Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
"Pink Killer" Wanted Poster, AI's Ability to Read Breast X-rays Is Comparable to That of Doctors

According to statistics from the World Health Organization, there were 2.3 million new cases of breast cancer worldwide in 2020, ranking first among all cancers and surpassing lung cancer to become the number one cancer.
However, if it can be detected early and treated in time, killing cancer cells before the tumor metastasizes, the mortality rate of breast cancer can be greatly reduced. Currently, the common method of initial screening for breast cancer is breast X-ray, and then the doctor will judge the health of the breast by analyzing and reviewing the X-ray. However, the review process consumes a lot of time and affects other patients' visits.
To this end, researchers at the University of Nottingham in the UK compared the ability of commercial AI and doctors to read breast X-rays, providing new ideas for the application of AI in clinical medicine.
Author | Xuecai
Editor | Three Sheep, Iron Tower
This article was first published on HyperAI WeChat public platform~
According to statistics from the American Cancer Society, the number of new cancer cases among American women in 2022 will be approximately 930,000, of which approximately 290,000 will be new breast cancer patients, accounting for 31%.At the same time, breast cancer patients accounted for 15% among cancer deaths, second only to lung cancer.
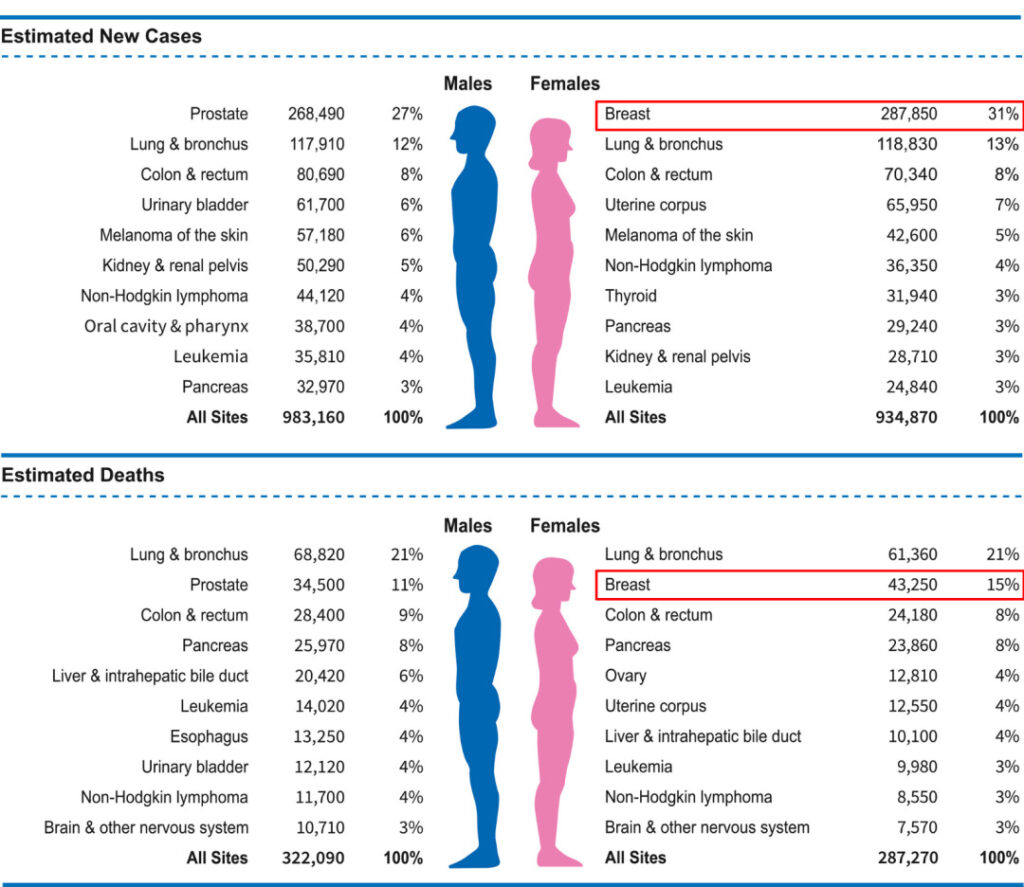
Figure 1: Number of new cancer cases (top) and cancer deaths (bottom) in the United States in 2022
In China,Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in the 21st century, and the number of new patients is increasing every year.

Figure 2: Number of new cancer cases in Chinese women from 2000 to 2016, with the gray color representing breast cancer cases
Breast cancer is a disease caused by abnormal breast cells growing out of control and forming tumors. If not treated in time, the tumors will metastasize and spread, eventually threatening life.However, if local tumors can be detected in the early stages of cancer and treatment is started, the five-year survival rate of cancer can reach 99%.
Currently, hospitals generally use mammography to screen for breast cancer. However, false positives may occur during the initial screening process., causing patients without cancer to undergo unnecessary tests. It can also lead to omissions, delaying the best treatment time for patients.
Therefore, many European countries review mammograms to eliminate as many false positives as possible. This approach works well.While reducing false positives, the cancer detection rate was also increased by 6%-15%.
However, reading and evaluating X-rays takes considerable time.In areas with a low doctor-patient ratio, reviewing X-rays not only takes up doctors' time, but also affects the early screening of other patients.
The application of AI has partially alleviated the workload of doctors. However, it seems unsafe to entrust AI to evaluate life and health.In this regard, Professor Yan Chen of the University of Nottingham in the UK said, "There is a lot of pressure to apply AI to clinical medicine, but we need to do it well to protect women's health."
To this end, Yan Chen's team compared the accuracy of commercial AI Lunit with that of doctors reading mammograms.The results showed that Lunit's ability to analyze mammograms was comparable to that of human physicians.This result has been published in "Radiology".

Paper link:
https://pubs.rsna.org/doi/10.1148/radiol.223299#_i13
Experimental procedures
Dataset:PERFORMS Dataset
This study selected two sets of PERFORMS datasets as the test sets of the model. Each set of PERFORMS datasets consists of 60 challenging X-rays, including malignant tumors (about 35%), benign tumors and normal results.The PERFORMS dataset has been used for entry testing and routine assessment of doctors in the UK National Health Service Breast Screening Programme (NHSBSP) for the past 30 years.
Evaluation Criteria:Annotation + Rating
When analyzing X-rays,The doctor will mark the suspicious locations., and finally make a rating of 1-5, corresponding to normal, benign, uncertain, suspicious and malignant.
The AI will rate the suspiciousness of each feature of the X-ray on a scale of 1-100.The highest score is considered as the score for the entire X-ray. If there are no suspicious features, it is considered 0 points.

Figure 3: Doctors and AI’s analysis of breast X-rays
A: The blue arrow indicates an unknown mass with a diameter of 8 mm, which was later identified as histological grade 2 ductal carcinoma;
B: The red cross is the abnormal feature discovered by AI, and the blue dot is the suspicious area marked by the doctor during analysis.
Comparison results:Specificity + Sensitivity
A total of 552 doctors participated in the competition, accounting for 68% of the total NHSBSP, including 315 radiologists, 206 radiographers and 31 clinicians.
After analyzing the two PERFORMS datasets, they considered 161 mammograms to be normal, 70 to have malignant tumors, and 9 to be benign tumors. Common features of malignant tumors included mass (64.3%), calcification (12.9%), asymmetry (11.4%), and architectural distortion (11.4%), with an average lesion size of 15.5 ± 9.2 mm.

Table 1: Results on the PERFORMS dataset
The average AUC of the human group was 0.88. The AUC of the AI group was 0.93, corresponding to the 96.8th percentile of the human group.However, there was no significant difference in AUC between the two groups.

Figure 4: AUC histogram of the doctor group and the AUC of AI (yellow line)
The average sensitivity and specificity of the human group were 90% and 76%, respectively. At the threshold recommended by the developer,The sensitivity and specificity of AI were 84% and 89%, respectively.

Table 2: Judgment results of the doctor group and AI with different thresholds
TP: true positive;
FP: false positive;
TN: true negative;
FN: false negative;
Sensitivity = TP / total number of positives;
Specificity = TN / total number of negatives.
In the ROC curve of AI, 52% doctors performed above the curve, 36% were below the curve, and 12% performed in line with the ROC curve.

Figure 5: ROC curve of AI, where the blue dots are the performance of different doctors
When the AI threshold was 3.06, the sensitivity of the AI was consistent with that of the doctors, detecting 63 malignant tumors and missing only 7. At this time, the specificity of the AI was not significantly different from that of the doctors.
When the threshold was set at 2.91, the AI had the same specificity as the physician group, with a sensitivity of 91%.The above results show that the sensitivity and specificity of Lunit's AI in analyzing breast X-rays are comparable to those of human doctors.

Figure 6: The impact of different thresholds on AI judgment results
A: The blue arrow indicates an asymmetric area, which was later identified as histological grade 2 ductal carcinoma;
B: Detection results when the AI threshold is 2.91, and the red cross is finally identified as a true positive;
C: The test results when the AI threshold was 3.06, no obvious abnormal features were found.
Professor Yan Chen said,The results of this study provide strong evidence for AI screening, showing that AI can analyze mammograms at the same level as human doctors.".
Breast cancer: the hidden pink killer
On World Cancer Day, February 4, 2021, the International Agency for Research on Cancer under the World Health Organization (WHO) stated thatLast year, there were 2.3 million new cases of breast cancer, accounting for 11.71% of the total number of cases, surpassing the number of new cases of lung cancer for the first time., becoming the "hidden pink killer".
At the same time, the highest incidence of breast cancer is among women in high-income countries, while the incidence is significantly lower among women in middle- and low-income countries. In addition, about 0.5-1% of breast cancers come from men.
However, the mortality rate of breast cancer itself is not high. From 2016 to 2020, 8 million women were diagnosed with breast cancer and survived, more than any other cancer.
Currently WHO is promoting the Global Breast Cancer Action around the world.It is hoped that the number of deaths from breast cancer worldwide can be reduced through early detection, timely diagnosis and comprehensive breast cancer management.

Figure 7: AI-assisted breast cancer screening
As a powerful tool for initial screening of breast cancer, AI can detect the early characteristics of breast cancer in a timely manner, and is expected to nip the "pink killer" in the bud.butIt may be too early to promote AI in clinical practice on a large scale, because changes in the environment and the algorithm itself will continue to have an impact, causing the sensitivity and specificity of AI to decrease over time.
Professor Yan Chen also believes thatOnce AI enters clinical application, we must have a mechanism to continuously evaluate and monitor it.". Now, research teams from all over the world are evaluating the detection results of AI and have achieved satisfactory results.In the future, with the help of efficient AI and perfect regulatory mechanisms, all kinds of diseases will have "nowhere to hide" and our health will be more stably protected.
Reference Links:
[1]https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.3322/caac.21708
[2]https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2667005422000047
This article was first published on HyperAI WeChat public platform~