Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
FlowベースのGRPOにおけるステップワイズおよび長期的サンプリング効果のモデリングによるスパース報酬の軽減
FlowベースのGRPOにおけるステップワイズおよび長期的サンプリング効果のモデリングによるスパース報酬の軽減
概要
テキストから画像生成に向けたフロー・マッチングモデルにGRPOを適用することは、有効であることが実証されている。しかし、従来のアプローチでは、各ノイズ除去ステップに対して、結果に基づく報酬を一様に伝播させているが、各ステップの局所的な影響を区別しておらず、ステップ間の相関関係を十分に捉えていない。さらに、現在のグループワイズなランク付け手法は、同一タイムステップでの軌道間比較に主眼を置き、軌道内での依存関係、すなわち特定の初期ノイズ除去行動が遅延した非明示的相互作用を通じて、後の状態に影響を与える可能性を無視している。本研究では、ステップごとの報酬スパース性を軽減し、ノイズ除去軌道内の長期的影響を明示的にモデル化するGRPOフレームワーク「TurningPoint-GRPO(TP-GRPO)」を提案する。TP-GRPOは以下の2つの鍵となる革新を実現している:(i)結果に基づく報酬をステップレベルの増分報酬に置き換え、各ノイズ除去行動の「純粋な」影響をより明確に分離できる高密度でステップに依存する学習信号を提供する;(ii)局所的な報酬トレンドを逆転させる「転換点(turning points)」——すなわち、その後の報酬の進化が全体的な軌道トレンドと一致するようなステップ——を特定し、これらの行動に集約された長期的報酬を付与することで、遅延した影響を捉える。転換点は増分報酬の符号変化のみに基づいて検出されるため、TP-GRPOは効率的かつハイパーパラメータを必要としない。広範な実験により、TP-GRPOが報酬信号をより効果的に活用し、生成品質を一貫して向上させることを示した。デモコードは以下のURLで公開されている:https://github.com/YunzeTong/TurningPoint-GRPO。
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from institutions including Tsinghua and Alibaba propose TP-GRPO, a GRPO variant that replaces sparse outcome rewards with dense step-level signals and identifies turning points to capture delayed effects, improving text-to-image generation by better modeling denoising trajectory dynamics without hyperparameters.
Key Contributions
- TP-GRPO replaces sparse outcome-based rewards with step-level incremental rewards to isolate the pure effect of each denoising action, reducing reward sparsity and improving credit assignment during RL fine-tuning of Flow Matching models.
- It introduces turning points—steps identified by sign changes in incremental rewards—that flip local reward trends and are assigned aggregated long-term rewards to explicitly model delayed, within-trajectory dependencies critical for coherent image generation.
- Evaluated on standard text-to-image benchmarks, TP-GRPO consistently outperforms prior GRPO methods like Flow-GRPO and DanceGRPO by better exploiting reward signals, with no added hyperparameters and efficient implementation.
Introduction
The authors leverage flow-based generative models and reinforcement learning to address sparse, misaligned rewards in text-to-image generation. Prior methods like Flow-GRPO assign the final image reward uniformly across all denoising steps, ignoring step-specific contributions and within-trajectory dynamics — leading to reward sparsity and local-global misalignment. To fix this, they introduce TurningPoint-GRPO, which computes step-wise rewards via incremental reward differences and explicitly models long-term effects of critical “turning point” steps that reverse local reward trends, enabling more accurate credit assignment without extra hyperparameters.
Method
The authors leverage a modified GRPO framework, TurningPoint-GRPO (TP-GRPO), to address reward sparsity and misalignment in flow matching-based text-to-image generation. The core innovation lies in replacing outcome-based rewards with step-level incremental rewards and explicitly modeling long-term effects via turning points—steps that flip the local reward trend to align with the global trajectory trend. This design enables more precise credit assignment across the denoising trajectory.
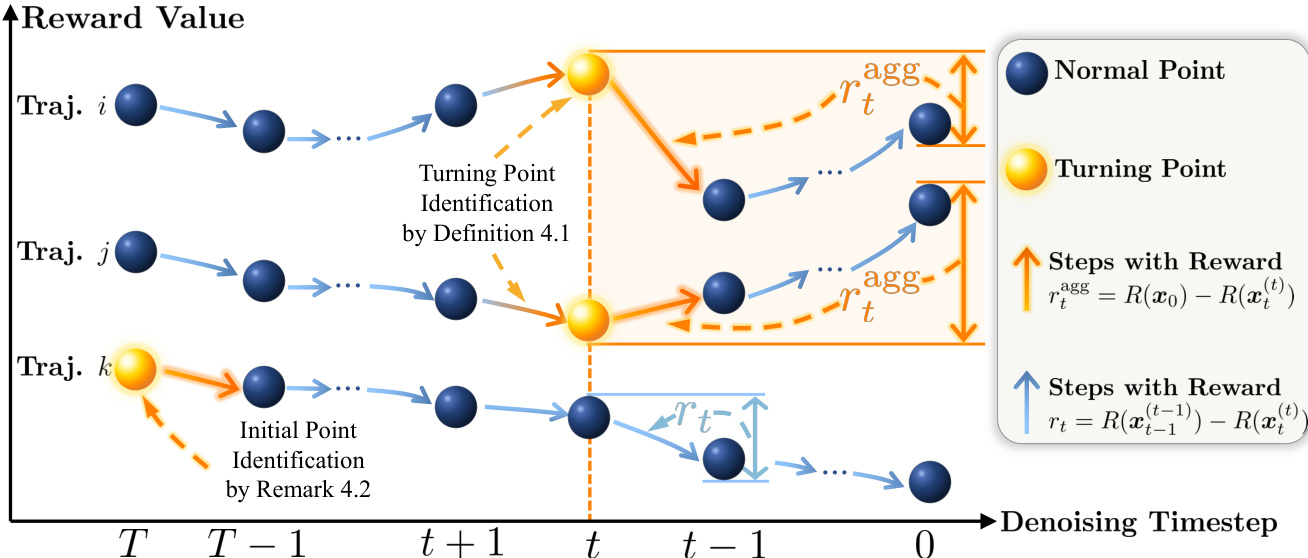
The method begins by sampling diverse trajectories using an SDE-based sampler, which injects stochasticity into the reverse-time denoising process. For each trajectory, intermediate latents are cached, and ODE sampling is applied from each latent to completion to obtain corresponding clean images. This allows the reward model to evaluate the cumulative effect of all preceding SDE steps. The step-wise reward rt for the transition from xt to xt−1 is then computed as the difference in reward between the ODE-completed images: rt=R(xt−1ODE(t−1))−R(xtODE(t)). This incremental reward isolates the “pure” effect of each denoising action, providing a dense, step-aware signal that avoids the sparsity inherent in propagating a single terminal reward.
Turning points are identified based on sign changes in these incremental rewards. A timestep t qualifies as a turning point if the local reward trend flips to become consistent with the overall trajectory trend. Specifically, the authors define a turning point using the sign consistency between the local step gain and the cumulative gain from that step to the end. As shown in the figure below, turning points are visually characterized by a local reversal in reward direction that aligns with the global trajectory trend, distinguishing them from normal points that either do not flip or misalign with the global direction.
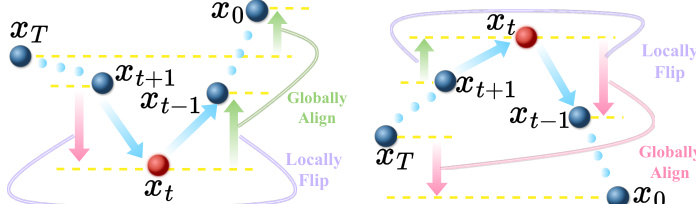
At identified turning points, the local step reward rt is replaced with an aggregated reward rtagg=R(x0)−R(xtODE(t)), which captures the cumulative effect from the turning point to the final image. This aggregated reward encodes the delayed, implicit impact of the denoising action on subsequent steps. The authors further refine this by introducing a stricter criterion—consistent turning points—that requires the aggregated reward to have a larger absolute value than the local reward, ensuring that only steps with significant long-term influence are selected.
To address the exclusion of the initial denoising step from turning point detection, the authors extend the framework via Remark 5.2. The first step is eligible for aggregated reward assignment if its local reward change aligns with the overall trajectory trend. This ensures that early, influential decisions are also modeled for their long-term impact.
The overall training process follows a group-wise ranking scheme. For each timestep, rewards (either rt or rtagg) are normalized across a group of trajectories to compute advantages. The policy is then optimized using a clipped objective that includes a KL regularization term to prevent excessive deviation from the reference policy. A balancing strategy is employed to maintain a roughly equal number of positive and negative aggregated rewards in each batch, preventing optimization bias.
Refer to the framework diagram for a visual summary of the method. The diagram illustrates how step-wise rewards are computed, turning points are identified, and aggregated rewards are assigned to capture long-term effects. It also highlights the inclusion of the initial step via Remark 5.2, ensuring comprehensive modeling of implicit interactions across the entire denoising trajectory.
Experiment
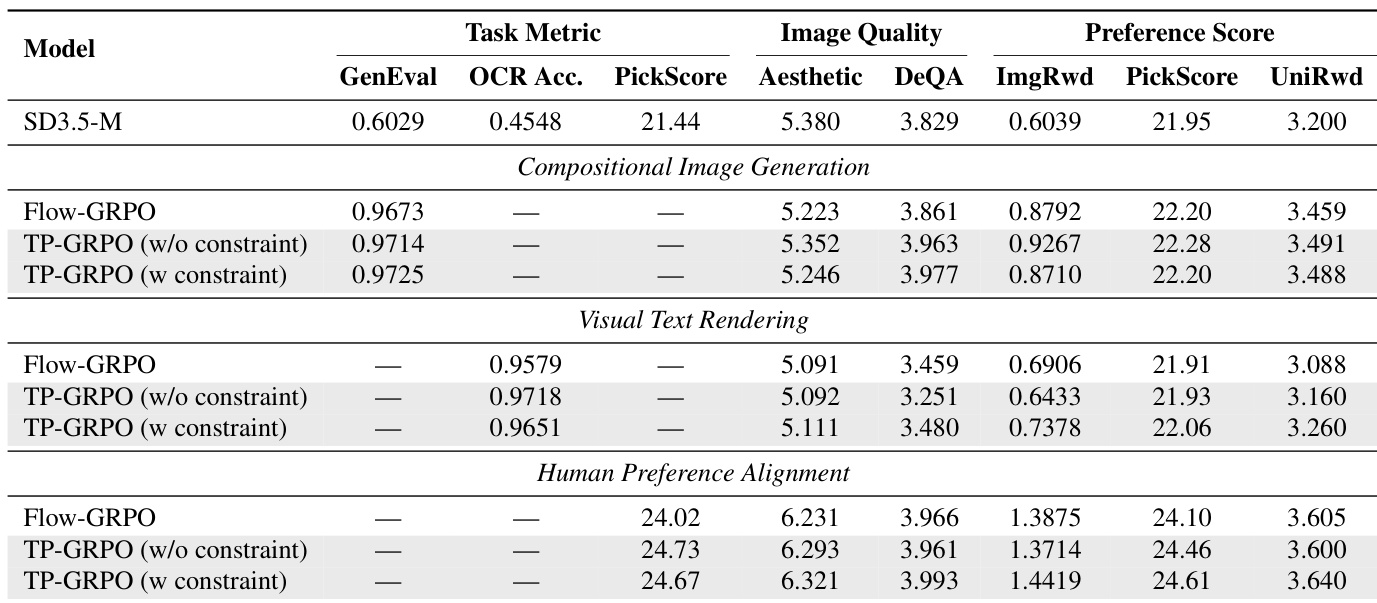
- TP-GRPO variants outperform Flow-GRPO across compositional image generation, visual text rendering, and human preference alignment, with improved accuracy, aesthetics, and content alignment without reward hacking.
- Training without KL penalty confirms TP-GRPO’s stronger exploratory capability and faster convergence, especially on non-rule-based rewards like PickScore.
- Reducing SDE sampling window size moderately (e.g., to 8 steps) improves efficiency and performance, but overly aggressive reduction harms turning-point capture.
- Noise scale α around 0.7 yields optimal stability; both lower and higher values degrade performance, though TP-GRPO remains robust across settings.
- Method generalizes to FLUX.1-dev base model, maintaining superior performance over Flow-GRPO under adjusted hyperparameters.
- Qualitative results show TP-GRPO better handles sparse rule-based rewards, avoids text omissions/overlaps, and produces more semantically coherent and aesthetically aligned outputs.
The authors use TP-GRPO to refine diffusion model training by incorporating step-level rewards and turning-point detection, which consistently improves performance across compositional image generation, visual text rendering, and human preference alignment tasks. Results show that both variants of TP-GRPO outperform Flow-GRPO in task-specific metrics while maintaining or enhancing image quality and preference scores. The method also demonstrates faster convergence and robustness across different base models and hyperparameter settings.