Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
OneStory: توليد فيديو متعدد المشاهد متماسك باستخدام ذاكرة تكيفية
OneStory: توليد فيديو متعدد المشاهد متماسك باستخدام ذاكرة تكيفية
الملخص
تُقدَّم القصص في مقاطع الفيديو الواقعية غالبًا من خلال عدة لقطات — أي لقطات متقطعة لكنها مرتبطة معنويًا، تُشكّل معًا سردًا متماسكًا. ومع ذلك، تواجه الطرق الحالية لإنشاء مقاطع فيديو متعددة اللقطات (MSV) صعوبات في نمذجة السياق الطويل بين اللقطات، نظرًا لاعتمادها على نوافذ زمنية محدودة أو شرطية واحدة فقط بناءً على لقطة رئيسية، مما يؤدي إلى تراجع الأداء في السياقات القصصية المعقدة. في هذا العمل، نقترح نموذج OneStory، الذي يتيح نمذجة سياقية عالمية ولكن مكثفة بين اللقطات، لتمكين إنشاء قصص سردية متسقة وقابلة للتوسع. يعيد OneStory صياغة مسألة إنشاء مقاطع الفيديو متعددة اللقطات إلى مهمة إنشاء اللقطة التالية، مما يسمح بتوليد لقطات متسلسلة بشكل تلقائي (autoregressive)، مع الاستفادة من نماذج التحويل من الصورة إلى الفيديو المُدرّبة مسبقًا (I2V) لتوفير شرط بصري قوي. نقدّم وحدتين رئيسيتين: أولًا، وحدة اختيار الإطارات (Frame Selection)، التي تبني ذاكرة عالمية ذات معنى قائمة على الإطارات المفيدة من اللقطات السابقة؛ وثانيًا، وحدة المُنظِّم التكيفي (Adaptive Conditioner)، التي تُطبّق تقنية التجزئة الموجهة بالأهمية لتكوين سياق مكثف يمكن استخدامه مباشرةً كشرط. كما قمنا بجمع مجموعة بيانات عالية الجودة تتضمن لقطات متعددة ونصوص تشير إلى السياق (referential captions)، لتعكس نمط السرد في العالم الحقيقي، وصممنا استراتيجيات تدريب فعّالة ضمن إطار "اللقطة التالية". وباستخدام نموذج I2V المُدرّب مسبقًا، وتم تدريبه على مجموعتنا المُختارة المكوَّنة من 60 ألف لقطة، يحقق OneStory أداءً متميزًا من حيث تماسك القصة في مشاهد متنوعة ومعقدة، سواء في البيئات المشروطة بالنص أو بالصورة، مما يمكّن من إنشاء قصص فيديو طويلة بتحكم دقيق وتجربة غامرة.
Summarization
Meta AI and University of Copenhagen researchers propose OneStory, a novel framework for multi-shot video generation that models global cross-shot context via a Frame Selection module and Adaptive Conditioner, enabling scalable, coherent long-form storytelling by reformulating the task as autoregressive next-shot prediction using pretrained image-to-video models.
Key Contributions
- The paper introduces a novel framework for multi-shot video generation that addresses the limitations of existing methods by enabling consistent and scalable narrative modeling through adaptive keyframe selection and cross-shot context propagation.
- It proposes an effective training strategy using a high-quality dataset of multi-shot videos with referential captions, allowing the model to maintain narrative coherence across discontinuous scenes.
- By reformulating multi-shot generation as a next-shot prediction task, the approach enhances long-range temporal consistency and supports dynamic evolution of story elements, overcoming the issue of memory loss in prior single-keyframe methods.
Introduction
The authors leverage recent progress in diffusion transformers for video generation to address the challenge of multi-shot video synthesis, where models typically generate only single continuous scenes, limiting their use in real-world storytelling applications. Existing methods either rely on fixed-window attention mechanisms or keyframe conditioning, both of which suffer from memory loss and narrative inconsistency due to the limited context window as shots progress.
- The proposed OneStory framework introduces three key innovations: (1) a Frame Selection module that identifies semantically relevant frames across all prior shots, (2) an Adaptive Conditioner that dynamically patchifies and injects contextual information into the generator based on frame importance, and (3) a training strategy using unified three-shot sequences and progressive coupling to enhance narrative coherence and scalability.
Dataset
- The authors use a high-quality multi-shot video dataset consisting of approximately 60,000 videos, including 50,000 two-shot and 10,000 three-shot sequences, all centered on human-centric activities and sourced from research-copyrighted videos.
- Shot boundaries are detected using TransNetV2, and only videos with at least two shots are retained. Each shot is captioned in two stages: first independently, then rewritten with reference to the prior shot’s content and caption, introducing referential expressions (e.g., “the same man”) to ensure narrative continuity.
- Captioning is performed using a vision-language model to generate coherent, context-aware descriptions.
- The dataset undergoes multi-stage filtering: keyword filters remove inappropriate content; CLIP and SigLIP filter out videos with irrelevant shot transitions; DINOv2 eliminates videos with overly similar shots, ensuring narrative progression and visual diversity.
- To enable stable training, the authors unify all samples into a three-shot format. For two-shot videos, a synthetic middle or first shot is generated either by inserting a random shot from another video or by augmenting the first shot with spatial or color transformations.
- The final shot in each sequence—real or synthetic—is used as the prediction target. The model is trained to generate this last shot conditioned on the first two shots and the corresponding caption, using a rectified-flow diffusion loss.
- For evaluation, the authors curate a benchmark of 64 six-shot test cases each for text-to-multi-shot video (T2MSV) and image-to-multi-shot video (I2MSV) generation, covering three storytelling patterns: main-subject consistency, insert-and-recall with an intervening shot, and composable generation, enabling comprehensive assessment of narrative coherence and cross-shot reasoning.
Method
The authors leverage a unified autoregressive framework for multi-shot video generation, reformulating the task as a next-shot prediction problem conditioned on prior visual context and a narrative caption. The model, named OneStory, is initialized from a pretrained image-to-video diffusion model and fine-tuned on a curated 60K dataset. The core architecture, as shown in the figure below, comprises three key components: a Frame Selection module, an Adaptive Conditioner, and a DiT-based diffusion backbone, which operate in tandem during both training and inference.
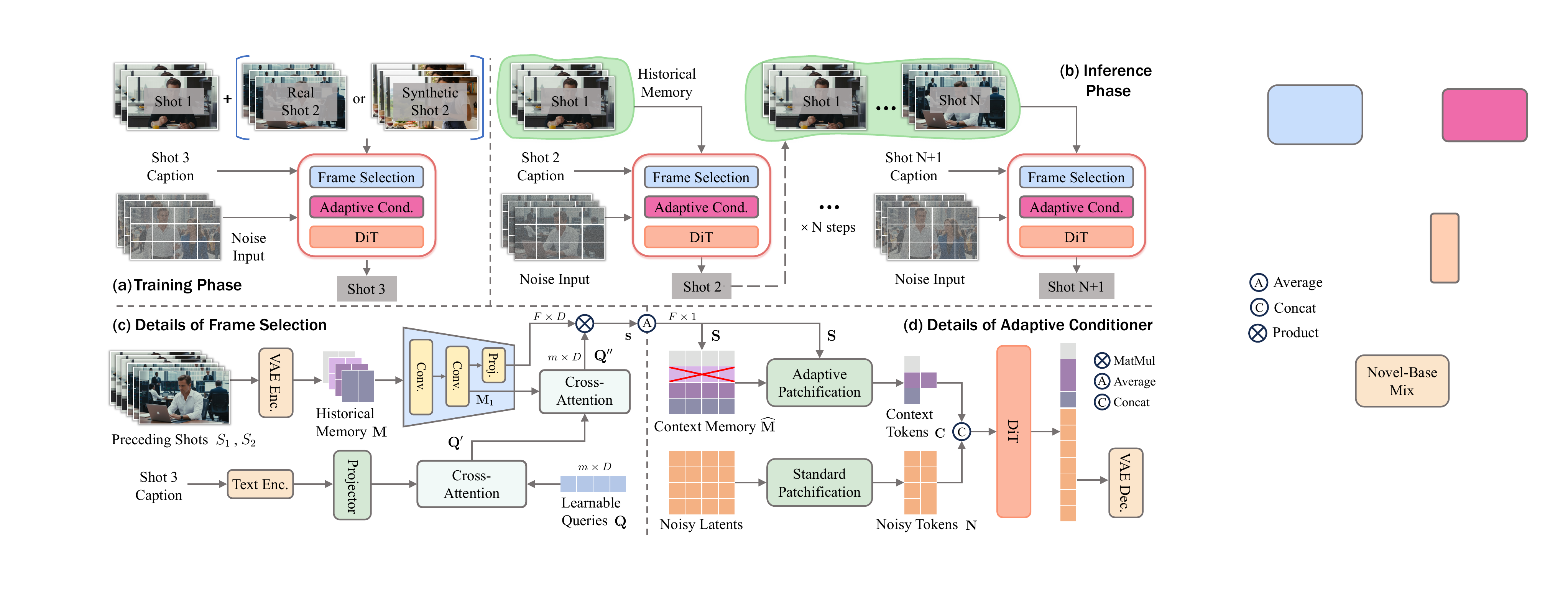
During generation, for the i-th shot, the model takes as input the caption Ci, the latent representations of all preceding shots {Sj}j=1i−1, and a noise tensor. The 3D VAE encoder first compresses each prior shot into a latent sequence, which is concatenated into a global historical memory M∈RF×Ns×Dv, where F is the total number of frames across prior shots and Ns is the spatial token count per frame. The Frame Selection module then identifies the most semantically relevant frames from this memory. It employs m learnable query tokens that first attend to the projected text features of Ci to capture the current shot’s intent, and then attend to the projected visual memory M1 to extract visual cues. Frame-wise relevance scores S∈RF are computed via a projection and mean aggregation over query-memory interactions. The top-Ksel frames are selected based on these scores to form a compact context memory M.
The Adaptive Conditioner processes this selected memory to generate a set of context tokens C that are efficiently injected into the diffusion process. It employs a set of patchifiers {Pℓ}ℓ=1Lp with varying kernel sizes. Based on the relevance scores S, frames in M are adaptively assigned to patchifiers: highly relevant frames are processed with finer, less compressive patchifiers, while less relevant ones use coarser ones. This content-driven allocation, illustrated in the figure below, contrasts with fixed temporal partitioning and ensures that critical visual information is preserved with minimal computational overhead.
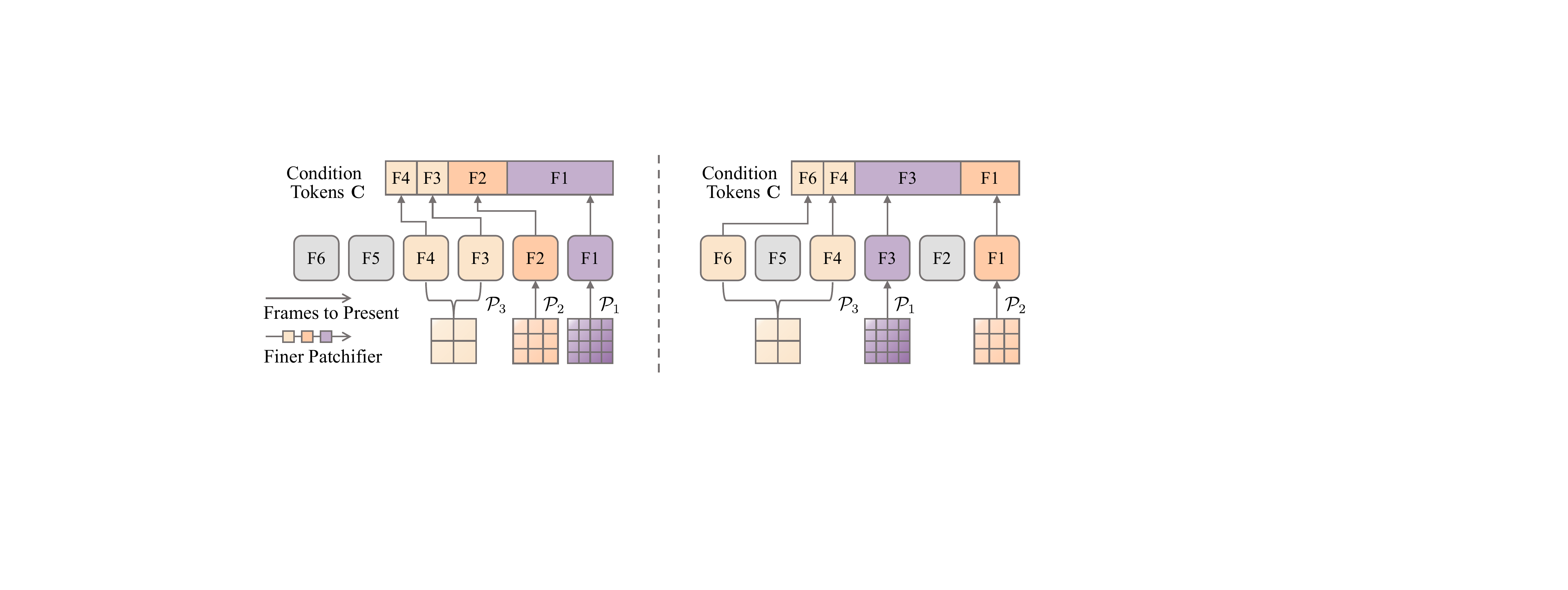
The resulting context tokens C are concatenated with the noisy latent tokens N of the current shot to form the input X for the DiT backbone. This concatenation enables joint attention between noisy and context tokens, facilitating rich cross-attention interactions that guide the denoising process. The model is trained with a joint objective that combines a standard shot generation loss Lshot with a supervision loss Lsel for the frame relevance scores. The latter is computed using pseudo-labels derived from DINOv2 and CLIP embeddings for real frames, and heuristic labels for synthetic frames, ensuring the Frame Selection module learns to prioritize semantically aligned context.
Experiment
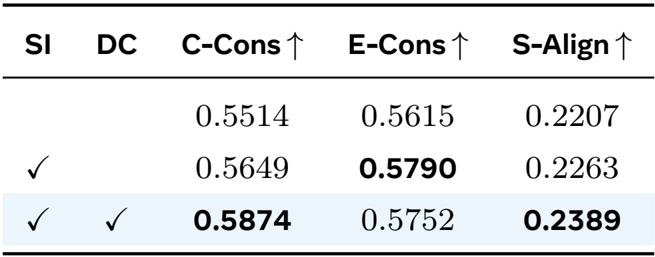
- Shot inflation and Decoupled Conditioning improve narrative consistency, while both baselines fail, highlighting the effectiveness of our adaptive memory in maintaining stable long-range identity cues.
- Shot inflation and Decoupled Conditioning improve narrative consistency, while both baselines fail, highlighting the effectiveness of our adaptive memory in maintaining stable long-range identity cues.
- Shot inflation and Decoupled Conditioning improve narrative consistency, while both baselines fail, confirming their complementary roles in cross-shot context modeling.
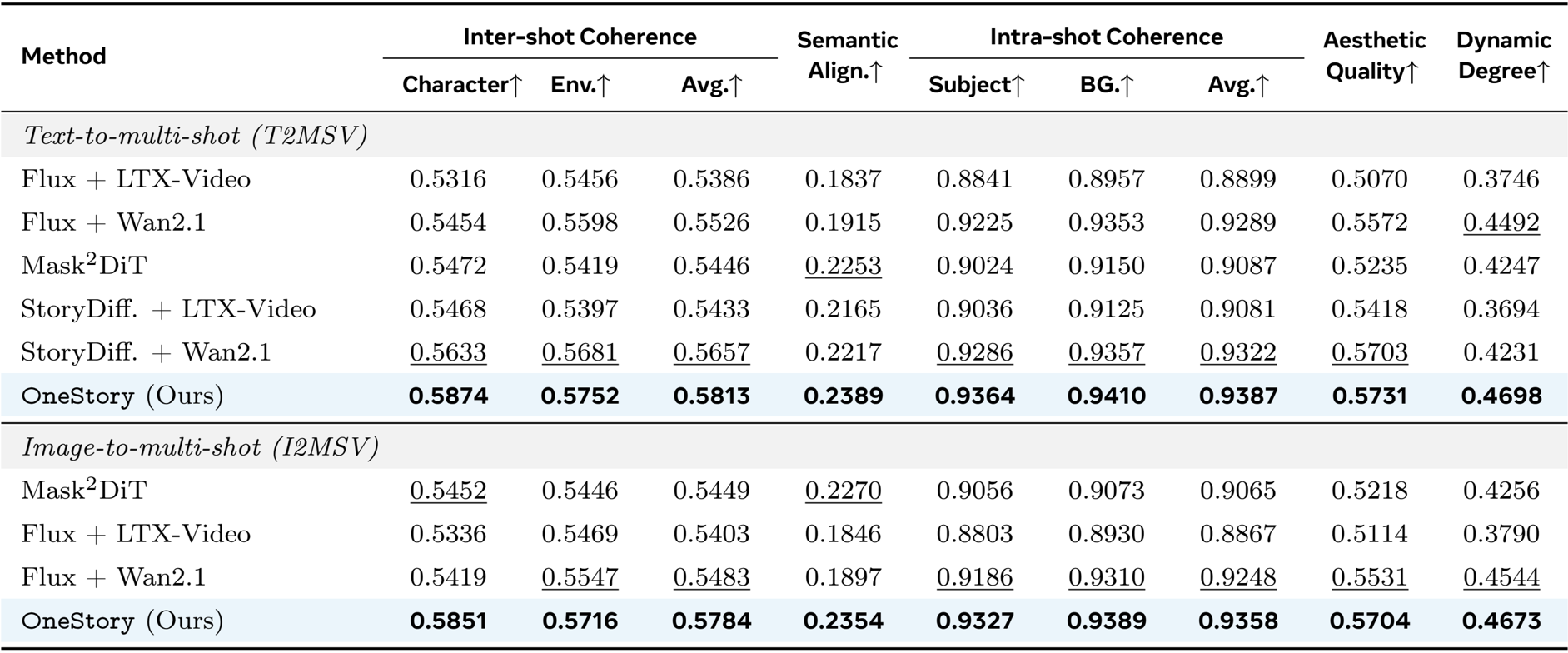
The authors use OneStory to generate multi-shot videos under both text- and image-conditioned settings, evaluating performance across inter-shot coherence, semantic alignment, intra-shot coherence, aesthetic quality, and dynamic degree. Results show OneStory consistently outperforms all baselines in both settings, achieving the highest scores across nearly all metrics, particularly in character and environment consistency, semantic alignment, and subject-background fidelity. This demonstrates its superior ability to maintain narrative continuity and visual quality across multiple shots.
The authors evaluate the impact of their Adaptive Conditioner (AC) and Frame Selection (FS) modules through ablation, showing that combining both yields the highest character consistency, environment consistency, and semantic alignment. Results confirm that each component contributes independently, with their joint use delivering the strongest narrative coherence.
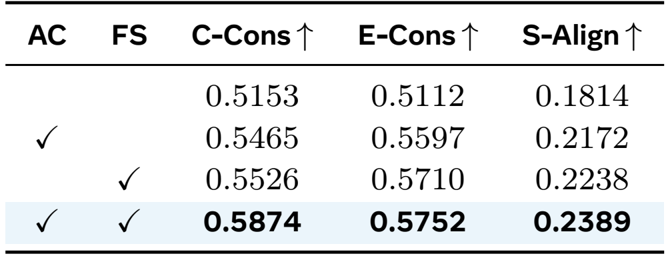
The authors evaluate the impact of their training strategies, showing that Shot Inflation alone improves environment consistency and semantic alignment, while combining it with Decoupled Conditioning yields the highest scores across all metrics, confirming the effectiveness of their two-stage curriculum for stable optimization and narrative coherence.
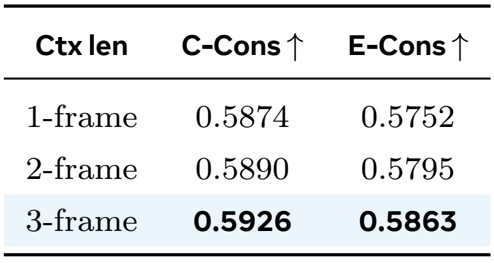
The authors evaluate the impact of context token length on cross-shot consistency, finding that increasing from one to three latent-frame equivalents improves both character and environment consistency. Results show a steady performance gain with more context tokens, confirming the efficiency of their adaptive memory in modeling temporal dynamics.