Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
InSight-o3: تمكين النماذج الأساسية متعددة الوسائط من خلال البحث البصري العام
InSight-o3: تمكين النماذج الأساسية متعددة الوسائط من خلال البحث البصري العام
Kaican Li Lewei Yao Jiannan Wu Tiezheng Yu Jierun Chen Haoli Bai Lu Hou Lanqing Hong Wei Zhang Nevin L. Zhang
الملخص
القدرة على تمكين الوكلاء الذكية الاصطناعية من "التفكير من خلال الصور" تتطلب مزيجًا معقدًا من التفكير والاستيعاب. ومع ذلك، لا تزال الوكلاء متعددة الوسائط المفتوحة الحالية تفتقر بشكل كبير إلى جانب التفكير، والذي يُعد حاسمًا في المهام الواقعية مثل تحليل المستندات التي تحتوي على رسومات أو مخططات كثيفة، أو التنقل عبر الخرائط. ولسد هذه الفجوة، نقدم O3-Bench، وهو معيار جديد مصمم لتقييم التفكير متعدد الوسائط مع التركيز المتداخل على التفاصيل البصرية. يتميز O3-Bench بمشاكل صعبة تتطلب من الوكلاء تجميع المعلومات البصرية الدقيقة من مناطق مختلفة في الصورة من خلال عملية تفكير متعددة الخطوات. وتظل هذه المشكلات صعبة للغاية حتى بالنسبة للأنظمة المتقدمة مثل OpenAI o3، التي حققت دقة فقط 40.8% على معيار O3-Bench. ولتحقيق تقدم، نقترح InSight-o3، وهي إطار عمل متعدد الوكلاء يتكون من وكيل تفكير بصري (vReasoner) ووكيل بحث بصري (vSearcher)، حيث نُقدّم مهمة البحث البصري العام — وهي مهمة تتمثل في تحديد مناطق ذات صلة أو ضبابية أو مفاهيمية وصفت بلغة حرة، بما يتجاوز مجرد الكشف عن كائنات أو أشكال بسيطة في الصور الطبيعية. ثم نقدم نموذجًا لغويًا متعدد الوسائط مُدرّب خصيصًا لهذه المهمة باستخدام التعلم المعزز. وبصفته وكيلًا يمكن دمجه بسهولة، يُمكّن vSearcher من تعزيز أداء النماذج متعددة الوسائط المتقدمة (كـ vReasoners) بشكل كبير على مجموعة واسعة من المعايير. ويُعد هذا خطوة ملموسة نحو بناء أنظمة مفتوحة قوية تشبه o3. يمكن الاطلاع على الكود والبيانات الخاصة بنا عبر الرابط: https://github.com/m-Just/InSight-o3.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology and Huawei propose INSIGHT-o3, a multi-agent framework with a purpose-trained visual search agent (vSearcher) that enables generalized visual search for relational or conceptual regions via reinforcement learning, significantly enhancing multimodal reasoning in open agents like OpenAI o3 on tasks requiring fine-grained visual integration, as demonstrated on the new O3-BENCH benchmark.
Key Contributions
-
The paper introduces O3-BENCH, a new benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal reasoning in complex, real-world tasks such as map navigation and cross-chart analysis, requiring agents to perform multi-step reasoning by integrating subtle visual details from disparate regions of high-information-density images—tasks that even frontier models like OpenAI o3 struggle with, achieving only 40.8% accuracy.
-
The authors propose INSIGHT-o3, a multi-agent framework that decomposes image reasoning into two specialized components: a visual reasoning agent (vReasoner) for high-level inference and a visual search agent (vSearcher) for locating conceptually or relationally described regions in images, enabling a divide-and-conquer approach to tackle interleaved reasoning more effectively.
-
They present InSight-o3-vS, a reinforcement-learned multimodal model trained for generalized visual search—locating fuzzy, relational, or conceptual regions described in free-form language—demonstrating significant performance gains when used as a plug-and-play component, improving GPT-5-mini’s accuracy on O3-BENCH from 39.0% to 61.5% and Gemini-2.5-Flash’s on V*-Bench from 80.1% to 87.6%.
Introduction
The ability for AI agents to reason with complex, high-information-density visuals—such as maps, charts, and diagrams—is critical for real-world applications like document analysis and navigation, yet current open multimodal models struggle with the interleaved, multi-step reasoning required. Prior benchmarks and systems focus on simple object localization or single-region queries, falling short in handling relational, fuzzy, or conceptual region descriptions across spatially dispersed image areas. The authors introduce O3-BENCH, a new benchmark that evaluates deep visual reasoning through challenging, real-world tasks requiring cross-region evidence aggregation. To address this, they propose INSIGHT-o3, a multi-agent framework where a visual reasoning agent (vReasoner) is augmented by a specialized visual search agent (vSearcher). The vSearcher is trained via reinforcement learning to perform generalized visual search—locating conceptually described regions in arbitrary images using free-form language—enabling precise, plug-and-play enhancement of existing multimodal models. This approach significantly boosts performance on diverse benchmarks, demonstrating a practical path toward open, o3-like reasoning systems.
Dataset
- The O3-BENCH dataset is composed of 204 high-resolution, information-dense images: 117 composite charts and 87 digital maps, yielding 345 multi-choice QA pairs (163 chart-based, 182 map-based).
- Chart images are sourced from the "Diagram and Table" subset of MME-RealWorld and the Internet, filtered via PP-DocLayout_plus-L to retain only images with at least 8 detected layouts, ensuring high visual complexity. Map images are manually collected from the Internet using keyword searches, focusing on venue-level maps (e.g., campus, park, bus routes) that require reading legends and visually locating entities, while excluding large-scale cartography relying on world knowledge.
- Each QA pair includes six answer choices, with four distractors derived from the image or visually similar to the correct answer, and a sixth option (F) for "No Right Choice" in cases where no option is valid—this encourages models to evaluate the entire image.
- The dataset is constructed through a hybrid pipeline: automated pre-annotation using layout detection, OCR, and GPT-5 to generate five candidate questions per image, followed by rigorous human screening, validation, and rewriting to ensure factual accuracy, multi-hop reasoning, and clarity.
- To ensure difficulty, all candidate QAs are evaluated by three proprietary MLLMs (GPT-5-mini, Gemini-2.5-Flash, Doubao-Seed-1.6); items solved by all three are discarded. Final entries undergo cross-verification by independent reviewers for consistency and correctness.
- On average, each sample contains 8.7 layouts and 2.4 target layouts, with image resolutions ranging from 2K to 10K pixels (mean: 3,967 × 4,602 pixels), reflecting high information density and the need for fine-grained visual search.
- For training, the authors synthesize in-loop RL data by stitching low-to-medium-resolution images into collages from filtered subsets of Visual CoT and V*, ensuring target regions are small and require active search. Out-of-loop RL data are generated from InfographicVQA using PP-DocLayout_plus-L to detect and merge layout boxes, followed by GPT-5-nano to generate concise, visually grounded region descriptions that mimic real search queries.
- In both training data types, layout boxes are filtered for size, aspect ratio, and relevance, with strict rules to avoid trivial or overly large regions. Charts and tables are preserved as distinct units, and merged boxes are validated to maintain meaningful context.
- The final training data are designed to incentivize visual search: collages increase visual density and task difficulty, while out-of-loop data provide region descriptions that guide targeted exploration without revealing content, enabling effective reward shaping in reinforcement learning.
Method
The authors propose INSIGHT-O3, a two-agent framework designed to address the challenge of integrating high-level reasoning with detailed visual perception in multimodal language models. The system decomposes the problem-solving workflow into two specialized agents: a visual reasoning agent (vReasoner) and a visual search agent (vSearcher). The vReasoner is responsible for high-level, abstract reasoning and question decomposition, while the vSearcher specializes in locating and retrieving specific visual evidence from the input image. This separation allows the vReasoner to focus on logical inference, issuing requests for visual information when needed, and the vSearcher to efficiently locate and return the requested regions. The interaction between the agents follows a multi-turn protocol where the vReasoner generates a region description, the vSearcher locates the corresponding area in the image, and the returned cropped region is fed back to the vReasoner for further analysis. This process continues iteratively until the vReasoner can confidently produce a final answer. The framework is designed to be modular, enabling the vSearcher to act as a plug-and-play component that can enhance the performance of various vReasoner models.
The training of the vSearcher agent is conducted using a hybrid reinforcement learning (RL) algorithm that combines in-loop and out-of-loop components, as illustrated in the training pipeline. The out-of-loop component leverages pre-generated region descriptions paired with ground-truth bounding boxes, enabling efficient training through direct Intersection over Union (IoU) supervision. This allows the vSearcher to learn to accurately localize regions based on precise textual descriptions. In contrast, the in-loop component uses region descriptions generated on-the-fly by the vReasoner during training, which are more aligned with the real-world, dynamic tasks the agent will encounter during inference. This approach ensures that the vSearcher learns to handle the natural, often ambiguous, language used by the reasoning agent.
The reward function for the vSearcher is designed to encourage both accurate localization and the use of the provided tool. For the out-of-loop RL, the reward is a weighted sum of a format reward and an IoU reward, where the IoU reward is defined as rIoU=max{0,IoU(b,b∗)−α}/(1−α), with α being a threshold that determines the minimum acceptable overlap. This reward structure incentivizes the vSearcher to produce a region that is not only accurate but also to use the image cropping tool at least once to verify the result. For the in-loop RL, a pseudo IoU reward r^IoU is used, which is derived from the vReasoner's feedback. The vReasoner rates each vSearcher prediction as helpful or unhelpful based on its relevance to the task, and this rating is combined with the final answer correctness to form the pseudo reward: r^IoU=I[s=c=1]. This mechanism provides a more realistic, albeit noisier, form of supervision that reflects the actual utility of the vSearcher's output.
The training objective is based on the GRPO algorithm, with modifications to handle the hybrid training setup. The objective function for a batch of vSearcher outputs is defined as J(θ)=M1∑i=1M∣oi∣1∑t=1∣oi∣{min[γt(θ)A^t,clip(γt(θ),1−ϵ,1+ϵ)A^t]−βDKL[πθ∣∣πref]}. The advantage estimation differs between the two components: for the out-of-loop component, advantages are normalized using the group mean and standard deviation, while for the in-loop component, they are normalized globally across all dynamically generated tasks. This global normalization is necessary because the in-loop tasks do not form distinct groups, and the advantage estimates must be comparable across the entire set of on-the-fly generated queries. The policy model πθ is trained to maximize this objective, with the loss masked for tool-response tokens as they are not generated by the policy.
Experiment
- Main experiment: Trained InSight-o3-vS as a visual search agent under GPT-5-mini-2025-08-07 (vReasoner), achieving significant performance gains across multiple benchmarks when integrated with various vReasoners, including Gemini-2.5-Flash and GPT-5-nano.
- Generalization: InSight-o3-vS improves GPT-5-nano’s accuracy on VisualProbe-Hard from 21.7% to 31.4%, on O3-BENCH from 26.5% to 34.6%, and overall from 44.3% to 51.6%. Under Gemini-2.5-Flash, it achieves a 7–10% lead on V*-Bench and O3-BENCH.
- O3-BENCH performance: With InSight-o3-vS, GPT-5-mini closes the gap with Gemini-2.5-Flash on O3-BENCH from 21.4% to 8.2%, demonstrating the critical role of image-based reasoning.
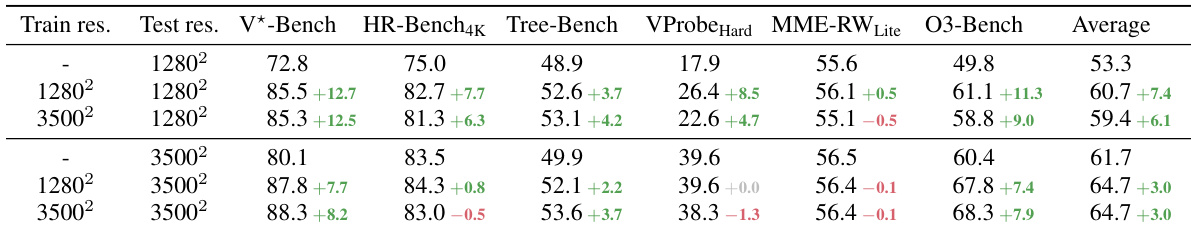
- Input resolution: Higher image resolution benefits performance, but InSight-o3-vS remains effective even at 0.8M pixels (25% of training resolution), with minimal performance drop and higher vSearcher call counts at lower resolutions.
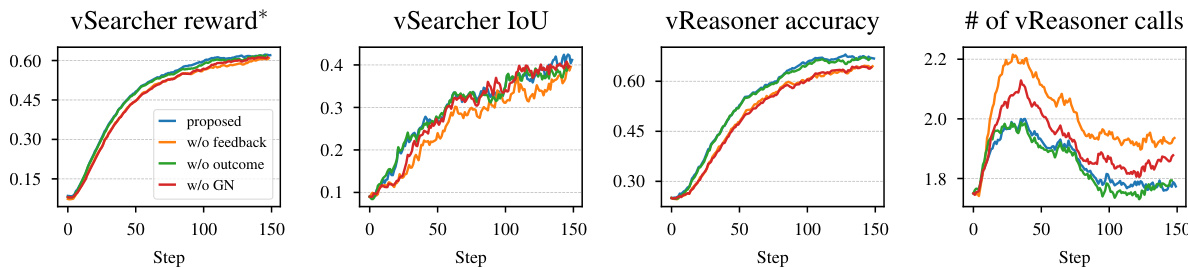
- Ablation studies: Hybrid RL training (in-loop + out-of-loop) outperforms individual components, with the full setup achieving best results. Reward design with feedback and global normalization improves performance over ablated variants.
- Target layout ablation: Providing target layouts to GPT-5-mini and Qwen2.5-VL-7B leads to significant accuracy gains on O3-BENCH, confirming the need for precise visual localization.
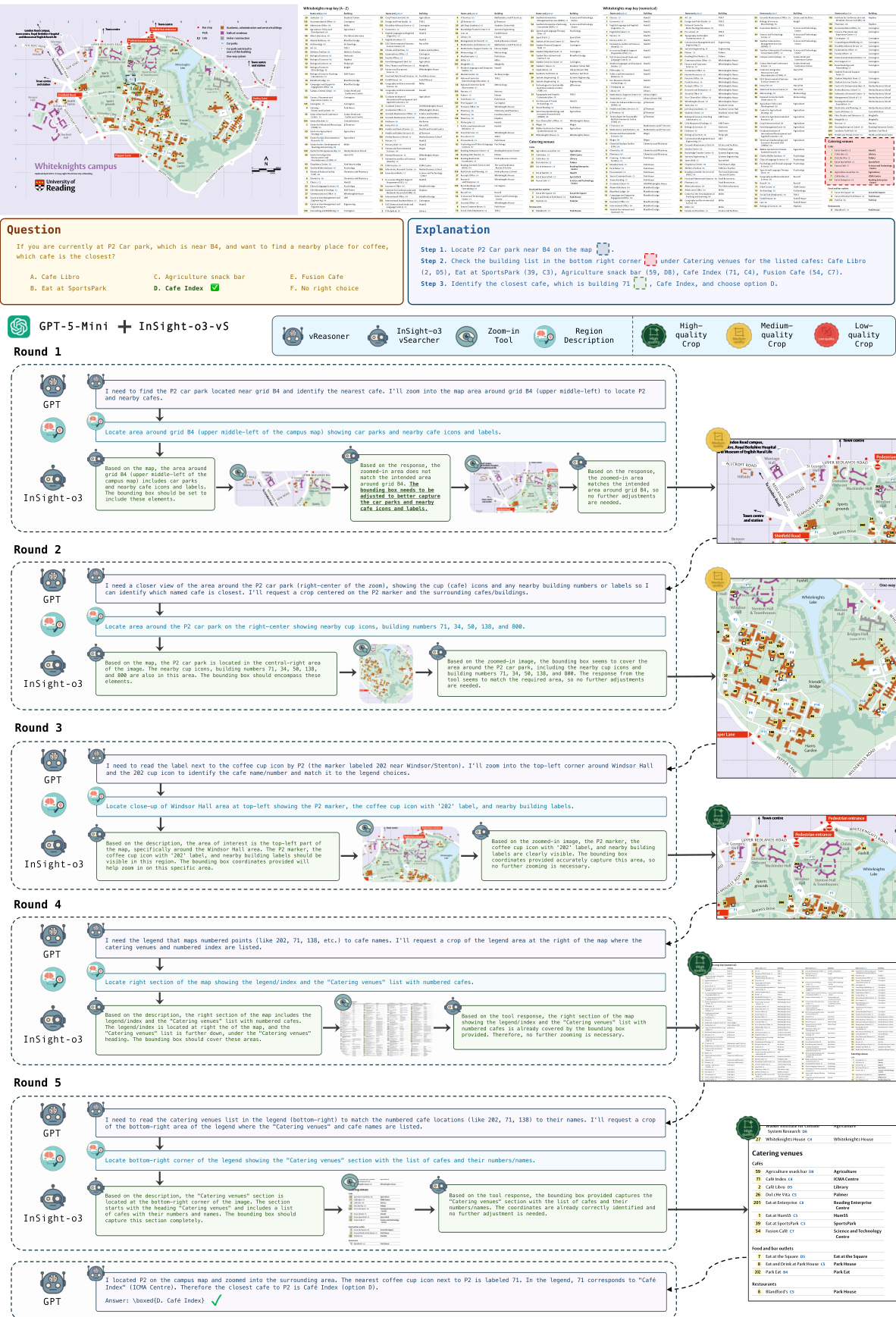
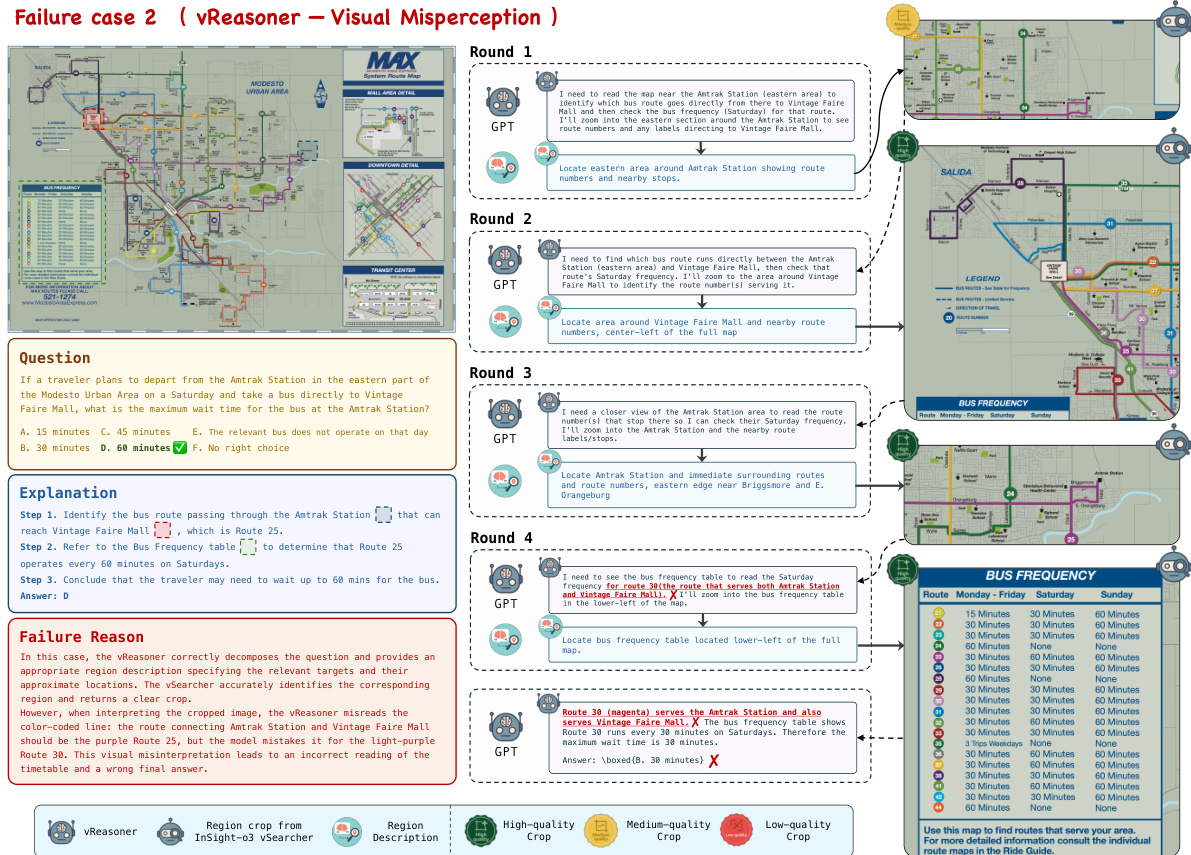
- Failure analysis: Most errors stem from vReasoner hallucination or misinterpretation of visual evidence, not vSearcher failures; InSight-o3-vS consistently returns high-quality crops aligned with natural language descriptions.
- Open model integration: InSight-o3 with Qwen3-VL-32B vReasoner outperforms both the base model and the non-RL baseline, indicating strong potential for open models.
The authors evaluate the impact of training and test image resolution on model performance, showing that higher resolution during training improves results across benchmarks. When the test resolution is increased, performance generally improves, but the benefit of using a vSearcher diminishes as the vReasoner can already perceive details clearly. The vSearcher's performance remains stable across different resolutions, with higher resolution leading to fewer vSearcher calls due to better initial image clarity.
The authors use InSight-o3-vS, a visual search agent trained with GPT-5-mini as the vReasoner, to enhance the performance of various multimodal models. Results show that InSight-o3-vS significantly improves the average performance of GPT-5-mini and Gemini-2.5-Flash across multiple benchmarks, particularly on O3-Bench, where it reduces the performance gap between these models and stronger baselines.
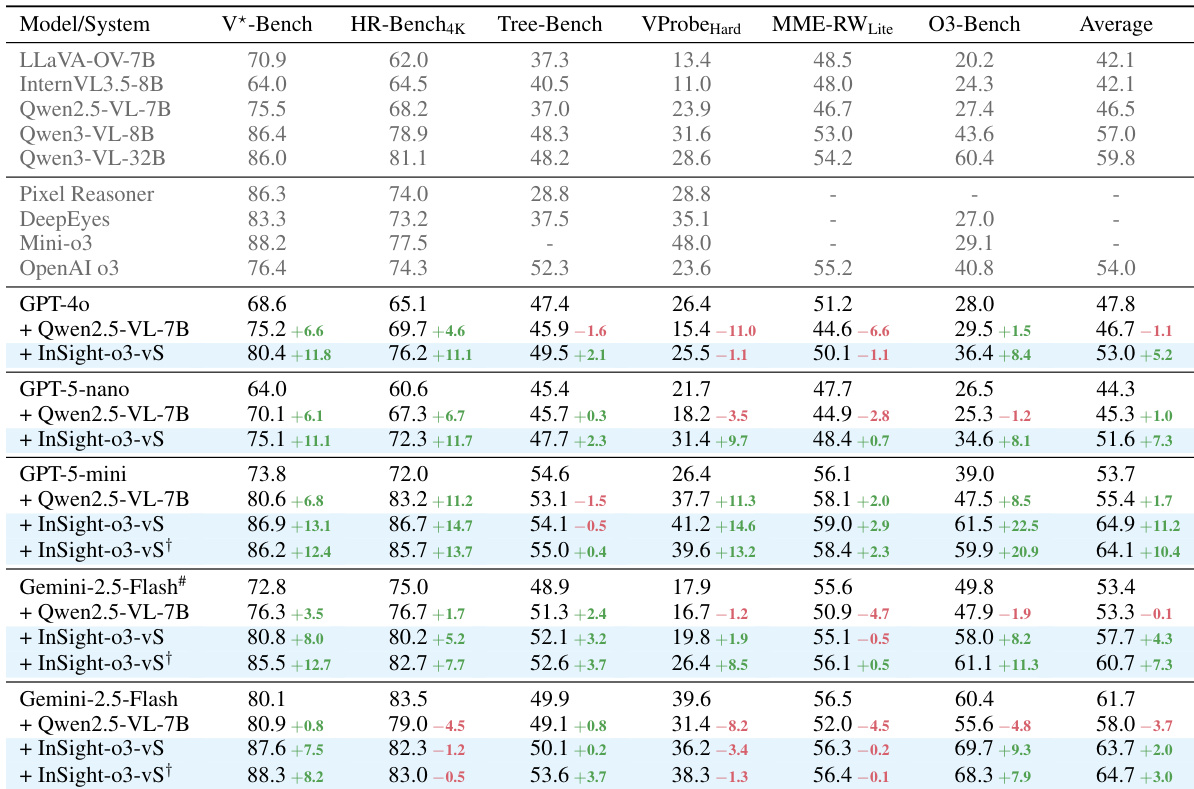
Results show that O3-Bench has a significantly higher average image resolution compared to HR-Bench4K and MME-RealWorld, and GPT-5-mini achieves lower average accuracy on O3-Bench than on the other two benchmarks. The average number of vSearch steps required for O3-Bench is also higher, indicating greater complexity in solving tasks on this benchmark.
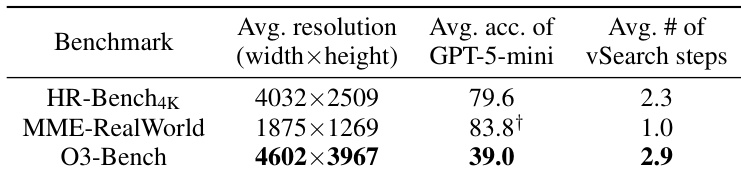
The authors use GPT-5-mini as the vReasoner and train a vSearcher, InSight-o3-vS, to assist it in visual reasoning tasks. Results show that InSight-o3-vS significantly improves GPT-5-mini's performance on O3-BENCH, increasing its score from 25.3% to 61.5% when both vSearcher and vReasoner are used together.
The authors use the provided training dynamics to analyze the impact of different reward design choices on the performance of InSight-o3-vS. Results show that the proposed reward setting consistently outperforms ablated variants across all metrics, with the "w/o feedback" variant exhibiting the worst performance. The number of vReasoner calls per QA decreases over time, indicating that the model learns to use the vSearcher more efficiently as training progresses.