Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
【ScienceAI Weekly】IBM's New AI Chip Improves Efficiency by 25 Times; Tsinghua University Releases AI-assisted Framework; DeepMind's New Tool Predicts 2.2 Million New Crystals

"ScienceAI Weekly" is a bimonthly column newly created by HyperAI. It mainly collects and presents the latest developments in the field of ScienceAI that are worth paying attention to in the near future from four dimensions: scientific research results, corporate dynamics, tool resources, and recent activities, in order to provide more valuable circle information and industry inspiration for practitioners and enthusiasts who have been paying attention to this field for a long time.
Let’s take a look at the ScienceAI progress that is worth noting in this issue!
Research results
GaUDI: a guided diffusion model for inverse molecular design

* Title:Guided diffusion for inverse molecular design
* Source:Nature Computational Science
* field:Molecular design, materials chemistry
* author:The Technion-Israel Institute of Technology team and the Ca' Foscari University of Venice research team
* Original text:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-023-00532-0
Method Description:
GaUDI is a guided diffusion model for inverse molecular design. It combines an equivariant graph neural network for property prediction with a generative diffusion model. By using single-target and multi-target task detection on a dataset of 475,000 polycyclic aromatic systems, researchers found that GaUDI is extremely effective in molecular design for organic electronics applications.
GaUDI improves conditional design, can generate molecules with optimal properties, even beyond the original distribution, and can identify molecules that are better than those in the dataset. In addition to point-wise targets, GaUDI can also be used for open-ended targets (such as minimum or maximum values), and in all cases, the effectiveness of the generated molecules is close to 100%.
SurfGen: A new model for computer-aided drug discovery

* Title:Learning on topological surface and geometric structure for 3D molecular generation
* Source:Nature Computational Science
* Field:Molecular design, drug discovery
* author:Zhejiang University and Carbon Silicon Intelligence Research Team
* Original text:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43588-023-00530-2
Method Description:
The SurfGen model designs molecules in a manner similar to the "key and lock" principle. It contains two equivariant neural networks - Geodesic-GNN and Geoatom-GNN, which capture the topological interactions on the pocket surface and the spatial interactions between ligand atoms and surface nodes, respectively.
SurfGen outperforms other methods on many benchmarks, with high sensitivity to pocket structure, which enables generative model-based approaches to address the thorny problem of mutation-induced drug resistance.
Tsinghua University research team releases AI-assisted framework - DeepSEED

* Title:
Deep flanking sequence engineering for efficient promoter design using DeepSEED
* Source:Nature Communications
* Field:Synthetic Biology
* author:Tsinghua University Research Team
* Original text:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-41899-y
Method Description:
DeepSEED consists of two deep learning modules: a conditional generative adversarial network (cGAN) to capture the dependencies between explicit and implicit patterns, and a prediction model based on DenseNet-LSTM to evaluate promoter performance. The two models are coupled using a genetic algorithm to achieve the optimal design of functional promoters through model iteration.
FIREANN: A general machine learning model for the response of atomic systems to external fields

* Title:
Universal machine learning for the response of atomic systems to external fields
* Source:Nature Communications
* Field:Atomic systems, machine learning
* author:Team from University of Science and Technology of China and Anhui University of Science and Technology
* Original text:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-42148-y
Method Description:
The research team proposed a general field-induced recursive embedding atom neural network (FIREANN) model that can integrate pseudo-field vector-dependent features into atomic descriptors to represent system-field interactions with strict rotational equivariance.
This "all-in-one" approach relates various response properties such as dipole moment and polarizability to field-dependent potentials in a single model, making it well suited for spectroscopic and dynamical simulations of molecules and periodic systems in the presence of electric fields. For periodic systems, FIREANN can overcome the intrinsic multi-valued problem of polarizability by training only atomic forces.
Company News
DeepMind releases GNoME, using deep learning to predict 2.2 million new crystals
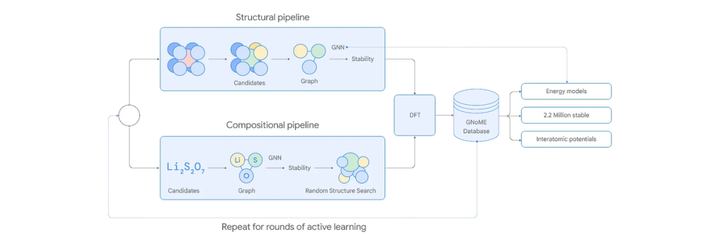
GNoME process diagram
Google DeepMind A paper recently published in Nature showed that with the help of its deep learning tool GNoME, researchers discovered 2.2 million new crystals in a short period of time (equivalent to nearly 800 years of knowledge accumulated by human scientists), of which 380,000 new crystals have stable structures, becoming the most likely potential new materials to be synthesized through experiments and put into use.
GNoME, which stands for Graph Networks for Materials Exploration, is a SOTA GNN model for new material research and development. It uses deep learning to predict the stability of new materials in a very short time, greatly improving the speed and efficiency of material research and development, and demonstrating the potential of using AI to develop new materials on a large scale.
DeepMind releases GraphCast, an AI model for weather forecasting
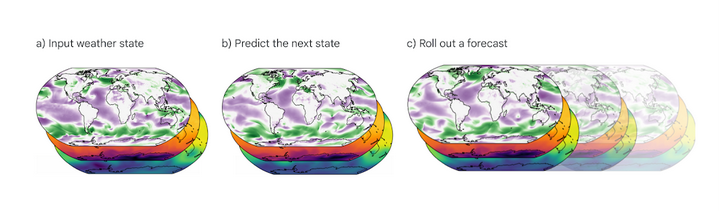
GraphCast can predict the weather for the next 6 hours based on the current and previous weather conditions.
Recently, Google DeepMind announced in its official blog the launch of a weather forecasting model based on machine learning - GraphCast, which can predict hundreds of weather variables for the next 10 days within one minute at a global resolution of 0.25°, significantly outperforming traditional weather forecasting methods.
The model also performed well in predicting extreme events, with GraphCast accurately predicting more than 90% out of 1,380 tested variables when compared to the industry gold standard weather simulation system, High Resolution Forecasting (HRES).
Biopharma and Sanofi reach large-scale strategic cooperation
BioMap announced a strategic partnership with Sanofi, a global top 10 pharmaceutical multinational company. According to the agreement, the two parties will jointly develop cutting-edge models for biotherapeutic drug discovery based on BioMap's Life Science AI Foundation Model. This cooperation is the first commercial cooperation based on a big model in the field of life sciences, and it also further promotes the parallel development of the two business models of "model development" and "AI drug pipeline development".
IBM launches new AI chip NorthPole, which is 25 times more energy efficient

Some time ago, IBM launched a brain-like AI chip, NorthPole, which can greatly improve energy, space and time efficiency. The relevant paper has been published in the international top journal Nature. According to reports, NorthPole is built on 12-nanometer node processing technology. Based on the ResNet-50 model, NorthPole's efficiency is significantly higher than the common 12-nanometer GPU and 14-nanometer CPU, and its energy efficiency has been improved by 25 times.
Paper address:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-03267-0
Xuanyan Biotech Completes Tens of Millions of Angel Round Financing
Shanghai Xuanyan Biotechnology Co., Ltd. previously announced the completion of an angel round of financing of tens of millions of yuan, led exclusively by Hainan Qianganghui Investment Partnership. The funds raised will be used for preclinical research on INTX-001, a world-new cancer target antibody drug, development of downstream IVD pipelines, and AI-based prediction of IVD products and software related to the progression of major diseases (early screening, metastasis, etc.).
Tools and Resources
AIor Science The main team of the new open source project Polymathic AI is revealed
The goal of the Polymathic AI program is to accelerate the development of versatile foundational models tailored for numerical datasets and scientific machine learning tasks.
To this end, Polymathic AI has brought together a team of pure machine learning researchers and domain scientists, who are guided by a scientific advisory group of world-leading experts, advised by Turing Award winner and Meta Chief Scientist Yann LeCun, and supported by a number of academic heavyweights including Miles Cranmer, Assistant Professor of AI+Astronomy/Physics at the University of Cambridge, in order to focus on developing basic models for scientific data and use cross-disciplinary shared concepts to solve industry challenges in AI for Science.
Project open source address:
https://github.com/PolymathicAI/
Alibaba Damo Academy releases remote sensing AI big model
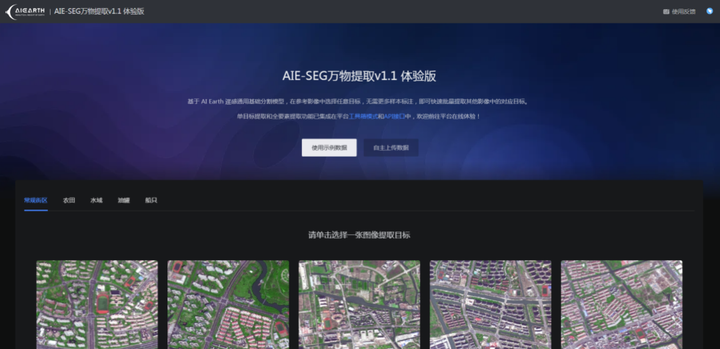
Not long ago, Alibaba Damo Academy released the industry's first remote sensing AI big model (AIE-SEG), which was the first to achieve the unification of image segmentation tasks in the remote sensing field. It can realize the rapid extraction of "zero samples of everything", identify nearly 100 types of remote sensing land objects such as farmland, water, and buildings, and automatically adjust the recognition results based on the user's interactive feedback, greatly improving the analysis efficiency of remote sensing applications such as disaster prevention and control, natural resource management, and agricultural production estimation.
The model has been made available on the AI Earth Earth Science Cloud Platform. In some specific scenarios, compared with traditional remote sensing models, the accuracy of instance extraction can be improved by 25%, and the accuracy of change detection can be improved by 30%.
Model address:
https://engine-aiearth.aliyun.com/#/app/aie-seg
Shanghai AI Lab opens source of first city-level NeRF real-life 3D model

At present, Shanghai AI Lab has officially open-sourced the world's first city-level NeRF real-life 3D large model "Scholar Skyline" (LandMark), which supports deployment in different application scenarios and provides free commercial use. This is also the first time that Shanghai AI Lab has publicly disclosed the core algorithm of the multi-branch GridNeRF model and the training strategy that matches it.
Scholar · Sky official website:
https://landmark.intern-ai.org.cn
Open source address:
https://github.com/InternLandMark/LandMark
Paper address:
https://city-super.github.io/gridnerf
AI Research Institute releases Uni3D, a 1 billion-parameter 3D vision universal model
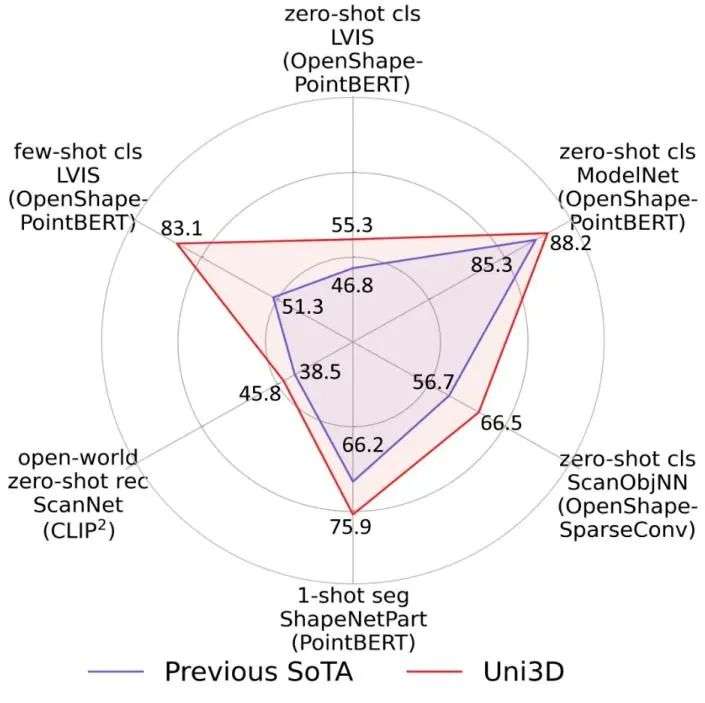
Recently, the Zhiyuan Research Institute has released the 1 billion parameter 3D vision universal model Uni3D, which has exceeded expectations in classification tasks, which are crucial to measuring universal vision capabilities, as well as zero-sample recognition, understanding, and segmentation tasks. It is reported that the Zhiyuan Vision team that produced Uni3D had previously released the 1 billion parameter universal vision model EVA. The key to the breakthrough of this 3D vision model is the use of ViT technology to upgrade the 2D pre-training basic experience to 3D.
Paper link:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.06773
Code/Model Links:
https://github.com/baaivision/Uni3D
https://huggingface.co/BAAI/Uni3D/tree/main/modelzoo
Recent Events
China Pharmaceutical University Biomedical Data Science Industry and Professional Development Conference

From December 8 to 9, 2023, the 2023 Biomedical Data Science Industry and Discipline Development Conference BDSC (The Biomedical Data Science Convention For Industry & Discipline Development) of China Pharmaceutical University will be held in Nanjing.
With the theme of "Seeking Truth with Data and Smart Medicine", the conference focused on the multidisciplinary cross-development of biomedicine and data science, deeply analyzed industry development trends, and explored the cutting-edge dynamics, academic achievements, and application practices of data science represented by artificial intelligence in many fields of concern to the industry, such as drug discovery, drug production, quality and safety, policy supervision, and digital transformation and upgrading of biomedicine companies.
Registration address:
https://www.huodongxing.com/event/2729440479800
"After the Future" AI4S Second International Summit Forum

On December 14, 2023, the "After the Future" AI4S Second International Summit Forum initiated by Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School will officially open at the Conference Center of Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School.
The event invited Professor David Baker, a member of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, Dr. Liu Tieyan, Distinguished Chief Scientist of Microsoft, Luo Yi, Distinguished Chair Professor of the University of Science and Technology of China, You Fengqi, a tenured professor of the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biomolecular Engineering at Cornell University, and Cheng Jun, a professor at the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Xiamen University, to give in-depth speeches on the development of AI for Science.
Registration address: