Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
تقرير فني عن RecGPT-V2
تقرير فني عن RecGPT-V2
الملخص
أظهرت النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs) إمكانات ملحوظة في تحويل أنظمة التوصية من مطابقة الأنماط السلوكية الضمنية إلى الاستدلال على النوايا الصريحة. وعلى الرغم من أن RecGPT-V1 نجح في تأسيس هذا النموذج من خلال دمج الاستدلال القائم على النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة في استخلاص اهتمامات المستخدم وتنبؤ تسميات العناصر، إلا أنه يعاني من أربع قيود جوهرية: (1) عدم الكفاءة الحسابية والتكرار المعرفي عبر مسارات استدلال متعددة؛ (2) قلة تنوع التفسيرات في التوليد عبر قوالب ثابتة؛ (3) ضعف القدرة على التعميم ضمن النماذج التعلمية المراقبة؛ و(4) تقييم مبسط يركز على النتائج فقط، ولا يتوافق مع المعايير البشرية. لحل هذه التحديات، نقدّم RecGPT-V2 مع أربع ابتكارات رئيسية. أولاً، نظام وكالات متعددة متسلسل الهيكلية (Hierarchical Multi-Agent System) يعيد هيكلة عملية الاستدلال على النوايا من خلال تعاون منسق، مما يزيل التكرار المعرفي ويضمن تغطية متنوعة للنوايا. وبالتكامل مع استدلال التمثيل الهجين (Hybrid Representation Inference) الذي يُكثّف سياقات سلوك المستخدم، يقلل إطار العمل استهلاك وحدات المعالجة الرسومية (GPU) بنسبة 60٪، ويزيد الاستدعاء الاستثنائي من 9.39٪ إلى 10.99٪. ثانيًا، إطار عمل Meta-Prompting يقوم بتوليد أوامر تكيفية سياقية بشكل ديناميكي، مما يُحسّن تنوع التفسيرات بنسبة +7.3٪. ثالثًا، التعلم المعزّز المقيد يخفّف من تناقضات المكافآت المتعددة، ويحقق تحسنًا بنسبة +24.1٪ في تنبؤ التسميات، و+13.0٪ في قبول التفسيرات. رابعًا، إطار عمل الوكيل كمحكم (Agent-as-a-Judge) يفكك عملية التقييم إلى استدلال متعدد الخطوات، مما يعزز التوافق مع تفضيلات البشر. أظهرت اختبارات A/B عبر الإنترنت على منصة تاوبارو تحسينات كبيرة: +2.98٪ في معدل النقر (CTR)، +3.71٪ في عدد الزوار الفعليين (IPV)، +2.19٪ في الوقت المستهلك (TV)، و+11.46٪ في معدل التفاعل العاطفي (NER). يثبت RecGPT-V2 الجدوى التقنية والقابلية التجارية لتطبيق الاستدلال القائم على النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة على نطاق واسع، ويُسهم في سد الفجوة بين الاستكشاف المعرفي والقيمة الصناعية.
One-sentence Summary
The authors propose RecGPT-V2, which addresses RecGPT-V1's four limitations through a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System eliminating cognitive redundancy while enabling diverse intent coverage, Meta-Prompting for dynamic explanation generation, constrained reinforcement learning for multi-reward optimization, and Agent-as-a-Judge for process-oriented evaluation, achieving 60% GPU reduction and significant Taobao performance gains including +11.46% novelty exposure rate.
Key Contributions
- RecGPT-V2 addresses critical deficiencies in prior systems including computational inefficiency from redundant intent reasoning and low-information-density explanations by introducing a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System with Hybrid Representation Inference, reducing GPU consumption by 60% and improving exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%.
- The framework overcomes homogenized expression and weak temporal adaptation through Meta-Prompting for dynamic context-aware explanation generation, which increases explanation diversity by 7.3% while capturing real-time signals like seasonal trends.
- Preference-aware reinforcement learning resolves multi-reward conflicts in complex generation tasks, achieving 24.1% higher tag prediction accuracy and 13.0% greater explanation acceptance, with online A/B tests on Taobao confirming significant gains in CTR (2.98%), IPV (3.71%), and NER (11.46%).
Introduction
Recommendation systems increasingly rely on personalized explanations to boost user engagement with suggested items, but static explanation approaches suffer from repetitive, context-ignorant outputs that reduce effectiveness. Prior work like RecGPT-V1 faced critical limitations: rigid prompt templates produced low-information-density explanations with poor adaptation to temporal trends or user context, while evaluation frameworks failed to capture key quality dimensions like stylistic diversity. The authors address this by introducing Meta-Prompting to dynamically synthesize context-aware prompt templates and preference-aware reinforcement learning that optimizes explanations via human-aligned multi-reward modeling. Together, these innovations shift explanation generation from inflexible templating to adaptive reasoning, directly tackling engagement shortcomings observed in live deployments.
Dataset
The authors use a bilingual e-commerce product title dataset for translation tasks. Key details include:
- Composition and sources: The dataset consists of paired Chinese product titles and their English translations, sourced from online retail platforms.
- Subset details:
- Contains user-generated product listings with verified translations.
- Specific split sizes are unspecified, but examples follow a strict {Chinese: English} format.
- No explicit filtering rules are stated; entries appear curated for direct translation relevance.
- Usage in training:
- The data forms the core training split for sequence-to-sequence translation models.
- Used as a single-task mixture without additional data sources or ratio adjustments.
- Processing:
- Raw titles undergo minimal preprocessing; the example shows direct character-level pairing.
- No cropping strategy is applied—full titles are preserved as input-output pairs.
- Metadata is derived implicitly from the paired structure, with no auxiliary annotations added.
Method
The authors leverage a comprehensive, multi-component architecture in RecGPT-V2 to overcome the computational inefficiency, cognitive redundancy, and evaluation limitations of its predecessor. The system is structured around three core innovations: Agentic Intent Reasoning, Dynamic Explanation Generation, and an Agentic Judge Framework, each addressing a specific bottleneck in the recommendation pipeline.
The Agentic Intent Reasoning module forms the backbone of the system, replacing RecGPT-V1’s parallel, redundant LLM routes with a coordinated Hierarchical Multi-Agent System (HMAS). This system operates in three stages: a Global Planner decomposes user intent into specialized personas by synthesizing user behavioral history, static/dynamic profile attributes, and real-time environmental signals (e.g., weather, trending events). These personas are then distributed to Distributed Expert agents, each responsible for generating item tags aligned with a specific intent facet. Finally, a Decision Arbiter consolidates the expert outputs, performing joint reasoning over the entire candidate tag pool to select the most behaviorally relevant, profile-consistent, and non-redundant tags for downstream retrieval. This coordinated architecture eliminates redundant full-context encoding and cognitive overlap, as illustrated in the comparison between RecGPT-V1’s isolated routes and RecGPT-V2’s HMAS.
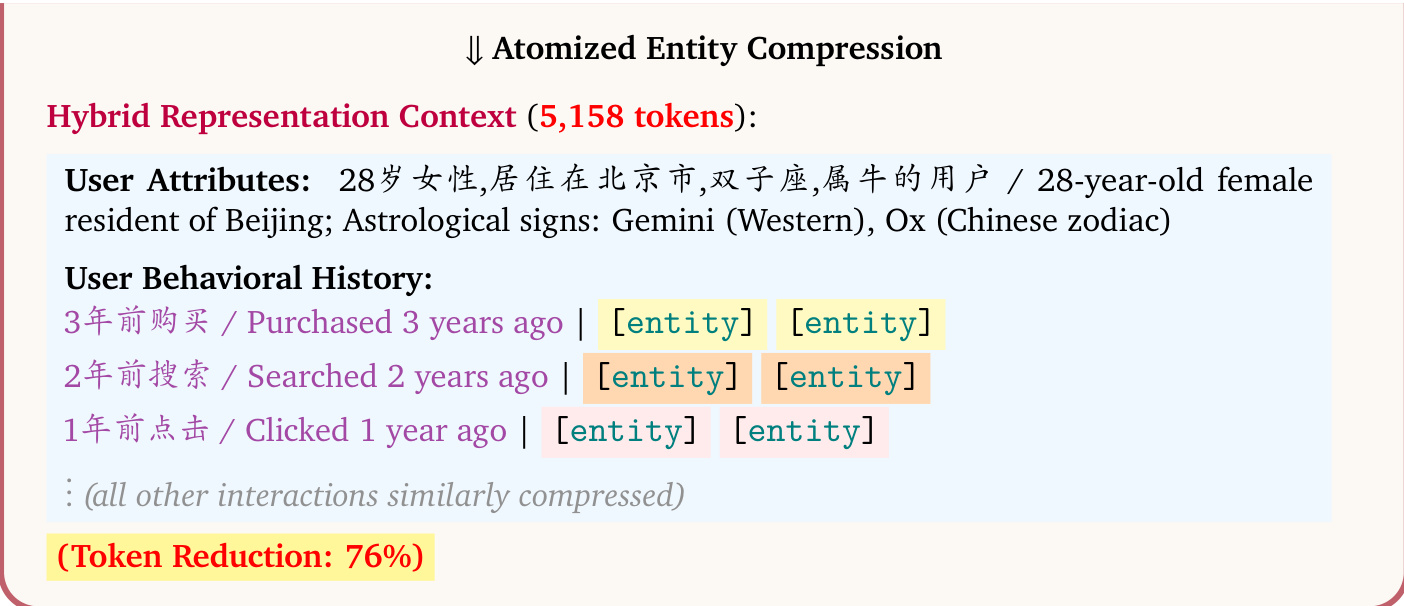
To enable this architecture at scale, the authors introduce Hybrid Representation Inference. This technique compresses the user’s lifelong behavioral sequence—often exceeding 32K tokens—into a compact hybrid context. The core of this compression is Atomized Entity Compression, which encodes item and query descriptions into dense vector representations using pretrained embedding models (e.g., BGE, Qwen3-Embedding). These vectors are then projected into the LLM’s input space via a lightweight, trainable adaptor network, replacing multi-token textual descriptions with single atomic tokens denoted as [entity]. This process achieves a 7x compression ratio while preserving semantic integrity, as shown in the example where a 21,349-token user profile is reduced to 5,158 tokens.
The authors further enhance efficiency through Infrastructure Engineering Optimizations, including a Disaggregated Prefill-Decode Serving Architecture. This design allocates separate GPU pools to the compute-intensive prefill phase (processing long contexts) and the memory-intensive decode phase (generating outputs), significantly improving Model FLOPs Utilization (MFU). Combined with the use of XQA kernels for FP8 precision inference, these optimizations reduce GPU consumption by 60% and improve MFU by 53.7% compared to RecGPT-V1.
For dynamic explanation generation, the authors move beyond RecGPT-V1’s fixed templates by introducing a Meta-Prompting framework. This two-stage process first synthesizes a contextually adaptive stylistic guideline based on user interests, item attributes, and situational signals (e.g., seasonal trends). The second stage then generates the final explanation conditioned on this guideline, enabling diverse, emotionally resonant, and timely outputs. This approach improves explanation diversity by +7.3% and better aligns with user expectations across expanded evaluation dimensions, including Timeliness, Informativeness, and Attractiveness.
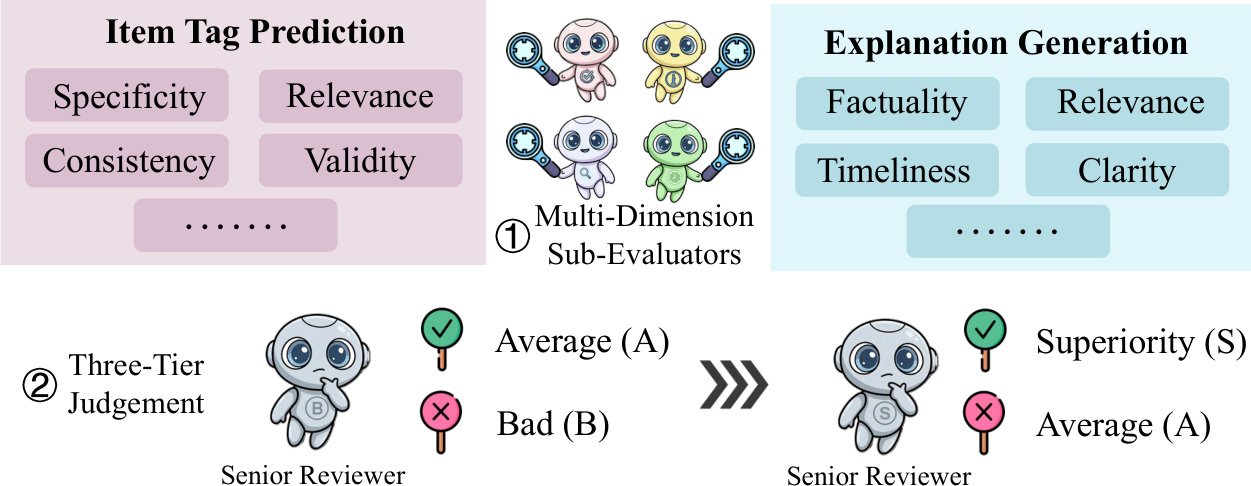
Finally, to address the limitations of outcome-focused evaluation, the authors propose an Agent-as-a-Judge framework. This system decomposes holistic quality assessment into Multi-Dimension Sub-Evaluators, each specializing in a specific criterion (e.g., Relevance, Factuality, Timeliness). A Senior Reviewer Agent then aggregates these sub-evaluations into a three-tier judgment (Superior, Average, Bad) through a structured, two-stage process: first detecting critical defects, then elevating high-quality outputs. This process-oriented evaluation improves human preference alignment by +0.46% on tag prediction and +1.76% on explanation generation. To enable continuous improvement, the authors introduce Judge-as-a-Reward, a distillation framework that converts these discrete judgments into dense, differentiable reward signals for reinforcement learning, establishing a self-reinforcing flywheel for policy optimization.
Experiment
- Conducted two-week online A/B test on Taobao comparing RecGPT-V2 against RecGPT-V1 across item and feed recommendation scenarios with 1% traffic allocation per group
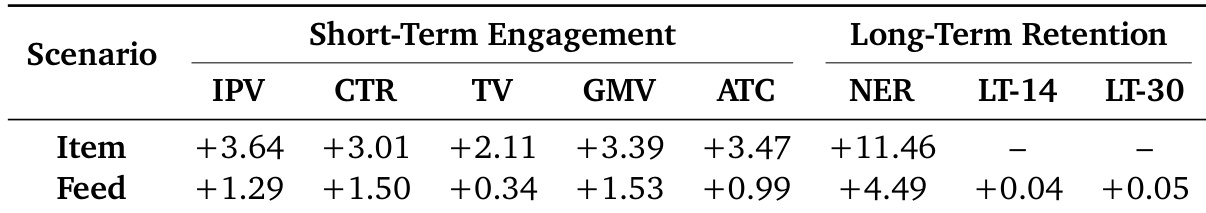
- Achieved significant improvements in short-term metrics: +3.40% IPV, +4.68% CTR, +4.05% TV, and +11.46% NER (Novelty Exposure Rate) versus baseline
- Demonstrated enhanced long-term retention with +0.04% LT-14 and +0.05% LT-30 user retention rates
- Validated dynamic intent adaptation through real-world case analysis showing context-aware recommendations integrating environmental signals like weather and holidays
- Reduced GPU consumption by 60% while improving generation quality for item tag prediction and explanation tasks
The authors use RecGPT-V2 in a two-week A/B test on Taobao, comparing it against RecGPT-V1 across item and feed recommendation scenarios. Results show consistent improvements in both short-term engagement and long-term retention, with the item scenario achieving the highest gains in IPV (+3.64%) and NER (+11.46%), while the feed scenario shows modest but meaningful retention gains (LT-14 +0.04%, LT-30 +0.05%).
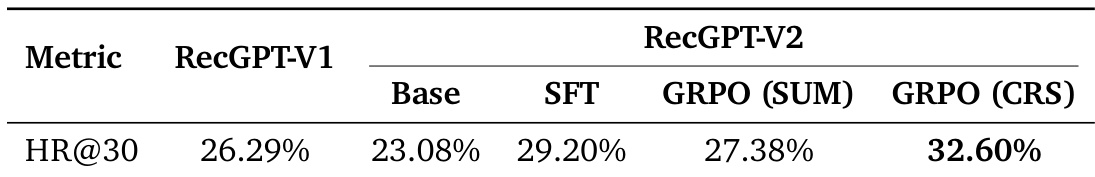
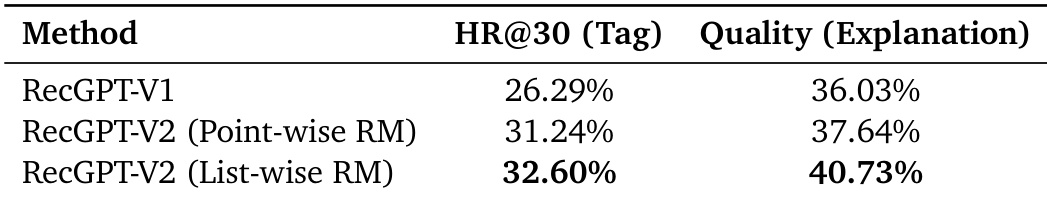
The authors evaluate RecGPT-V2 using two reward modeling approaches against RecGPT-V1, showing that List-wise RM achieves the highest HR@30 (Tag) at 32.60% and Quality (Explanation) at 40.73%, indicating improved tag prediction accuracy and explanation quality over prior versions. Results confirm that List-wise reward modeling enhances both retrieval effectiveness and explanatory output compared to Point-wise RM and the baseline.
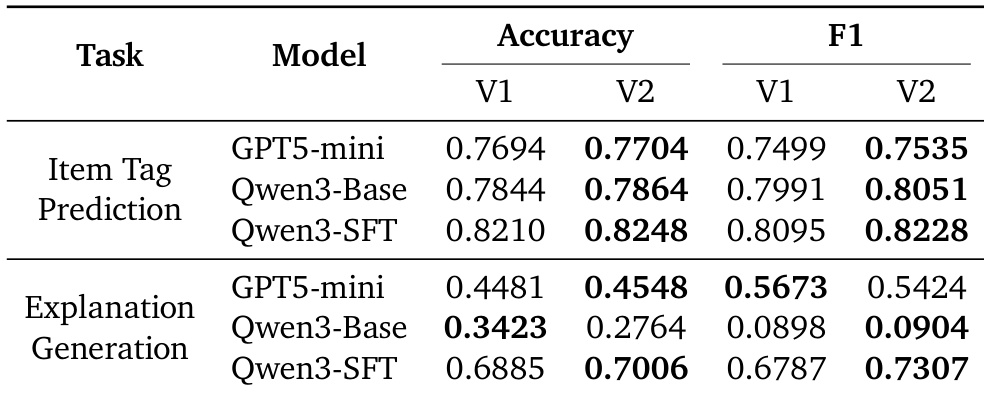
The authors evaluate RecGPT-V2 against baseline models on item tag prediction and explanation generation tasks, showing consistent improvements in both accuracy and F1 score across all tested models. For item tag prediction, Qwen3-SFT achieves the highest performance with 0.8248 accuracy and 0.8228 F1 in V2, while for explanation generation, Qwen3-SFT also leads with 0.7006 accuracy and 0.7307 F1 in V2, indicating enhanced generation quality. These results support the system’s effectiveness in producing more precise and contextually relevant outputs.
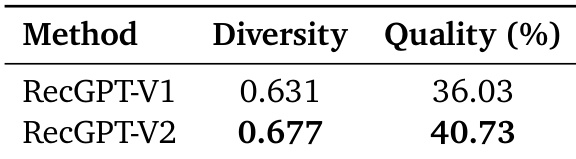
The authors evaluate RecGPT-V2 against RecGPT-V1 using diversity and quality metrics, showing that RecGPT-V2 achieves higher diversity (0.677 vs. 0.631) and quality (40.73% vs. 36.03%). These results indicate improved recommendation variety and output accuracy in the updated system.
The authors evaluate RecGPT-V2 using HR@30 across multiple configurations, showing that the GRPO (CRS) variant achieves the highest score at 32.60%, outperforming both the baseline RecGPT-V1 (26.29%) and other variants including SFT (29.20%) and GRPO (SUM) (27.38%). Results indicate that the CRS optimization strategy contributes most significantly to recall performance.