Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Bonsai, Acquired by Microsoft Two Years Ago, Has Become an Important Killer at Build 2020

Yesterday, Microsoft Build 2020 was held online for the first time. On the first day of the conference, several blockbuster new products were released, including AI supercomputers, industrial system AI development platform Bonsai project, etc., from which we can get a glimpse of Microsoft's AI layout.
Microsoft's Build 2020 conference is here as scheduled, and this is the first time it has been held online.
The focus of this year's conference is still cloud computing and artificial intelligence.

At this conference, Microsoft focused on introducing the industrial system AI development platform Project Bonsai.The project actually originated from an acquisition by Microsoft two years ago.
Project Bonsai Original family: Bonsai
Founded in early 2014, Bonsai is an artificial intelligence startup based in Berkeley, California.
CEO Mark Hammond worked at Microsoft in the late 1990s and early 2000s.
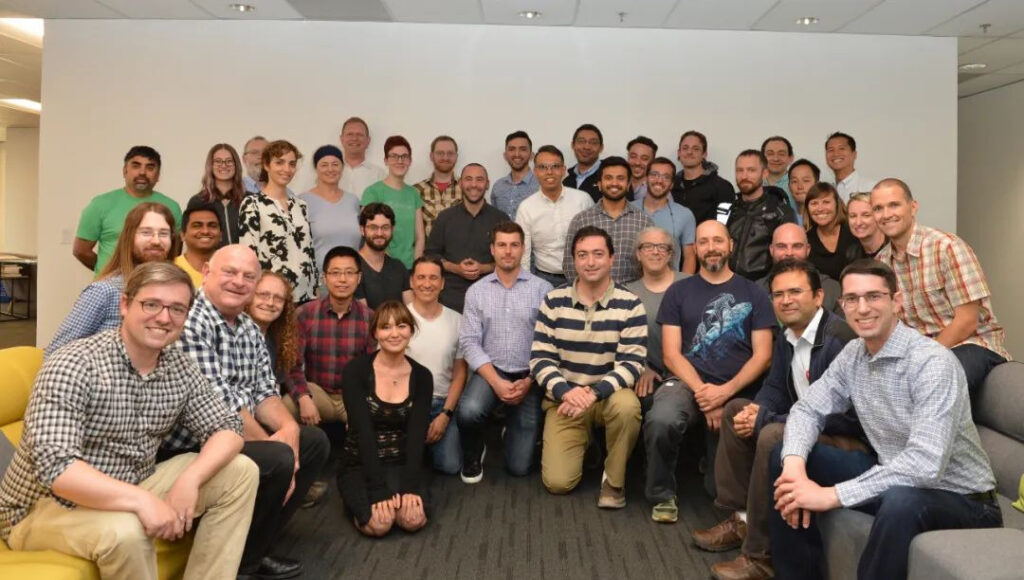

The company's main business is to apply reinforcement learning to the industrial field, using the "machine teaching" method to accelerate the model training process, thereby solving automation problems in the industry. It is mainly used in robotics, energy, industry, and autonomous driving.
In September 2017, Bonsai established a new reinforcement learning benchmark for programming industrial control systems. Demonstrating this achievement using a robotics task, the platform successfully trained a simulated robot arm to grasp and stack blocks by breaking the task down into simpler sub-concepts.
Their new technique performs 45 times faster than a similar approach from Google DeepMind.
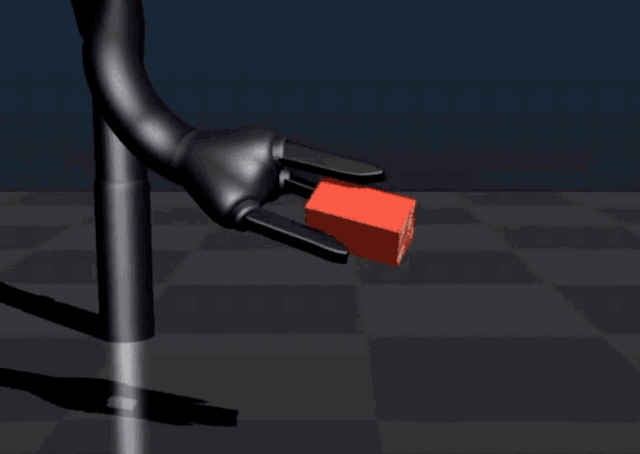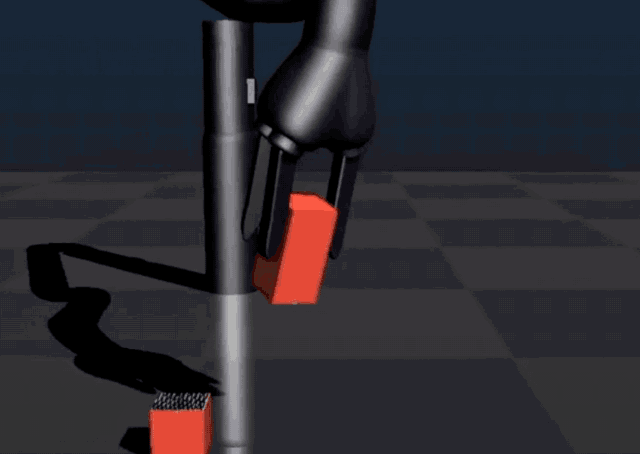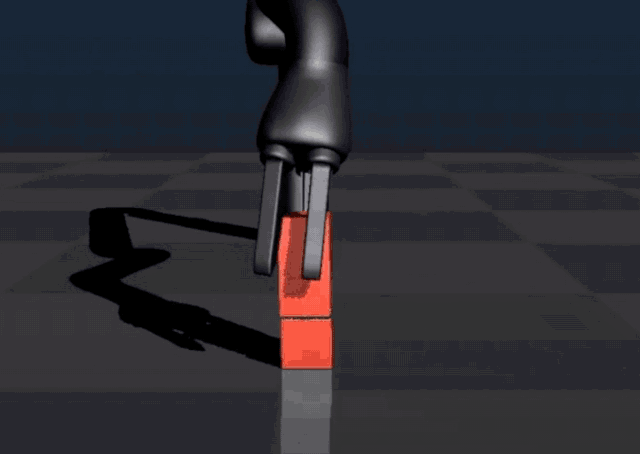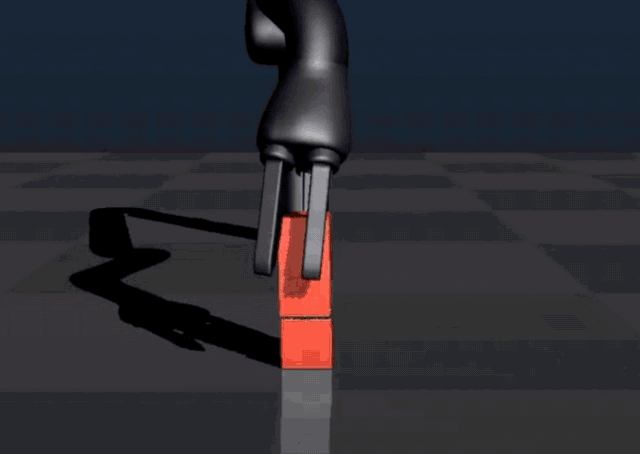
In June 2018, Microsoft announced the acquisition of Bonsai, claiming that it had built the "brain" of industrial intelligent systems.
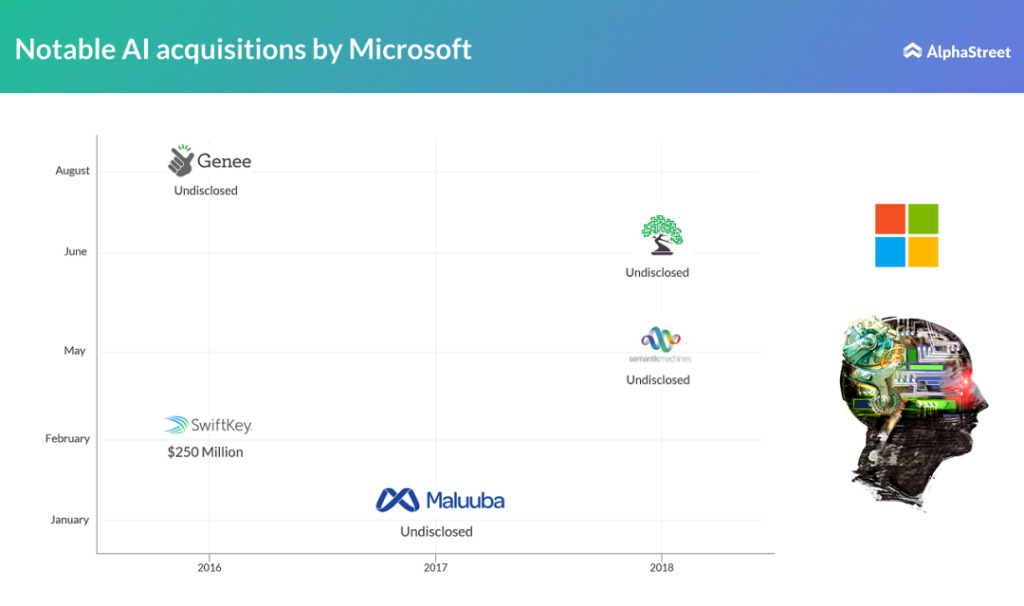
Although Microsoft did not disclose the acquisition amount, according to data provided by market research firm Crunchbase, the company has raised a total of US$13.6 million in the past, with venture capital coming from ABB Technology Ventures, New Enterprise Associates, Samsung, Siemens and Microsoft's own venture capital company, M12.
Through this acquisition, Microsoft will combine Bonsai with Azure to better promote its products to various vertical industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and automotive, building powerful autonomous industrial systems for the latter.
Project Bonsai: Microsoft's largest layout in industrial scenarios
After the acquisition was completed, Bonsai became Project Bonsai released at Build 2020, and also became Microsoft's largest layout in industrial applications.
Project Bonsai is an AI platform for building autonomous industrial control systems and a "machine teaching" service that combines machine learning, calibration, and optimization capabilities to automate the core control systems of machinery in industries such as manufacturing, chemicals, construction, energy, and mining to help manage various types of industrial equipment.

Application scenarios include decision deployment in core control systems such as robotic arms, bulldozer blades, forklifts, underground drills, rescue vehicles, wind farms and solar power plants.
Project Bonsai aims to create control systems that use a combination of digital feedback loops and human experience to inform actions and recommendations, allowing the system to complete tasks such as calibration faster and more accurately than a human operator.
Previous industrial control systems required expertise to develop and maintain, which caused great inconvenience to production. Project Bonsai simplifies the process so that even people without an AI background can apply it at work.
Bonsai does for AI what databases do for data, abstracting away the low complexity of AI and providing developers with a runtime environment and tools to write AI models.
How Project Bonsai came to be
The primary purpose of the Project Bonsai development platform is to assist in the development of industrial applications by providing a safe and repeatable testing ground for autonomous machines before actual use.
The development idea is to combine machine teaching, reinforcement learning and digital simulation.
Machine teaching and simulation
In order to simulate the problems that will be encountered in reality, Bonsai adopts the simulation method of "digital twin", which refers to the virtual representation of the real system.
For example, a model that learns to control a bulldozer will receive information about variables in the simulated environment, such as information about the soil or the distance of people walking nearby, before deciding on an action.
Hosted on Azure, Project Bonsai replicates millions of different real-world scenarios a system might encounter, including edge cases like sensor and component failures.
Developers and professionals in other fields can use Bonsai's customized programming language to impart their expertise to AI, just like writing courseware.
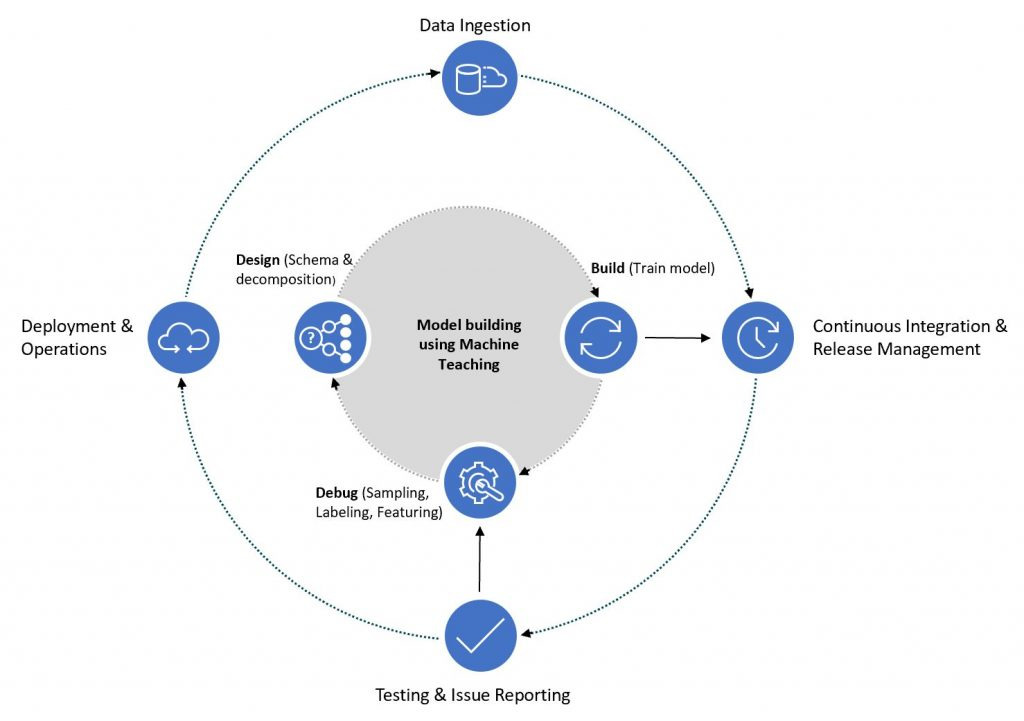
By learning these key knowledge, the Bonsai system can select the best reinforcement learning model more quickly, test different operations in a simulated environment, and provide the most effective solution, thus avoiding many time-consuming and ineffective explorations.
Once trained, the models are deployed either in a decision support capacity, integrating with existing monitoring software to provide recommendations and predictions, or directly for decision empowerment, where the models can develop solutions to challenging situations.
At the same time, these decisions are improved over time to maximize returns, and experts can adjust the system to arrive at a feasible solution.
Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning
Another technique, calledHierarchical reinforcement learning,The idea is to solve problems by breaking down the workload into simpler concepts (or sub-concepts), training them individually, and then combining them again.
The engine automatically selects the best algorithm to train the model, lays out the neural network and adjusts its parameters. The platform can run multiple simulations in parallel to reduce training time, and the prediction results of the trained model flow to software or hardware through the library provided by Bonsai.
To help developers and engineers become familiar with the features of Project Bonsai, Microsoft also launched an experimental platform called Project Moab for the first time at this conference.
It is an open source balancing robot with three arms, a joystick controller, and the ability to balance a small ball on a transparent plate on top. The tool provides a simulated environment for users to experiment with the simulator.
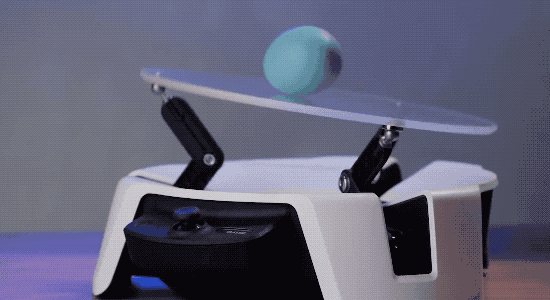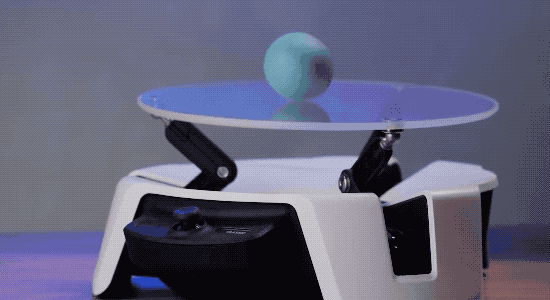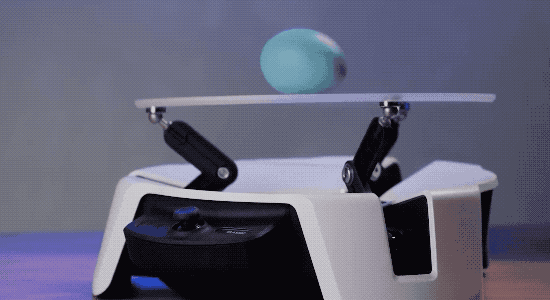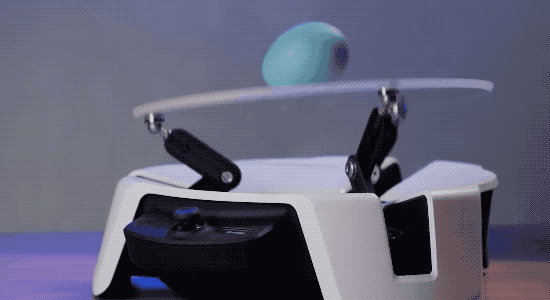
Microsoft's AI layout from Bonsai
Just as Microsoft’s founding vision was to “enable everyone to benefit from computers,” Microsoft also hopes that everyone can benefit from artificial intelligence.
In recent years, in addition to investing in artificial intelligence technologies and tools, Microsoft has also stepped up its efforts in industrial-grade applications of artificial intelligence.
The acquisition of Bonsai is one of those steps.
Microsoft has also gained a foothold in the AI competition, with a comprehensive AI product portfolio ranging from entry-level ML platforms to advanced AI platforms for industrial systems.
Microsoft pointed out at this Build conference that the Bonsai project is only the first step in its vision of helping industrial customers build autonomous systems.
References:
-- over--