Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Nemotron 3 Nano: نموذج هجين ممبَا-ترانسفورمر مزيج الخبراء المفتوح والفعال للتفكير الوظيفي
Nemotron 3 Nano: نموذج هجين ممبَا-ترانسفورمر مزيج الخبراء المفتوح والفعال للتفكير الوظيفي
الملخص
نقدّم نيمترون 3 نانو 30B-A3B، وهو نموذج لغوي هجين من نوع Mixture-of-Experts يدمج بين معمارية Mamba وTransformer. تم تدريب نيمترون 3 نانو مسبقًا على 25 تريليون رمز نصي، بما في ذلك أكثر من 3 تريليون رمز فريد جديد مقارنةً بنمط نيمترون 2، تلاه تدريب مُراقب وتحسين على نطاق واسع باستخدام التعلم بالتحفيز (RL) في بيئات متنوعة. يحقق نيمترون 3 نانو دقة أفضل مقارنةً بالجيل السابق نيمترون 2 نانو، مع تفعيل أقل من نصف عدد المعلمات في كل عملية تمرير أمامي. كما يُظهر أداءً يفوق نماذج مفتوحة مماثلة في الحجم، مثل GPT-OSS-20B وQwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507، بـ 3.3 أضعاف في سرعة الاستنتاج (inference throughput)، مع الحفاظ على دقة أعلى في معايير شائعة. ويُظهر نيمترون 3 نانو تحسينًا ملحوظًا في القدرات العاملة (agentic)، والاستنتاج المنطقي، والدردشة، كما يدعم طول سياق يصل إلى مليون رمز. ونُطلق نسختين من النموذج على منصة Hugging Face: النسخة المُدرّبة مسبقًا (Base) ونسخة النموذج بعد التدريب الإضافي (post-trained) من نيمترون 3 نانو 30B-A3B.
One-sentence Summary
NVIDIA presents Nemotron 3 Nano, a 31.6B-parameter Mixture-of-Experts hybrid Mamba-Transformer model activating only 3.2B parameters per forward pass, which achieves better accuracy than its predecessor while delivering up to 3.3× higher inference throughput than comparable models; this efficient architecture demonstrates enhanced agentic reasoning capabilities, supports context lengths up to 1 million tokens, and is publicly released on Hugging Face for research and development applications.
Key Contributions
- Nemotron 3 Nano introduces an open, efficient Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) Hybrid Mamba-Transformer architecture for agentic reasoning, replacing standard FFN layers with sparse MoE layers to achieve better accuracy while activating only 3.2B parameters per forward pass out of 31.6B total. This design specifically addresses the need for high-performance reasoning with constrained computational resources during inference.
- The model employs a specialized training approach including pretraining on 25 trillion tokens with a Warmup-Stable-Decay learning rate schedule and a dedicated long-context phase (LC-Phase) using 121 billion tokens to support context lengths up to 1 million tokens. This methodology enables significant efficiency gains, achieving up to 3.3× higher inference throughput compared to competitive models while maintaining accuracy.
- Nemotron 3 Nano scales reinforcement learning in post-training through multi-environment RL using the open-sourced Nemo-Gym framework, enabling simultaneous training across diverse environments and introducing reasoning control features like on/off switching and token budget management. This results in best-in-class performance for reasoning and agentic tasks, with the fully open-sourced weights, training recipe, and code released on HuggingFace.
Introduction
Agentic reasoning applications demand models that balance accuracy, speed, and extreme context handling, but existing approaches often sacrifice inference throughput for long-context capability or lack openness for real-world deployment. Prior MoE and Transformer-based systems struggled with inefficient scaling beyond standard context lengths, limiting their utility in complex, token-intensive tasks. The authors introduce Nemotron 3 Nano, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts Hybrid Mamba-Transformer model that achieves competitive accuracy while delivering up to 3.3 times higher inference throughput and supporting 1 million token contexts. They further contribute full transparency by releasing model weights, training recipes, data, and code on HuggingFace.
Dataset
The authors use a multi-source pretraining corpus and specialized post-training datasets for Nemotron 3 Nano. Key components include:
-
Dataset Composition & Sources
- Web crawl: English/Common Crawl snapshots (CC-MAIN-2013-20 to 2025-26)
- Code: GitHub, Common Crawl code pages, synthetic code
- Specialized: STEM/math textbooks, scientific coding, multilingual content (19 languages)
- SFT/RL: Competition math/code, tool-use trajectories, safety data, terminal tasks
-
Key Subset Details
- Nemotron-CC-v2.1: 2.5T new English tokens from 3 Common Crawl snapshots; includes synthetic rephrasing (Medium-High-Quality data) and translation from 9 languages to English (LLM-filtered for quality).
- Nemotron-CC-Code-v1: 428B high-quality code tokens; processed via Lynx rendering + Phi-4 LLM cleaning to preserve code/math structure, with noise removal.
- Nemotron-Pretraining-Code-v2: Refreshed GitHub code (post-April 2025) + synthetic data; includes Qwen3-32B-generated code dialogues, LLM-rewritten Python (syntax-verified), and Python→C++ transpilation.
- Nemotron-Pretraining-Specialized-v1: Synthetic STEM data (4.3M RQA examples, 31.7B tokens); generated via NeMo Data Designer with cross-domain "InfiniByte" problem breeding and stratified sampling.
- SFT/RL Datasets: 18M samples total; includes 128k-token synthetic long-context data, formal Lean proofs (300k examples), and multilingual translations (5 languages).
-
Data Usage & Processing
- Pretraining uses a two-phase curriculum: initial diversity-focused mix (94% of training), shifting to high-quality data (Wikipedia, etc.); 15-category mixture balancing quality tiers (e.g., crawl-medium to syn-crawl-high).
- SFT applies chat templates to agentic tasks; dynamic sampling trains smaller datasets over multiple epochs.
- RL uses 12K+ tasks across math, coding, tool use, and instruction-following environments with schema-based rewards.
- All synthetic data undergoes LLM-judge filtering for quality, repetition checks, and political/nationalistic bias removal.
-
Additional Processing
- Code/math standardization: Equations converted to LaTeX; Python linted (Pylint) post-rewriting.
- Multilingual filtering: langdetect tool ensures target-language dominance; non-translatable content skipped.
- Safety: Unsafe prompts wrapped with refusal templates; content-safety classifier filters responses.
- No cropping strategy mentioned; long-context data validated up to 256k tokens.
Method
The authors leverage a hybrid Mamba-Transformer architecture enhanced with sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) layers to construct the Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B Base model. This design replaces standard feed-forward networks with MoE layers to improve accuracy while maintaining a low active parameter count per forward pass—3.2B active parameters out of 31.6B total, excluding embeddings. The MoE layers employ squared ReLU activation and a learned MLP router with sigmoid gating, and the model uses RMSNorm for normalization without positional embeddings dropout or linear layer bias. Embedding and projection weights are untied to further optimize performance.
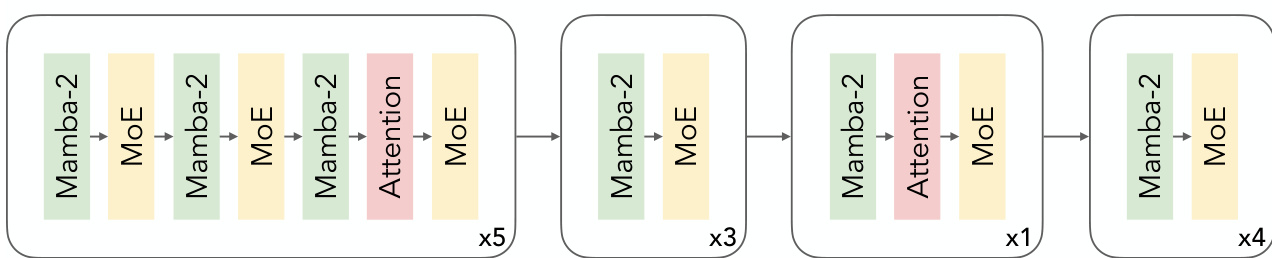
Refer to the framework diagram, which illustrates the block composition of the model. The architecture alternates between Mamba-2 blocks and MoE layers, with attention layers strategically placed at specific intervals. The sequence begins with five repetitions of a block containing Mamba-2, MoE, Mamba-2, MoE, Mamba-2, Attention, MoE. This is followed by three repetitions of a block with Mamba-2, MoE, Attention, MoE. A single instance of Mamba-2, Attention, MoE follows, and the sequence concludes with four repetitions of Mamba-2, MoE. This layered structure balances state-space modeling with attention-based context capture, while MoE enables dynamic expert selection for computational efficiency.
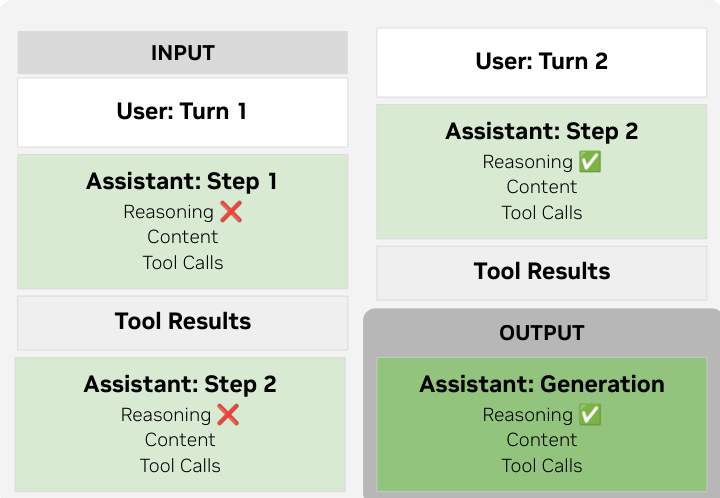
For post-training, the model supports reasoning control via a structured chat template that enables multi-step and multi-turn reasoning flows. In multi-step scenarios, reasoning tokens from prior steps are preserved to allow continuity, while in multi-turn interactions, prior reasoning is discarded upon new user input. Tool calls are formatted using XML-style tags to minimize escaping overhead, following conventions from GLM-4.5 and Qwen3-Coder. As shown in the figure below, the template materializes only the current turn’s reasoning into the prompt during generation, ensuring context relevance while preserving state across steps.
The training process begins with pretraining over 25 trillion tokens using a Warmup-Stable-Decay learning rate schedule: warming up to 10−3 over 8.4 billion tokens, holding at peak for 20 trillion tokens, then decaying to 10−5 over the final 5 trillion. The AdamW optimizer is used with β1=0.9, β2=0.95, and weight decay of 0.1. MoE layers are stabilized using DeepSeek’s aux-loss-free load balancing with an update rate of 10−3 and a load balancing loss coefficient of 10−4. A long-context extension phase follows, using continuous pretraining on 121 billion tokens with a 256k-token sequence length, incorporating 8-way context, tensor, expert, and 4-way pipeline parallelism on H100 GPUs. The data blend includes 79% downscaled Phase 2 data, 20% document QA, and 1% synthetic retrieval data, with a mixture of 512k and 4k sequences to preserve short-context performance.
Post-training scales significantly with multi-environment reinforcement learning (RLVR), orchestrated via NeMo Gym and NeMo RL. The RLVR stage trains on all environments simultaneously using synchronous GRPO with masked importance sampling, 128 prompts per step, and 16 generations per prompt. The MoE router weights are frozen to stabilize training, and expert bias is updated using the aux-loss-free load balancing approach. A curriculum strategy dynamically adjusts task difficulty by modeling pass rates as a Gaussian distribution that shifts from easy to hard samples over time, preventing overfitting and ensuring balanced domain coverage.
For RLHF, a generative reward model (GenRM) is trained using the GRPO algorithm on data from HelpSteer3 and synthetic safety blends. The GenRM produces individual helpfulness scores and a ranking score for paired responses, with reward defined as:
R=−C1Iformat−∣Ph1−Gh1∣−∣Ph2−Gh2∣−C2∣Pr−Gr∣,where C1=10 and C2=1. During RLHF, a circular comparison strategy reduces pairwise comparisons from O(N2) to O(N) by comparing each response only with its successor. A Group Relative Length Control mechanism adjusts rewards based on normalized reasoning and answer lengths within each prompt group, applying zero-sum penalties and optional conciseness bonuses for top-quality short responses. This reduces verbosity by 30% without sacrificing accuracy.
Finally, the model is quantized to FP8 using Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) with ModelOpt and Megatron-LM. A selective quantization strategy preserves self-attention layers and their feeding Mamba layers in BF16 due to high sensitivity, while quantizing weights, activations, and KV cache to FP8. Conv1D layers within Mamba blocks remain in BF16 to maintain accuracy-efficiency balance.
Experiment
- Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B (31.6B total parameters, 3.2B activated per forward pass) validated superior efficiency and accuracy versus prior models, achieving 3.3× higher inference throughput than Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507 and 2.2× versus GPT-OSS-20B on 8K input/16K output scenarios while matching or exceeding their benchmark accuracy.
- Base model evaluations showed it surpassed Qwen3-30B-A3B-Base on Code, Math, and General Knowledge benchmarks including MMLU and GPQA, with significant gains on MMLU-redux CoT (+5.27 average accuracy).
- Reinforcement Learning from Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) outperformed heavily fine-tuned supervised learning (SFT) across all domains, including mathematical reasoning and agentic tasks.
- FP8 quantization achieved 99% median accuracy recovery versus BF16 while enabling larger batch sizes and higher throughput, validated across multiple benchmarks.
- Minimal DPO training reduced tool hallucination rates to 0% on AIME25 and 0.7% on GPQA, while improving accuracy by 3.7–4.04 percentage points.
- Demonstrated robustness with prompt sensitivity scores below 1 across datasets and supported 1M-token context lengths, outperforming competitors on RULER.
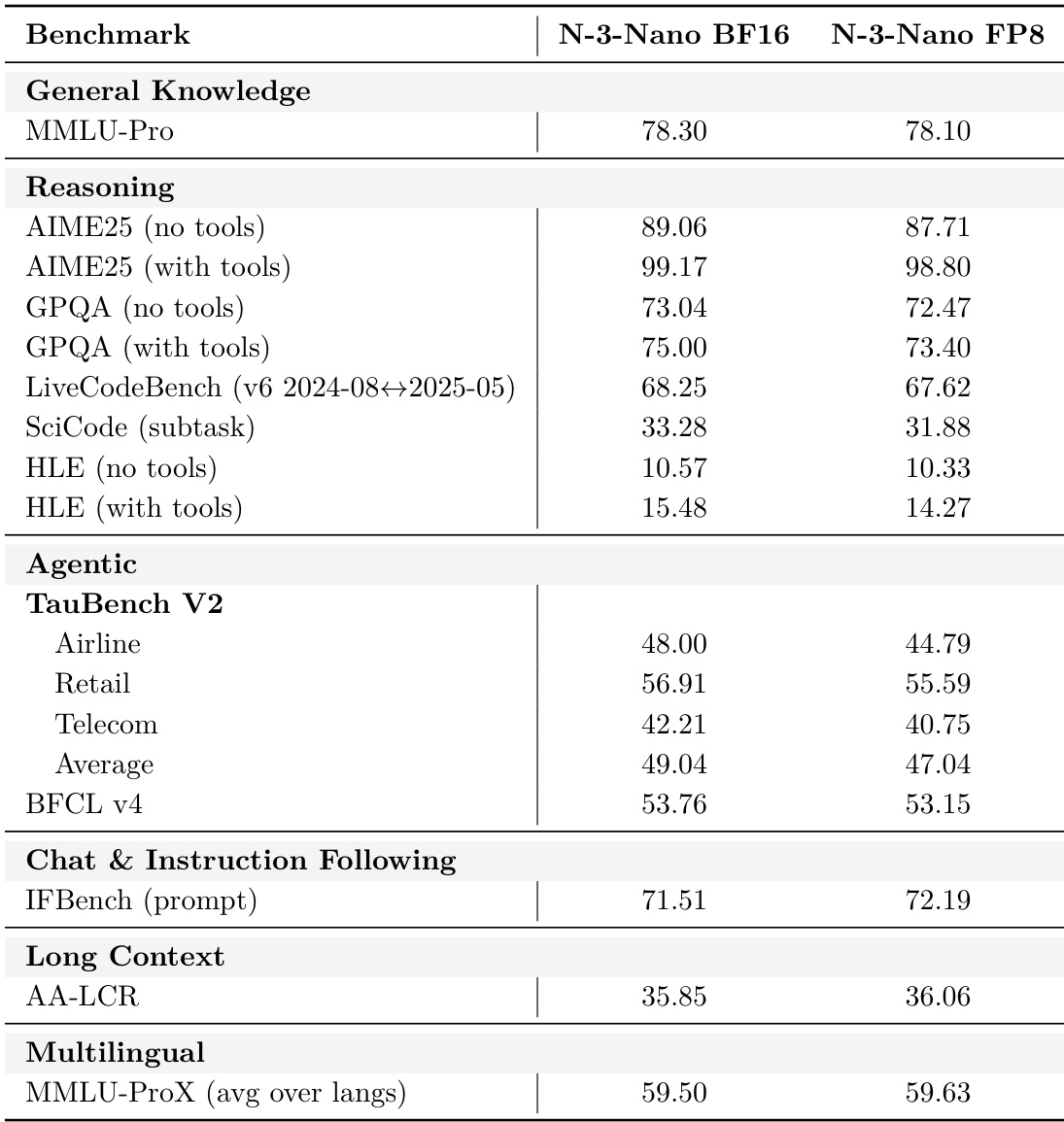
The authors use post-training quantization to convert Nemotron 3 Nano from BF16 to FP8 and report accuracy comparisons across multiple benchmarks. Results show the FP8 model retains approximately 99% median accuracy relative to the BF16 version, with minor performance trade-offs in specific reasoning and agentic tasks. The quantized model maintains strong performance in chat, long-context, and multilingual benchmarks while enabling higher inference throughput.
The authors compare Nemotron 3 Nano 30B-A3B Base against Qwen3-30B-A3B-Base across multiple benchmarks, showing that Nemotron 3 Nano outperforms Qwen3 in Math, Code, Commonsense Understanding, and Long Context tasks, while trailing slightly in General Knowledge and Multilingual benchmarks. Results indicate Nemotron 3 Nano achieves higher scores on GSM8K, MATH, HumanEval, and RULER at 64K and 128K context lengths, demonstrating stronger reasoning and long-context capabilities despite lower performance on MMLU and MMLU Global Lite.
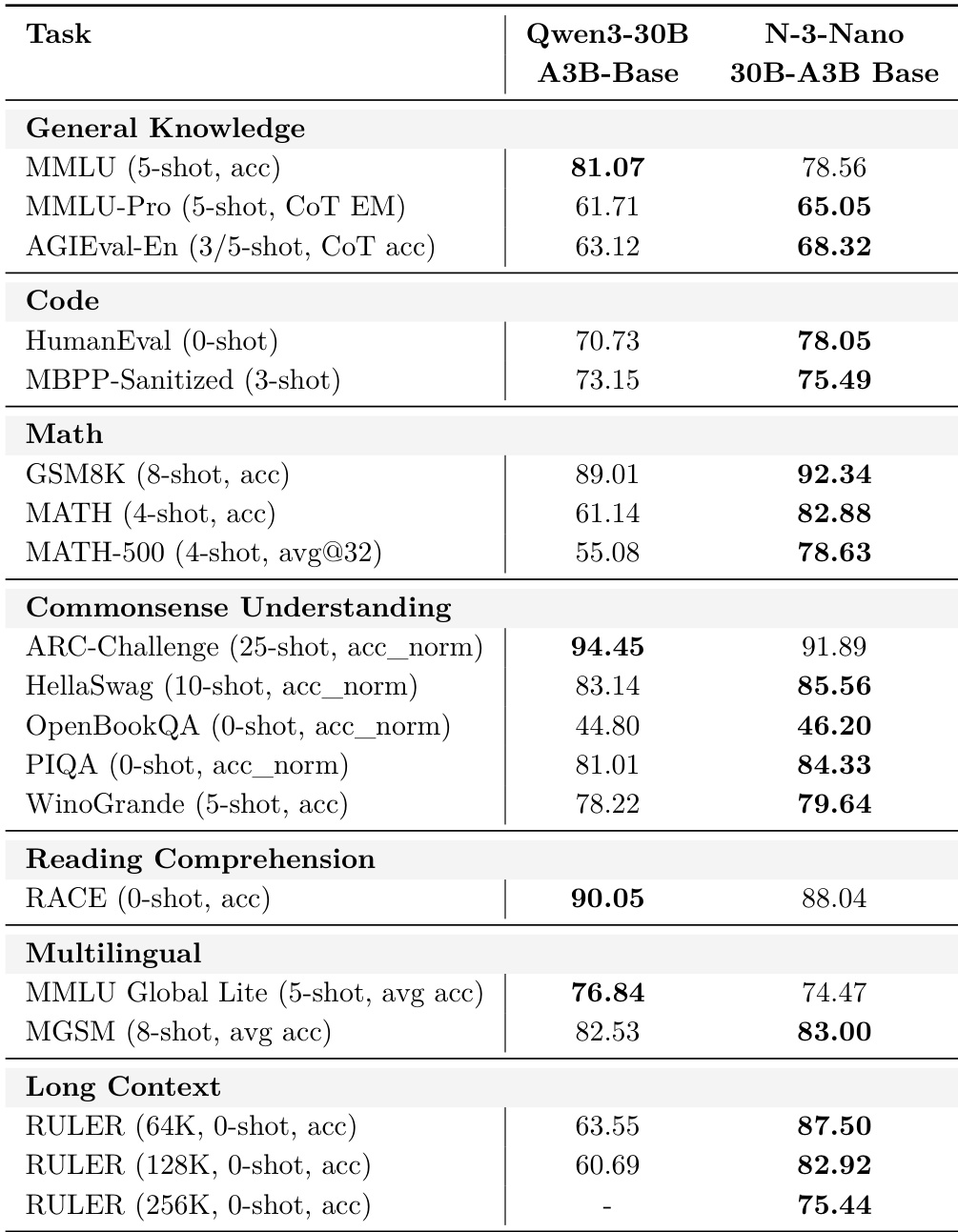
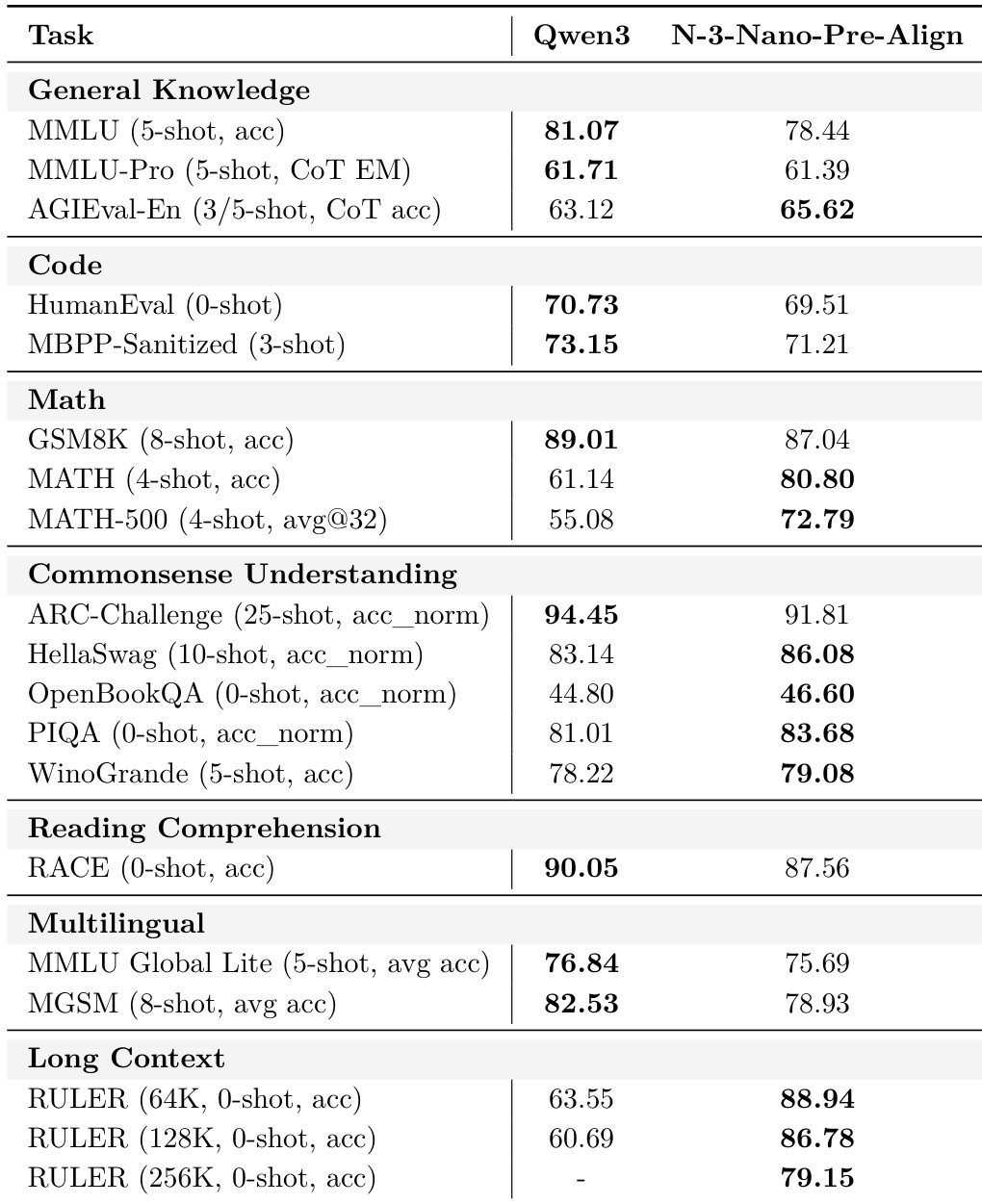
The authors compare the pre-alignment base checkpoint of Nemotron 3 Nano with Qwen3-30B-A3B-Base across multiple benchmarks, showing that while Qwen3 leads in general knowledge and multilingual tasks, Nemotron 3 Nano outperforms it in math, commonsense understanding, and long-context reasoning. Results indicate Nemotron 3 Nano’s pre-alignment base exhibits stronger performance on math and reading comprehension, and significantly higher scores on RULER at 64K and 128K context lengths. The comparison highlights trade-offs in early-stage model capabilities, with Nemotron 3 Nano showing particular strength in structured reasoning and long-context tasks despite trailing in some knowledge and multilingual benchmarks.
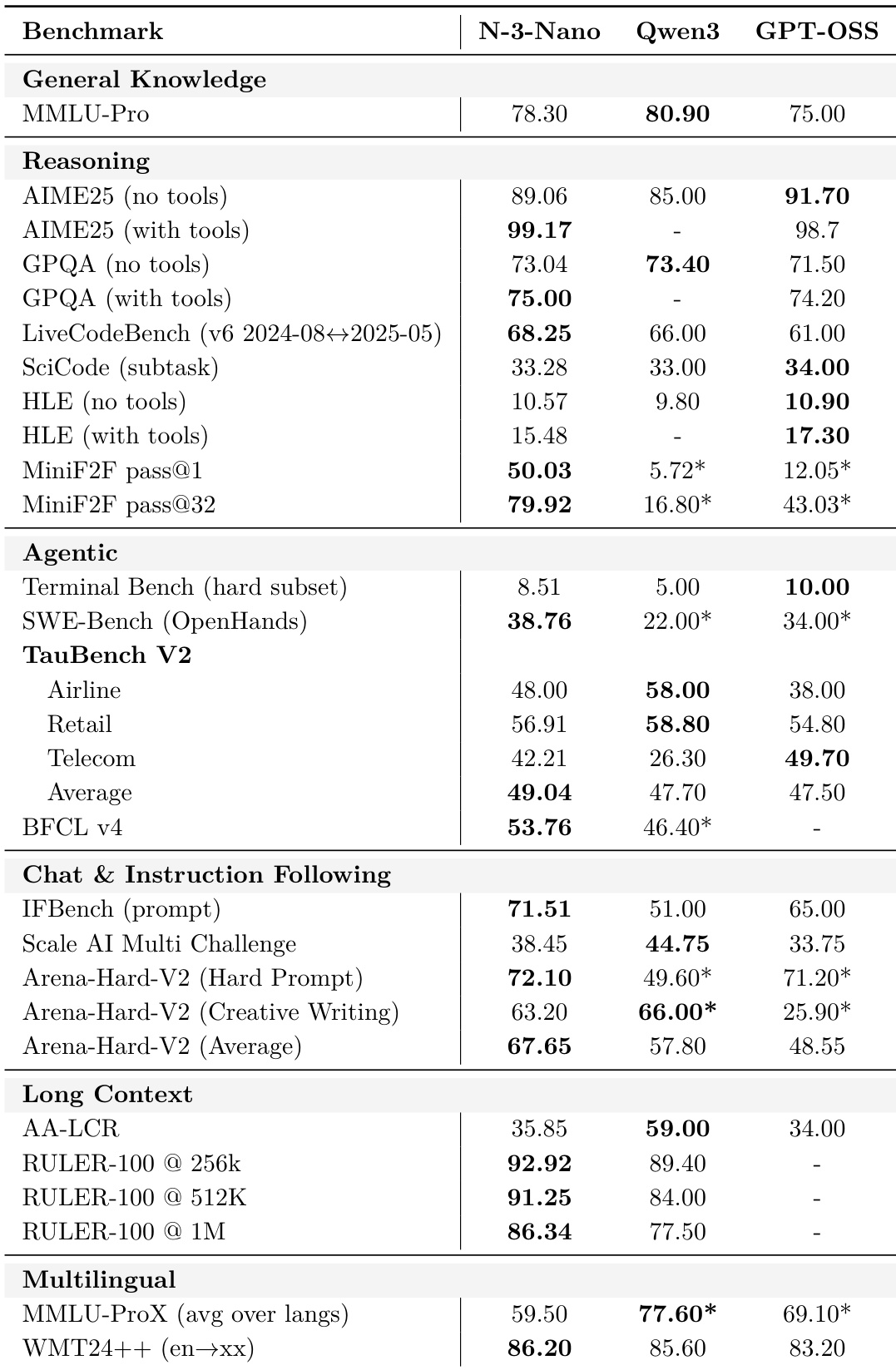
Results show Nemotron 3 Nano outperforms Qwen3-30B-A3B-Thinking-2507 and GPT-OSS-20B on agentic benchmarks like Terminal Bench and SWE-Bench, and leads in long-context tasks such as RULER-100 at 256K and 1M tokens. It also achieves competitive scores in reasoning and chat categories, with strong performance on IFBench and Arena-Hard-V2, while matching or exceeding Qwen3 in multilingual translation tasks. The model demonstrates consistent superiority in tool-augmented and instruction-following scenarios, particularly where structured outputs or environment constraints are required.
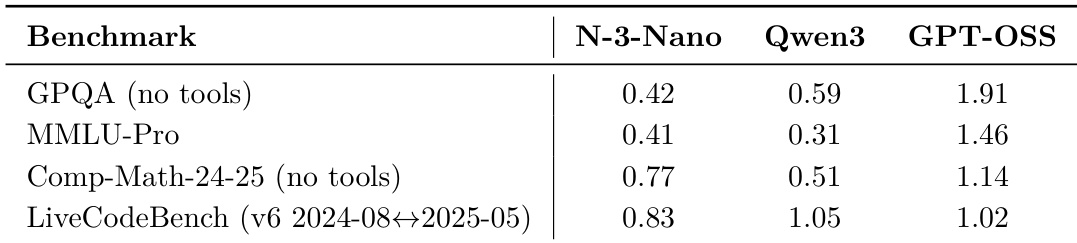
The authors evaluate Nemotron 3 Nano against Qwen3 and GPT-OSS on four reasoning and coding benchmarks, reporting scores normalized to a common scale. Results show Nemotron 3 Nano outperforms Qwen3 on all four benchmarks and significantly underperforms GPT-OSS, which achieves the highest scores across the board. The data reflects Nemotron 3 Nano’s strong relative performance among open models but highlights GPT-OSS as the current leader in these specific tasks.