Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Ten "best" Events in AI in 2024: Hidden Trends and Industry Challenges

In 2024, the AI wave is still surging forward fiercely, showing no signs of decline, quietly reshaping the world's contours and writing record-breaking innovative events.
This year, both infrastructure suppliers such as NVIDIA and Broadcom and cloud service providers such as Microsoft have achieved strong growth in AI business revenue. This year, NVIDIA has surpassed Apple and Microsoft several times to become the world's most valuable company. Market research firm IoT Analytics' research data for the GenAI market shows that NVIDIA's data center GPU revenue increased by 142% in 2024, bringing its market value to over $3.5 trillion.
It was also the year that OpenAI and xAI both raised more than $6 billion in funding rounds, and the tech-heavy Nasdaq index broke through 20,000 points for the first time…
Observing the continued rise in the enthusiasm for AI development, market research firm IoT Analytics has selected the top ten events in this field that are worth paying attention to in 2024:
01 ,The most noteworthy AI cybersecurity events
Nation-state hackers use LLMs to improve attack capabilities
February 14, 2024Microsoft announced that nation-state hackers from Russia, China, North Korea, and Iran have been using OpenAI's tools to improve their attack capabilities.
Microsoft said the groups use AI in different ways. For example, Russia's GRU often uses large language models (LLMs) to study "various satellite and radar technologies that may be relevant to conventional Ukrainian military operations." Meanwhile, North Korean hackers have reportedly used LLMs to generate content for spear-phishing campaigns, while Iranian hackers have used the models to write more convincing emails.
02 ,Most influential AI regulations
EU AI Act
On March 13, 2024, the European Parliament passed the EU AI Act, which will come into effect on August 1, 2024.

As the world’s first formal and comprehensive AI regulation, it divides AI into four risk categories based on the potential harm that (abuse) of AI may cause, thus setting rules for the use of AI within the EU:
1. Unacceptable risk
AI systems are used in scenarios that are explicitly prohibited, including but not limited to:
* Subconscious, manipulative, or deceptive behavior to distort behavior or compromise decision making;
* exploiting vulnerabilities related to age, disability or socioeconomic status;
* Biometric classification to infer sensitive attributes (such as race or political views): does not include the tagging and filtering of lawfully obtained biometrics by law enforcement;
* social scoring, such as evaluating or categorizing people or groups based on social or personal characteristics, which may result in unfair treatment of those people;
* Infer emotions in the workplace or academic setting, except for medical or safety reasons.
2. High risk
The highest risk level allowed, most of the EU AI legislation focuses on the regulation of this category of systems, which includes but is not limited to:
* used as a safety component or in products covered by EU laws listed in Annex I of the EU AI Directive and which must undergo a third-party conformity assessment under those laws;
*Use scenarios listed in Annex III of the EU AI Directive, such as permitted biometric operations and critical infrastructure.
*Appendix I:
https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/annex/1
*Appendix III:
https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/annex/3
High-risk AI providers must meet operational requirements, such as establishing risk management systems, conducting data governance, and providing technical documentation to demonstrate compliance.
3. Limited risk
This category is smaller in the bill and has looser transparency requirements. In short, developers and providers of these systems must ensure that end users know they are interacting with AI.
4. Minimal risk
Such applications are unregulated and include most AI applications on the EU market, such as AI video games and spam filters.
While the EU’s AI Act has been hailed as the first of its kind, other countries have either already initiated the legislative process to regulate AI or have provided guidelines that are consistent with existing laws but are not intended to be as binding as the EU’s AI Act.
For example,The Japanese government released the "Business Artificial Intelligence Guidelines 1.0" in April 2024.This is a voluntary guideline based on existing laws to encourage the responsible development and use of artificial intelligence.The Brazilian Senate proposed Bill No. 2338/2024 in May 2024.This is the country's first bill aimed at regulating artificial intelligence, including algorithm design and technical standards, and was passed in December 2024.
In the United States, although there is no federal regulation, at least 24 U.S. states, Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and Washington, D.C. have proposed AI-related bills in 2024. At least 31 states, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands have adopted and implemented these resolutions.
03 ,The most influential AI hardware development
Nvidia Blackwell series and its delayed release
On March 18, 2024, NVIDIA announced its new Blackwell GPU architecture at GTC 2024 and released 3 GPUs: B100, B200 and GB200 (combining a Grace CPU and 2 B200s).
Nvidia promises that the Blackwell series will achieve huge improvements in performance and energy efficiency, and is expected to have significant performance improvements over the H series, including a 6x increase in the number of queries processed per second and a 30x increase in the number of tokens output per GPU per second.
However, there have been delays in the release of the Blackwell series. In August 2024, Nvidia reportedly told cloud service providers thatThe much-anticipated B200 AI chip, originally expected to be released in the fourth quarter of 2024, will be delayed until 2025.The reason was a design flaw that was discovered "unusually late in the production process."
While Nvidia CFO Colette Kress assured investors during the November 2024 quarterly earnings call that GPUs were in full production, and reports indicate that Nvidia is on track to release the B200 in December 2024, no news of a B200 or B100 release has appeared publicly to date (as of January 8, 2025).
04 ,Most influential mergers and acquisitions
Microsoft and Inflection AI
On March 19, 2024, Microsoft established a new consumer AI division called Microsoft AI. When establishing this division,Microsoft has hired Mustafa Suleyman and Karén Simonyan, co-founders of US AI startup Inflection AI, as well as most of the Inflection AI team.Additionally, Microsoft has entered into a number of commercial agreements with Inflection AI, including a non-exclusive license to use Inflection AI intellectual property (among other transactions).
Essentially, according to the UK Competition and Markets Authority (CMA), Microsoft acquired most of Inflection AI's assets, and the CMA believes that such a transaction falls within its merger control jurisdiction, even if Inflection AI continues to exist as a separate entity (just with new leadership and employees). However, the CMA added that although some have called the deal a "quasi-merger," it does not create "the potential for a substantial lessening of competition," while noting that it would conduct regulatory review if similar situations raise competition concerns.
Regulators question whether such deals create an unfair market environment. Microsoft's acquisition of Inflection AI is just one of them. In early 2024,The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) announced that it would investigate multibillion-dollar investments by Amazon in Anthropic, Google in Anthropic, and Microsoft in OpenAI (each of which resulted in a large company acquiring a large stake in a smaller company).It aims to determine whether these companies have gained actual control of entities without mergers or direct acquisitions, thereby avoiding regulatory scrutiny and creating an unfair market competition situation.
While quasi-mergers and acquisitions are not new concepts, they seem to be popping up more and more frequently as the AI race continues to heat up, and global regulators, while not blocking these deals (so far), appear to be taking notice.
05 ,The most important large model development
Meta open source model LLaMA 3.1 beats closed source model
LLaMa 3.1 is comparable to or even better than ChatGPT and Claude. On July 13, 2024, Meta launched an updated version of LLaMA 3.1 and released benchmark comparison results of the model with mainstream models from companies such as OpenAI, Anthropic, and Mistral.
According to Meta, LLaMA 3.1 405B outperformed OpenAI’s GPT-4 and GPT-4o, as well as Anthropic’s Claude 3.5 Sonnet model, in seven of 15 benchmarks (the Claude model led in six). In tests where it didn’t achieve the highest score, LLaMA 3.1 generally performed on par with other top models.
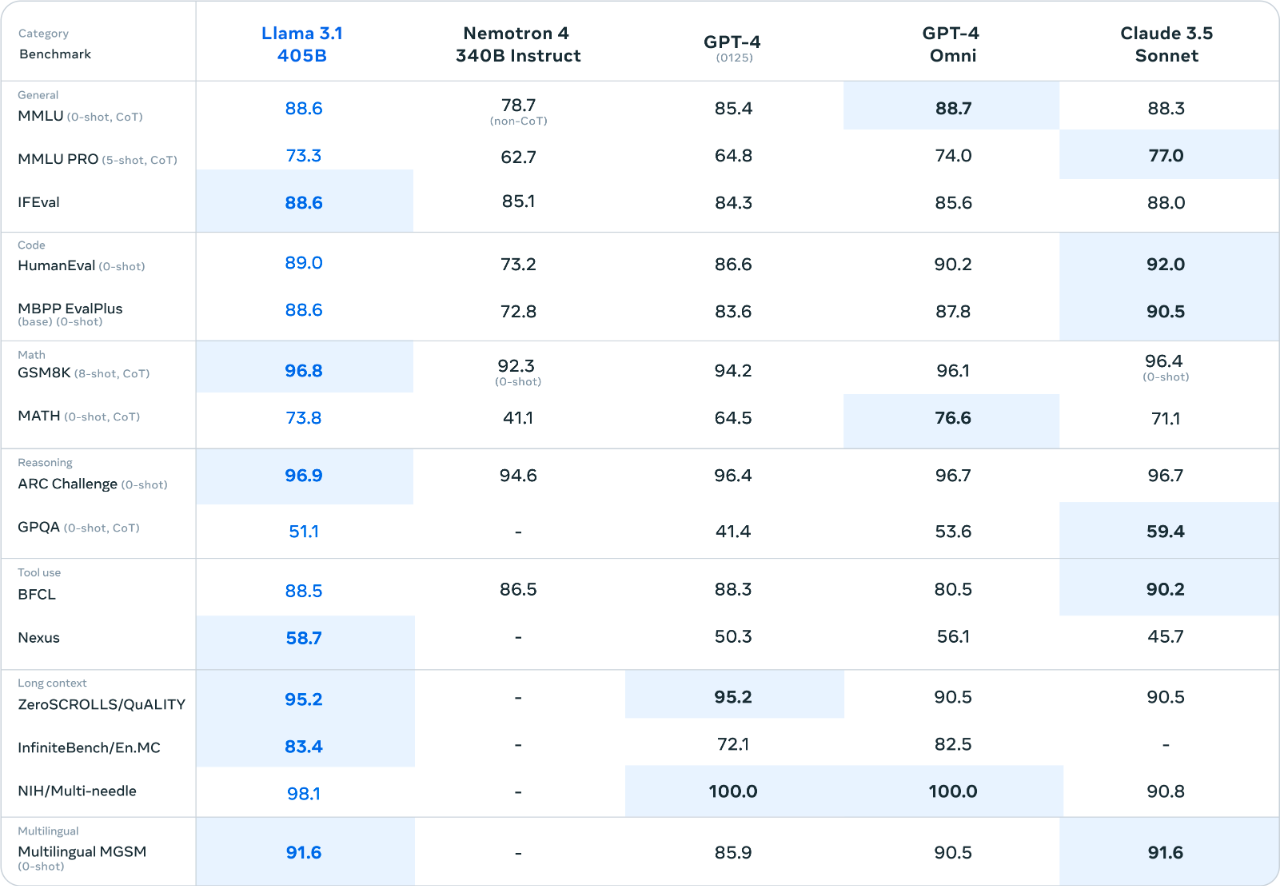
In similar benchmarks of the 8-billion-parameter and 70-billion-parameter LLaMA 3.1 models (LLaMA 3.1 8B and LLaMA 3.170B, respectively), the two models outperformed competing models from Google, Mistral, and OpenAI in 11 of 12 tests. It’s worth noting that while Meta ran the same 15 tests on the two smaller models as the 405B version, three of those tests did not include data from the other comparison models.
* Use Open WebUI to deploy the Llama 3.1 405B model in one click:
https://hyper.ai/cn/tutorials/33221
06 ,The most notable AI-related layoffs
Klarna
On August 27, 2024, Swedish payment company Klarna announced that it had cut hundreds of jobs and said that it expected layoffs to expand further in the future as AI took over customer consultation business. The reason why this incident is regarded as the most typical case of AI replacing human labor is mainly because the company clearly stated thatIts AI-based chatbot can complete the workload of 700 employees and reduce the average problem resolution time from 11 minutes to 2 minutes. In this case, AI completely replaced human labor.In addition, Klarna also announced that it will suspend recruitment for all positions except engineers for a period of time.
However, Klarna is not alone.
July 2024US tax software company Intuit announced that it will lay off 1,800 employees to focus on developing AI tools such as "Intuit Assist".And made it clear that these layoffs were not for cost-saving considerations. At the same time, Intuit said it would hire at least the same number of employees in engineering, products, and customer-facing areas such as sales and marketing to support its 2025 AI plan. Although Intuit's layoffs are larger, the company is only strategically shifting to AI, while Klarna has already achieved AI substitution.
Technology practitioners who do not have AI skills are also facing the pressure of industry transformation. The above two cases show that AI can take over non-technical positions such as customer service. At the same time, large technology companies have also made significant cuts in technical positions in the process of refocusing on AI business. The unemployment rate in the technology industry continued to fluctuate in 2024. After reaching a four-year high of 3.7% in June, it fell back in September and remained around 2.5%.
Major tech job cuts in 2024 include:
* January
Global tech giant Google has laid off more than 1,000 employees across multiple teams, including hardware and Google Assistant teams, to focus more on its AI products, such as Gemini GenAI (formerly Bard). Google CEO Sundar Pichai noted that more layoffs are expected throughout 2024 as Google continues to reallocate resources to AI (in December 2024, Pichai announced the cut of 10% management positions).
* 6 months
Microsoft, the global software and cloud service giant, announced that it will lay off more than 1,000 employees in its mixed reality and Azure departments. Jason Zander, executive vice president of Microsoft's strategic mission and technology, said in a company email that the move is to devote more energy to defining the "AI wave and helping its customers succeed in applying AI."
* August
Cisco, a multinational network hardware and software company, has laid off about 7% of its employees and shifted its investment direction to AI, including the construction of AI networks for cloud applications and AI infrastructure. This is another round of layoffs after it laid off nearly 4,000 employees in February 2024.
More layoffs due to AI are expected in 2025. According to a study by IoT Analytics in early 2024, AI and GenAI have become the most popular skills for employers. In addition, a survey of more than 900 US corporate executives by Staffing Industry Analysts in 2024 found that30% of companies have replaced some employees with AI, and among companies planning to use AI in 2025, 38% said they expect to replace employees with the technology next year.
However, AI may just be a scapegoat for some companies. It is worth noting that many companies may use AI as an excuse for layoffs - attributing it to AI sounds less negative than directly admitting that layoffs are for cost cutting or profit improvement. In addition, attributing layoffs to AI can also motivate investors because it means increased efficiency and productivity.
In February 2024, Mark Zuckerberg, CEO of US technology giant Meta, shared his views that layoffs are a reflection of the reality of the post-epidemic era. During the epidemic, the company "overexpanded" in response to uncertainty and is now trying to streamline the company to improve operational efficiency.
07 , The biggest challenges facing AI companies
Unable to improve LLM performance
Large LLM development projects have failed to meet expectations. In September 2024, OpenAI completed the first round of training of a new large language model, which is called Orion internally. OpenAI hopes that it will achieve a leap forward similar to the GPT-4o released in May 2024 compared to GPT-4 Turbo. However, according to reports,The model currently fails to live up to expectations, and the performance gap with existing models is not as significant as GPT-4o versus GPT-4 Turbo, or GPT-4 versus GPT-3.5.
OpenAI isn’t the only company to have suffered setbacks, however. Google and Anthropic also appear to have failed to meet market expectations for updates to their Gemini and Claude models, and have delayed the release of their new versions as a result.
The new data restrictions have driven a paradigm shift in LLM development. In recent years, the expectations of large language model companies for major breakthroughs in their models are mainly based on "scaling laws" -That is, more computing power, larger data sets, and larger models will bring about a leap in AI capabilities.
However,A new problem arises in 2024:There is limited new (human) information available to train LLMs.Early LLMs relied heavily on sources such as the internet to learn, drawing on decades of human knowledge. However, relatively little new reliable human-generated information has been added in the past two years.
Another problem has become more apparent since the public release of LLM: AI cannibalism.Generative AI (GenAI) has been widely used in online content creation, causing LLM to gradually ingest AI-generated content. This cycle of ingestion not only further reduces and dilutes human-generated content, but also may affect the accuracy of the information learned by the model.
Some people question the limitations of AI, while others rethink the meaning of progress. Faced with problems such as limited LLM breakthroughs and insufficient new data, AI research institutions seem to be accepting the fact that "scaling laws" are not truly universal. Some people in the AI field believe that various models are gradually approaching their capabilities. However, there are also optimists who believe that "scaling laws" should be viewed as dynamic and need to adapt to new development paradigms, so new strategies should be adopted in the AI training and development process, such as "test-time scaling."
The new features make up for the limited progress of LLM. Although the development of LLM may be plateauing, AI companies are still working hard to add value to existing models. For example, OpenAI launched a preview of the o1 and o1-mini models in September 2024, and officially released them in December of the same year, and also announced the upcoming o3 model. Although the o1 model takes a long time to process queries, it uses a "chain of thought" approach to build and correct answers before answering (similar to the way humans break down ideas when solving complex problems), thereby improving reasoning ability and answer accuracy.
In addition, in October 2024, OpenAI released ChatGPT Search, which enables ChatGPT to search the web, and users can find information through the ChatGPT interface and get results with source citations. Finally, in December 2024, OpenAI and Google launched Sora (based on DALL-E 3) and Veo2, respectively, further expanding the video generation capabilities.
08 ,The most important AI research achievements
Two Nobel Prizes
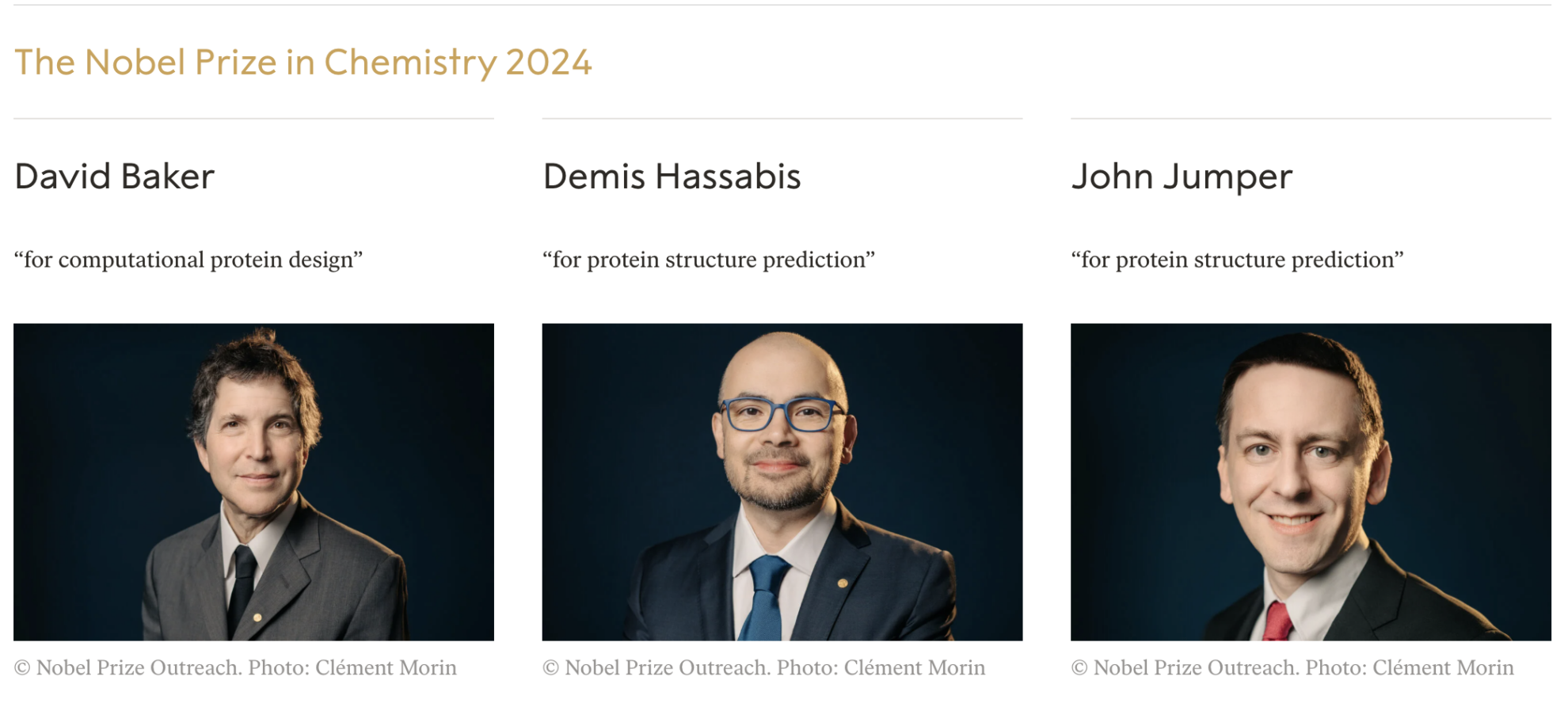
On October 8 and 9, 2024, the Nobel Prizes in Physics and Chemistry were awarded for AI-related research for the first time. The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to Princeton University physicist and professor emeritus John J. Hopfield and University of Toronto professor emeritus and former Google researcher Geoffrey Hinton for their development of machine learning techniques using artificial neural networks.

At the same time, Sir Demis Hassabis, CEO and co-founder of Google DeepMind, and John M. Jumper, director of research at Google DeepMind and co-developer of AlphaFold, won the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry in recognition of their development of an AI algorithm that can accurately predict protein structure, successfully solving the protein structure prediction problem that has plagued the scientific community for 50 years.
09 ,The largest enterprise-level AI investment
Amazon
Amazon is investing heavily in data centers and AI. In an earnings call on October 31, 2024, CEO Andy Jassy said,The company's capital expenditure (CAPEX) will reach $75 billion in 2024, with AWS and AI accounting for the largest share.So far, Amazon's spending on data center expansion (including property and equipment) has reached US$22.6 billion, an increase of US$81% year-on-year.
Amazon is not the only company investing in data centers. It is estimated that by 2024, the combined CAPEX of giants such as Amazon, Microsoft, Alphabet, and Meta will exceed $200 billion. These large technology companies have also announced that they plan to continue to increase their CAPEX.Morgan Stanley, a major US investment bank, predicts that the CAPEX of hyperscale enterprises will exceed US$300 billion in 2025.While most of this spending is for high-end GPUs and the massive data centers built to house them, there are also supporting costs, such as the energy costs to run the servers.
These AI-related technology companies are trying to convince investors that the corresponding expenditures are upfront investments in disruptive technologies, similar to the "if you build it, users will come" model - that is, the infrastructure must be in place before future profitable products can operate (for example, trains need to be laid before the railways can run). However, people still doubt whether the revenue can match the costs.
For example, while building a data center (including facilities, servers, etc.) and ongoing energy expenses can be included in the calculation of return on investment (ROI), data centers will not always remain the same. GPU manufacturers will continue to develop more powerful chips, and companies may need to continuously upgrade their equipment to remain competitive and cope with more advanced AI computing needs. In addition, the increase in computing power will also lead to higher energy consumption, further increasing operating costs.
10 ,The largest AI-related financing
Databricks, OpenAI, and xAI
December 17, 2024Databricks, an AI cloud data platform headquartered in the United States, announced the completion of a $10 billion Series J financing.It became the largest venture capital investment in 2024. After this round of financing, Databricks' valuation reached US$62 billion.
OpenAI and xAI also received huge investments. In October 2024, OpenAI announced the completion of its Series B financing, raising $6.6 billion and a post-financing valuation of $157 billion. This was the largest round of venture capital in 2024 until Databricks took the title.
Previously, Elon Musk's xAI completed its Series B financing in May 2024, raising $6 billion, which briefly became the largest financing round of the year. Subsequently, in November 2024, xAI announced the completion of its Series C financing, raising $6 billion, and the company's valuation rose to $50 billion.
References:
https://iot-analytics.com/ai-2024-10-most-notable-stories