Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
FLUX.1 سياق: مطابقة التدفق للإ génération والتحرير الصورى في الفضاء المخفي باستخدام السياق
FLUX.1 سياق: مطابقة التدفق للإ génération والتحرير الصورى في الفضاء المخفي باستخدام السياق
الملخص
نقدّم نتائج التقييم لنموذج FLUX.1 Kontext، وهو نموذج توليد مطابق للتدفق (flow matching) يُوحّد توليد الصور وتحريرها. يُولِّد النموذج مناظرًا جديدة من خلال دمج السياق الدلالي المستمد من المدخلات النصية والصورية. وباستخدام نهج بسيط يعتمد على تسلسل الربط (sequence concatenation)، يُعَالِج FLUX.1 Kontext مهام التحرير المحلي والمهام التوليدية داخل السياق ضمن معمارية موحدة واحدة. مقارنةً بالنماذج الحالية للتحرير التي تُظهر تدهورًا في اتساق الأشخاص والكائنات واستقرارها عبر جولات متعددة، نلاحظ أن FLUX.1 Kontext يُحسّن الحفاظ على الكائنات والشخصيات، مما يُسهم في تعزيز المرونة في سير العمل التكراري. ويحقق النموذج أداءً تنافسيًا مع أنظمة الحالة الراهنة (state-of-the-art)، مع تسريع كبير في زمن التوليد، ما يمكّن من تطبيقه في تطبيقات تفاعلية وسير عمل سريعة للتجريب الأولي (rapid prototyping). ولتأكيد هذه التحسينات، نقدّم "KontextBench"، وهو معيار شامل يضم 1026 زوجًا من الصور والنصوص، يغطي خمس فئات مهام: التحرير المحلي، التحرير الشامل، الإشارة إلى الشخصية، الإشارة إلى الأسلوب، وتحرير النص. وتُظهر التقييمات التفصيلية أداءً متفوقًا لنموذج FLUX.1 Kontext من حيث جودة النتيجة في الجولة الواحدة، واستقرار النتائج عبر الجولات المتعددة، مما يُشكّل معايير جديدة لنماذج المعالجة الموحدة للصور.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Black Forest Labs propose FLUX.1 Kontext, a unified generative flow matching model that integrates image generation and editing via simple sequence concatenation, enabling robust multi-turn consistency and faster inference than prior models, with demonstrated superiority on KontextBench across local and global editing, character and style reference, and text editing tasks.
Key Contributions
-
FLUX.1 Kontext addresses the challenge of maintaining character and object consistency across multiple iterative edits, a critical limitation in current generative image editing systems that often suffer from visual drift and degradation in identity preservation during story-driven or brand-sensitive workflows.
-
The model introduces a unified flow matching architecture that processes both text and image inputs through simple sequence concatenation, enabling seamless integration of local editing, global modifications, style transfer, and text-driven generation within a single, fast inference framework without requiring parameter updates or fine-tuning.
-
Evaluated on KontextBench—a new benchmark with 1026 image-prompt pairs across five task categories—FLUX.1 Kontext achieves state-of-the-art performance in both single-turn image quality and multi-turn consistency, while delivering 3–5 second generation times at 1024×1024 resolution, making it suitable for interactive and rapid prototyping applications.
Introduction
The authors leverage flow matching in latent space to enable in-context image generation and editing, addressing the growing demand for intuitive, accurate, and interactive visual content creation in applications ranging from storytelling and e-commerce to brand asset management. Prior approaches, while effective for single edits, suffer from character drift across multiple iterations, slow inference speeds, and reliance on synthetic training data that limits realism and consistency. The main contribution is FLUX.1 Kontext, a unified, flow-based model trained via velocity prediction on concatenated context and instruction sequences, which achieves state-of-the-art performance with high fidelity, character consistency across multi-turn edits, and interactive inference speeds of 3–5 seconds per 1024×1024 image. The model supports iterative, instruction-driven workflows with minimal visual drift, enabling complex creative tasks like narrative generation and product editing, and is evaluated through KontextBench, a real-world benchmark of 1026 image-prompt pairs.
Dataset
- The dataset, KontextBench, is composed of 1,026 unique image-prompt pairs derived from 108 base images sourced from diverse real-world contexts, including personal photos, CC-licensed art, public domain images, and AI-generated content.
- It covers five core tasks: local instruction editing (416 examples), global instruction editing (262), text editing (92), style reference (63), and character reference (193), ensuring broad coverage of practical in-context editing scenarios.
- The authors use KontextBench to evaluate model performance, with the full dataset serving as a test set for human evaluation and benchmarking. The data is not split into training and validation sets, as the focus is on assessing real-world applicability rather than model training.
- No explicit cropping or image preprocessing is described, but the dataset emphasizes authentic, real-world use cases, with prompts and edits collected through crowd-sourcing to reflect actual user behavior.
- Metadata is constructed around task type, image source, and editing scope, enabling fine-grained analysis of model performance across different editing modalities.
- The benchmark is designed to support reliable human evaluation and is released alongside FLUX.1 Kontext samples and baseline results for reproducibility and community use.
Method
The authors leverage a rectified flow transformer architecture trained in the latent space of a convolutional autoencoder, building upon the FLUX.1 model. The overall framework, as illustrated in the high-level overview, integrates both text and image conditioning to generate target images. The model begins by encoding input images into latent tokens using a frozen autoencoder, which are then processed alongside text tokens. The architecture employs a hybrid block design: the initial portion consists of double stream blocks, where image and text tokens are processed separately with distinct weights, and their representations are combined through attention over concatenated sequences. This is followed by a series of 38 single stream blocks that process the combined image and text tokens. After this processing, the text tokens are discarded, and the remaining image tokens are decoded back into pixel space.
To enhance computational efficiency, the model utilizes fused feed-forward blocks inspired by Dehghani et al., which reduce modulation parameters and fuse attention and MLP linear layers to enable larger matrix-vector operations. The model incorporates factorized three-dimensional Rotary Positional Embeddings (3D RoPE) to encode spatial and temporal information for each latent token, with positions indexed by (t,h,w). For context images, a constant offset is applied to their positional embeddings, effectively treating them as occurring at a virtual time step, which cleanly separates the context and target image tokens while preserving their internal spatial structure.
The training objective is a rectified flow-matching loss, which optimizes the model to predict the velocity field of a linearly interpolated latent between a target image and noise. This loss is defined as the expectation of the squared difference between the predicted velocity and the ground truth velocity. The timestep t is sampled from a logit-normal distribution, where the mode μ is adjusted based on the data resolution. During sampling, the model can generate images conditioned on both a text prompt and an optional context image, enabling both image-driven edits and free text-to-image generation. The model is trained on relational pairs of (x∣y,c), where x is the target image, y is the context image, and c is the text prompt. The training process starts from a pre-trained text-to-image checkpoint and jointly fine-tunes the model on both image-to-image and text-to-image tasks.
Experiment
- FLUX.1 Kontext validates unified image generation and editing through a single architecture, demonstrating superior character and object consistency in iterative workflows compared to existing models.
- On KontextBench, a benchmark with 1026 image-prompt pairs across five categories (local editing, global editing, character reference, style reference, text editing), FLUX.1 Kontext [pro] achieves top performance in text editing and character preservation, with FLUX.1 Kontext [max] leading in general character reference and outperforming competitors in computational efficiency by up to an order of magnitude.
- In image-to-image tasks, FLUX.1 Kontext [max] and [pro] achieve state-of-the-art results in local editing and character reference, with AuraFace similarity scores confirming improved facial consistency.
- In text-to-image evaluation on Internal-T2I-Bench and GenAI Bench, FLUX.1 Kontext demonstrates balanced performance across prompt following, aesthetics, realism, typography accuracy, and speed, outperforming FLUX1.1 [pro] and showing progressive gains from [pro] to [max], while avoiding the "bakeyness" common in other models.
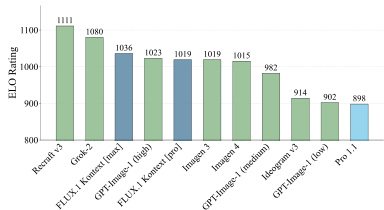
Results show that FLUX.1 Kontext [pro] achieves the highest ELO rating among the evaluated models, outperforming competitors such as GPT-Image-1 and Recraft-3 in the benchmark. The authors use this ranking to demonstrate the model's superior performance in image generation and editing tasks, particularly in maintaining consistency and quality across diverse inputs.
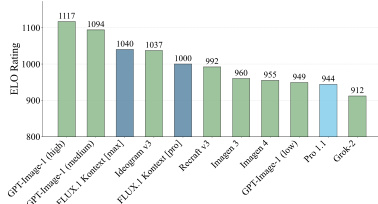
Results show that FLUX.1 Kontext [pro] achieves the highest ELO rating among the evaluated models, outperforming competitors such as Recraft v3 and ImageGen 3 in the benchmark. The model demonstrates strong performance across editing tasks, with the highest scores in text editing and character preservation, as reflected in the evaluation results.

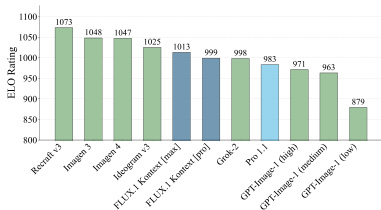
Results show that FLUX.1 Kontext [pro] achieves the highest ELO rating among the evaluated models, outperforming competitors such as Recraft 3, Imagen 3, and GPT-Image-1 (medium) in the benchmark. The model demonstrates strong performance in text editing and character preservation, consistent with its design for unified image generation and editing tasks.
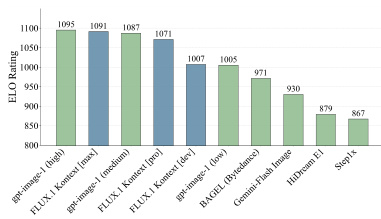
Results show that FLUX.1 Kontext [max] achieves the highest ELO rating among all evaluated models, outperforming competitors such as gpt-image-1 and Gen-4 in the benchmark. The model demonstrates superior performance in image-to-image tasks, particularly in text editing and character reference, as reflected in its top ranking across multiple evaluation categories.
Results show that FLUX.1 Kontext [max] achieves the highest ELO rating of 1080 in the image-to-image evaluation, outperforming other models including Recraft v3 and GPT-Image-1 (tigh). The authors use KontextBench to evaluate performance across multiple editing tasks, with FLUX.1 Kontext [pro] consistently ranking among the top performers, particularly excelling in text editing and character preservation.