Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Klear:統合型マルチタスク音声・映像共同生成
Klear:統合型マルチタスク音声・映像共同生成
Jun Wang Chunyu Qiang Yuxin Guo Yiran Wang Xijuan Zeng Chen Zhang Pengfei Wan
概要
音声・映像の同時生成技術は急速に進展しているものの、依然として大きな課題が残っている。非商用のアプローチは、音声と映像の非同期化、口元と発話の不整合、単モーダルな品質劣化といった問題に直面しており、これらは弱い音声・映像対応モデリング、一般化能力の限界、高品質な密なキャプションデータの不足に起因している。これらの課題に対処するため、本研究では「Klear」を提案し、モデルアーキテクチャ、学習戦略、データ構築の3つの観点から検討を深める。アーキテクチャ面では、統一されたDiTブロックとOmni-Full Attention機構を備えた単一タワー構造を採用し、高精度な音声・映像の同期と強力なスケーラビリティを実現した。学習戦略においては、段階的なマルチタスク学習フレームワークを導入——タスク間の統合最適化を実現するためのランダムモーダルマスキングと、複数段階にわたるカリキュラム学習を採用することで、堅牢な表現学習を実現し、音声・映像の整合性を持つ世界知識を強化するとともに、単モーダルの崩壊を防止した。データ面では、初めての大規模な音声・映像・キャプションの密なキャプション付きデータセットを提供するとともに、数百万もの多様で高品質かつ厳密に同期された音声・映像・キャプションの三つ組を自動的にアノテーション・フィルタリングする新規なデータ構築パイプラインを提案した。こうした基盤の上に構築されたKlearは、大規模データセットへのスケーリングを実現し、同時生成および単モーダル生成の両設定において、高忠実度かつ意味的・時間的に整合された指示追従型生成を実現するとともに、分布外の状況にも堅牢に一般化する性能を発揮した。さまざまなタスクにおいて、従来手法を大幅に上回る性能を達成し、Veo 3と同等の水準に到達する成果を示した。本研究は、次世代の音声・映像合成に向けた統一的かつスケーラブルな道筋を提示した。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Kuaishou Technology propose KLEAR, a unified single-tower audio-video generation framework with Omni-Full Attention and progressive multitask training, enabling high-fidelity, temporally aligned, and instruction-following synthesis across joint and unimodal tasks, achieving performance comparable to Veo 3 while overcoming prior limitations in audio-visual synchronization and unimodal degradation through a large-scale, densely captioned dataset and scalable training strategy.
Key Contributions
-
We introduce KLEAR, a unified multi-task audio-video generation framework that achieves high-fidelity, semantically and temporally aligned outputs in both joint and unimodal settings, with performance comparable to Veo 3, addressing persistent issues like audio-visual asynchrony and lip-speech misalignment.
-
The framework features a single-tower architecture with unified DiT blocks and an Omni-Full Attention mechanism that jointly attends to audio, video, and their corresponding captions, enabling deep cross-modal fusion and strong alignment, while a progressive multitask training strategy with random modality masking prevents unimodal collapse and enhances generalization.
-
We present the first large-scale audio-video dataset with dense captions—81 million high-quality, strictly aligned triplets—generated via an automated pipeline, which enables robust training and demonstrates strong out-of-distribution generalization across benchmarks.
Introduction
The authors leverage recent advances in generative AI to address persistent challenges in audio-video joint generation, where models often suffer from audio-visual asynchrony, poor lip-speech alignment, and degradation in unimodal outputs. Prior work is limited by weak cross-modal interaction due to suboptimal architectures—such as dual-tower designs with shallow fusion—lack of diverse, high-quality training data, and single-task training regimes that induce bias and hinder generalization. To overcome these, the authors introduce KLEAR, a unified multi-task framework featuring a single-tower architecture with unified DiT blocks and an Omni-Full Attention mechanism that jointly models audio, video, and their corresponding captions for tight spatio-temporal alignment. They employ a progressive multitask training strategy with random modality masking and a performance-adaptive curriculum to enhance representation robustness and prevent unimodal collapse. Additionally, they introduce a large-scale, high-quality dataset of 81 million dense-captioned audio-video triplets, generated via an automated pipeline. KLEAR achieves state-of-the-art performance across joint and unimodal tasks, matching Veo 3 in quality while demonstrating strong out-of-distribution generalization.
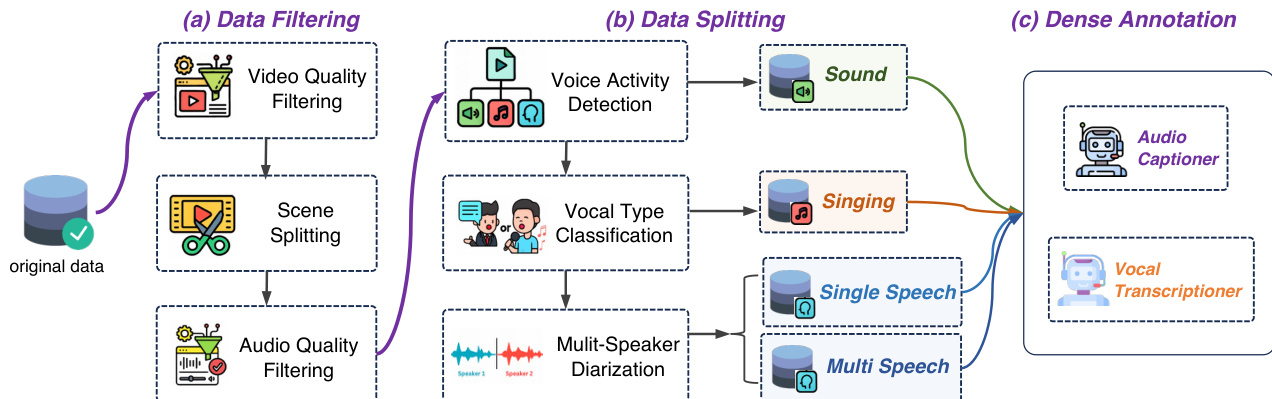
Dataset
- The dataset is composed of automatically annotated audio-visual samples, including single-speaker speech, multi-speaker speech, singing, and natural sound clips, with a final post-filtering retention rate of 27%.
- Video filtering is based on dynamic quality (motion ratio, camera stability), static quality (sharpness, aesthetics, color saturation), content naturalness (no watermarks or excessive effects), and safety; low-resolution, low SNR/MOS, or high-silence videos (>20%) are discarded. Scene splitting ensures each sample contains only one coherent scene.
- Audio filtering removes low SNR, poor MOS, clipped, distorted, or noisy samples, enforces less than 20% silence, and ensures high fidelity and consistent formatting. Audio-visual alignment is verified using Synchformer (temporal) and ImageBind (semantic) to ensure strong synchronization.
- The dataset is split by audio type: vocal and non-vocal. From the vocal subset, three distinct splits are created—singing, single-speaker speech, and multi-speaker speech—each of which undergoes dense captioning.
- Each split is annotated using specialized models: Whisper-Large-v3, SenseVoice, and Qwen2.5-Omni for speech and singing transcripts; Qwen2.5-Omni and Gemini 2.5-Pro for audio captions; and a video expert model for detailed video descriptions. Speaker attributes (gender, age) are extracted for vocal content.
- All annotations are integrated into unified dense captions, forming a richly labeled dataset.
- The authors use this dataset for training, combining the splits with tailored mixture ratios to balance representation across speech, singing, and sound categories, ensuring diverse and high-quality input for model training.
Method
The authors leverage a unified single-tower architecture to enable joint audio-video generation, addressing the limitations of cascaded and dual-tower approaches. The model, named KLEAR, employs a multimodal diffusion transformer (MM-DiT) as its core backbone, which processes inputs from four modalities: video, video-related text, audio-related text, and audio. Each modality is individually encoded into latent representations using dedicated encoders—video via a 3D causal visual encoder, and text and audio via respective embedding models. These encoded sequences are then fed into the MM-DiT module, which generates latent variables for both video and audio in separate streams. The generated latents are subsequently decoded independently to produce the final audio and video outputs. Refer to the framework diagram for a visual overview of this process.

The MM-DiT module utilizes a full-attention mechanism to facilitate comprehensive cross-modal interaction. Specifically, the hidden states of video, video-related text, audio-related text, and audio are scaled, normalized, and concatenated for attention computation. The attention mechanism computes query, key, and value matrices for each modality, which are then combined to form the attention output. This is expressed as Q=QV⊙QVT⊙QAT⊙QA, K=KV⊙KVT⊙KAT⊙KA, and V=VV⊙VVT⊙VAT⊙VA, where the ⊙ operator denotes concatenation. The attention output is calculated as Atn(Q,K,V)=Softmax(dkQK⊤)V. The resulting attention values are split back into separate modalities, undergo scaling, normalization, residual connection, and feedforward processing, and are then passed to the next MM-DiT block. This approach ensures that all modalities are unified within a joint full-attention framework, enabling effective fusion.
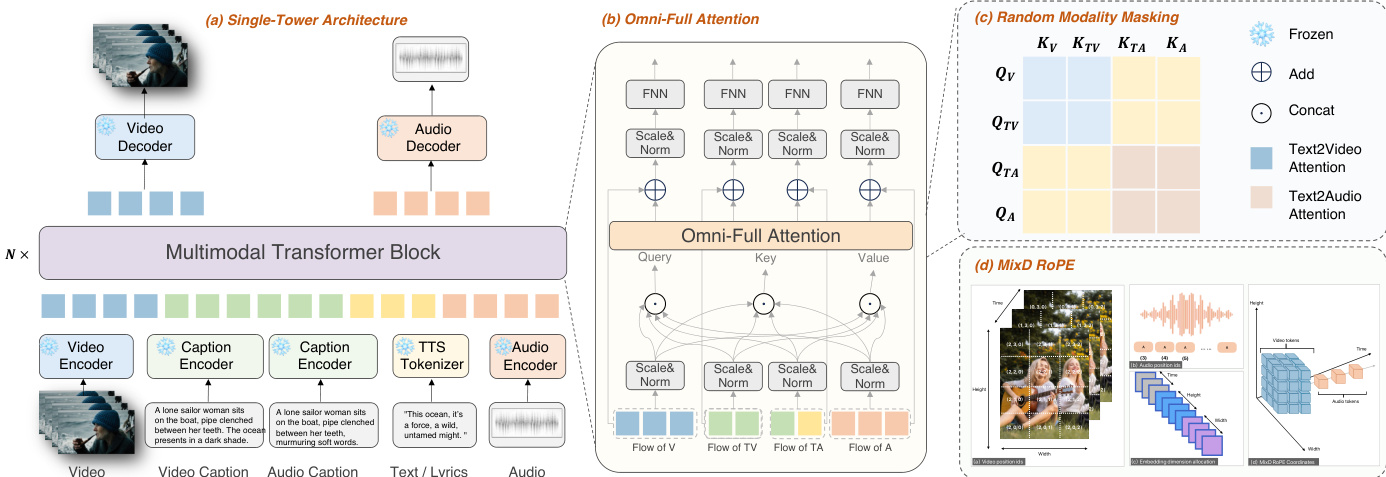
To enhance positional encoding, the model incorporates Mixed Dimension Rotary Position Embedding (MixD-RoPE). For video, a 3D RoPE is applied across temporal, width, and height dimensions, capturing both absolute and relative position dependencies. For audio, compatible 1D temporal positional encodings are used, with the position IDs initialized by incrementing the maximum temporal position ID of the video modality. This design ensures a shared temporal position ID between video and audio, facilitating synchronized processing. The model is trained using a flow-matching objective, where the denoising network ϵθ(⋅) learns to predict the velocity field that transforms pure Gaussian noise to the data distribution. The training loss is defined as LFM=Et,c,x0,x1∥(x1−x0)−ϵθ(tx1+(1−t)x0,t,c)∥22, with t∼U(0,1), x0∼N(0,I), and x1∼pdata.
Experiment
- KLEAR validates its effectiveness through comprehensive experiments across multiple tasks, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance in audio-video joint generation, unimodal quality, and cross-modal consistency.
- On TI2AV, TI2V, T2V, and T2A tasks, KLEAR surpasses task-specialized baselines, achieving 34% higher unimodal quality than cascaded methods and 18% higher than joint baselines, while matching or exceeding specialized models.
- Qualitative results show superior lip-sync accuracy, emotional expressiveness, singing/rap performance, and audio-visual synchronization, with KLEAR achieving phoneme-level alignment and natural prosody fusion, outperforming Universe-1 and Ovi.
- Ablations confirm the single-tower architecture with omni full attention outperforms dual-tower designs, with better cross-modal alignment and robustness despite distribution mismatch in pretrained towers.
- Multi-task masking improves cross-modal correlation and generalization, enabling strong performance on downstream tasks like I2V and I2AV.
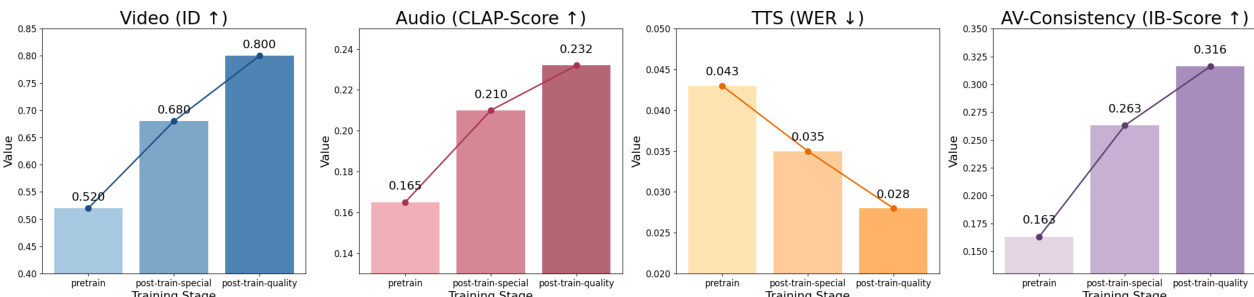
- Progressive training strategy significantly enhances model capabilities, with post-training on high-quality data yielding additional gains, and removing the schedule causing notable performance drops.
The authors use a unified single-tower architecture with omni full attention to achieve superior audio-video consistency and unimodal performance across multiple tasks. Results show that their approach outperforms both cascaded and joint baselines, with the "All Tasks (Ours)" method achieving the highest scores in video quality, audio quality, and audio-video synchronization.
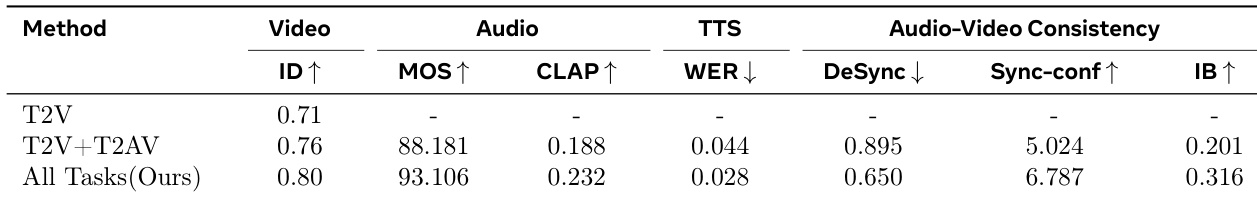
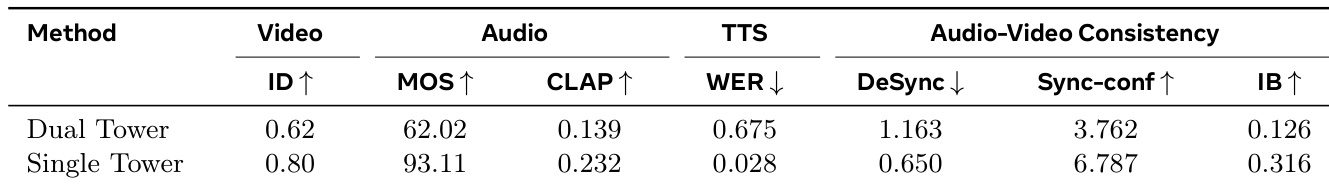
The authors compare a dual-tower and a single-tower architecture for audio-video generation, with the single-tower model achieving superior performance across all metrics. Results show the single-tower approach outperforms the dual-tower variant in video quality, audio quality, and audio-video consistency, demonstrating the effectiveness of the unified architecture and omni full attention mechanism.
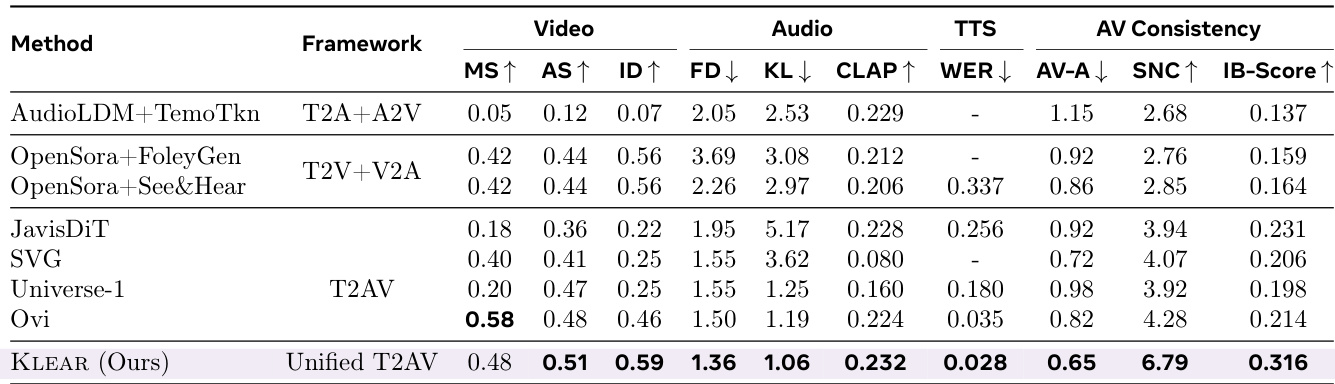
Results show that KLEAR achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple audio-video generation tasks, outperforming prior methods in video quality, audio quality, and audio-visual consistency. The unified T2AV framework with omni full attention enables superior cross-modal alignment, as evidenced by higher scores in metrics such as MS, AS, ID, and IB-Score compared to cascaded and dual-tower baselines.
The authors use the provided charts to evaluate the impact of different training stages on model performance across multiple metrics. Results show that the post-train-quality stage consistently improves all evaluated metrics—video identity, audio CLAP score, TTS WER, and AV-consistency—compared to earlier stages, indicating that high-quality data and progressive training significantly enhance model performance.