Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
ループを閉じる:RPG-Encoderを用いたユニバーサルリポジトリ表現
ループを閉じる:RPG-Encoderを用いたユニバーサルリポジトリ表現
概要
現在のリポジトリエージェントは、既存の手法が意味的深さに欠ける孤立したAPIドキュメントや依存関係グラフに依存しているため、断片化的な表現に起因する推論のギャップに直面している。本研究では、リポジトリの理解(comprehension)と生成(generation)を、統一されたサイクル内における逆過程として捉える。すなわち、生成は意図を実装に展開するプロセスであり、理解は実装を再び意図に圧縮するプロセスである。この課題に対処するため、本研究では「RPG-Encoder」というフレームワークを提案する。このフレームワークは、静的な生成用ブループリントとしてのリポジトリ計画グラフ(Repository Planning Graph; RPG)を、統一的かつ高忠実度の表現へと一般化するものである。RPG-Encoderは以下の3つのメカニズムにより、推論ループを閉じる。(1) リフトされた意味特徴とコード依存関係を統合したRPGへ、生のコードをエンコードする;(2) グラフのトポロジーを段階的に進化させることで、リポジトリの規模に依存しないメンテナンスコストを実現し、オーバーヘッドを95.7%削減する;(3) 構造に配慮したナビゲーションを統一インターフェースとして提供する。 評価において、RPG-EncoderはSWE-bench Verifiedにおいて93.7%のAcc@5を達成し、最先端のリポジトリ理解性能を確立した。また、SWE-bench Live Liteにおいては、最良のベースラインを10%以上上回った。これらの結果は、複雑なコードベースにおける本手法の優れた細粒度の局所化精度を示している。さらに、RepoCraftにおいて98.5%の再構成カバレッジを達成し、RPGが元のコードベースを高忠実度で再現可能な能力を裏付け、意図と実装の間の閉ループを完全に実現したことを確認した。
One-sentence Summary
Microsoft Research Asia, UCSD, and Tsinghua University researchers propose RPG-Encoder, a unified framework that transforms the Repository Planning Graph into a bidirectional, high-fidelity representation bridging code comprehension and generation—achieving 93.7% Acc@5 on SWE-bench and 98.5% reconstruction coverage by fusing semantic intent with dependency topology while reducing maintenance costs by 95.7% via incremental updates.
Key Contributions
- We reframe repository reasoning as a bidirectional cycle between comprehension and generation, introducing the RPG as a unified representation that fuses semantic intent with structural dependencies to close the reasoning gap in existing fragmented methods.
- RPG-Encoder implements semantic lifting to encode code into RPG nodes and edges, and uses incremental diff-based updates to maintain the graph with 95.7% lower overhead, enabling scalable, drift-free evolution aligned with code changes.
- Evaluated on SWE-bench Verified (93.7% Acc@5) and RepoCraft (98.5% reconstruction coverage), RPG-Encoder outperforms baselines by over 10% in understanding and 24.3% in reconstruction, proving its high-fidelity, structure-aware utility for complex codebases.
Introduction
The authors leverage the Repository Planning Graph (RPG) — originally designed for code generation — to build RPG-Encoder, a unified representation that bridges repository comprehension and generation as inverse, bidirectional processes. Prior methods suffer from fragmented representations: API docs lack structural context, while dependency graphs miss semantic intent, forcing agents to infer connections or rationale manually — and both incur high maintenance costs due to drift or static updates. RPG-Encoder addresses this by encoding code into a semantically rich, topology-aware RPG; evolving it incrementally via commit diffs to cut maintenance overhead by 95.7%; and using it as a unified interface for structure-aware navigation. It achieves state-of-the-art results on SWE-bench tasks and 98.5% reconstruction coverage on RepoCraft, proving RPG’s fidelity and closing the loop between intent and implementation.
Dataset
- The authors use six real-world Python repositories selected for popularity and structural complexity to build the RepoCraft benchmark for evaluating automated repository reconstruction.
- They construct a documentation dataset by compiling source files in each repo’s docs/ directory using Sphinx, converting reStructuredText or Markdown into a unified textual format that captures class, function, and module definitions.
- The compiled documentation serves as ground-truth specification for baseline agents, mirroring the reference material human developers consult.
- Across the six repositories, the documentation spans 7,320 files and over 2.5 million tokens, forming a substantial context for testing long-context understanding.
- No training split, mixture ratios, or cropping strategies are described; the dataset is used as-is for evaluation, with metadata derived directly from compiled documentation nodes including function signatures and parameter descriptions.
Method
The authors leverage the RPG-Encoder to transform a raw codebase into a structured, semantically grounded Repository Planning Graph (RPG), which serves as a unified reasoning substrate for agentic code understanding. The architecture is organized into three core phases: Encoding, Evolution, and Operation, each addressing a distinct lifecycle stage of the codebase representation.
As shown in the figure below, the RPG-Encoder bridges the gap between verbose, implementation-heavy code and high-level functional intent by synthesizing a dual-view graph that integrates both semantic hierarchy and execution dependencies. This enables agents to reason about the repository not just as a collection of files, but as a coherent, navigable system.
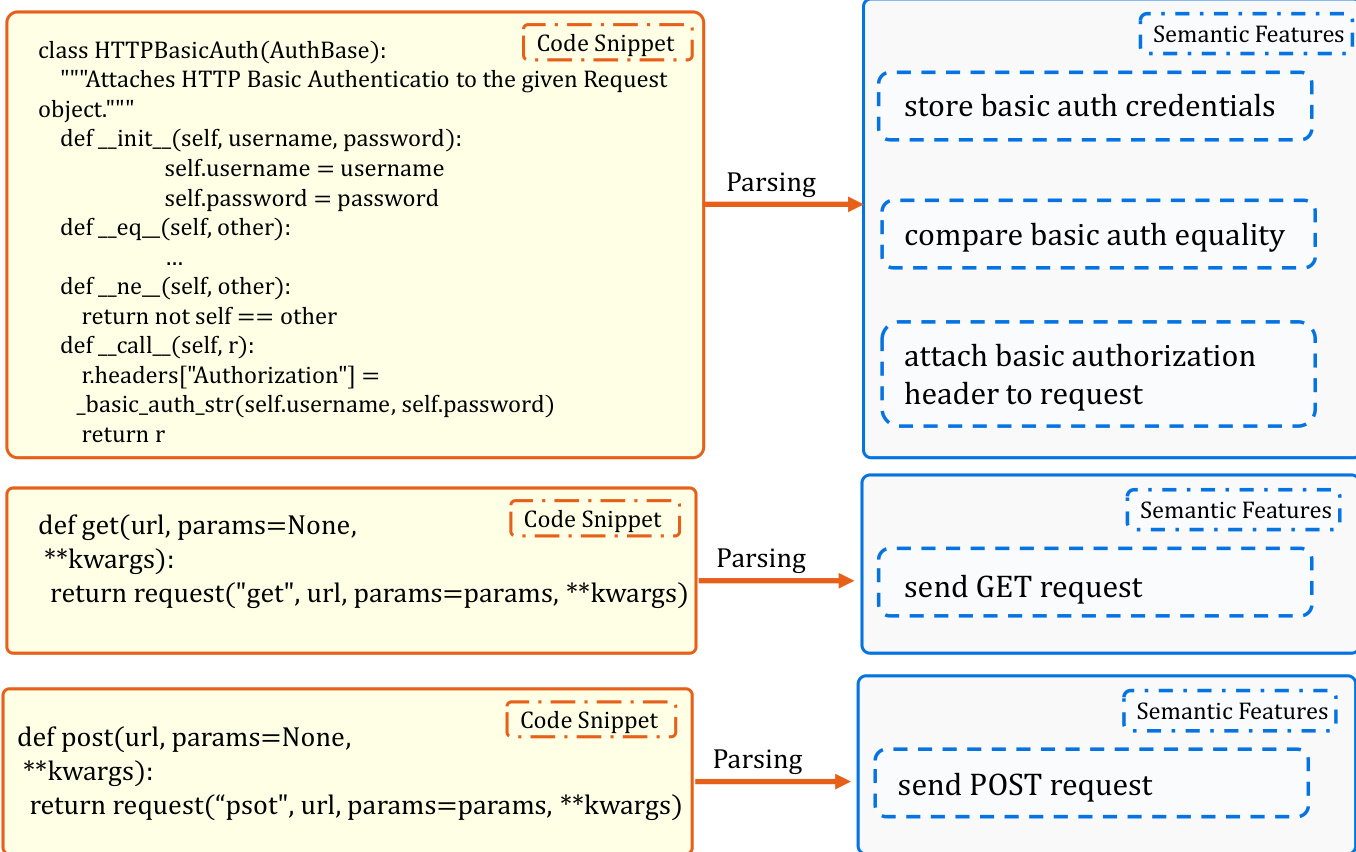
The Encoding phase begins with Semantic Lifting, where the system parses the entire codebase to extract atomic semantic features for each function and class. These features are expressed as concise, implementation-agnostic verb-object phrases (e.g., “store basic auth credentials”, “send GET request”) that capture behavioral intent rather than internal logic. This step is performed globally across the repository to ensure consistent granularity and avoid local biases. The extracted features are then aggregated into file-level summaries, establishing functional edges that link files to their constituent functions.
Next, Functional Abstraction reorganizes these low-level features into a hierarchical structure by identifying latent functional centroids (e.g., “DataProcessing”, “ModelTraining”) that serve as high-level nodes. This is achieved through LLM-guided clustering: the model analyzes the semantic features of all file-level nodes to induce abstract categories, then recursively assigns each node to the most semantically compatible parent. To ensure structural stability, intermediate nodes are inserted when direct parent-child relationships lack sufficient granularity.
Artifact Grounding anchors this abstract hierarchy to physical code artifacts. For each high-level node, the system computes its minimal directory scope by aggregating the paths of all descendant leaf nodes and applying a Trie-based branching analysis to extract meaningful, non-redundant directory LCAs. This ensures that abstract functional concepts (e.g., “DataPreprocessing”) are tied to concrete paths (e.g., “sklearn/preprocessing”). Finally, dependency edges are injected via AST analysis, mapping imports, calls, and inheritance relationships to complete the RPG.
The Evolution phase maintains the RPG incrementally in response to codebase changes. For each commit, the system parses the diff to identify affected entities and applies one of three atomic operations: Deletion, Modification, or Addition. Deletions trigger recursive pruning of empty parent nodes to preserve structural hygiene. Modifications are evaluated for semantic drift; if the functional intent shifts beyond a threshold, the node is re-routed to a new domain via deletion and reinsertion. Additions are inserted via top-down semantic routing, where the LLM selects the most appropriate parent node based on feature alignment, ensuring the hierarchy remains semantically coherent.
The Operation phase exposes the RPG as a unified reasoning substrate through three core tools. SearchNode enables intent-based discovery by matching behavioral phrases against semantic features or performing keyword-based snippet search. FetchNode retrieves precise source context and metadata for verified entities, ensuring agents reason on ground-truth code. ExploreRPG facilitates topological traversal along dependency or functional edges, allowing agents to uncover call chains, upstream dependencies, or semantically related modules. Together, these tools enable multi-dimensional navigation that integrates functional intent with physical implementation.
The RPG’s dual-view structure—partitioned by functional and dependency edges but sharing a unified node set—allows seamless context switching during retrieval. This design reduces information overload by serving as both a knowledge source (storing semantic features and metadata) and a process encoder (inducing topological order via edges), exposing the causality and hierarchy essential for architectural comprehension.
Experiment
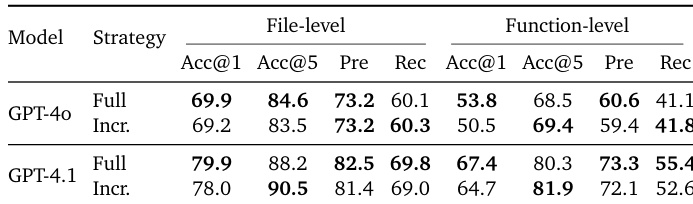
- RPG significantly improves repository understanding by enhancing file and function localization, outperforming baselines through combined semantic and topological guidance that filters noise while ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- RPG serves as a complete representational substrate for repository reconstruction, enabling near-lossless recovery of structure and functionality, with code volume and modularity closely matching human-written projects.
- Semantic features and topological dependencies are mutually reinforcing: removing either degrades performance, confirming that both are essential for accurate localization and structural fidelity.
- RPG enables efficient, cost-effective navigation by reducing redundant exploration and concentrating reasoning on relevant code, achieving higher accuracy per unit cost than baselines.
- Incremental RPG updates maintain high fidelity with minimal computational overhead, making long-term repository evolution sustainable without sacrificing performance.
- RPG induces structured agent behavior, promoting a “search-then-zoom” pattern that leverages topology for global context before drilling into implementation details, reducing search and scope-related failures.
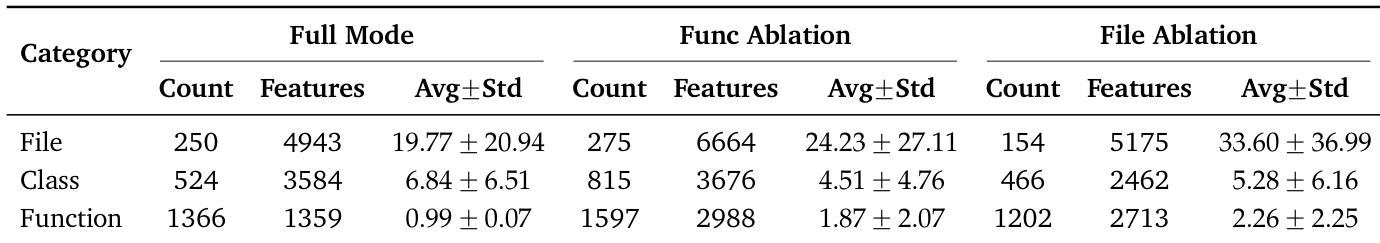
- Ablations confirm that hierarchical constraints are critical: removing file or function metadata leads to structural collapse, merging modules or losing granularity, underscoring RPG’s role in preserving architectural intent.
The authors use RPG to enhance repository understanding and reconstruction, demonstrating consistent gains in localization accuracy and structural fidelity across multiple benchmarks and models. Results show that integrating semantic features with topological constraints enables agents to precisely map high-level intent to implementation units while reducing redundant exploration. Ablation studies confirm that both semantic grounding and structural connectivity are mutually reinforcing, with their combined use yielding superior performance over text-based or partial graph baselines.
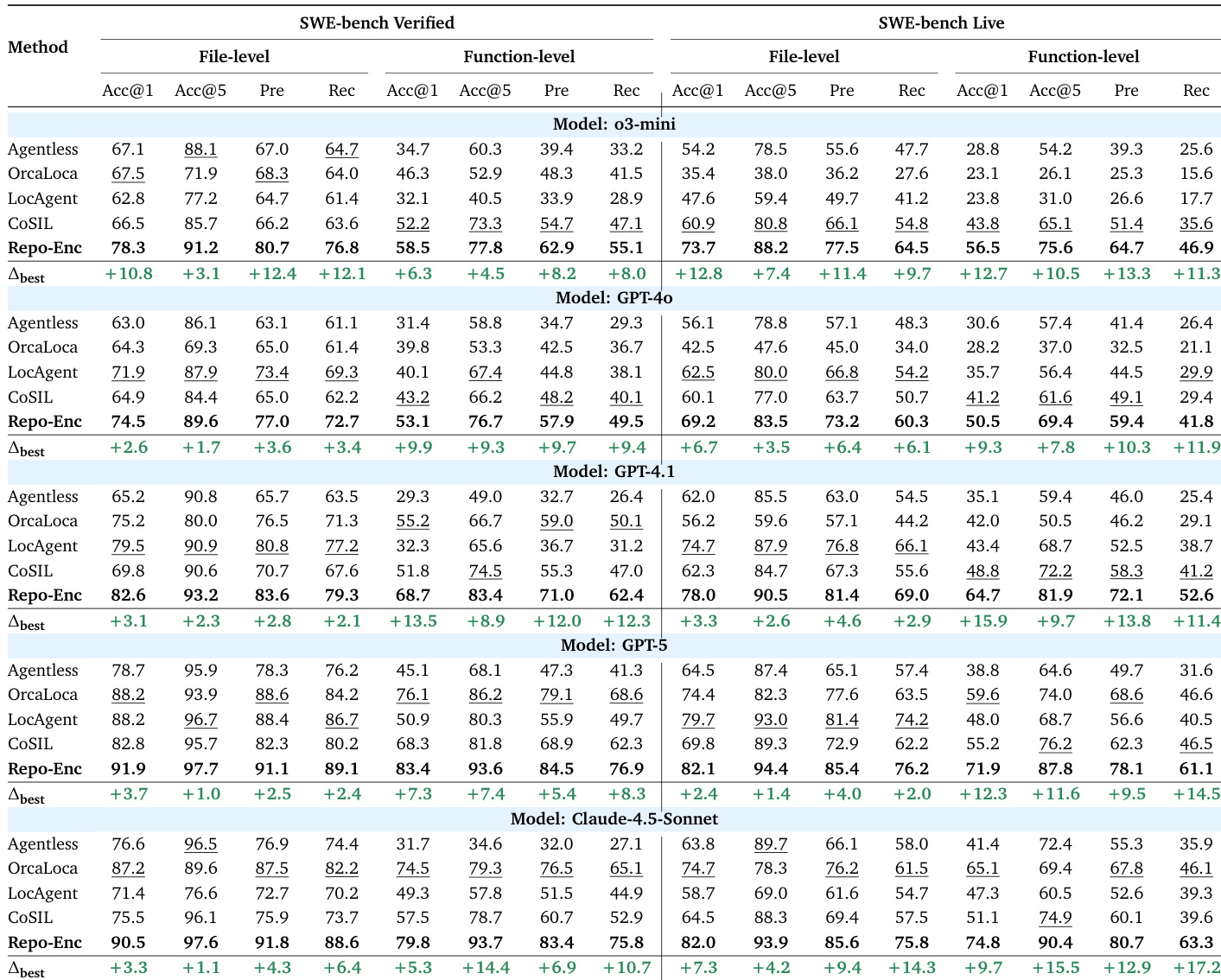
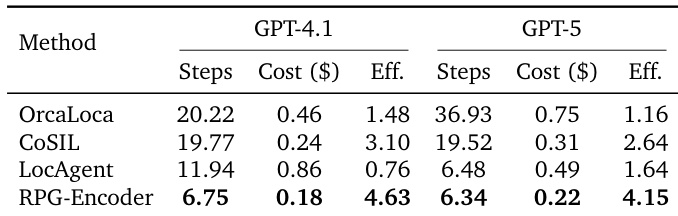
RPG-Encoder significantly improves cost efficiency in repository understanding tasks, achieving higher accuracy per dollar spent compared to all baselines across both GPT-4.1 and GPT-5. It reduces both the number of reasoning steps and monetary cost while maintaining superior performance, demonstrating that structured navigation enables more focused and economical exploration of codebases.
The authors use ablation experiments to isolate the impact of hierarchical structure on repository reconstruction, showing that removing file or function metadata leads to significant shifts in code organization. Without file-level boundaries, models consolidate features into fewer, denser files; without function metadata, they generate more classes and functions to compensate for lost procedural guidance. These findings confirm that explicit topological signals are essential for preserving modularity and structural fidelity during reconstruction.
The authors use RPG to enhance repository understanding by integrating semantic and topological signals, which improves both file-level and function-level localization accuracy across multiple models. Results show that RPG-guided agents consistently outperform baselines in precision and recall, particularly at the function level, where structural constraints help map high-level intent to specific code units. Ablation studies confirm that both semantic features and dependency graphs are critical, as removing either degrades performance and increases reasoning cost.
RPG-Encoder consistently achieves higher cost-effectiveness across multiple LLMs by reducing both the number of reasoning steps and monetary cost per task, demonstrating that structured navigation enables more efficient exploration than baseline methods. While some baselines like LocAgent show low cost on weaker models, RPG-Encoder maintains superior efficiency on stronger models such as GPT-4.1 and GPT-5, where it balances precision with minimal resource expenditure. This efficiency stems from RPG’s ability to guide agents toward relevant code regions early, minimizing redundant tool calls and context consumption.