Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Costs Dropped 100 Times! Nonprofit E11 Bio's New Results Map the Connections Between Millions of Cells in the Brain

The human brain is one of the most complex structures in the known universe. It consists of approximately 100 billion neurons, each connected to other neurons through thousands of synapses, forming an unimaginably complex network. This network not only controls our bodies, but also shapes our thoughts, emotions, and consciousness. From simple reflex actions to profound philosophical thoughts, every function of the brain demonstrates its extraordinary complexity.
Despite decades of intensive research into the brain, our understanding of its mysteries remains limited.Among the 125 most cutting-edge scientific issues in the world released by Science, 16 are closely related to brain science.These questions go straight to the core, such as how do the structure and function of the brain work together? How do complex neural networks shape behavior and cognition? These unsolved mysteries not only reveal the deep challenges of brain science research, but also reflect the urgent desire of mankind to explore the working mechanism of the brain.
At the same time, brain-related diseases are becoming a global challenge. The social burden brought by brain diseases such as depression, Alzheimer's disease, and Parkinson's disease is increasing year by year. However, the current prevention and treatment methods for these diseases are still limited. This limitation calls for the scientific community to increase investment, deeply analyze the occurrence and development mechanism of brain diseases, and bring more accurate and efficient treatment plans to patients.
In this context, E11 Bio came into being in 2022. As the first non-profit Focused Research Organization (FRO),E11 Bio is committed to building a full-stack brain structure mapping technology.Providing scientists and medical researchers with powerful tools to unlock the complex structure and function of the brain.
E11 Bio official website:
https://e11.bio/
E11 Bio: A cutting-edge team using science to illuminate the mysteries of the brain
To support the development of breakthrough science and technology and solve key social problems, in 2017,Former Google CEO Eric Schmidt and his wife Wendy Schmidt founded the philanthropic initiative Schmidt Futures.The program aims to advance breakthroughs in global science and technology by funding and supporting cutting-edge research.
As Schmidt Futures has grown, its vision has become more focused. In 2021, a new organization called Convergent Research was spun off as an independent nonprofit focused on creating and supporting FROs. These FROs are like startups in the scientific community.It consists of a team focused on a specific goal, led by a CEO who can devote themselves to research without having to worry about research funding or commercialization pressure.
The biotechnology company E11 Bio is the first FRO operated in a non-profit form. It was founded in 2022 and is headquartered in Alameda, California. Its co-founder and CEO is Andrew Payne. He has extensive experience in the forefront of space and molecular methods.He is particularly good at super-resolution microscopy and spatially resolved studies of genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics.
After studying engineering physics at the University of Toronto, Andrew Payne joined Ed Boyden's group at MIT to pursue a PhD, focusing on developing neural circuit architecture mapping technology applicable to the mammalian brain scale.He created a disruptive spatially resolved molecular microscopy technology that expanded microscopic imaging from the original 4 colors to 4 billion digital colors.This technology provides a new perspective for the precise mapping of brain structure. The related paper was published in Science under the title "In situ genome sequencing resolves DNA sequence and structure in intact biological samples".
Paper address:
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.aay3446

In addition to Andrew Payne, the E11 Bio team consists of many top scientists, including chief neuroanatomy scientist Johan Winnubst, optical connectomics experts Julia Michalska and Hugo Damstra, and machine learning scientist Arlo Sheridan, etc.

It is worth mentioning that the team's operations are strongly supported by Chief Operating Officer Jun Axup, who was previously the Chief Scientific Officer and Partner of IndieBio, a leading global life science accelerator, and holds a Ph.D. in Chemical Biology from the Scripps Research Institute.She has extensive entrepreneurial experience in the fields of immuno-oncology, protein engineering, laboratory automation robotics, CRISPR and precision medicine.She has co-founded 2 start-ups and is passionate about increasing human health span, unlocking the mysteries of the brain and addressing the global challenge of climate change.

The establishment of E11 Bio not only marks a new exploration of the non-profit research model, but also provides an unprecedented innovative path for solving major scientific problems.
PRISM Technology Release: A New Engine to Drive the Whole-Brain Connectomics Revolution
Since its inception, E11 Biois committed to building an open and scalable single-cell brain mapping technology platform.The goal is to make this technology as popular as DNA sequencing, so that every neuroscientist can use it easily. After two years of continuous efforts, E11 Bio has made important breakthroughs in the field of brain science research.
On December 3, E11 Bio announced the launch of PRISM technology.This technology was developed by E11 Bio in collaboration with Sam Rodriques' laboratory at the Crick Institute, Joergen Kornfeld's laboratory at the Max Planck Institute/LMB in Cambridge, England, Ed Boyden's laboratory at MIT, and the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). The advent of PRISM marks a new milestone in brain science research towards whole-brain connectomics.
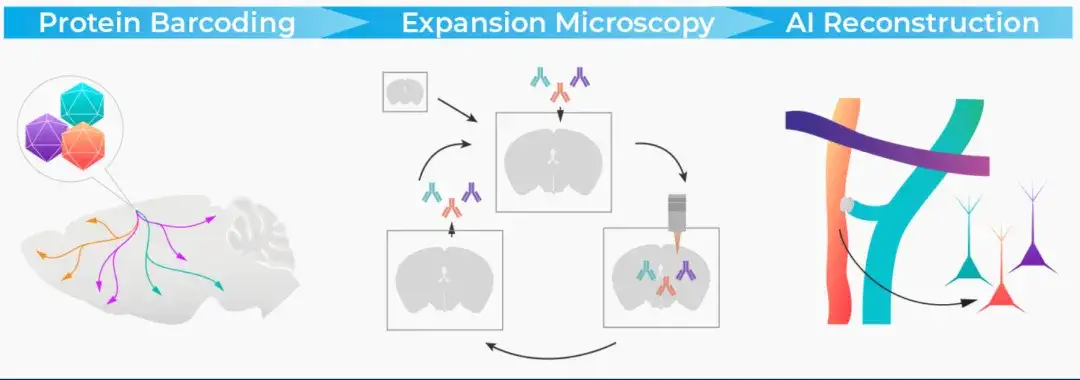
The core of PRISM technology is to map the connections between millions of cells throughout the brain at a very low cost.This allows whole-brain connectomics research to expand from small brains such as fruit flies to more complex mammalian brains such as mice, providing the possibility for future exploration of the human brain.
Specifically,PRISM significantly improves the quality and interpretability of brain image data by performing optical connectome reconstruction through iterative staining with molecular annotations.The researchers instructed each cell to generate a different combination of proteins as a cell identity (barcode). With the help of extended microscopy and special staining procedures, these barcodes can provide accurate annotations for image data. This annotation further assisted the development of an AI-based "self-correcting" image segmentation model, significantly reducing the need for manual proofreading and successfully reducing costs by about 95%.
At the same time, PRISM has also solved the key cost problem in traditional connectome research through multiple technical optimizations. For example, the combination of light sheet microscopy and expansion microscopy technology allows researchers to achieve similar resolution and throughput at one-tenth the cost of electron microscopy; in addition, the use of GPU-accelerated segmentation algorithms (such as local shape descriptors) further improves efficiency, and the segmentation cost is 10-100 times lower than the Wellcome Trust's estimate.This series of innovations is expected to reduce the overall cost of whole-brain connectomics by at least 100 times.
* The Wellcome Trust is a biomedical research charity based in London, UK. Founded in 1936, it aims to fund medical and biological science research worldwide to improve the health of people and animals.
PRISM technology not only lowers the threshold for brain science research, but also provides crucial support for the development of artificial intelligence that is closer to humans, the treatment of brain diseases, and the simulation of human brain circuits. The breakthrough results of this technology will greatly promote the frontier progress of neuroscience.Details of the PRISM study will be published in a paper, a preprint of which will be released early next year, and a beta version of the method will also be made public.
Uncovering the ultimate secrets of the human brain, the global brain science competition is in full swing
In order to fully reveal the mysteries of the brain, promote the development of brain-like intelligent technologies, and provide new solutions for the diagnosis and treatment of brain diseases, countries have launched large-scale scientific research projects led by the government.
In 2005, Swiss neuroscientist Professor Henry Markram, with support from the Swiss federal government,The Blue Brain Project was launched at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Lausanne.
In 2013,President Obama launched the Brain Research Through Innovative Neurotechnologies (BRAIN) program.Led by the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
In 2014, with a total of US$365 million in funding from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and the Japan Council for Medical Research and Development,Japan has also launched a 10-year "Brain Mapping Using Integrated Neurotechnologies for Disease Research" (BRAIN/MINDS) program.
In the same year, Chinese brain science researchers discussed the goals, tasks and feasibility of the Chinese Brain Science Plan at the Xiangshan Science Conference; in 2016,my country has listed "brain science and brain-like research" as a major national scientific and technological innovation and engineering project in the "13th Five-Year Plan", marking the full launch of the "China Brain Project". In 2021, my country's "Brain Science and Brain-like Research" program was officially launched.
Although my country's brain project started relatively late, it has shown strong research capabilities. For example, the Center for Excellence in Brain Science and Intelligence Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has long been committed to the research of brain networks and neurological diseases, especially in the establishment of primate models, and is in an international leading position.
Tsinghua University, Peking University, Fudan University, Shandong University and other universities have established special brain science research centers, focusing on the fields of neural network modeling, brain disease mechanisms and brain-like artificial intelligence. In addition, the Shanghai Brain Science and Brain-like Research Center, as China's first comprehensive brain science research institution, focuses on large-scale brain mapping and brain disease research, providing strong support for this field.
As global brain science research is in full swing and with the deep integration of AI technology, we have reason to believe that future brain science research will achieve revolutionary breakthroughs in brain-like computing, brain disease treatment, and intelligent technology innovation, and make important contributions to promoting social progress and improving human well-being.
References:
1.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9568407/
2.https://www.fastcompany.com/90684882/these-focused-research-organizations-are-taking-on-gaps-in-scientific-discovery
3.https://indiebio.co/team/jun-axup/
4.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ar