Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
After the Heavy Rain, This Dataset Can Be Used for Assessment and Reconstruction

From July 18 to today, Henan has experienced a rare and continuous heavy rainfall process, with Zhengzhou becoming the prefecture-level city with the heaviest rainfall. Heavy rainstorms and extremely heavy rainstorms have hit the entire city, with an average cumulative rainfall of 449 mm. Both daily and hourly rainfall have exceeded the extreme values since meteorological records began, causing concern and worry among people across the country.
Among them, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University alone has suffered economic losses of more than 1 billion yuan due to the deployment of valuable equipment and precision instruments such as CT, MRI, hyperbaric oxygen chamber, computer room, etc. on the first floor or the underground floor. It is conservatively estimated that this has caused economic losses of more than 1 billion yuan.
Rescue is urgent, how can technology play a role?
In the past, rescue workers learned about the disaster situation through people’s requests for help and on-site assessments, but the assessment process could take several hours, which was extremely detrimental to rescue work.
In terms of disaster monitoring, although the relevant departments have a complete ground monitoring system, it is still unable to meet more refined monitoring needs due to limitations in coverage and convenience.Nowadays, drones and satellite remote sensing are used in disaster relief and post-disaster reconstruction, among which satellite remote sensing technology has become a necessary supplement.
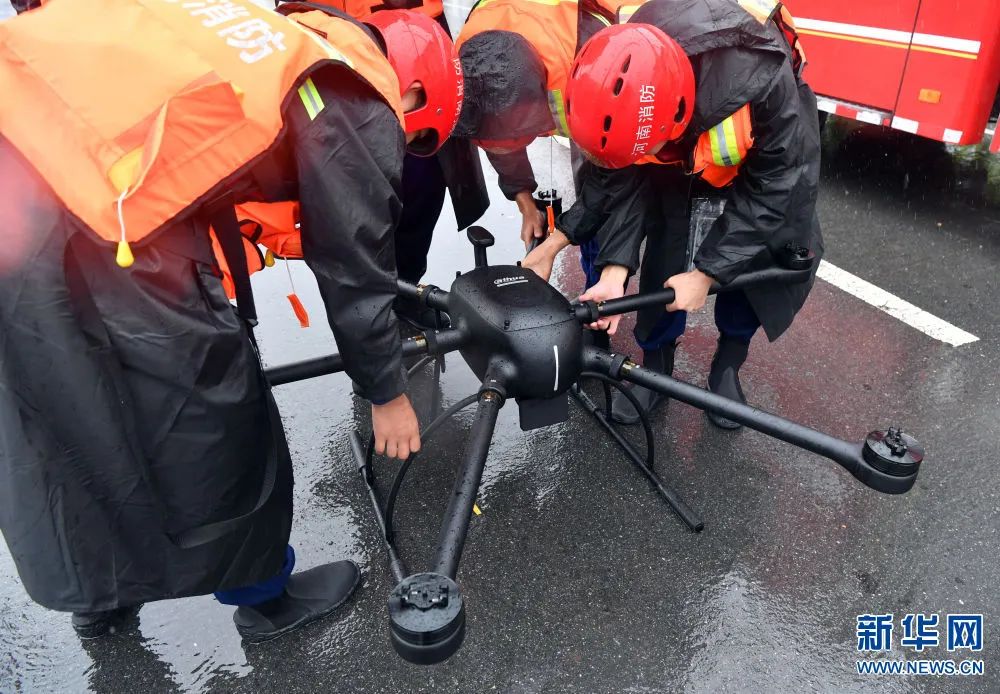

Drone equipment used at the site of the Henan rainstorm disaster
It played an important role in observation, search, lighting, delivery, and shouting to comfort people.
Remote sensing's high repetition frequency and large-scale synchronous information collection capabilities can fill in the gaps in past monitoring to a greater extent, and provide wider-ranging and more accurate real-time data for indicators such as the scope and extent of disasters in the target area.
In terms of remote sensing images, the use of multispectral and SAR image data combined with machine learning technology can help relevant departments identify areas with severe disasters, which requires more timely remote sensing images and analysis solutions.
xBD: The world's largest disaster loss assessment dataset
In 2019, the xView2 Disaster Damage Assessment Challenge, led by the U.S. Department of Defense, enabled the use of a high-resolution satellite imagery post-disaster assessment dataset. The xBD dataset is not only the first building damage assessment dataset to date, but also one of the largest and highest quality public datasets of annotated high-resolution satellite remote sensing images.
The xBD dataset provides multi-band satellite images before and after various disaster events, including constructed polygons, classification labels of damage types, grade labels of damage extent, and corresponding satellite metadata. In addition, the dataset also contains labels for bounding boxes and environmental factors such as fire, water, smoke, etc.

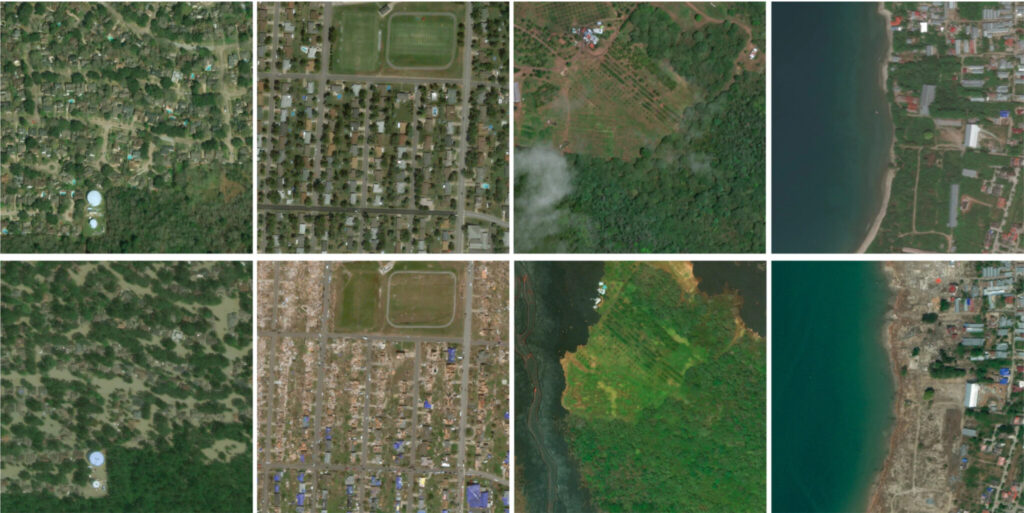
The dataset covers dozens of disaster images from 15 countries around the world
The dataset contains 850,000 building annotations from 50,000 square kilometers of remote sensing images (0.3 meter accuracy) from 15 countries. Seven disaster types are included:Wildfires, landslides, dam failures, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes/tsunamis, and wind and flood damage.
xView2 xBD Disaster Damage Assessment Dataset
Issued by:Maxar/DigitalGlobe
Data format:png etc.
Data size:30.3 GB
Update time:October 28, 2020
Download Locationsite:Dataset Download

Schematic diagram of images in the dataset
The dataset includes Train training set, Test test set, HoldoutKeep Setand Tier3 Dataset:
- TrainImage pairs (before and after the disaster) and ground truth information about buildings and damage extent were provided for the pixel segmentation task.
- TestImages only, for challenge ranking purposes;
- HoldoutIt will be kept confidential during the challenge, with the purpose of testing the generalization performance of the results submitted by the verified challenge teams;
- Tier3 DatasetAvailable midway through the challenge and as additional/supplemental training sets covering additional hazard spans and geographic areas.
The significance of AI in disaster relief and reconstruction
Flood disasters, due to their wide geographical distribution and frequent occurrence, cause the highest economic losses among all natural disasters. Public facilities such as roads, railways, bridges, power and gas lines will all be destroyed to varying degrees.
For sudden natural disasters, relevant rescue personnel are required to minimize reaction time, respond quickly, take action, minimize losses and save lives. In addition, in order to better deploy resources in the disaster-stricken areas, it is necessary to timely grasp the location and extent of the disaster and optimize rescue resources.
When disaster strikes, every second counts.Although humans are insignificant in the face of natural disasters, the addition of new technologies and artificial intelligence has given us more confidence in the face of crises and given cities in desperate situations more hope of survival.

Let's believe in the light