, and the results were encouraging - DeepSeek's answer accuracy was as high as 91.73%, slightly surpassing ChatGPT-4.0's 90.98%.
Based on this achievement, we have enough reason to believe that in the future, both domestic general-purpose large language models and large language models focusing on vertical fields will have huge potential.They will play a key role in the prevention and control of chronic diseases such as diabetes, effectively promote the digital transformation of chronic disease diagnosis and treatment, and contribute powerful scientific and technological power to protecting public health.
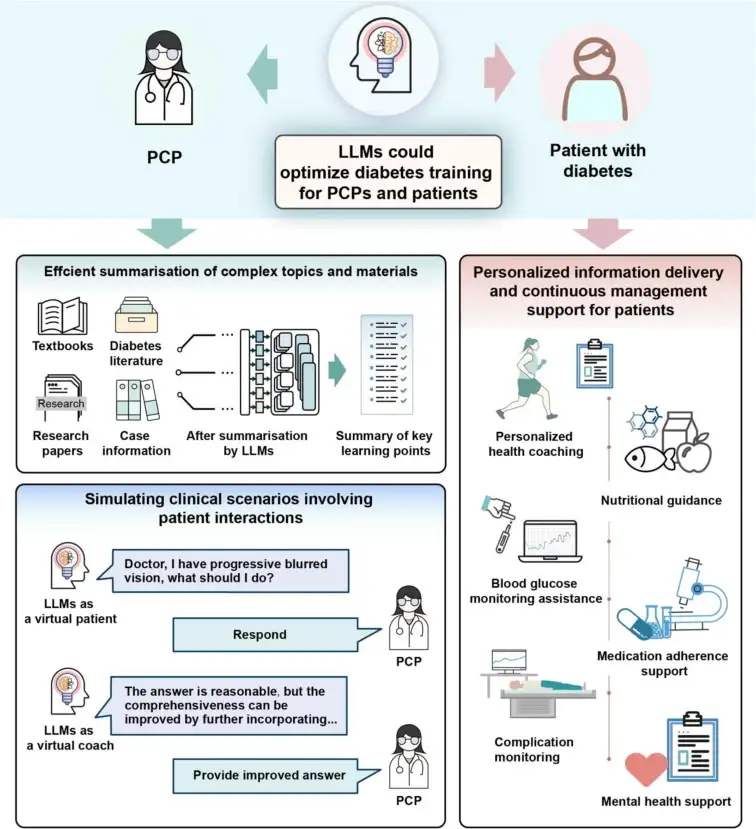
Development of LLMs in Healthcare Training
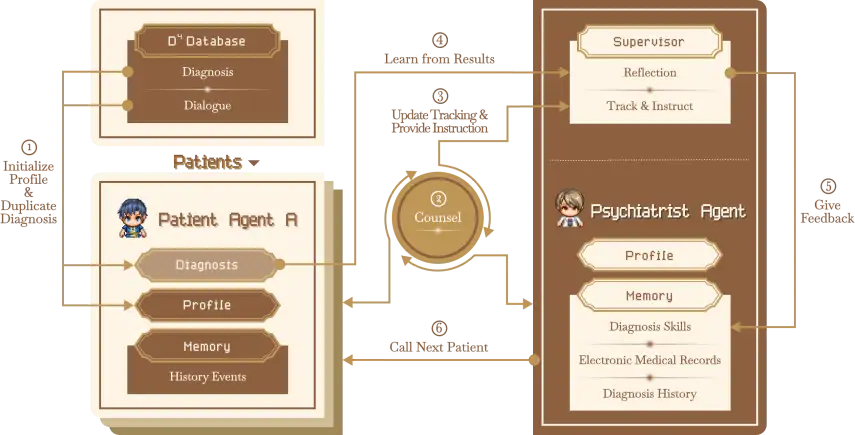
From diabetes care to psychiatric training
The use of LLM in medical training is not limited to the field of diabetes care. In recent years, several research teams at home and abroad have tried to combine LLM with deep learning (DL) technology to build intelligent training platforms for different medical specialties.
Take AMC (Agent Mental Clinic) built by Professor Wu Mengyue's team at X-LANCE Laboratory of Shanghai Jiao Tong University as an example. The system simulates psychological diagnosis and treatment scenarios through automated dialogue agents, which can not only assist in the initial screening of depression, but also provide training for trainee psychiatrists and provide some guidance and help before they officially enter the department for internship. This model provides psychiatrists with useful rehearsals and guidance before they enter formal clinical work, greatly shortens the time cost of professional training, and provides patients with higher-quality initial diagnosis advice.
DeepDR-LLM: A new model for diabetes diagnosis and treatment that integrates vision and language
At present, the Large Language Model (LLM) has made remarkable achievements in the field of medical information processing and knowledge generation, showing its powerful capabilities. It can quickly integrate massive medical data, provide rich data support for medical decision-making, and generate preliminary diagnostic suggestions based on patient symptoms and medical history, thus improving medical efficiency to a certain extent.
But even so,LLM still cannot completely replace the innovative spirit, critical thinking and clinical decision-making ability that are unique to doctors. When doctors face complex conditions, comprehensive judgments based on experience and expertise, as well as keen insights into individual differences in patients, are essential factors in the medical process. In view of this, many researchers are actively engaged in exploring the integration of LLM and deep learning (DL) technology, striving to further improve the accuracy of clinical decision-making.
In the exploration of this cutting-edge field, the achievements of Professor Sheng Bin's team at Shanghai Jiao Tong University are particularly impressive.The DeepDR-LLM model, developed by the team in collaboration with top international institutions, was published in the internationally renowned academic journal Nature Medicine.Once this achievement was released, it caused a strong shock in the international medical community and received high praise from many medical giants. Professor Eric Topol, a pioneer in precision medicine, Professor Daniel J. Drucker, winner of the Wolf Prize in Medicine, and Professor Margaret Chan, Honorary Director-General of the World Health Organization and Founding Dean of the Vanke School of Public Health and Health at Tsinghua University, all gave full recognition to it.
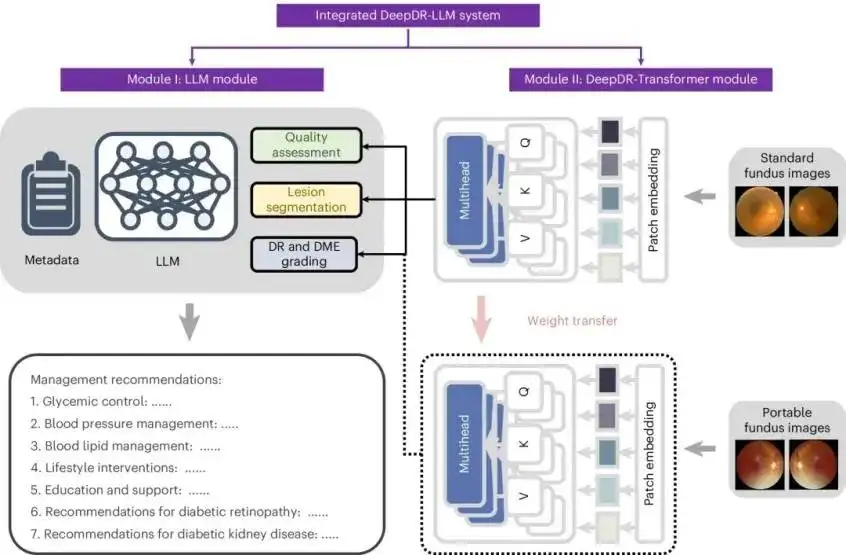
Looking back at traditional diabetes care training, doctors mainly rely on a large amount of written materials and long-term accumulated clinical experience to improve their professional capabilities. Although this method is effective, it has problems such as low efficiency and limited timeliness of materials.
As the world's first integrated vision-large language model system for diabetes diagnosis and treatment, DeepDR-LLM is an innovative model in the field of diabetes diagnosis and treatment.It cleverly combines the powerful knowledge processing capabilities of LLM and the precise image analysis technology of DL, achieving a major breakthrough in functionality. The system can not only quickly and accurately answer various professional questions related to diabetes diagnosis and treatment, but also assist doctors in diagnosing diabetic retinopathy with the help of fundus image analysis, helping doctors to detect potential lesion risks in the early stages of the disease.
It is worth mentioning thatThe DeepDR-LLM system also has strong scalability and can be seamlessly connected with DeepSeek. The performance can be further enhanced by incorporating DeepSeek's reasoning capabilities through MoE technology. After a series of technical iterations and innovations, the DeepDR-LLM system has not only significantly improved the quality of diabetes care training, allowing doctors to more efficiently master cutting-edge knowledge and diagnostic skills, but also provided practical and efficient technical support for clinical practice, bringing more accurate and timely diagnosis and treatment hope to diabetic patients.
Diabetes prevention and treatment is an important issue in the global health field, and primary care physician training is a key link in improving the overall medical level. Primary care physicians are the "frontline guards" who protect public health, and the quality of their training is the core link in improving the overall medical level, which is directly related to the breadth and depth of medical services.
In this context, Professor Sheng Bin's team, through close cooperation and integrated innovation with a multidisciplinary expert team, focused on the application of large language models (LLM) in the field of diabetes care training and conducted in-depth exploration. This exploration is of great significance. It not only opens up new ideas for optimizing medical training with the help of advanced artificial intelligence technology, but also lays a solid foundation for the widespread application of medical artificial intelligence in interdisciplinary and multi-field areas in the future.
Today, the combination of "AI + doctor" is showing tremendous power and gradually reshaping the distribution pattern of medical resources. This golden partnership cleverly combines the advantages of both: the humanistic care and rich clinical experience of doctors are retained, giving patients warmth and trust; at the same time, AI gives doctors decision-making support that transcends individual cognitive limitations, making diagnosis and treatment more accurate and efficient. When the AI system is like a tireless medical assistant, able to parse the latest medical literature in real time, automatically generate differential diagnosis maps, and simultaneously update the global diagnosis and treatment consensus, grassroots doctors seem to be given the "superpower" to break through the limitations of time and space, and can obtain the most cutting-edge medical knowledge and diagnostic ideas even in remote areas.
The impact of this medical revolution is far-reaching, and its value goes far beyond improving the level of diabetes prevention and treatment itself.It also provides a unique Chinese solution for global medical equity.Imagine that rural doctors can obtain diagnosis and treatment advice at the same level as academicians with the help of AI systems such as DeepSeek and Deep DR-LLM, which greatly narrows the gap in urban and rural medical levels; urban experts can also be freed from tedious and repetitive work and devote more energy to the study of complex cases, promoting the continuous development of medicine. With such technological empowerment, "no serious illness outside the county" is no longer just an unattainable slogan, but is gradually becoming a reality, injecting strong intelligent kinetic energy into the construction of a human health community.
Looking ahead
As the global medical environment is changing with each passing day, technology empowerment has become an important "tool" to improve the quality of medical services. The deep integration of cutting-edge technology and medical practice can not only effectively fill the many long-standing shortcomings in primary medical training, but also open up a broader development space for the application of medical artificial intelligence and help it reach new heights.
With the continuous optimization of LLM technology and the continuous expansion of clinical applications, more exciting innovative results are expected to take root, bringing tangible health benefits to the majority of patients, injecting continuous wisdom and vitality into the vigorous development of the global medical system, and allowing the medical industry to bloom more brilliantly under the promotion of science and technology.