Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
AI Weekly Paper Report: Latest Research From Alibaba, Xiamen University, Zhejiang University, and More, Covering Reinforcement Learning Optimization Algorithms, GUI Agents, Multimodal Context Compression, and More
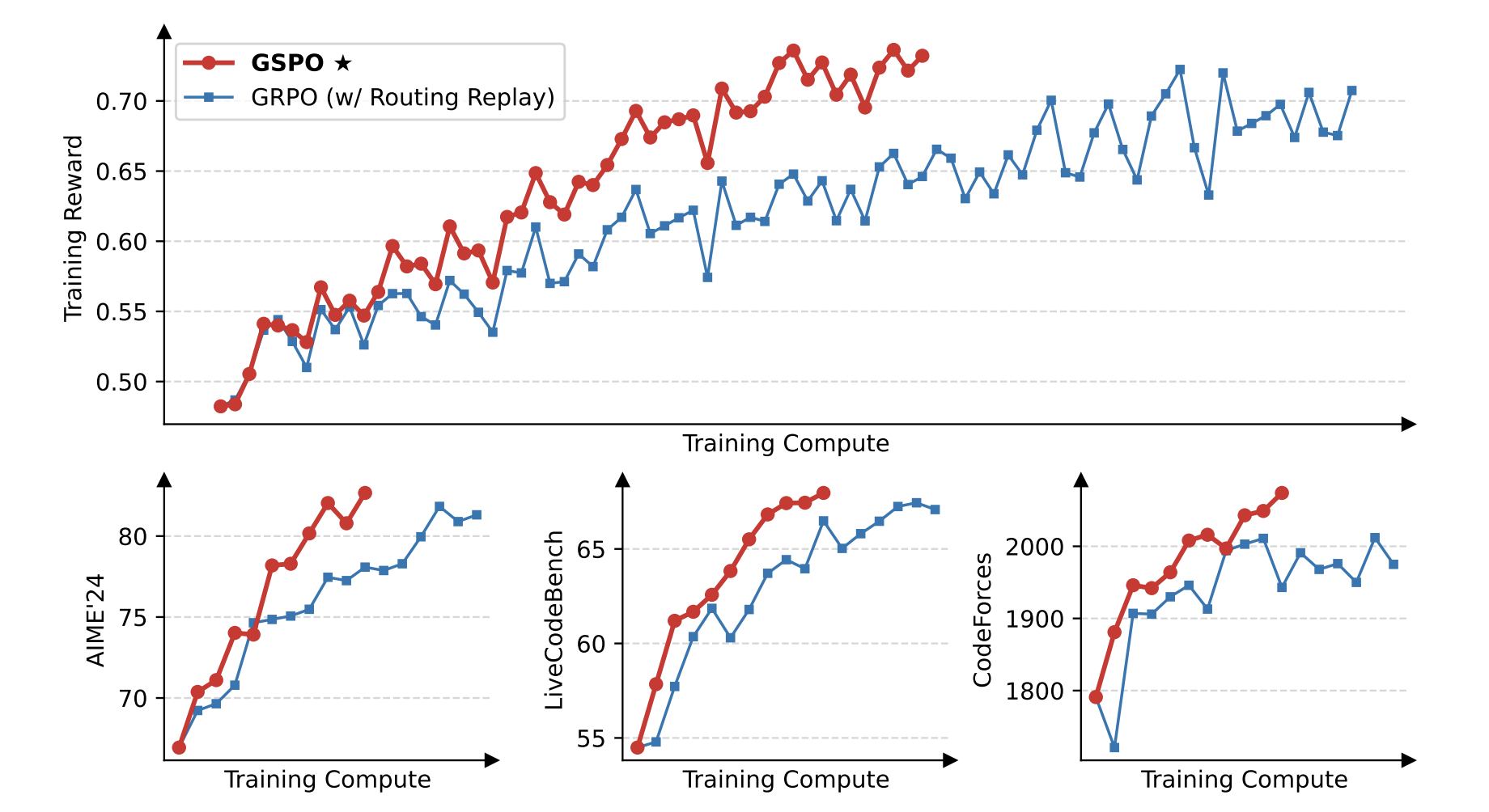
As large-scale language models continue to scale, efficient and stable reinforcement learning training becomes a key challenge. To address this, Alibaba Group's Qwen team proposed a novel reinforcement learning algorithm, Group Sequence Policy Optimization (GSPO).
Unlike traditional methods that rely on token-level importance ratios, GSPO defines importance ratios based on sequence probabilities and performs truncation, rewards, and optimization at the sequence level, significantly improving training stability and efficiency. GSPO performs exceptionally well within the Mixture-of-Experts architecture, simplifying the design of reinforcement learning infrastructure and significantly improving the performance of the latest Qwen3 model.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/FOrdj
Latest AI Papers:https://go.hyper.ai/hzChC
In order to let more users know the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence in academia, HyperAI's official website (hyper.ai) has now launched a "Latest Papers" section, which updates cutting-edge AI research papers every day.Here are 5 popular AI papers we recommend, let’s take a quick look at this week’s cutting-edge AI achievements⬇️
This week's paper recommendation
1 Group Sequence Policy Optimization
This paper introduces Group Sequence Policy Optimization (GSPO), a stable, efficient, and high-performance reinforcement learning algorithm for training large language models. Unlike previous algorithms that use token importance ratios, GSPO defines importance ratios based on sequence likelihood and performs sequence-level pruning, rewards, and optimization.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/FOrdj
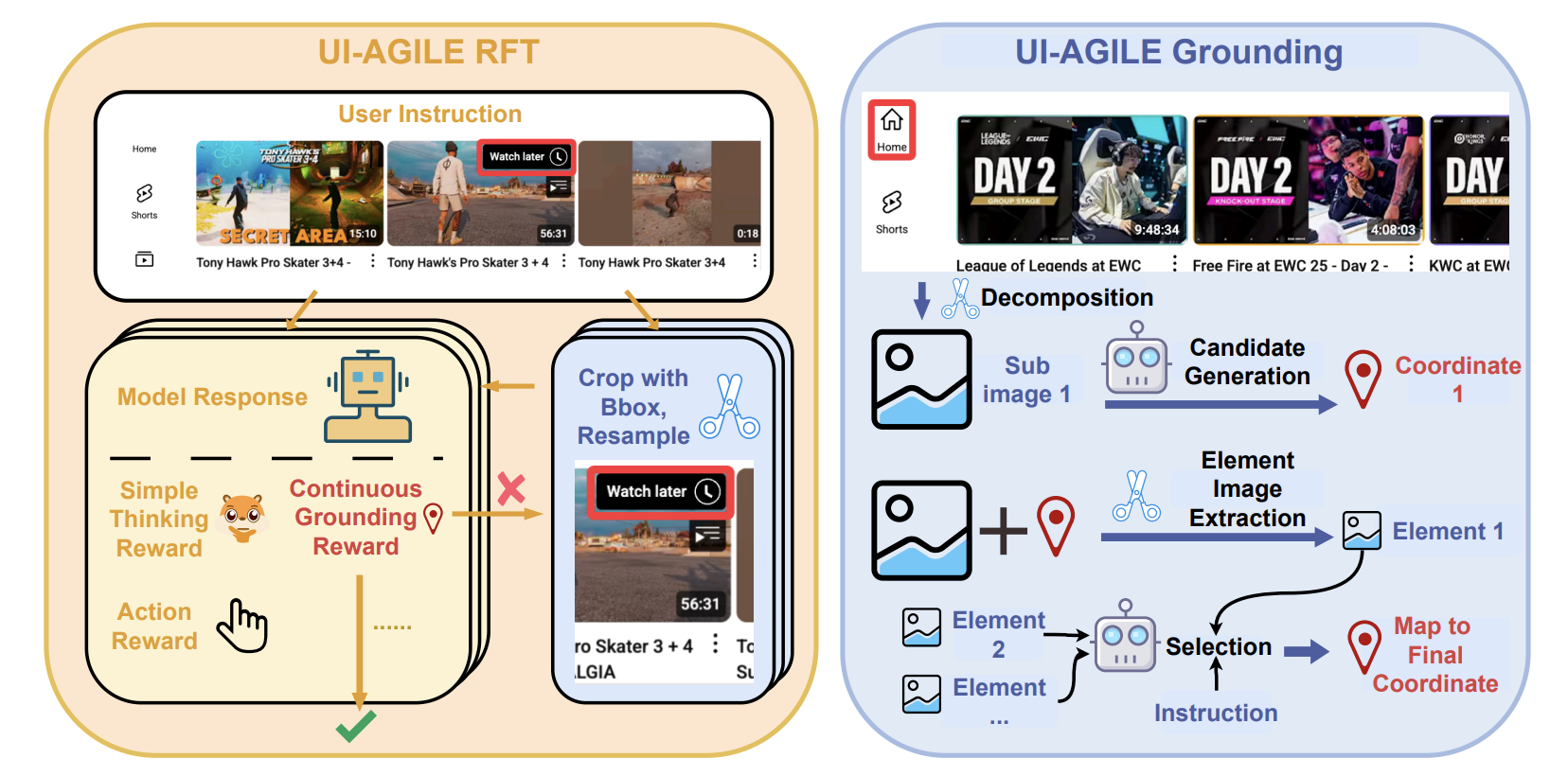
2 UI-AGILE: Advancing GUI Agents with Effective Reinforcement Learning and Precise Inference-Time Grounding
Existing GUI agent training and inference methods still face challenges such as inference design difficulties, ineffective reward mechanisms, and visual noise interference. This paper proposes a novel method—selective decomposition alignment—which significantly improves alignment accuracy on high-resolution interfaces by dividing the image into smaller, more manageable parts. Experimental results demonstrate that UI-AGILE achieves state-of-the-art performance on two benchmark tasks: ScreenSpot-Pro and ScreenSpot-v2.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/SRpdE
3 When Tokens Talk Too Much: A Survey of Multimodal Long-Context Token Compression across Images, Videos, and Audios
This paper presents the first systematic review and summary of the rapidly developing research area of multimodal long-context token compression. Given the unique characteristics and redundancy of different modalities, researchers have categorized existing methods by the type of data they primarily address, enabling quick access to methods applicable to specific research areas: image-centric compression, video-centric compression, and audio-centric compression.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/nOYw4
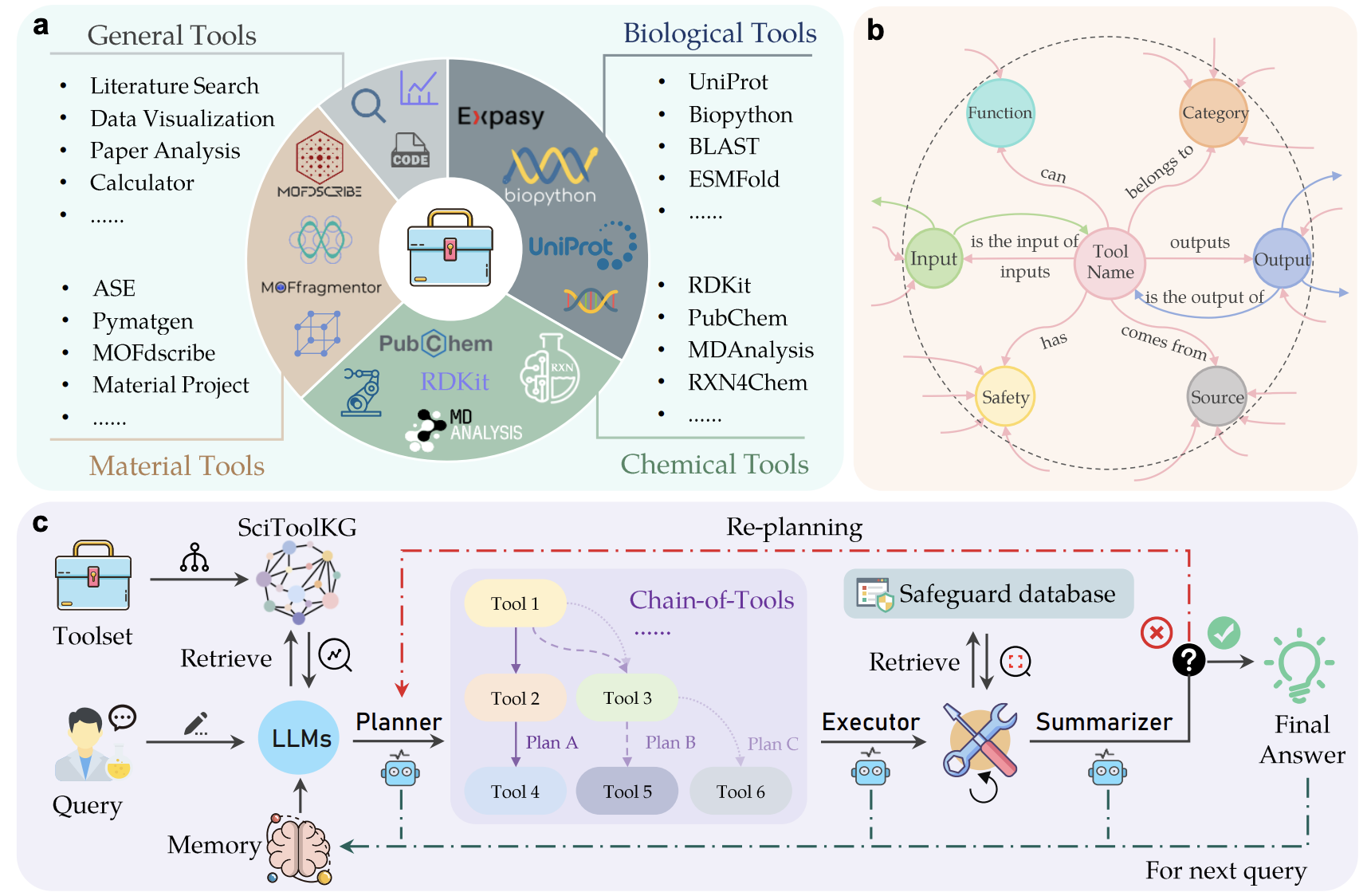
4 SciToolAgent: A Knowledge Graph-Driven Scientific Agent for Multi-Tool Integration
This paper presents SciToolAgent, an agent powered by the LLM that automates the operation of hundreds of scientific research tools across biology, chemistry, and materials science. At its core, SciToolAgent is a scientific tool knowledge graph that leverages a graph-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) mechanism to enable intelligent tool selection and execution. The system also integrates a comprehensive safety check module to ensure responsible and ethical tool use.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/IOiRk
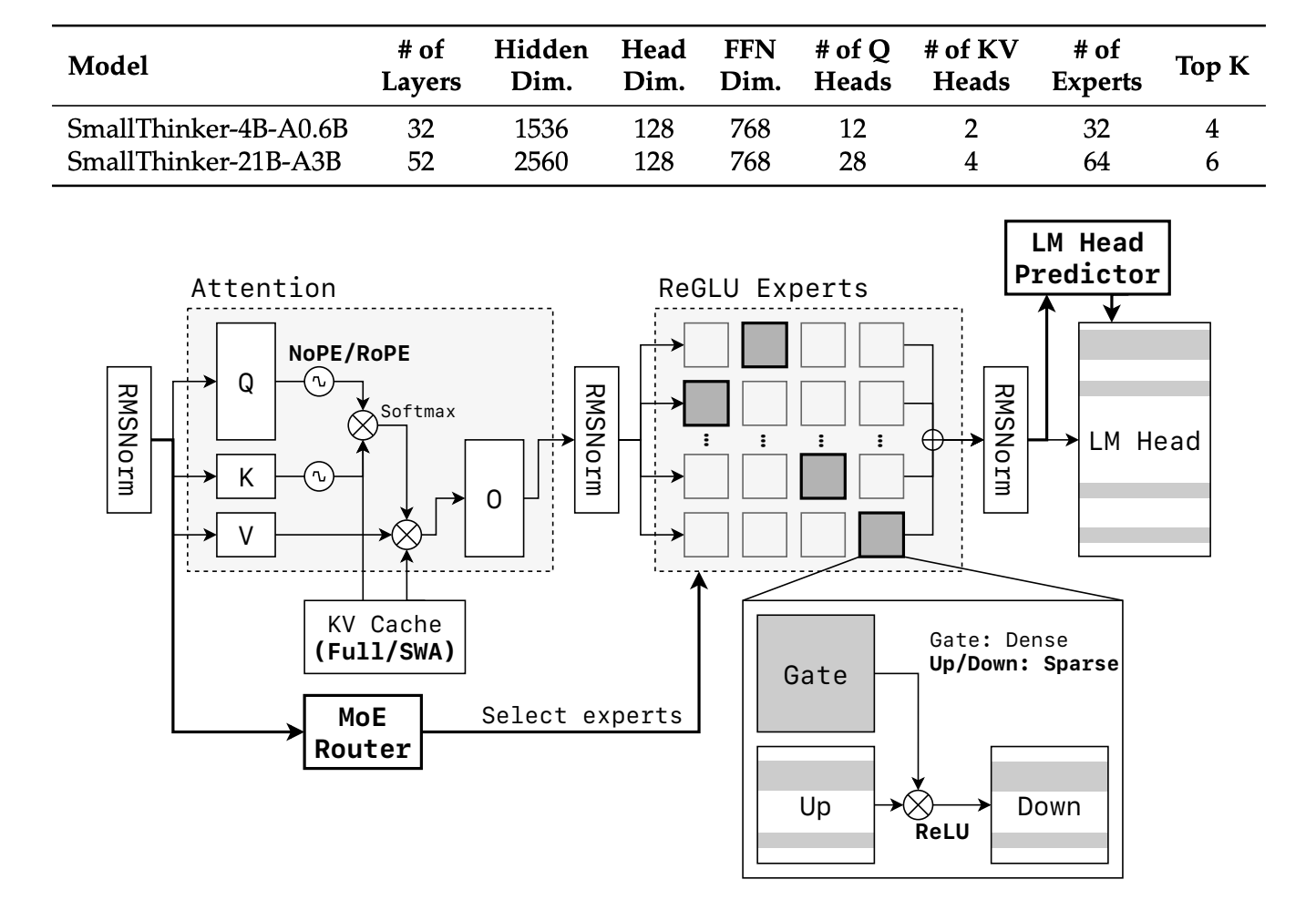
5 SmallThinker: A Family of Efficient Large Language Models Natively Trained for Local Deployment
This paper presents SmallThinker, a set of LLMs designed natively for local devices (rather than compressed from cloud models). They are specifically tailored to address the unique limitations of local devices: weak computing power, limited memory, and slow storage. SmallThinker is architecturally redesigned to operate efficiently in constrained environments. At its core, it features an innovative "deployment-oriented" architecture that translates system constraints into design principles.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/tSwpG
The above is all the content of this week’s paper recommendation. For more cutting-edge AI research papers, please visit the “Latest Papers” section of hyper.ai’s official website.
We also welcome research teams to submit high-quality results and papers to us. Those interested can add the NeuroStar WeChat (WeChat ID: Hyperai01).
See you next week!