Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
マルチエージェントAIシステムの開発と課題に関する大規模研究
マルチエージェントAIシステムの開発と課題に関する大規模研究
Daniel Liu Krishna Upadhyay Vinaik Chhetri A.B. Siddique Umar Farooq
概要
マルチエージェントAIシステム(MAS)であるLangChain、CrewAI、AutoGenなどの急速な登場により、大規模言語モデル(LLM)アプリケーションの開発と統合のあり方が大きく変化している。しかし、こうしたシステムが実際の開発現場でどのように進化し、維持管理されているかについては、まだ十分に理解されていない。本研究では、オープンソースMASにおける初めての大規模な実証的調査を報告する。8つの主要なシステムを対象に、42,000件を超える独自のコミットと4,700件以上の解決済み課題を分析した結果、開発プロファイルは「持続的」「安定的」「バースト型」の3種類に分類された。これらのプロファイルは、エコシステムの成熟度に顕著な差異が存在することを示している。変更内容のうち40.8%を占めるのは「改善的コミット」であり、これは機能強化が修正保守(27.4%)や適応的更新(24.3%)よりも優先されていることを示唆している。課題に関するデータから、最も頻度が高い問題はバグ(22%)、インフラ構成(14%)、エージェント間の連携課題(10%)であることが明らかになった。また、2023年以降、すべてのフレームワークにおいて課題報告件数が急増している。課題の解決時間の中央値は1日未満から約2週間の範囲にあり、多くの課題は迅速に対応されているが、少数の課題については長期的な注目が必要なことが明らかになった。これらの結果は、現在のエコシステムが成長の勢いと同時に脆弱性を抱えていることを示しており、長期的な信頼性と持続可能性を確保するためには、テストインフラの強化、ドキュメントの品質向上、メンテナンス手法の改善が不可欠であることを強調している。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Louisiana State University and the University of Kentucky present the first large-scale empirical study of open-source multi-agent AI systems, analyzing over 42K commits and 4.7K issues across eight leading frameworks like LangChain and AutoGen. They identify three development profiles—sustained, steady, and burst-driven—and reveal that perfective commits (40.8%) dominate over corrective (27.4%) and adaptive (24.3%) changes, indicating a strong focus on feature enhancement. Key challenges include bugs, infrastructure, and agent coordination, with resolution times varying widely, highlighting the ecosystem’s rapid growth and underlying fragility.
Key Contributions
-
This study presents the first large-scale empirical analysis of open-source multi-agent AI systems (MAS), examining over 42,000 commits and 4,700 resolved issues across eight leading frameworks, revealing distinct development profiles—sustained, steady, and burst-driven—that reflect varying levels of ecosystem maturity and long-term maintenance practices.
-
The analysis identifies perfective maintenance (40.8% of commits) as the dominant activity, significantly outpacing corrective (27.4%) and adaptive (24.3%) changes, indicating a strong focus on feature enhancement over bug fixing and system adaptation, with recurring issues centered on bugs, infrastructure, and agent coordination challenges.
-
Issue resolution times are generally fast, with median times ranging from under a day to two weeks, though distributions are skewed, and issue reporting surged starting in 2023, highlighting both the rapid growth and underlying fragility of the MAS ecosystem, underscoring the need for improved testing, documentation, and maintenance infrastructure.
Introduction
The authors leverage large-scale software mining of eight leading open-source multi-agent AI systems—such as AutoGen, CrewAI, and LangChain—to analyze real-world development and maintenance practices. These systems, which orchestrate specialized agents to solve complex tasks through collaboration, have gained traction as a paradigm shift from monolithic LLM applications, enabling more scalable and modular AI workflows. However, prior work has largely focused on architectural innovation and benchmarking, leaving a critical gap in understanding how these systems evolve in practice. The study reveals significant variation in development patterns—sustained, steady, and burst-driven—along with a strong emphasis on feature enhancement (40.8% of commits) over bug fixes (27.4%) and adaptive updates (24.3%), indicating a maintenance imbalance. Common issues include bugs, infrastructure instability, and agent coordination failures, with resolution times skewed toward rapid fixes but a notable minority requiring weeks. The authors’ main contribution is the first empirical characterization of MAS ecosystems at scale, exposing systemic fragility and underscoring the urgent need for better testing, documentation, and long-term maintenance strategies to ensure reliability and sustainability.
Dataset
- The dataset comprises two primary components: closed issues and commit histories from eight popular open-source GitHub repositories implementing multi-agent system (MAS) architectures.
- The issues dataset was collected via the GitHub GraphQL API, resulting in 10,813 closed issues across all repositories.
- The commit dataset was compiled by cloning each repository and extracting all commit records, yielding an initial 44,041 commits.
- For issue analysis, only issues with associated pull requests (PRs) were retained, reducing the total to 4,731 issues. Of these, 3,793 were further labeled, enabling analysis of issue categorization.
- Commit data underwent preprocessing to remove duplicates caused by Git operations like cherry-picking and rebasing, reducing the total to 42,267 unique commits.
- The preprocessed datasets were split into repository-specific subsets based on the research questions, with detailed breakdowns provided in Table II.
- The authors use the filtered issue and commit data to analyze development and maintenance patterns, with the issue dataset supporting RQ2 on issue reporting and resolution, and the commit dataset supporting RQ1 on commit activity and types.
- No cropping strategy was applied; instead, metadata such as issue labels, PR links, and commit timestamps were extracted and structured to support longitudinal and categorical analysis.
Experiment
- Three distinct development profiles identified: sustained high-intensity (LangChain), steady consistent (Haystack), and burst/sporadic (SuperAGI), with commit regularity varying significantly (CV from 48.6% to 456.1%).
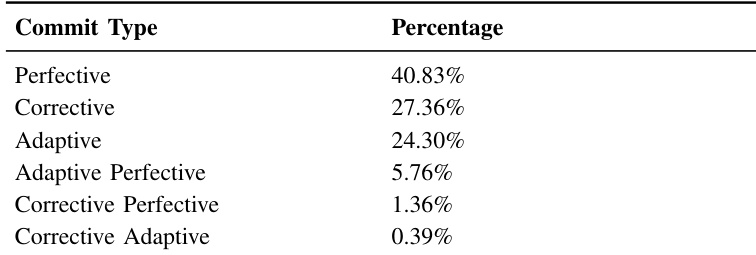
- Perfective maintenance dominates commit activity (40.83%), exceeding corrective (27.36%) and adaptive (24.30%) types, indicating a feature-driven development phase with minimal mixed-commit practices (<8%).
- Code churn analysis reveals rapid prototyping in SuperAGI (3M lines added in early 2023), deliberate refactoring in Haystack (large deletions), and ongoing architectural restructuring in LangChain (repeated churn peaks).
- Ecosystem-level evolution shows cumulative code growth of 10–20 million lines and over 100K files changed by 2025, with a shift toward balanced code additions and deletions post-2023, signaling increased focus on maintainability.
- Issue reporting intensified in 2023 across most frameworks, with Haystack and Semantic Kernel leading in volume (4,000+ issues), while resolution times vary widely (1 to over 10 days median), with right-skewed distributions indicating long-tail issue resolution.
- Bug reports (22%), infrastructure (14%), data processing (11%), and agent-specific issues (10%) are the most prevalent concern types, with technical implementation challenges dominating over community or UX issues.
- Topic modeling of agent issues shows 58.42% focus on agent capabilities (e.g., planning, coordination, integration), while 32.51% center on technical operations (e.g., evaluation, model training, function calling), highlighting a tension between innovation and deployment stability.
- On the analyzed dataset (42,266 commits, 4,700 resolved issues), the ecosystem exhibits rapid growth post-2023, driven by LLM adoption, with development prioritizing feature enhancement over bug fixing, and significant variation in project maturity and maintenance efficiency.
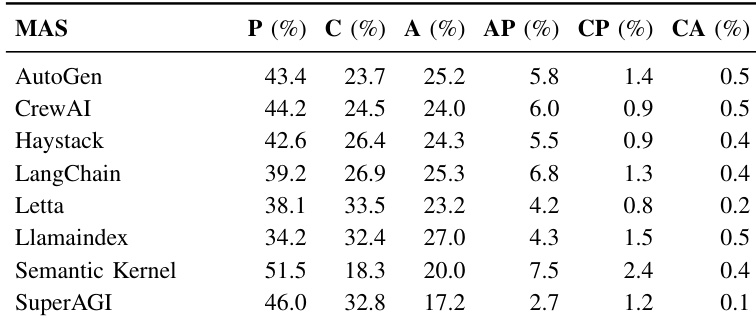
The authors use a fine-tuned DistilBERT model to classify commits into maintenance types and analyze the distribution across MAS frameworks. Results show that perfective maintenance dominates, with Semantic Kernel having the highest ratio at 51.5% and the lowest corrective maintenance at 18.3%, while SuperAGI exhibits a higher corrective ratio of 32.8%, indicating less stable architecture.
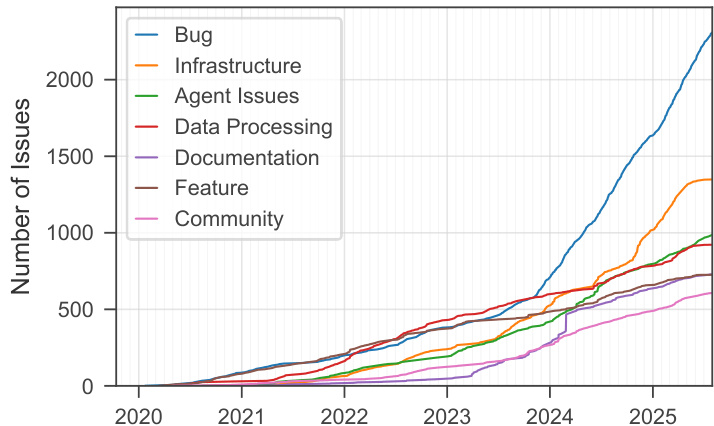
Results show that issue activity across multi-agent AI frameworks intensified significantly after 2023, with Bug reports growing most rapidly and surpassing 2,000 by 2025. Infrastructure, Agent Issues, and Data Processing issues also increased steadily, while Documentation and Community issues remained at lower levels throughout the period.
The authors use a fine-tuned DistilBERT model to classify 42,266 commits into maintenance types, revealing that perfective commits account for 40.83% of all changes, significantly more than corrective (27.36%) and adaptive (24.30%) commits. Results show that single-maintenance commits make up 92.49% of the total, with combined maintenance types representing only 7.51%, indicating a strong preference for atomic, focused development tasks.
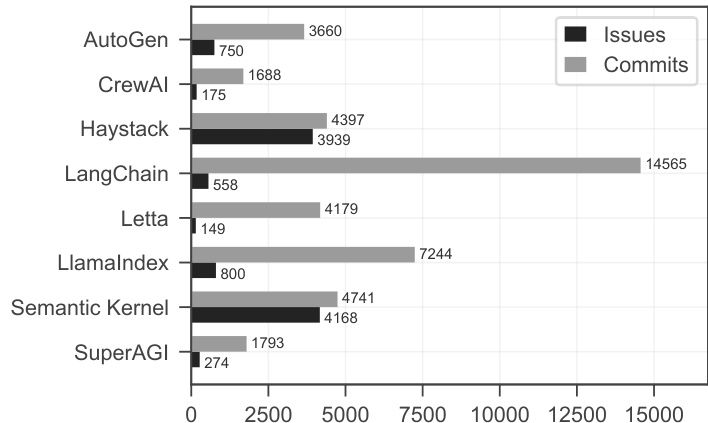
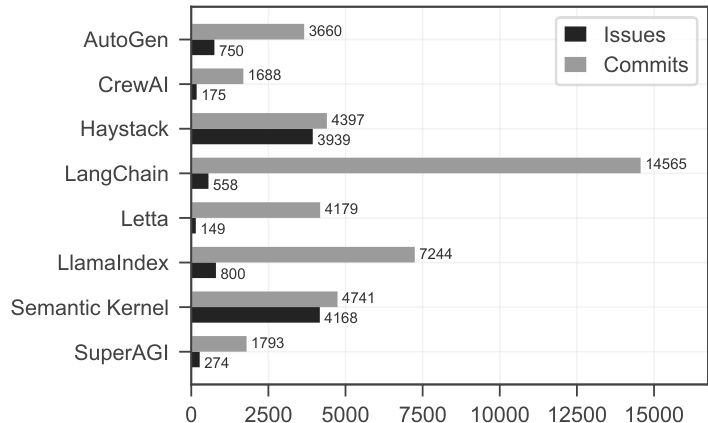
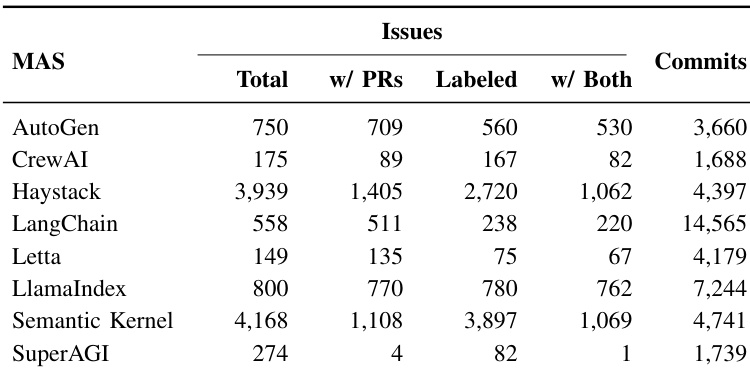
The authors analyze issue and commit data across multiple multi-agent AI frameworks, showing that Haystack and Semantic Kernel have the highest issue volumes with 3,939 and 4,168 issues respectively, while SuperAGI has the lowest at 274. Commits follow a similar pattern, with Haystack and LangChain having the most commits at 4,397 and 14,565 respectively, and SuperAGI having the fewest at 1,739.
The authors use a bar chart to compare the number of issues and commits across seven multi-agent AI frameworks, showing that LangChain has the highest number of commits at 14,565 while Haystack leads in issue count with 4,397. The data reveals significant variation in development activity, with some frameworks like AutoGen and CrewAI having low numbers in both metrics, indicating differing levels of community engagement and project maturity.