Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
SnapGen++:エッジデバイスにおける効率的で高忠実度の画像生成のためのDiffusion Transformersの活用
SnapGen++:エッジデバイスにおける効率的で高忠実度の画像生成のためのDiffusion Transformersの活用
概要
拡散変換器(DiTs)の最近の進展により、画像生成の分野で新たな基準が確立されたが、計算量およびメモリ消費が非常に高いことから、端末内での実装は依然として現実的ではない。本研究では、モバイルおよびエッジデバイス向けに最適化された効率的なDiTフレームワークを提案する。本フレームワークは、厳格なリソース制約下でも変換器レベルの生成品質を実現する。我々の設計は、以下の3つの主要な要素を統合している。第一に、グローバルな文脈モデリングとローカルな詳細の保持のバランスを取る、適応型グローバル-ローカルスパースアテンション機構を備えたコンパクトなDiTアーキテクチャを提案する。第二に、統一されたスーパーネットワーク内において、異なる容量を持つサブDiTを共同最適化するエラスティックトレーニングフレームワークを提案する。これにより、単一のモデルがハードウェア環境に応じて動的に最適化され、効率的な推論が可能となる。第三に、少数ステップの教師モデルからの知識伝達を統合した、知識誘導型分布マッチング蒸留(Knowledge-Guided Distribution Matching Distillation)というステップ蒸留パイプラインを開発した。この手法は、高忠実度かつ低遅延な生成(例:4ステップ)を実現し、リアルタイムな端末内利用に適している。これらの貢献を統合することで、多様なハードウェア環境に展開可能なスケーラブルかつ効率的で高品質な拡散モデルの実現が可能となる。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Snap Inc., the University of Melbourne, and MBZUAI propose a compact Diffusion Transformer with adaptive sparse attention and elastic training, enabling real-time, high-fidelity text-to-image generation on mobile devices via K-DMD distillation, achieving 4-step inference in under 2 seconds while maintaining transformer-level quality across diverse hardware.
Key Contributions
-
The paper addresses the challenge of deploying high-quality diffusion transformers (DiTs) on mobile and edge devices, where existing models are too large and computationally expensive due to quadratic attention complexity and billion-scale parameters, limiting real-time on-device image generation.
-
It introduces a compact DiT with an adaptive global-local sparse attention mechanism that dynamically balances global context and local detail, combined with an elastic training framework enabling a single supernetwork to support multiple sub-DiTs for efficient inference across diverse hardware.
-
The proposed K-DMD (Knowledge-Guided Distribution Matching Distillation) framework distills knowledge from few-step teacher models into a student DiT, achieving high-fidelity 1024×1024 image generation in just 4 steps with 1.8 seconds latency on mobile devices, outperforming prior on-device U-Net-based systems.
Introduction
The authors leverage diffusion transformers (DiTs), which have achieved state-of-the-art performance in text-to-image generation, to address the growing demand for high-fidelity, on-device image synthesis. While large DiT models offer superior quality and flexibility, their quadratic attention complexity and massive parameter counts make them impractical for mobile and edge devices, which face strict compute, memory, and power constraints. Prior on-device systems rely on lightweight U-Net architectures that trade generative quality for efficiency, leaving a significant performance gap. To bridge this gap, the authors introduce SnapGen++, an efficient DiT architecture with a three-stage design featuring adaptive global-local sparse attention that reduces computational overhead at high resolutions. They further propose an Elastic Training Framework that enables a single supernetwork to dynamically deploy sub-DiTs optimized for diverse hardware, ensuring consistent performance across devices without retraining. Finally, they employ Knowledge-Guided Distribution Matching Distillation to transfer the capabilities of a full-step teacher to a compact student model, enabling high-fidelity generation in just 1.8 seconds on a mobile device.
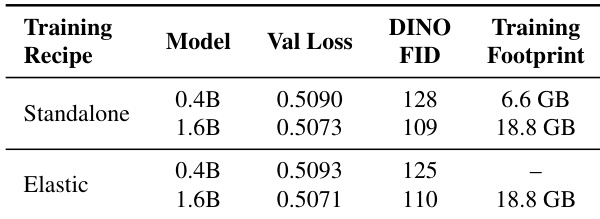
Method
The authors present a comprehensive framework for efficient diffusion transformer (DiT) deployment on edge devices, integrating a three-stage architecture, an elastic training paradigm, and a knowledge-guided distillation pipeline. The overall framework is structured around a three-stage DiT architecture, as illustrated in the framework diagram. This architecture consists of a sequence of downsample, middle, and upsample blocks, each composed of DiT layers with adaptive sparse self-attention (ASSA). The downsample and upsample blocks process the input at different resolutions, while the middle blocks operate at the base resolution. The DiT blocks themselves are composed of a series of attention and feed-forward network (FFN) modules, with the attention mechanism being the core component that enables efficient computation.
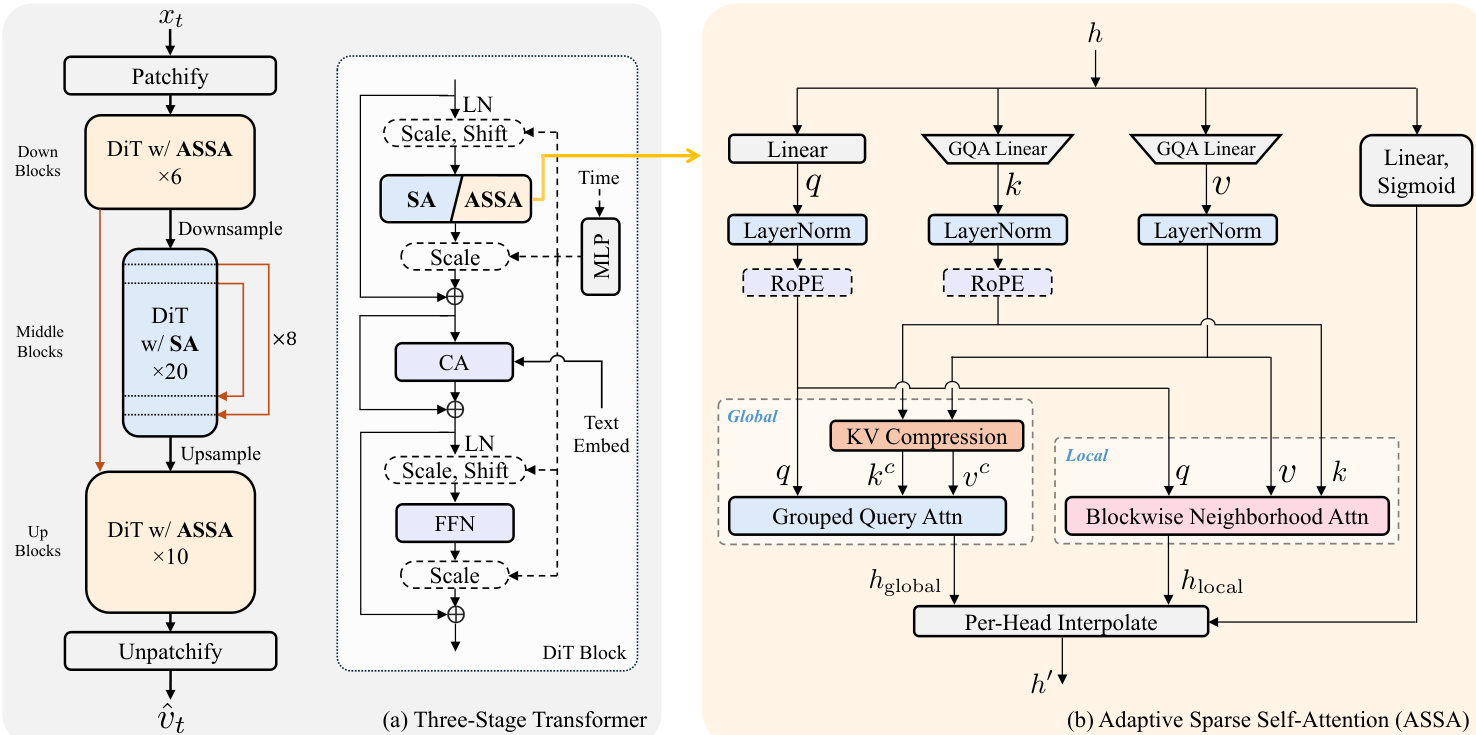
The attention mechanism within the DiT block is designed to balance global context modeling and local detail preservation through an adaptive sparse self-attention (ASSA) module. This module combines global and local attention pathways. The global pathway uses grouped query attention (GQA) to efficiently model long-range dependencies, while the local pathway employs blockwise neighborhood attention (BNA) to capture fine-grained spatial details. The BNA mechanism divides the input feature map into non-overlapping blocks and computes attention only within each block and its immediate neighbors, significantly reducing the computational complexity compared to full self-attention. The attention outputs from both pathways are then combined through a per-head interpolation mechanism, which adaptively fuses the global and local representations based on the input features.
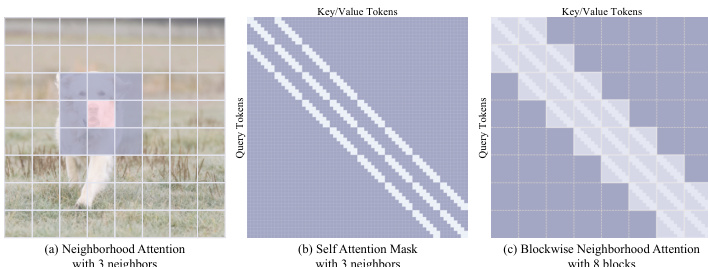
To enable deployment across diverse hardware, the authors introduce an elastic training framework. This framework is designed to jointly optimize subnetworks of varying capacities within a single supernetwork. The supernetwork is constructed by parameterizing the model with a full width, and subnetworks of smaller widths are derived by slicing the projection matrices in the attention and feed-forward network (FFN) layers along the hidden dimension. This parameter sharing allows for efficient inference across different hardware platforms, from low-end Android devices to high-end smartphones, without the need for separate model training. The training process involves sampling subnetworks of different widths in each iteration and optimizing them under a unified flow-matching objective. To ensure stable convergence, a lightweight distillation loss is applied between each subnetwork and the full-capacity supernetwork, which helps to transfer knowledge and stabilize the gradient updates.
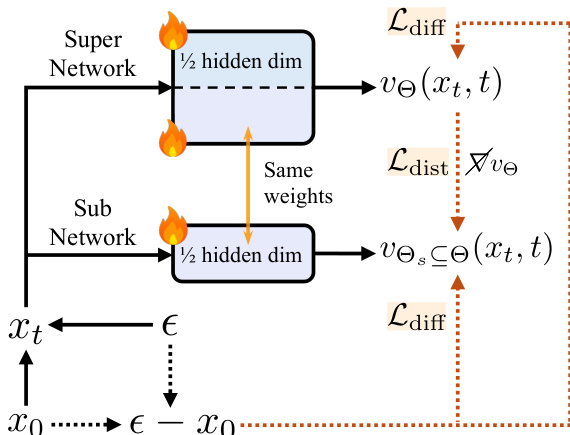
Finally, the authors develop a knowledge-guided distribution matching distillation (K-DMD) pipeline to achieve high-fidelity image synthesis with reduced inference latency. This pipeline combines the distribution matching distillation (DMD) objective with knowledge transfer from few-step teacher models. The DMD objective computes the KL divergence between the real score from the teacher and the student output distribution estimated by a critic model. To further leverage the power of the large-scale few-step teacher, the authors incorporate output-level and feature-level distillation losses into the training objective. This enables stable convergence across models of varying capacities without requiring additional hyperparameter tuning. The critic model is updated alternatively with the flow-matching loss on the student's distribution, ensuring that the student learns to generate high-quality outputs that are consistent with the teacher's behavior.
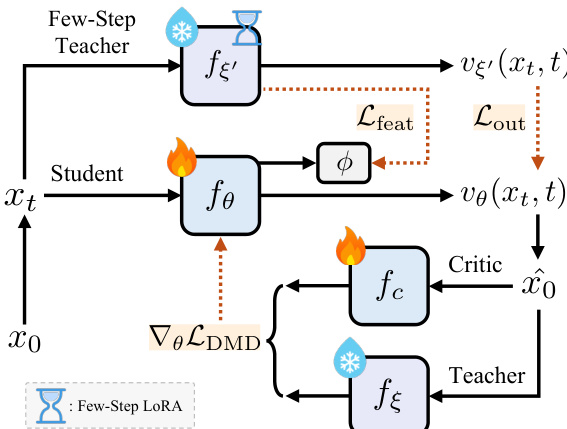
Experiment
- Ablation studies validate the effectiveness of the three-stage DiT architecture with Adaptive Sparse Self-Attention (ASSA), reducing inference latency from 2000 ms to 293 ms while maintaining validation loss at 0.513 on ImageNet-1K at 256×256 resolution.
- The full Efficient DiT achieves a validation loss of 0.509 on ImageNet-1K, surpassing SnapGen (0.5131) with comparable latency and improved visual quality.
- On-device evaluation shows the small (0.4B) and full (1.6B) variants achieve 360 ms and 1.8 s generation times on iPhone 16 Pro Max, respectively, with high-quality 1024×1024 outputs.
- Quantitative benchmarks (DPG-Bench, GenEval, T2I-CompBench) show the 0.4B model outperforms models up to 20× larger, while the 0.3B variant achieves the highest throughput.
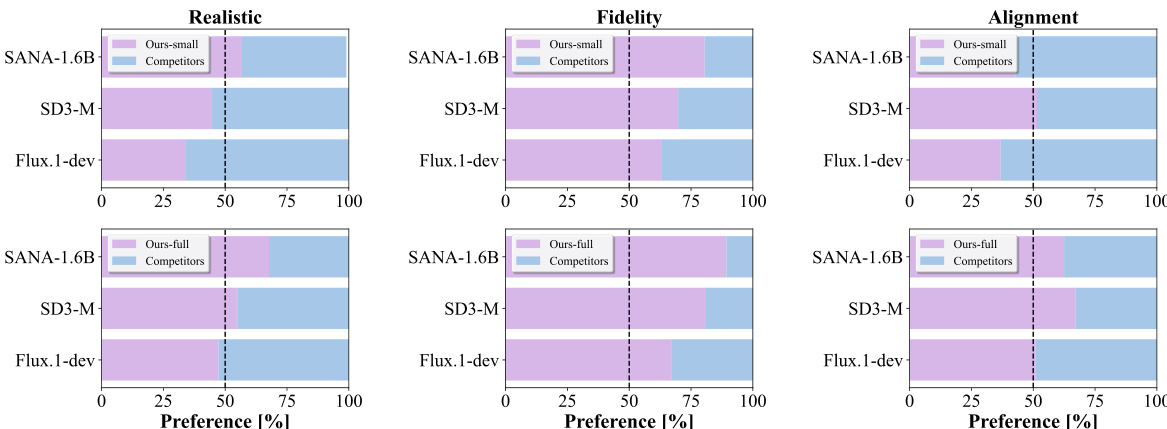
- Human evaluation confirms the full model surpasses larger baselines (e.g., Flux.1-dev, SD3-M) in realism and fidelity, with strong text-image alignment.
- Knowledge-guided distribution matching distillation enables high-quality 4-step generation, matching 28-step baseline performance with minimal quality loss.
The authors conduct a human preference study comparing their small (0.4B) and full (1.6B) models against SANA, SD3-M, and Flux.1-dev across realism, fidelity, and text-image alignment. Results show that the full model outperforms all baselines in fidelity and realism, while the small model achieves strong performance, surpassing larger models like Flux.1-dev and SANA on most attributes.
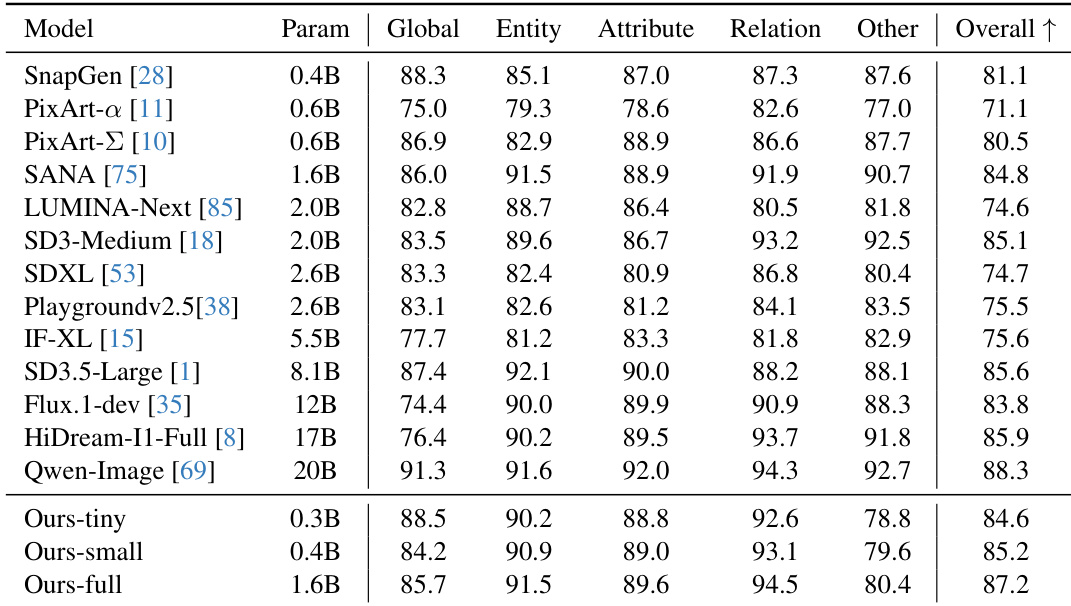
The authors use a series of architectural ablations to develop an efficient DiT model optimized for on-device deployment, achieving a significant reduction in latency while maintaining or improving generation quality. Results show that their full model, with 1.6B parameters, outperforms larger models such as Flux.1-dev and SD3.5-Large across multiple benchmarks, achieving the highest overall score of 87.2, while the small variant (0.4B) surpasses models up to 20 times larger in performance and efficiency.
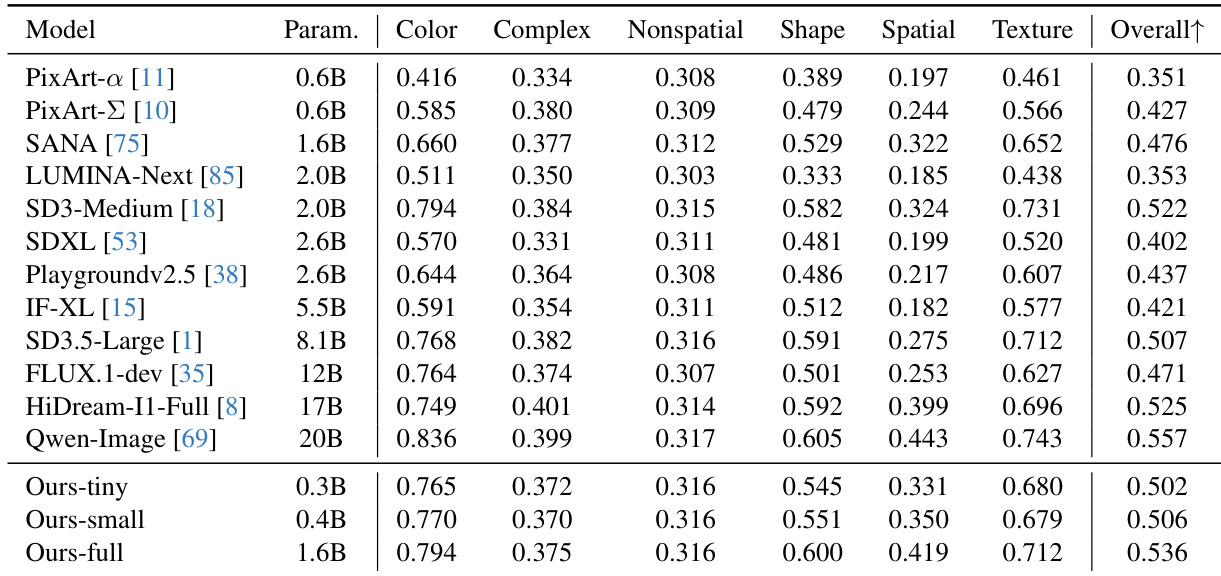
The authors use a series of architectural ablations to develop an efficient DiT model optimized for on-device deployment, achieving a significant reduction in latency while maintaining or improving generation quality. Results show that their final model, Ours-full, achieves a validation loss of 0.536 and outperforms larger models like SD3.5-Large and Flux.1-dev across multiple benchmarks, demonstrating strong trade-offs between efficiency and visual fidelity.
The authors use a series of architectural ablations to develop an efficient DiT model optimized for on-device deployment, achieving a significant reduction in latency while maintaining or improving generation quality. Results show that their full model achieves a validation loss of 0.509, outperforming the baseline SnapGen model in both latency and perceptual quality, and surpasses larger models in benchmark evaluations.

The authors use a training recipe comparison to evaluate the impact of elastic training on model performance and efficiency. Results show that elastic training achieves comparable validation loss and DINO FID scores to standalone training while eliminating the need for separate training of different model sizes, thus reducing the overall training footprint.