Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
AI Paper Weekly丨Unified Modeling of Molecules and materials/covering 6 Types of Memory and multi-agent framework/simulating Operating System interaction...5 Popular Papers at a Glance
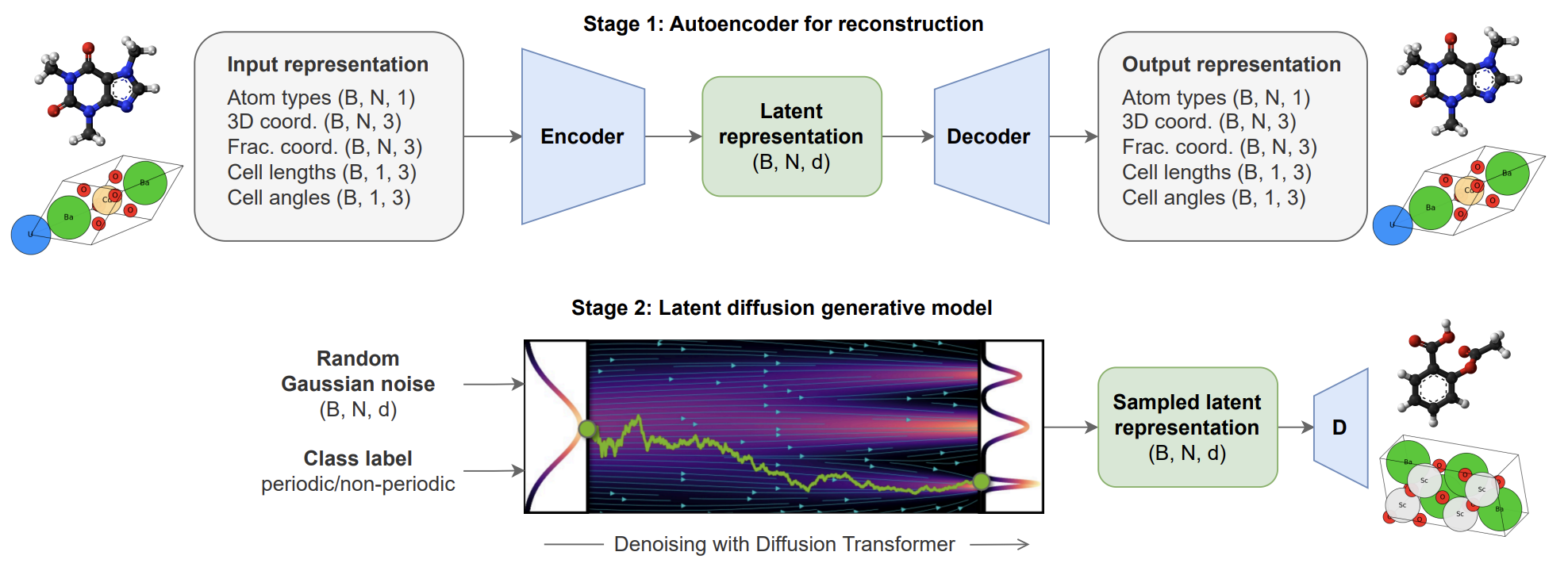
Diffusion models have become an important tool for generating 3D atomic systems due to their powerful generative capabilities and high flexibility. These models generate new structures by simulating the random motion of particles in a medium, and this approach has proven to be very effective in capturing complex atomic arrangements. However, although the underlying physical laws of these systems are the same, current generation methods are usually designed for specific types of systems (such as molecules or crystals) and lack versatility.
Based on this, the University of Cambridge and Meta's Basic Artificial Intelligence Research Department jointly proposed the All-atom Diffusion Transformer (ADiT), the first unified latent space diffusion framework that can simultaneously generate periodic materials and non-periodic molecular systems. Experimental results show that the jointly trained ADiT can generate realistic and effective molecular and material structures, and its performance has reached the state-of-the-art level comparable to models designed specifically for molecules or crystals.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/ln9AL
Latest AI Papers:https://go.hyper.ai/hzChC
In order to let more users know the latest developments in the field of artificial intelligence in academia, HyperAI's official website (hyper.ai) has now launched a "Latest Papers" section, which updates cutting-edge AI research papers every day.Here are 5 popular AI papers we recommend, let’s take a quick look at this week’s cutting-edge AI achievements⬇️
This week's paper recommendation
1 All-atom Diffusion Transformers: Unified generative modeling of molecules and materials
This paper proposes the All-Atom Diffusion Transformer (ADiT), a unified latent diffusion framework that can jointly generate periodic materials and non-periodic molecular systems using the same model: the autoencoder maps the unified all-atom representation of molecules and materials to a shared latent embedding space; the diffusion model is trained to generate new latent embeddings, which can be decoded by the autoencoder to sample new molecules or materials. Experimental results show that the jointly trained ADiT achieves state-of-the-art results comparable to molecular and crystal-specific models.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/ln9AL
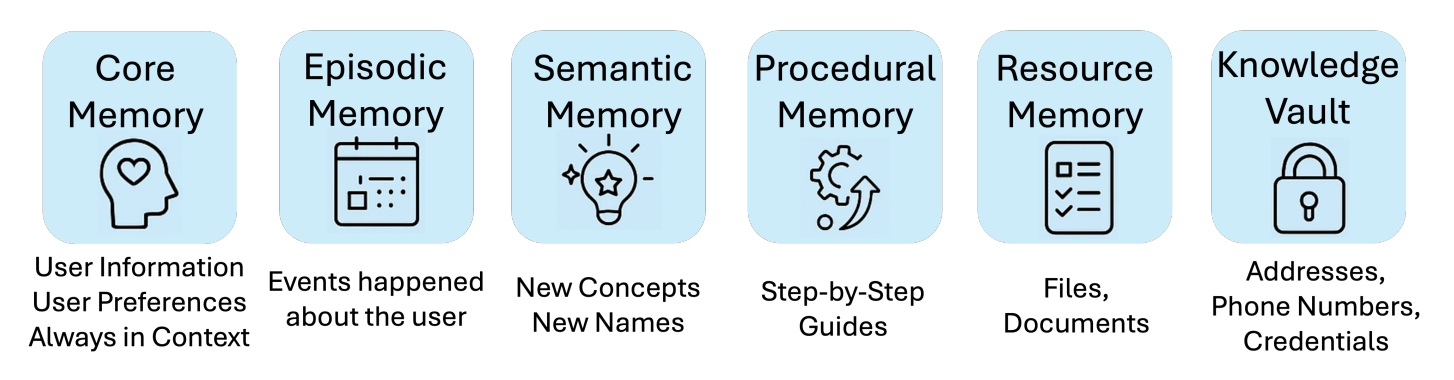
2 MIRIX: Multi-Agent Memory System for LLM-Based Agents
This paper introduces MIRIX, a modular multi-agent memory system that addresses the most pressing challenges in the field, making language models truly memorable. Unlike previous approaches, MIRIX goes beyond text to encompass rich visual and multimodal experiences, making memory truly useful in real-world scenarios. MIRIX consists of six memory types combined with a multi-agent framework that dynamically controls and coordinates the update and retrieval process. This design enables agents to persistently store, reason about, and accurately retrieve diverse, long-term user data at scale.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/L9XYi
3 NeuralOS: Towards Simulating Operating Systems via Neural Generative Models
This paper introduces NeuralOS, a neural framework that simulates the graphical user interface of an operating system by directly predicting screen frames in response to user input. NeuralOS combines a recurrent neural network for tracking the computer state and a diffusion-based neural renderer for generating screen images. Experimental results show that NeuralOS successfully renders realistic GUI sequences, accurately captures mouse interactions, and reliably predicts state transitions such as application launches.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/1w0lf
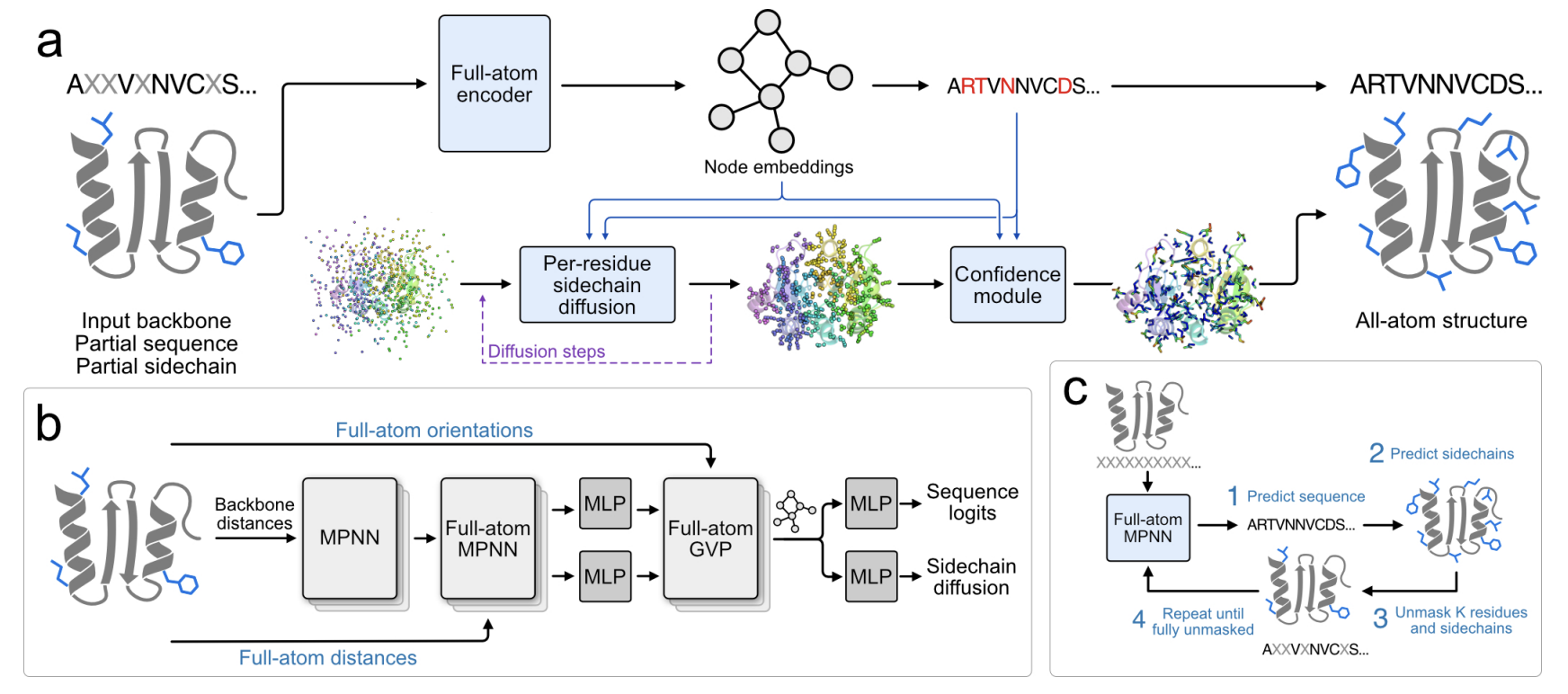
4 Sidechain conditioning and modeling for full-atom protein sequence design with FAMPNN
In this paper, we propose FAMPNN (all-atom MPNN), a method that explicitly models the sequence identity and side-chain conformation of each residue, where the probability distributions of the discrete amino acid identity and continuous side-chain conformation of each residue are learned by jointly categorical cross-entropy and diffusion loss objectives. The advantages of explicit all-atom modeling extend beyond sequence recovery to practical protein design applications, such as zero-shot prediction of experimental binding and stability measurements.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/PiNf7
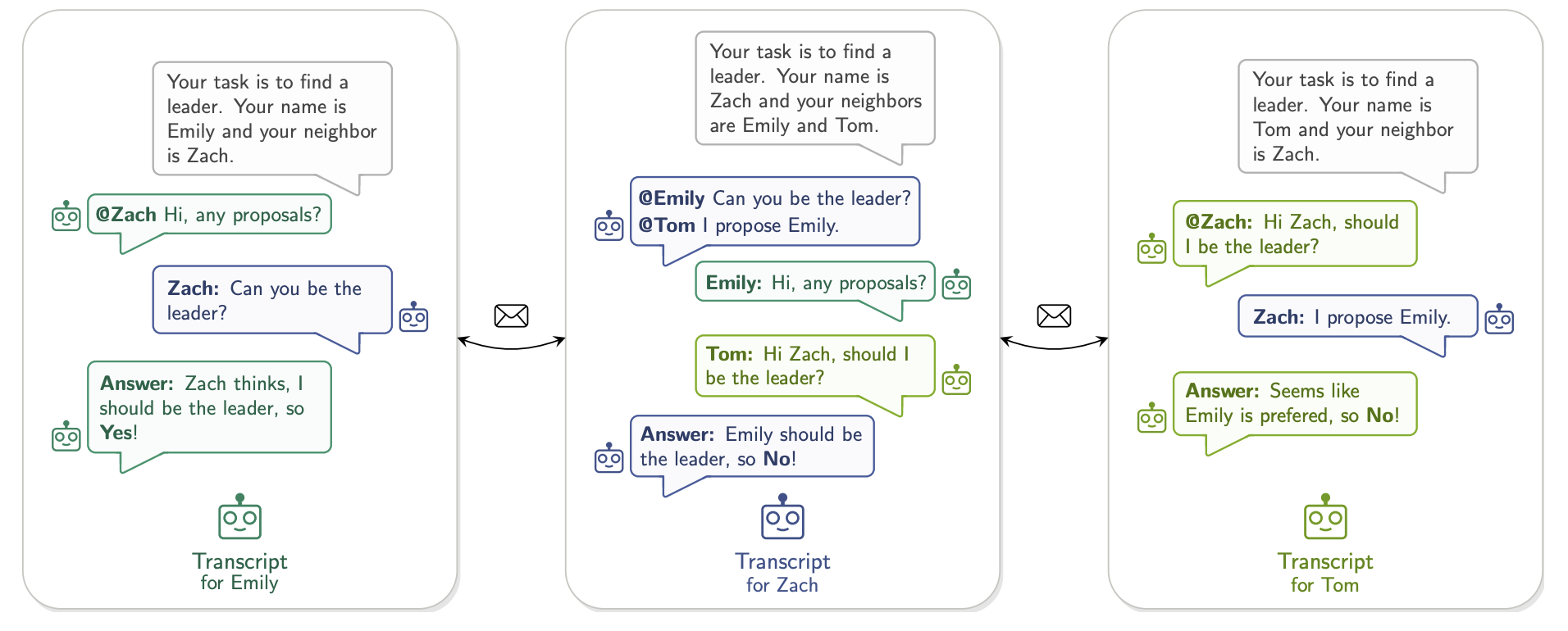
5 AgentsNet: Coordination and Collaborative Reasoning in Multi-Agent LLMs
In this paper, we propose AgentsNet, a new benchmark for multi-agent reasoning. Drawing on classic problems in distributed systems and graph theory, AgentsNet evaluates the ability of multi-agent systems to collaboratively form problem-solving strategies, self-organize, and communicate effectively under a given network topology. Our results show that AgentsNet is virtually unlimited in size and can be extended with the development of new generations of LLMs.
Paper link:https://go.hyper.ai/58KXr
The above is all the content of this week’s paper recommendation. For more cutting-edge AI research papers, please visit the “Latest Papers” section of hyper.ai’s official website.
We also welcome research teams to submit high-quality results and papers to us. Those interested can add the NeuroStar WeChat (WeChat ID: Hyperai01).
See you next week!