Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Hailstorm Center Collects Data, Large Models Support Extreme Weather Forecasts, "Storm Chasers" Are on Stage
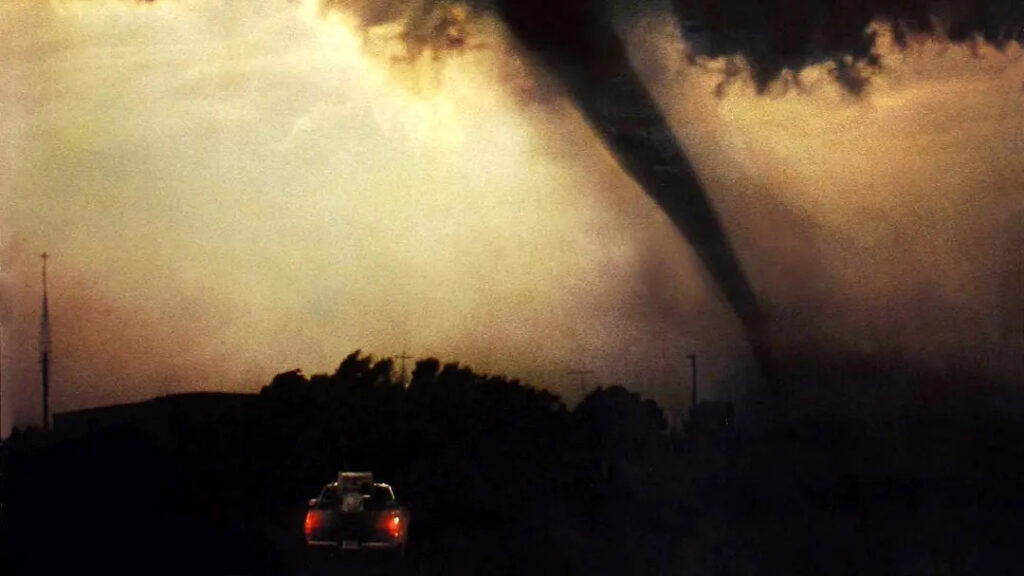

In the well-known adventure disaster film "Twister" released in 1996, the protagonist brought detection equipment into the center of the tornado in order to conduct in-depth research on tornadoes and realize real-time data recording.
Inspired by this movie, Australian meteorologists Joshua Soderholm and Julian Brimelow started their own storm-chasing journey.They also successfully brought a small weather sensor hailsonde into a hail storm to collect meteorological data during the hailstorm, revolutionizing the way extreme weather is studied.

For more movie details, please see:https://movie.douban.com/subject/1292454/
The ice probes are similar in shape to hailstones and weigh about 24 grams. They are attached to the balloon and released into the hailstorm together. After entering the center of the hailstorm, the two separate.Ice exploration is like hail, it experiences the trajectory of hail in a hailstorm and records the growth conditions of hail as it moves in a hailstorm.In addition, the ice probe recorded significant ice growth and followed the supercell's mesocyclone for half a revolution.

"It started as an extracurricular project to see if we could use existing technology to build a device like the one in the movie. We had to solve a lot of engineering problems during the production process to ensure that the ice probe could survive the extreme conditions of a hailstorm," said Joshua Soderholm.

「Gathering data from the epicenter of a hailstorm is like chasing the white whale of meteorology—both dangerous and fascinating.The data collected from the Hailstorm Center will improve our ability to simulate hailstorms and provide direct evidence for the behavior of hail in hailstorms. But this is not as easy as it sounds, it requires you to be in the right place at the right time and encounter the right hailstorm."
After a few days of bad luck, they hit a supercell and successfully released two ice probes into the hailstorm.A supercell is a single strong thunderstorm system with a horizontal scale of more than ten kilometers and a life span of tens of minutes to hours. It is larger, more persistent, and has more severe weather than an ordinary mature single thunderstorm.After being captured by the supercell, the ice probe separated from the balloon and then floated with the hailstorm like hail, and was eventually carried to an area 7 km away by winds of more than 120 km/h.
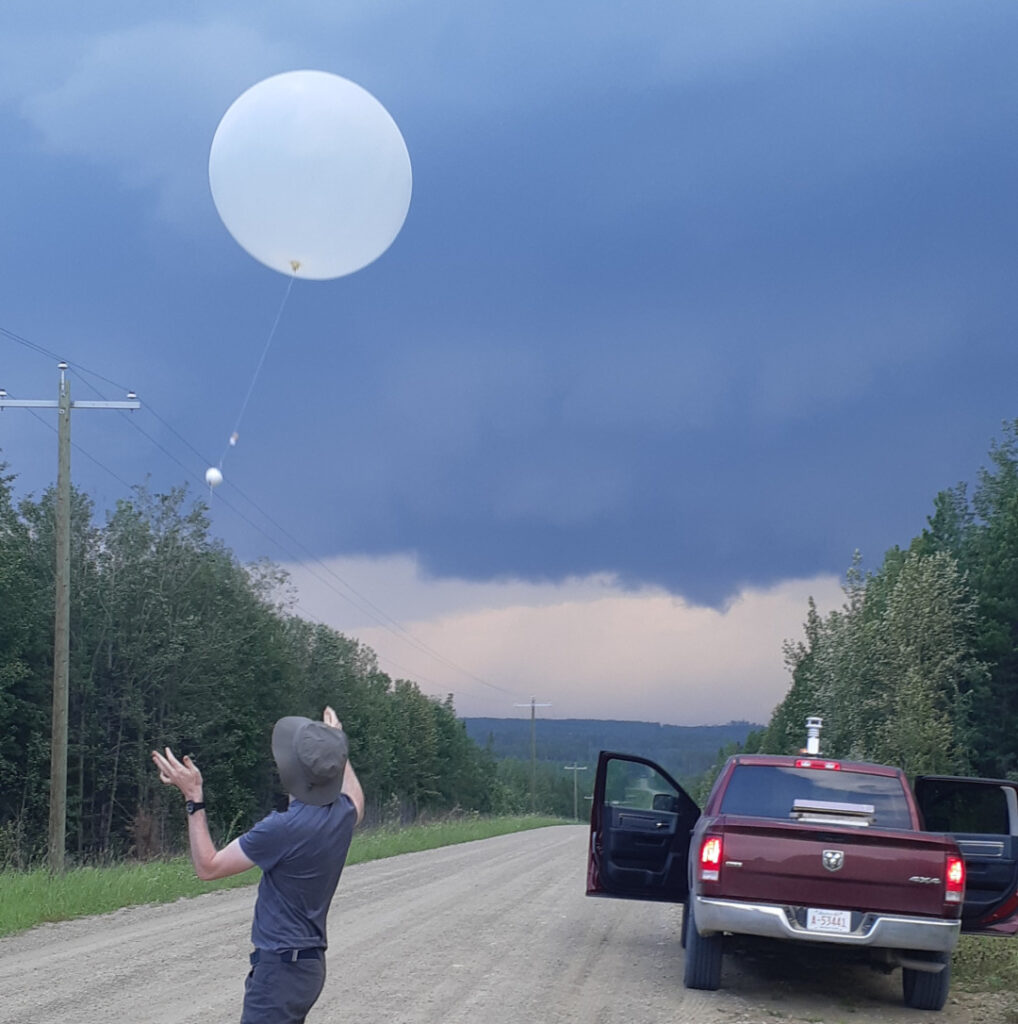

Based on this research, they are planning to use more ice probes to record the next supercell and collect ice probes that fall on the ground to conduct more in-depth research on the falling hail.
Unpredictable weather systems
Weather forecasting requires human participation. Even with the use of supercomputers, satellite data and radar data, it is still difficult to make accurate predictions about weather systems. In 1961, American meteorologist Edward Norton Lorenz tried to use a computer program to predict future weather.
After getting the result, he used the output value of the program in the middle step as the input value of the next step and ran the program again. However, since the input value only retains 3 decimal places, and the program runs with 6-digit floating point numbers,This one thousandth of a deviation causes the program's output value to be completely different from the result obtained last time.
Based on this, he proposed the concept of chaotic system. The meteorological system is a typical chaotic system, which is not completely random, but can easily change dramatically due to changes in certain factors.In other words, the meteorological system is a very sensitive system.
The "butterfly effect" is an exaggerated but typical example. A butterfly flapping its wings twice in the tropical rain forest of South America may bring a tornado to the United States. The source of all this is that the butterfly disturbs the initial variables of the system.

Therefore, it is difficult to achieve completely accurate weather forecasts.That is, Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP), which first divides the forecast area into grids and then uses supercomputers to solve partial differential equations through numerical simulation.
This method is very time-consuming. Even if a supercomputer with hundreds of nodes is used, it will take several hours to predict the weather for the next 10 days. At the same time, due to the limitation of grid resolution,Some small-scale meteorological processes will be parameterized by approximate functions, which will cause errors in meteorological forecasts.
Because of this,It is difficult for NWP to be perfect for small-scale extreme weather and medium- and long-term meteorological forecasts.After the formation of Typhoon Dusurui this year, different institutions used supercomputers to predict its path based on different models, and the structures were very different. Even the predictions made by the same model were constantly revised as meteorological conditions changed, and relatively accurate predictions could not be made until the typhoon made landfall.
The subsequent Typhoon No. 6 Kanu also had a unique movement. It suddenly turned across the Pacific Ocean, then began to wander, and finally hit Japan directly, leaving even supercomputers confused.

At the same time, since the weather forecasts made by various agencies vary greatly, weather forecasts still require the participation of forecasters.The forecaster will combine all weather forecast results and make the final weather forecast based on local climate characteristics, terrain conditions, personal experience, etc.But it still can't be guaranteed to be completely correct. There's nothing you can do about it, the weather system is just so unpredictable.

Extreme weather chaser
Small-scale supercells are a loophole in medium- and long-term weather forecasts.The characteristics of supercells are that they form quickly and are difficult to predict, and are prone to extreme weather such as thunderstorms, hail, heavy rain or tornadoes..
On the evening of August 16, 2021, Haidian District, Beijing, encountered a supercell and heavy rain. The water under the Hanhe Road Railway Bridge rose to 1.75 meters in 30 minutes, resulting in the death of 2 people. On the afternoon of August 13, 2023, Dafeng District, Yancheng City, Jiangsu Province encountered a tornado, killing 2 people and injuring 15 people. The formation of this tornado was also related to the supercell.

However, spectacular meteorological landscapes such as thunderstorms, hail, and tornadoes can feast the eyes of explorers, and therefore attract many storm chasers like Soderholm. Whenever a typhoon approaches or a supercell is about to form nearby, storm chasers will make full preparations and rush towards the storm.
At the same time, as the first witness of extreme weather,Storm chasers can also collect first-hand information on extreme weather and provide valuable materials for meteorological research.Enrich the database of existing computational models and AI models and make important contributions to the development of meteorology.
A large meteorological model comparable to NWP
As early as 2021, Alibaba Cloud revealed that the DAMO Academy and the National Meteorological Center jointly developed an AI algorithm for weather forecasting.It has also successfully predicted several severe convective weather events. In September of the same year, Deepmind published an article in Nature, using a deep generative model to make real-time rainfall forecasts.
Earlier this year, Deepmind officially launched GraphCast, which can forecast global weather for the next 10 days with a resolution of 0.25° within one minute. In April, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology and Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory jointly developed the "Fengwu" weather forecast model, which further reduced the error compared to GraphCast.
Subsequently, Huawei launched the Pangu weather model. As the model introduced a three-dimensional neural network,For the first time, Pangu's forecast accuracy exceeded the most accurate NWP forecast system currently available.Recently, Tsinghua University and Fudan University have successively released the "NowCastNet" and "Fuxi" models.The former is very useful in short-term extreme weather forecasts, while the latter extends the forecast period to 15 days.
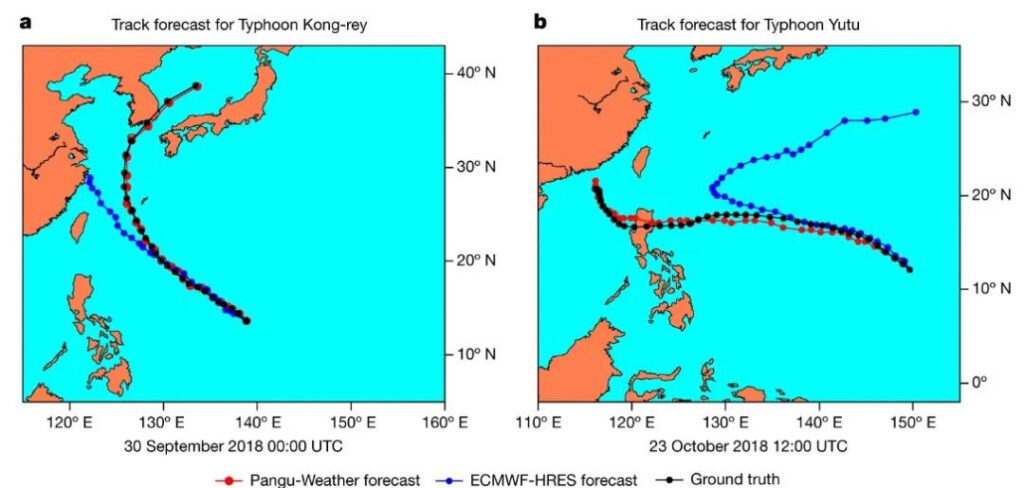
and the path forecast of Typhoon Yutu No. 26 (Figure b)
Red: Pangu model predictions
Blue: ECMWF forecast
Black: Actual situation
It can be seen that the large-scale meteorological forecasting models are constantly approaching and even partially exceeding the traditional NWP analysis model in terms of forecast accuracy and forecast time.At the same time, compared with NWP, AI large-scale weather forecasting requires lower equipment conditions and takes less time. Using only a Google TPU v4, GraphCast can predict future weather within minutes.
However, existing AI models can only predict future weather by learning from past weather data.Therefore, in scenarios of extreme weather and sudden weather, large models also need the assistance of other algorithms, and are inseparable from human participation.At this time, the meteorological data provided by the storm chasers active in the center of the storm becomes even more important for the optimization of the AI big model. Humans and big models work together to make an excellent "Storm Chaser".