Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
DreamID-V:拡散トランスフォーマーを活用した高忠実度顔交換における画像から動画へのギャップの橋渡し
DreamID-V:拡散トランスフォーマーを活用した高忠実度顔交換における画像から動画へのギャップの橋渡し
Xu Guo Fulong Ye Xinghui Li Pengqi Tu Pengze Zhang Qichao Sun Songtao Zhao Xiangwang Hou Qian He
概要
ビデオフェイススワッピング(VFS)は、ターゲット動画のポーズ、表情、照明、背景および動的情報をきめ細かく保持しつつ、ソースの顔情報を滑らかに埋め込むことを要求する。既存の手法は、アイデンティティの類似性や属性の保持を維持しつつ、時間的に一貫性のある出力を得ることが困難である。この課題に対処するため、本研究では、画像フェイススワッピング(IFS)の優位性を動画領域へシームレスに転移する包括的なフレームワークを提案する。まず、アイデンティティアンカー型ビデオ合成器を事前学習するための新しいデータパイプライン「SyncID-Pipe」を導入し、これをIFSモデルと組み合わせて、明示的な監視を可能にする双方向ID四重組(bidirectional ID quadruplets)を構築する。このペアデータに基づき、本研究では、モダリティに応じた条件を判別的に注入するための中心的な「モダリティ認識型条件付けモジュール」を備えた、初めての拡散変換器(Diffusion Transformer)ベースのフレームワーク「DreamID-V」を提案する。さらに、合成データから実データへのカリキュラム学習メカニズムと、アイデンティティの一貫性を強化する強化学習戦略を提案することで、困難な状況下でも視覚的リアリズムとアイデンティティの一貫性を向上させる。限られたベンチマーク問題に対処するため、多様なシーンを網羅する包括的なベンチマーク「IDBench-V」を新たに導入した。広範な実験により、DreamID-Vが最先端手法を上回ることを実証するとともに、さまざまなスワップ関連タスクへのシームレスな適応性も示した。
One-sentence Summary
Xu Guo, Fulong Ye, and colleagues from Tsinghua University and ByteDance's Intelligent Creation Lab propose DreamID-V, a diffusion transformer-based framework with modality-aware conditioning and identity-coherence reinforcement learning that enables high-fidelity video face swapping by bridging image face swapping advances with temporal consistency, outperforming prior methods on IDBench-V across diverse real-world scenarios.
Key Contributions
- Video Face Swapping (VFS) faces challenges in maintaining identity similarity, attribute preservation, and temporal consistency, especially when directly applying Image Face Swapping (IFS) methods frame-by-frame, leading to flickering and jittering artifacts.
- The authors propose DreamID-V, the first Diffusion Transformer-based VFS framework with a Modality-Aware Conditioning module for discriminative multi-modal condition injection, enabling high-fidelity identity transfer and coherent facial dynamics.
- A novel data pipeline, SyncID-Pipe, constructs bidirectional ID quadruplets using an Identity-Anchored Video Synthesizer and IFS models, while a Synthetic-to-Real Curriculum and Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning enhance realism and robustness, validated on the new IDBench-V benchmark.
Introduction
Face swapping in video (VFS) is critical for applications in entertainment, creative design, and digital identity, but it faces major challenges in maintaining temporal identity continuity, pose consistency, and environmental fidelity—issues that are less pronounced in image-based face swapping (IFS). While IFS methods achieve high identity and attribute fidelity, direct frame-by-frame application to video leads to flickering and jittering due to lack of temporal coherence. Existing diffusion-based VFS approaches improve consistency but still lag behind IFS in identity preservation and attribute accuracy, largely due to insufficient explicit supervision and weak modeling of dynamic facial motion. The authors propose DreamID-V, a novel video face swapping framework built on Diffusion Transformers (DiT), which bridges the IFS-VFS gap through a three-part innovation: a data pipeline called SyncID-Pipe that leverages IFS models to generate high-quality, temporally consistent video data via an Identity-Anchored Video Synthesizer; a Modality-Aware Conditioning mechanism for effective multi-modal condition injection; and an Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning strategy to enhance robustness under complex motions. To support rigorous evaluation, they introduce IDBench-V, a comprehensive benchmark covering diverse poses, expressions, and lighting conditions. The framework achieves state-of-the-art performance in both identity similarity and temporal coherence, demonstrating significant improvements over prior methods and strong adaptability across swap-related tasks.
Dataset
- The dataset, IDBench-V, consists of 200 real-world source video–target image pairs designed to evaluate video face swapping under challenging, realistic conditions.
- Source videos are collected to cover diverse and difficult scenarios such as small faces, extreme head poses, severe occlusions, complex and dynamic expressions, and cluttered multi-person scenes.
- The target images are carefully selected to match the identities in the source videos, ensuring paired data for evaluation.
- The training set is derived from OpenHumanVid, with additional filtering applied based on identity similarity to create consistent source-target pairs.
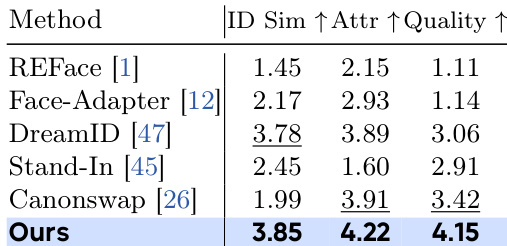
- The benchmark is used to evaluate both image-based and video-based face swapping methods, with comparisons against SOTA models including FSGAN, REFace, Face-Adapter, DreamID, Stand-In, and CanonSwap.
- For evaluation, three main dimensions are assessed: Identity Consistency (using ArcFace, InsightFace, and CurricularFace with frame-wise similarity variance), Attribute Preservation (pose and expression fidelity), and Video Quality (via Fréchet Video Distance with ResNext).
- Additional metrics from VBench—background consistency, subject consistency, and motion smoothness—are used to evaluate temporal and spatial coherence.
- No explicit cropping is applied; instead, the original video frames and target images are used as-is, with metadata constructed to ensure identity alignment and scenario categorization.
Method
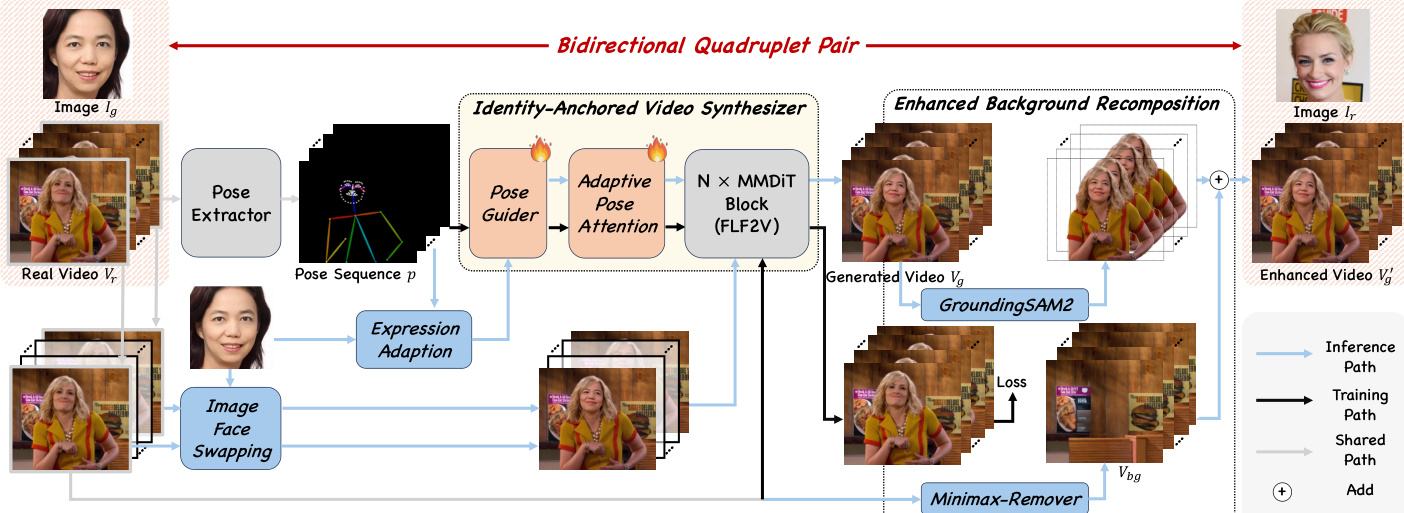
The authors propose DreamID-V, a diffusion-based framework for video face swapping (VFS) that leverages a Diffusion Transformer (DiT) architecture to achieve high-fidelity identity transfer while preserving temporal consistency and dynamic attributes. The overall framework is built upon a novel data curation pipeline, SyncID-Pipe, which generates bidirectional ID quadruplets to bridge the gap between image and video face swapping. This pipeline first employs an Identity-Anchored Video Synthesizer (IVS) to reconstruct a target video conditioned on a source identity and a pose sequence. The IVS is trained using a reconstruction objective on a large-scale portrait dataset, where a First-Last-Frame video foundation model (FLF2V) is conditioned on the initial and final frames of a portrait video and its extracted pose sequence. To inject motion information effectively, the authors introduce an Adaptive Pose-Attention mechanism, which uses a lightweight Pose Guider to extract pose features and align them with the latent features of the DiT. This mechanism employs trainable linear layers to project pose features into the attention space, enabling precise spatiotemporal alignment with the noisy latent video through a modified attention formula that combines standard self-attention with pose-conditioned attention.
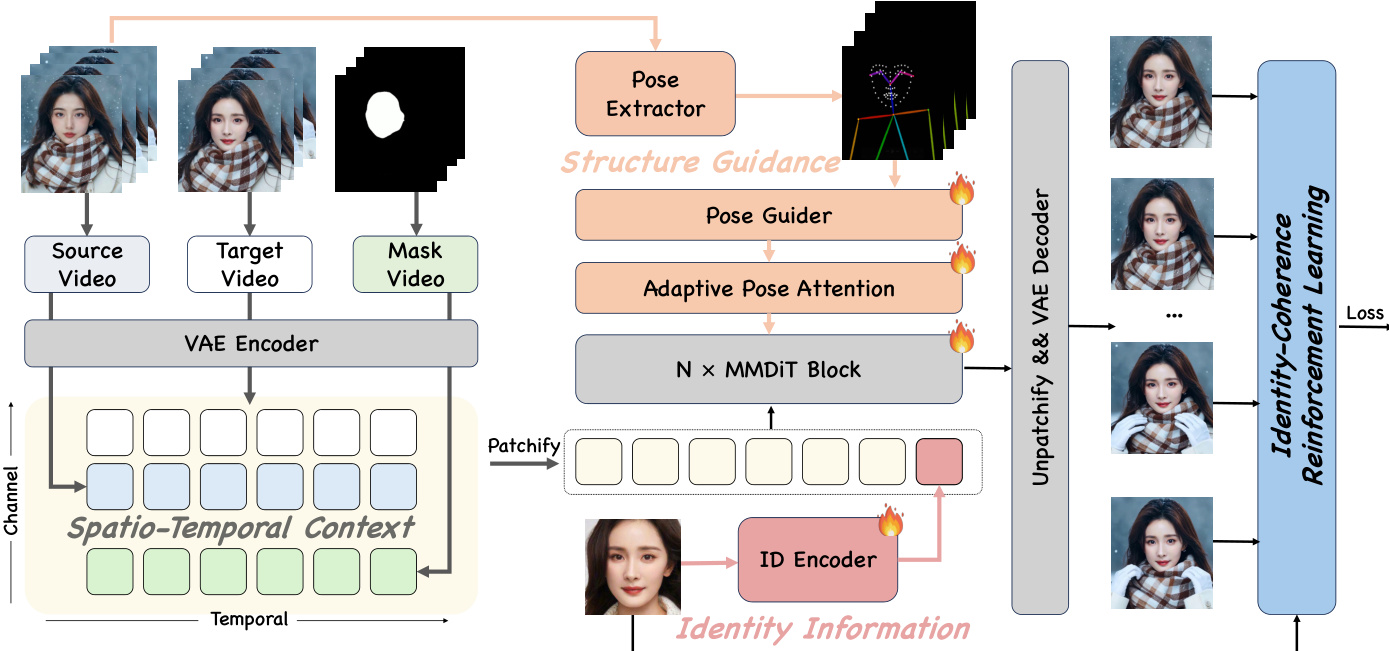
The core of the DreamID-V framework, as illustrated in the figure below, is the Modality-Aware Conditioning (MC) module, which enables the discriminative injection of multiple conditions. This module decomposes the input conditions into three distinct types: Spatio-Temporal Context, Structural Guidance, and Identity Information. The Spatio-Temporal Context module injects the reference video and a dilated face mask, which are concatenated with the latent source video along the channel dimension to provide precise contextual information for background and lighting preservation. The Structural Guidance module uses the pose sequence as a structural cue, leveraging the pre-trained Adaptive Pose-Attention mechanism to control motion attributes and preserve fine-grained expressions without disrupting high-level features. In contrast, the Identity Information module treats the target identity as a high-level semantic feature, encoding it into embeddings via a dedicated ID encoder and concatenating them with the latent features along the token dimension to enable full interaction through the DiT's attention mechanism.
To enhance visual realism and identity consistency, the training process incorporates a Synthetic-to-Real Curriculum and an Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning (IRL) strategy. The training begins with a synthetic stage, where the model is trained on forward-generated paired data to achieve high identity similarity. This is followed by a real augmentation stage, which fine-tunes the model using backward-real paired data augmented with an Enhanced Background Recomposition module. This module uses foreground masks and a MinimaxRemover to extract a clean background from the real video, which is then combined with the foreground from the generated video to create a more realistic and consistent output. Finally, the IRL mechanism addresses temporal identity consistency by dynamically re-weighting the loss based on frame-wise identity fidelity. This is achieved by defining a Q-value as the inverse of the cosine similarity between the generated frame and the target identity, which is then used to weight the flow matching loss, thereby steering the model to focus on refining identity preservation in challenging frames.
Experiment
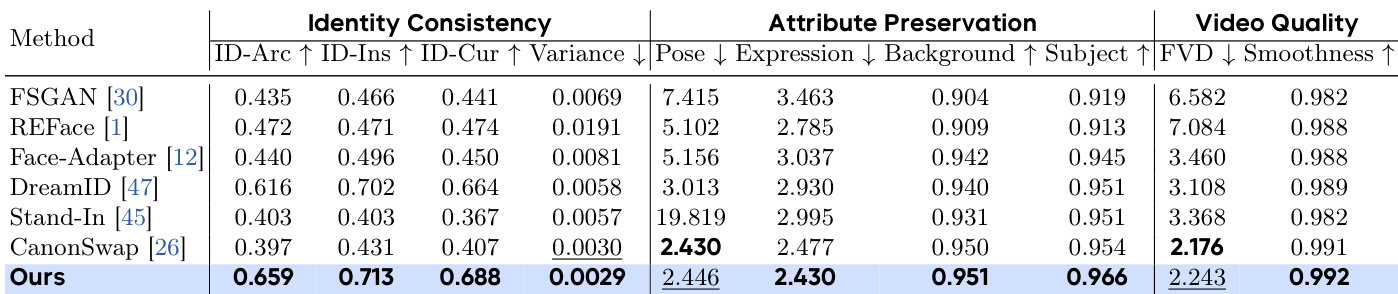
- Quantitative comparisons on IDBench show DreamID-V achieves the highest scores in identity similarity, attribute preservation, and video quality across all metrics, outperforming state-of-the-art models including CanonSwap, Face-Adapter, DreamID, and Stand-In. On the IDBench user study with 19 evaluators, DreamID-V received the best average scores (1–5 scale) in all three dimensions.
- Qualitative analysis in Fig. 4 demonstrates superior identity similarity, expression preservation, background consistency, and robustness under occlusion and complex expressions, significantly outperforming Face-Adapter, Stand-In, CanonSwap, and DreamID.
- Ablation studies in Tab. 3 and Fig. 5 confirm the effectiveness of each component: the SyncID-Pipe enables high identity similarity by bridging VFS and IFS domains; the Sync-to-Real training strategy balances realism and identity preservation; and the Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning (IRL) stage significantly improves identity similarity, especially under profile views and complex motions, while reducing inter-frame variance.
- The model exhibits strong versatility, successfully extending to accessory, outfit, headphone, and hairstyle swapping with expanded training data, as shown in Fig. 6.
- T-SNE visualization in Fig. 9 confirms that synthetic videos generated by the IVS module are distribution-aligned with the DiT-based model’s latent space, enabling faster convergence and improved performance when training with synthetic data.
Results show that the ablation study demonstrates the effectiveness of each component in DreamID-V. The full model (e) achieves the highest ID-Arc score of 0.659 and the lowest variance of 0.0029, indicating superior identity similarity and temporal consistency. It also achieves competitive performance in pose and expression preservation, with FVD scores comparable to the best-performing variant, highlighting the importance of the Identity-Coherence Reinforcement Learning stage in maintaining high identity similarity under complex motions.
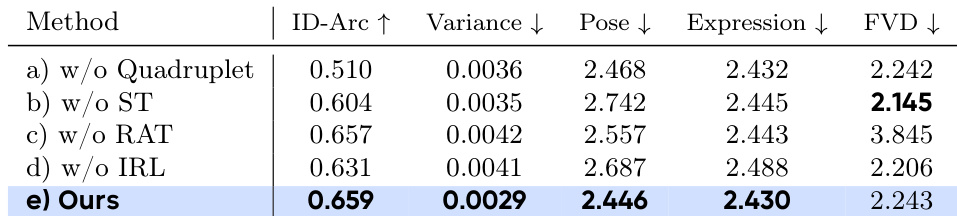
Results show that DreamID-V achieves the highest identity consistency across all metrics, with the best ID-Arc, ID-Ins, and ID-Cur scores, and the lowest variance, indicating strong temporal stability. It also outperforms all compared methods in attribute preservation and video quality, particularly excelling in pose and expression fidelity while maintaining high smoothness and low FVD.
Results show that DreamID-V achieves the highest scores across all evaluated metrics, with an ID similarity of 3.85, attribute preservation of 4.22, and video quality of 4.15, outperforming all compared methods. The authors use a combination of synthetic-to-real training and identity-coherence reinforcement learning to achieve high identity similarity and robust attribute preservation while maintaining photorealistic video quality.