Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Youtu-Agent:自動生成とハイブリッドポリシー最適化によるエージェント生産性のスケーリング
Youtu-Agent:自動生成とハイブリッドポリシー最適化によるエージェント生産性のスケーリング
概要
既存の大規模言語モデル(LLM)エージェントフレームワークには、二つの大きな課題が存在する。一つは高い構成コストであり、もう一つは能力の静的化である。高品質なエージェントを構築するには、ツールの統合やプロンプト工学に膨大な手作業が必要となる一方で、展開後のエージェントは高コストなファインチューニングを伴わずに動的な環境に適応できない。これらの課題に対処するため、本研究では、LLMエージェントの自動生成と継続的進化を目的としたモジュール型フレームワーク「Youtu-Agent」を提案する。Youtu-Agentは、実行環境、ツールキット、コンテキスト管理を分離する構造化された構成システムを備えており、柔軟な再利用と自動合成を可能にする。さらに、標準的なタスク向けの「Workflow」モードと、複雑かつ非標準的な要件に対応する「Meta-Agent」モードという二つの生成パラダイムを導入。これらは、ツールコード、プロンプト、構成ファイルを自動生成可能である。また、ハイブリッドなポリシー最適化システムを構築した。第一に、「Agent Practice」モジュールは、パラメータ更新なしにコンテキスト内最適化を通じてエージェントが経験を蓄積し、性能を向上させる仕組みを提供する。第二に、「Agent RL」モジュールは分散学習フレームワークと統合され、エンドツーエンドかつ大規模な形で任意のYoutu-Agentに対するスケーラブルかつ安定した強化学習を実現する。実験の結果、Youtu-Agentはオープンウェイトモデルを用いてWebWalkerQA(71.47%)およびGAIA(72.8%)で最先端の性能を達成した。自動生成パイプラインは81%以上のツール合成成功率を達成し、「Practice」モジュールはAIME 2024/2025においてそれぞれ+2.7%および+5.4%の性能向上を実現した。さらに、Agent RLトレーニングにより7B規模のLLMにおいて40%の高速化を達成しつつ、安定した性能向上を実現。数学および一般/マルチホップQAベンチマークにおいて、コーディング/推論能力と検索能力がそれぞれ最大35%および21%向上した。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Tencent Youtu Lab, Fudan University, and Xiamen University propose Youtu-Agent, a modular framework enabling automated generation of LLM agents via Workflow and Meta-Agent modes, with a hybrid policy optimization system combining training-free experience accumulation and scalable reinforcement learning, achieving state-of-the-art performance on WebWalkerQA and GAIA while reducing configuration costs and enabling continuous evolution without expensive fine-tuning.
Key Contributions
- Youtu-Agent introduces a modular, YAML-based architecture that decouples environments, toolkits, and agents, enabling automated generation of executable agent configurations—including tool code and prompts—reducing configuration costs and supporting flexible, reusable component design.
- The framework implements a dual-paradigm generation system: Workflow mode for deterministic, routine tasks and Meta-Agent mode for dynamic, complex requirements, allowing autonomous synthesis of agent behavior without manual intervention.
- It features a hybrid optimization pipeline with the Agent Practice module, which improves performance via in-context experience accumulation using only 100 samples and $18 cost, and the Agent RL module, which enables stable, scalable reinforcement learning with 40% speedup and 128-GPU support, boosting AIME 2024 accuracy from 10% to 45% on Qwen2.5-7B.
Introduction
The authors leverage the growing trend of LLM-based agents for real-world task automation, where the dual challenges of high configuration costs and static capabilities hinder scalable deployment. Prior frameworks rely on labor-intensive prompt engineering or costly fine-tuning, with limited adaptability and poor scalability. Youtu-Agent addresses these issues through a modular, YAML-driven architecture that separates environment, tools, and agent logic, enabling automated generation of both agent configurations and executable tool code. It introduces two generation modes—Workflow for deterministic tasks and Meta-Agent for dynamic scenarios—alongside a hybrid optimization system: the Agent Practice module enables low-cost, gradient-free self-improvement via parallel rollouts and experience sharing, while the Agent RL module supports stable, scalable reinforcement learning with solutions to concurrency and entropy explosion. The framework achieves strong performance on benchmarks using only open-source models, demonstrating significant gains in task completion, accuracy, and training efficiency.
Dataset
- The dataset, named AgentGen-80, comprises 80 diverse task descriptions designed to evaluate automated agent generation, spanning from simple information retrieval to complex multi-step automation.
- It is curated specifically for this study, as no established benchmarks existed for the task, and includes a balanced mix of task types to ensure comprehensive evaluation.
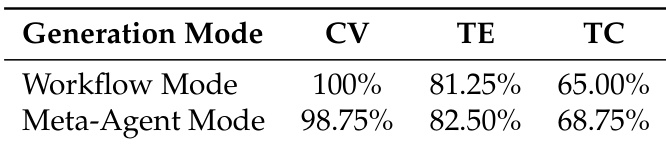
- The evaluation focuses on three key dimensions: Configuration Validity (CV), assessing whether the generated YAML configuration is structurally correct and semantically complete; Tool Executability (TE), measuring whether synthesized tools compile and run as expected; and Task Completion (TC), testing end-to-end success in achieving the specified task.
- The dataset is used entirely for evaluation, with no training data drawn from it; it serves as a standardized testbed to measure model performance across the three quality dimensions.
- No cropping or metadata construction is applied—each task description is used in its original form, with evaluation conducted on the full output of the agent generation pipeline.
Method
The Youtu-Agent framework is structured around a modular architecture designed to decouple execution components and enable automated generation and continuous optimization of large language model (LLM) agents. The core execution framework consists of three hierarchical layers: the Environment Layer, the Tools Layer, and the Agent Layer. The Environment Layer provides the foundational execution context, abstracting low-level capabilities such as browser navigation, command execution, or sandboxed code environments. This abstraction allows tools and agents to operate across different backends with minimal modification. The Tools Layer encapsulates atomic and composite operations, categorized into environment-related tools, environment-independent utilities, and Model Context Protocol (MCP) tools for external service integration. The Agent Layer houses the LLM-driven planner/executor, which operates through a perceive–reason–act loop. To manage long-horizon interactions and control context window size, a Context Manager module is integrated within this layer, pruning stale information while preserving essential task history.

The framework is supported by a YAML-based structured configuration system that declaratively specifies all components, including environment, tools, agent instructions, and context management settings. This standardized format facilitates both manual composition and automated synthesis. The automated generation mechanism leverages this configuration system to produce complete agent configurations from high-level task descriptions, employing two distinct paradigms. The Workflow mode follows a deterministic four-stage pipeline: Intent Clarification and Decomposition, Tool Retrieval and Ad-hoc Tool Synthesis, Prompt Engineering, and Configuration Assembly. This pipeline enables rapid development for well-defined, routine tasks. For more complex or ambiguous requirements, the Meta-Agent mode deploys a higher-level Architect Agent that dynamically plans the generation process. This meta-agent utilizes a set of callable tools—search_tool, create_tool, ask_user, and create_agent_config—to conduct multi-turn clarification, retrieve or synthesize tools, and assemble the final configuration.

Beyond execution, the framework emphasizes continuous agent improvement through two primary optimization components. The Agent Practice module enables low-cost, experience-based improvement without parameter updates. It integrates Training-free Group Relative Policy Optimization (Training-free GRPO), which operates by performing multiple rollouts on a small dataset to generate diverse solution trajectories. An LLM evaluator assesses the relative quality of these trajectories, distilling a semantic group advantage from contrasting successful and failed trials. This experiential knowledge is then injected into the agent's context during online testing as a form of "textual LoRA," guiding reasoning without modifying model weights. The Agent RL module provides a complete pipeline for end-to-end reinforcement learning, supporting scalable and stable training. This module integrates with modern RL frameworks via a custom connector, addressing scalability through RESTful API wrapping, Ray-based concurrency, and hierarchical timeout logic. Stability is ensured by filtering invalid tool calls, reducing off-policy updates, and correcting advantage estimation bias.

The end-to-end RL training pipeline is structured into three main components: the RL Framework, the Connector, and the Agent Framework. The RL Framework handles data loading, rollout generation, loss computation, and policy updates. The Connector acts as a bridge, translating between the RL framework and the Youtu-Agent execution environment. It includes an LLM Proxy, Bridging Protocols, and a Data Store, enabling seamless communication and data exchange. The Agent Framework, which includes the Youtu-Agent core, manages the agent's lifecycle, from initialization to execution and reward computation. This modular design allows for efficient integration and scalable training of agents across distributed systems.
Experiment
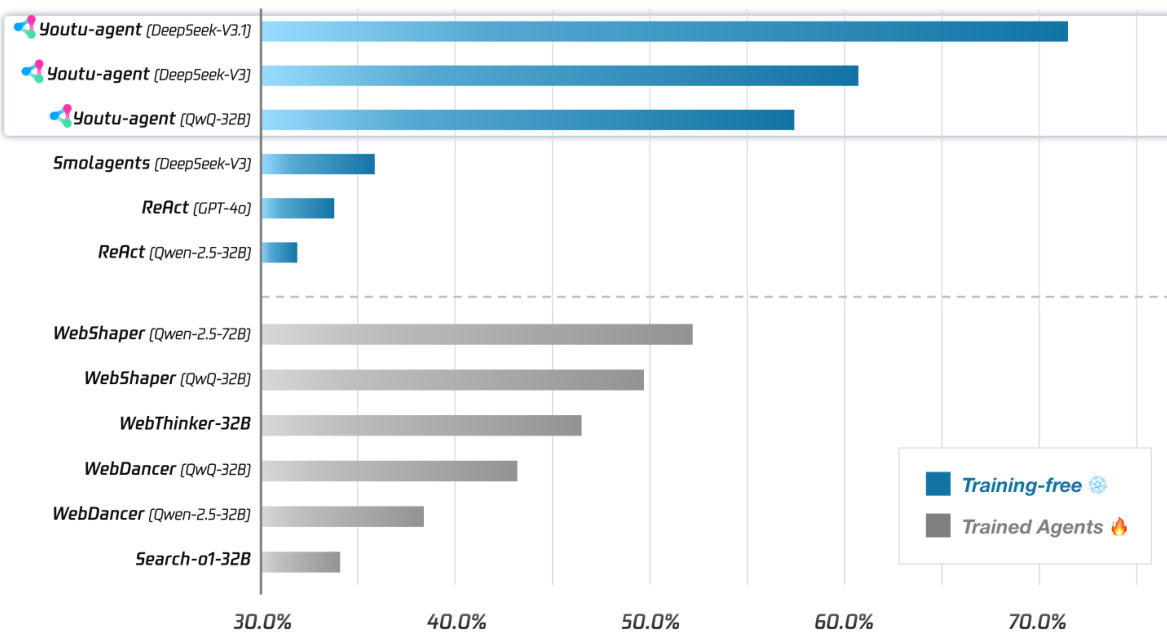
- Framework Efficiency: Achieved 71.47% pass@1 on WebWalkerQA and 72.8% pass@1 on GAIA (text-only subset) using only open-source models, establishing a strong open-source baseline for general agent capabilities.
- Automated Agent Generation: The Workflow and Meta-Agent modes achieved 100% and 98.75% configuration validity, respectively, with 81.25%–82.50% tool executability and 65.00%–68.75% task completion, demonstrating effective automated tool and agent configuration synthesis.
- Continuous Experience Learning: Training-free GRPO in the Agent Practice module improved performance by +2.7% on AIME 2024 and +5.4% on AIME 2025 with only 100 training examples and zero gradient updates, achieving comparable results to expensive RL methods at a fraction of the cost.
- Scalable and Stable Agent RL: The Agent RL module reduced training iteration time by 40% and improved Qwen2.5-7B accuracy on AIME 2024 from 10% to 45%, with consistent gains across math/code and search tasks, validating enhanced scalability and stability in large-scale RL training.
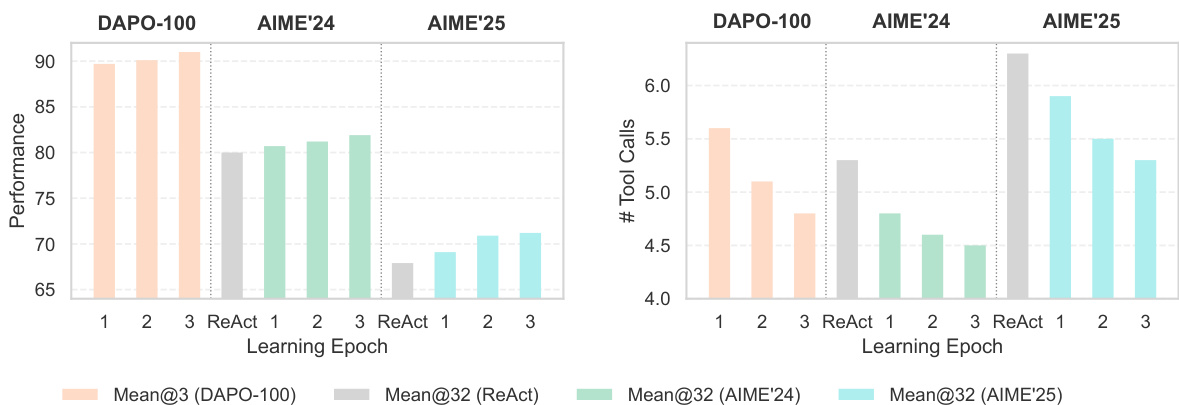
The authors use a training-free approach to improve agent performance on mathematical reasoning benchmarks, achieving +2.7% and +5.4% absolute improvements on AIME 2024 and AIME 2025 respectively, with no parameter updates and only 100 training examples. This demonstrates that experience accumulation through in-context learning can effectively enhance agent capabilities at low cost.
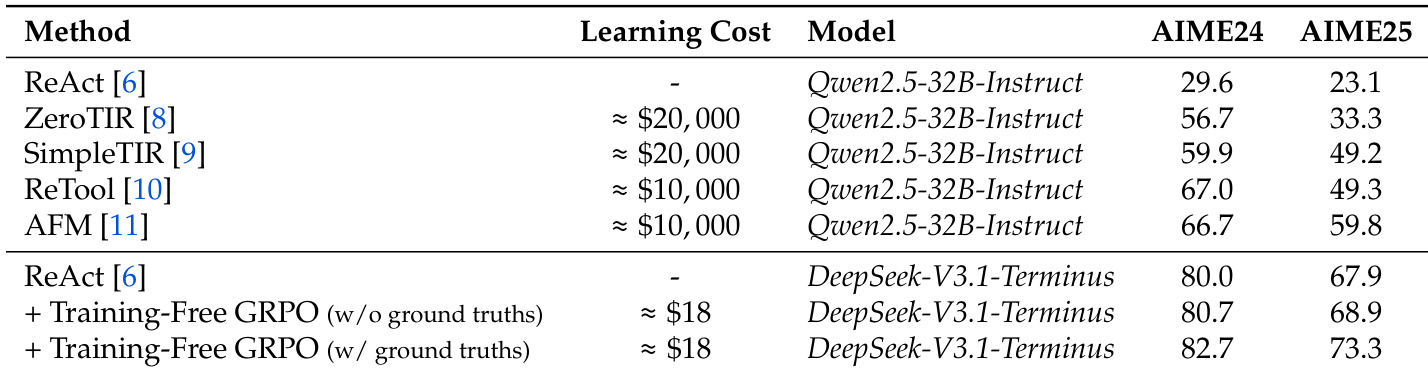
The authors evaluate the effectiveness of their Training-Free GRPO method on AIME 2024 and AIME 2025 benchmarks, showing that it achieves 80.7% and 68.9% accuracy respectively when trained without ground truths, and 82.7% and 73.3% when trained with ground truths, outperforming the ReAct baseline. These results demonstrate that the method enables significant performance improvements with minimal learning cost and no parameter updates.
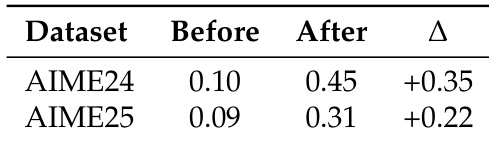
The authors use the Agent Practice module to improve agent performance on mathematical reasoning benchmarks, achieving a +0.35 absolute improvement on AIME 2024 and a +0.22 improvement on AIME 2025. Results show that the training-free GRPO method enables effective learning through experience accumulation without parameter updates, leading to significant gains in accuracy.
Results show that the Training-free GRPO method achieves consistent performance improvements across learning epochs on AIME 2024 and AIME 2025, with Mean@32 accuracy increasing from epoch 1 to 3. The number of tool calls decreases over epochs, indicating that the agent learns more efficient problem-solving strategies without parameter updates.
The authors compare two automated generation modes in Youtu-Agent, showing that the Meta-Agent mode achieves slightly higher task completion rates (68.75% vs. 65.00%) while maintaining comparable tool executability and configuration validity. Results indicate that both modes are effective, with the Meta-Agent mode demonstrating marginally better end-to-end performance.