Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
العامة من أقل إلى أكثر: فتح المزيد من التحكّم من خلال التوليد في السياق
العامة من أقل إلى أكثر: فتح المزيد من التحكّم من خلال التوليد في السياق
Shaojin Wu Mengqi Huang Wenxu Wu Yufeng Cheng Fei Ding Qian He
الملخص
رغم الاستكشاف الواسع لطريقة التوليد المُوجهة بالمواضيع في توليد الصور بفضل تطبيقاتها المتنوعة، تظل تواجه تحديات في قابلية التوسع من حيث البيانات وامتداد الموضوعات. أما التحدي الأول، فيكمن في صعوبة الانتقال من تجميع مجموعات بيانات ذات موضوع واحد إلى مجموعات متعددة المواضيع، وتوسيعها على نطاق واسع. أما التحدي الثاني، فيكمن في أن معظم الطرق الحديثة تركز على توليد صور ذات موضوع واحد، مما يجعل تطبيقها صعبًا في السيناريوهات التي تتضمن أكثر من موضوع. في هذه الدراسة، نقترح نموذجًا مُتسلسلًا لتصنيع البيانات يتميز بالاتساق العالي لمعالجة هذا التحدي. يعتمد هذا النموذج على القدرات الطبيعية للتوليد داخل السياق التي تمتلكها نماذج التحويلات التبادلية (diffusion transformers)، ويُنتج بيانات مزدوجة ذات اتساق عالٍ في السياقات متعددة المواضيع. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، نقدّم نموذج UNO، الذي يتكون من تطابق متعدد الوسائط تدريجي وتمديد موضع دوراني عام. وهو نموذج متعدد الصور مُوجّه بالمواضيع، يتم تدريبه بشكل تكراري من نموذج نص إلى صورة. أظهرت التجارب الواسعة أن طريقةنا تحقق اتساقًا عاليًا مع الحفاظ على التحكم الفعّال في كل من التوليد الموجه بموضوع واحد والمتعدد المواضيع.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from ByteDance propose UNO, a multi-image conditioned subject-to-image model with progressive cross-modal alignment and universal rotary position embedding, enabling high-consistency, controllable generation across single and multi-subject scenarios by leveraging a diffusion transformer-based data synthesis pipeline that overcomes scalability and expansibility limitations of prior methods.
Key Contributions
- Existing subject-driven image generation methods face significant limitations in data scalability and subject expansibility, as real-world datasets struggle to capture diverse subject variations, and most models are restricted to single-subject scenarios.
- The authors introduce UNO, a multi-image conditioned subject-to-image model built through iterative training from a text-to-image foundation, enhanced with progressive cross-modal alignment and universal rotary position embedding to mitigate attribute confusion in multi-subject control.
- A novel data synthesis pipeline leverages in-context generation in diffusion transformers to produce high-resolution, high-consistency multi-subject paired data, enabling the model to achieve state-of-the-art performance on DreamBench and multi-subject benchmarks in both subject fidelity and text controllability.
Introduction
The authors address the challenge of scalable, controllable image generation where models must faithfully reproduce specific visual subjects while adhering to diverse text prompts. This is critical for real-world applications like film production and design, where both subject consistency and prompt fidelity are essential. Prior methods face a fundamental data bottleneck: real-world paired datasets are scarce, especially for multi-subject scenarios, while synthetic data often suffer from low resolution, poor quality, or limited domain coverage. Existing models are typically trained on fixed, limited data, leading to trade-offs between subject similarity and text controllability, and poor scalability to new subjects.
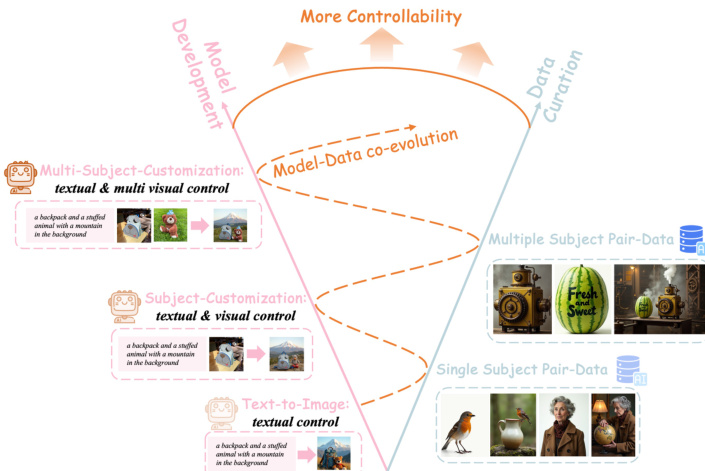
To overcome this, the authors propose a model-data co-evolution paradigm where less-capable models generate increasingly high-quality synthetic data for training more advanced models. This enables continuous improvement in both data richness and model controllability. Technically, they introduce UNO, a multi-image conditioned subject-to-image model built on diffusion transformers, trained iteratively from a text-to-image base model. UNO features progressive cross-modal alignment and a universal rotary position embedding (UnoPE) to mitigate attribute confusion when scaling subject control. A key innovation is a systematic synthetic data pipeline that uses in-context generation to produce high-resolution, high-consistency multi-subject paired data through multi-stage filtering.
The main contribution is a scalable, self-improving framework that breaks the data bottleneck by enabling less-to-more generalization. UNO achieves state-of-the-art performance on both single- and multi-subject generation benchmarks, demonstrating strong subject fidelity and text controllability without sacrificing scalability.
Dataset
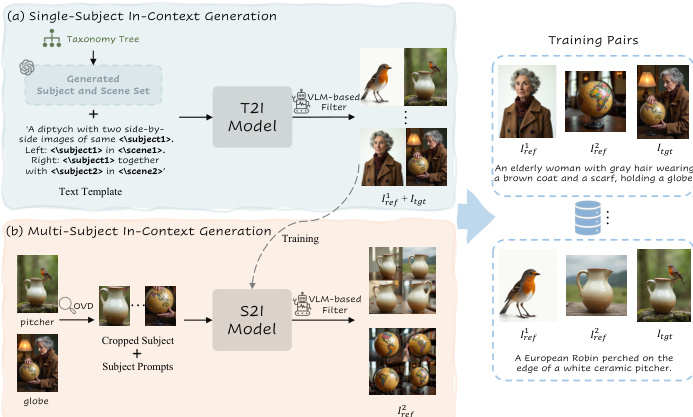
- The dataset is synthesized using a multi-stage pipeline that generates high-resolution, subject-consistent image pairs, addressing the scarcity of high-quality, diverse data for subject-driven image generation.
- It is composed of two main subsets: single-subject in-context data and multi-subject in-context data, both generated via a DiT-based text-to-image (T2I) model.
- The single-subject data is derived from a taxonomy tree built on 365 base classes from Object365, expanded using a Large Language Model (LLM) to generate diverse subject instances (e.g., by age, profession, attire) and scene descriptions, resulting in millions of text prompts for T2I generation.
- Generated image pairs are processed through a two-step filtering pipeline: first, DINOv2 similarity between reference and target images filters out low-consistency pairs; second, a Vision-Language Model (VLM) evaluates appearance, details, and attributes, producing a final consistency score used to retain high-quality samples.
- The multi-subject data is generated by first training a subject-to-image (S2I) model on the single-subject data, then using it to generate new reference images for additional subjects. An open-vocabulary detector (OVD) identifies extra subjects in the target image, but instead of using cropped versions directly, the S2I model generates new, contextually consistent reference images to avoid copy-paste artifacts.
- Final multi-subject data includes triplets of images: Iref1, Iref2, and Itgt, where both reference images are subject-consistent and the target image contains multiple subjects in a coherent scene.
- The dataset supports three high-resolution formats: 1024×1024, 1024×768, and 768×1024, enabling diverse training scenarios.
- The model training uses a progressive framework: Stage I fine-tunes a pretrained T2I model on single-subject data to create an S2I model, and Stage II continues training on multi-subject data to enhance multi-subject consistency.
- A universal rotary position embedding (UnoPE) is introduced to reduce attribute confusion during subject control scaling.
- The final dataset is used in a mixture of training splits, with varying proportions of single- and multi-subject data, and the VLM-based filtering ensures only high-quality pairs are retained, directly improving downstream performance on metrics like DINO and CLIP-I scores.
Method
The authors leverage a diffusion transformer (DiT) architecture as the foundation for their model-data co-evolution paradigm, which is designed to enable subject-to-image (S2I) generation with enhanced controllability. The core framework begins with a text-to-image (T2I) DiT model, which operates on latent patches using full transformer layers, diverging from traditional U-Net backbones. This model incorporates multi-modal attention, where position-encoded tokens from both text and image inputs are projected into query, key, and value representations, allowing cross-modal interaction within a unified space. The input to the DiT model is formed by concatenating the encoded text token c with the noisy latent zt=E(Itgt), where E(⋅) is the VAE encoder.
To adapt this T2I model for S2I generation, the authors introduce a two-stage iterative training framework, referred to as UNO, which progressively aligns the model's cross-modal capabilities. The training process begins with single-image conditions, where the model is trained to generate images conditioned on a single reference image Iref1 and a text prompt. The input for this stage, denoted as z1, is constructed by concatenating the text token c, the noisy latent zt, and the encoded reference image token E(Iref1). This initial phase establishes a baseline for subject-consistent generation. Following this, the model undergoes a second stage of training with multiple reference images Iref=[Iref1,Iref2,…,IrefN], where the input z2 is formed by concatenating the text token, the noisy latent, and the encoded tokens of all reference images. This progression from single to multi-image conditions allows the model to learn more complex contextual relationships.
A critical component of the UNO framework is the Universal Rotary Position Embedding (UnoPE), which addresses the challenge of integrating multiple reference images into the DiT's position encoding scheme. The original DiT architecture assigns position indices (i,j) to image tokens based on their spatial location in the latent grid, while text tokens are assigned a fixed index of (0,0). To maintain the implicit position correspondence of the original model when introducing reference image tokens, UnoPE reuses this format but assigns position indices starting from the maximum height and width of the noisy image tokens. For a reference image zrefN, the adjusted position index is defined as (i′,j′)=(i+w(N−1),j+h(N−1)), where w(N−1) and h(N−1) are the width and height of the previous reference image's latent. This ensures that the reference images are placed in a distinct, non-overlapping region of the position space, preventing the model from over-relying on the spatial structure of the reference images and instead focusing on the semantic information derived from the text prompt.
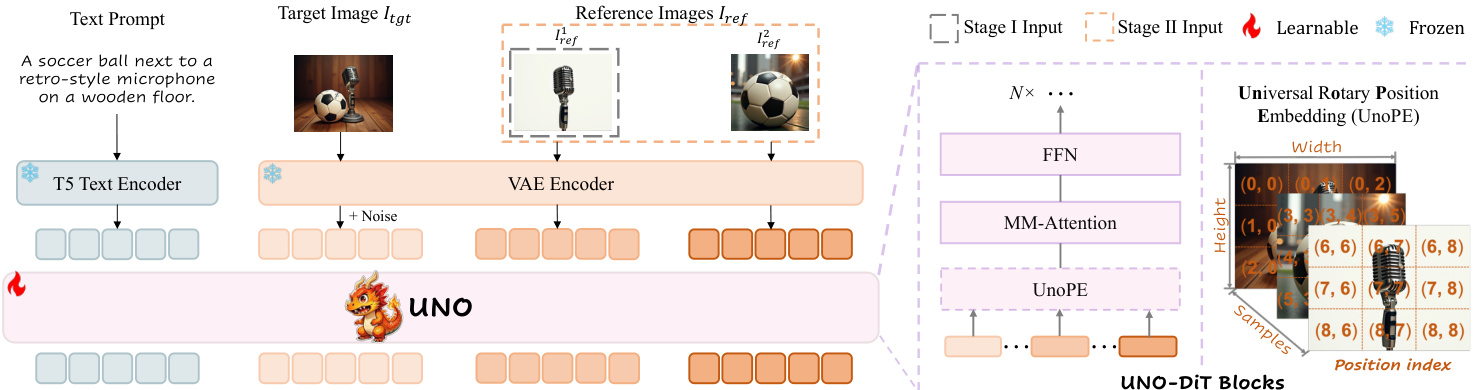
The UNO-DiT blocks, which constitute the core of the model, are structured to process these multi-modal inputs. The architecture includes a Feed-Forward Network (FFN) and a multi-modal attention (MM-Attention) layer, with the UnoPE module providing the necessary position embeddings for the reference image tokens. The model is trained in an iterative manner, where the initial training on single-image data establishes the subject-to-image capabilities, and the subsequent training on multi-image data enables the model to handle more complex, multi-subject generation tasks. This progressive training strategy, combined with the novel UnoPE, allows the model to unlock the in-context generation capabilities of the base T2I model, resulting in a highly controllable and subject-consistent S2I generation system.
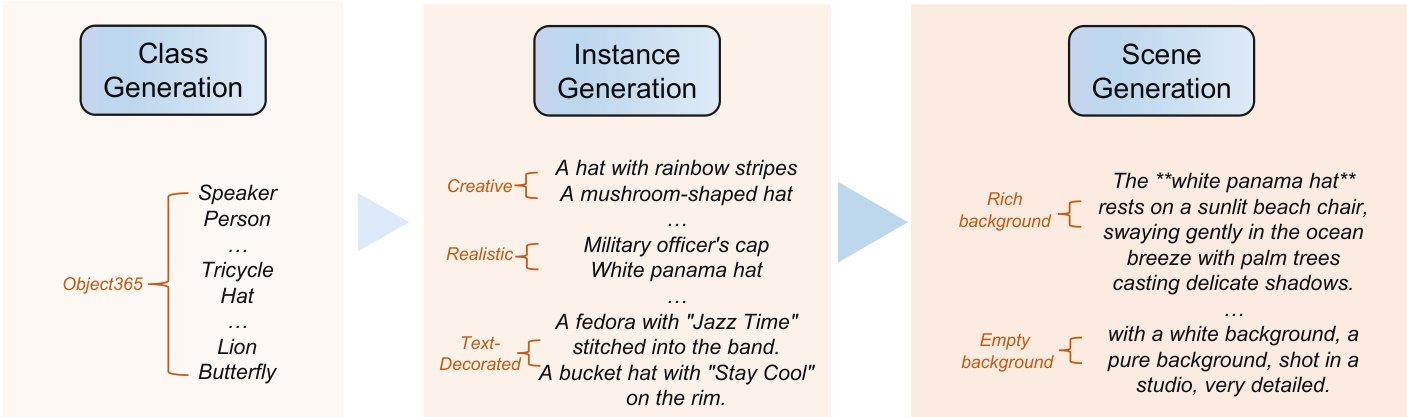
The synthetic data used for training is generated through a sophisticated in-context data curation framework. This pipeline begins with a taxonomy tree to create diverse subject instances and scenes. A diptych text template is then used to guide a state-of-the-art T2I model, such as FLUX.1, to generate subject-consistent image-pair data. The generated data is filtered for quality and consistency using a combination of DINOv2 for feature-based similarity and a Vision-Language Model (VLM) with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning to provide a fine-grained evaluation of subject consistency. This curated data, which includes both single-subject and multi-subject pairs, is then used to train the UNO model, forming a closed-loop system where the model and data evolve together.
Experiment
- Conducted single-subject and multi-subject driven image generation experiments using UNO, a tuning-free method based on a DiT architecture, trained with LoRA (rank 512) on 8 A100 GPUs.
- Validated progressive cross-modal alignment: training first on single-subject data (5,000 steps) then multi-subject data (5,000 steps) significantly improves subject consistency and text fidelity.
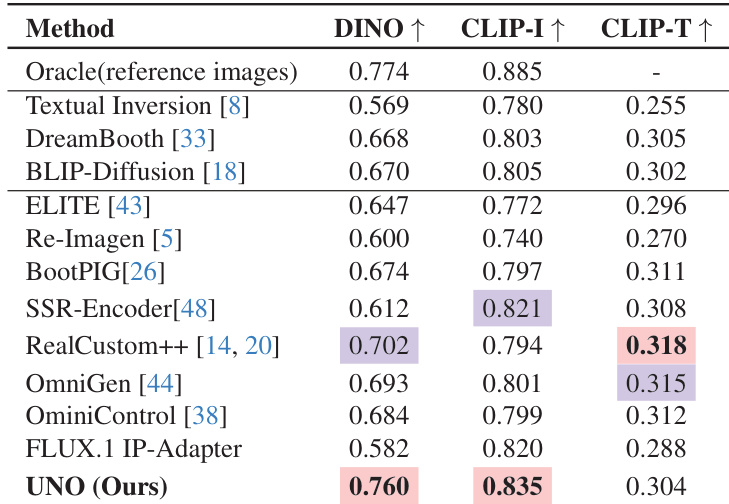
- On DreamBench, UNO achieved state-of-the-art results in zero-shot single-subject generation with CLIP-I score of 0.835 and DINO score of 0.760, surpassing existing tuning-free and tuning-based methods.
- In multi-subject generation, UNO achieved the highest DINO and CLIP-I scores, with competitive CLIP-T scores, demonstrating strong subject consistency and adherence to text edits.
- User study (n=30) confirmed UNO outperforms baselines across five dimensions: subject similarity, text fidelity (subject and background), composition quality, and visual appeal.
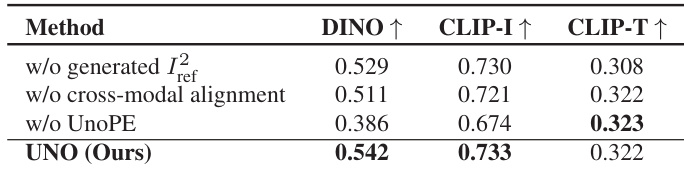
- Ablation studies show that in-context data generation, progressive cross-modal alignment, and the proposed UnoPE position encoding are critical for performance; removing any component leads to significant drops in subject similarity and text alignment.
- LoRA rank analysis indicates performance plateaus beyond rank 128, with rank 512 selected for optimal balance of performance and efficiency.
- Demonstrated strong generalization in diverse applications including virtual try-on, identity preservation, logo design, and stylized generation, despite limited training data in these domains.
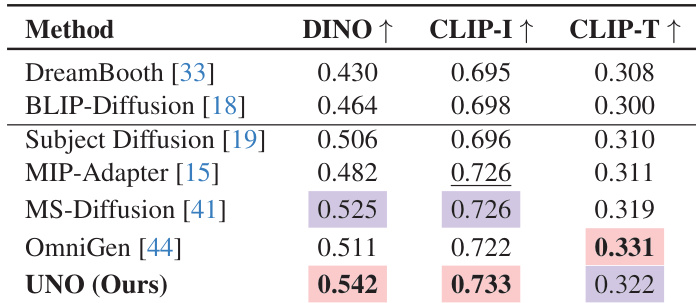
Results show that UNO achieves the highest DINO and CLIP-I scores among all compared methods, with values of 0.542 and 0.733 respectively, indicating superior subject similarity. It also attains a competitive CLIP-T score of 0.322, demonstrating strong text fidelity in single-subject driven generation.
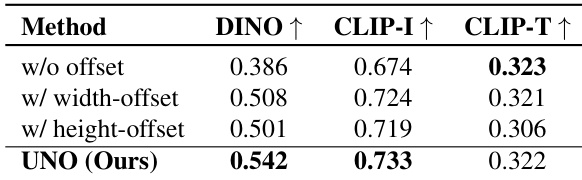
The authors evaluate the impact of different position index offset methods on model performance, with results showing that the proposed UNO method achieves the highest DINO and CLIP-I scores, indicating improved subject similarity, while maintaining competitive CLIP-T scores for text fidelity. The inclusion of height-offset and width-offset components leads to incremental improvements, with UNO outperforming both individual offset variants and the baseline without any offset.
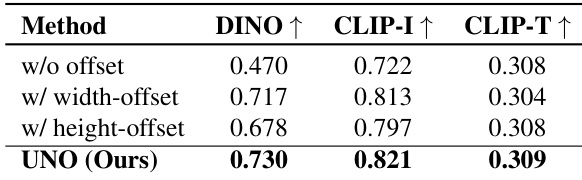
Results show that the proposed UnoPE method, which incorporates height-offset, achieves the highest DINO and CLIP-I scores of 0.730 and 0.821 respectively, outperforming variants without offset or with width-offset. The model also maintains a competitive CLIP-T score of 0.309, indicating strong text fidelity while improving subject similarity.
The authors use Table 4 to evaluate the effect of progressive cross-modal alignment on model performance. Results show that removing cross-modal alignment leads to a significant drop in DINO and CLIP-I scores, indicating reduced subject similarity, while CLIP-T scores remain relatively stable. The model with progressive alignment achieves the highest DINO and CLIP-I scores, demonstrating its effectiveness in improving subject consistency.
Results show that UNO achieves the highest DINO and CLIP-I scores of 0.760 and 0.835 respectively, outperforming all compared tuning-based and tuning-free methods in single-subject driven generation. The model also attains a competitive CLIP-T score of 0.304, demonstrating strong text fidelity alongside superior subject similarity.