Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
GARDO:報酬ハッキングを伴わずに拡散モデルを強化する
GARDO:報酬ハッキングを伴わずに拡散モデルを強化する
Haoran He Yuxiao Ye Jie Liu Jiajun Liang Zhiyong Wang Ziyang Yuan Xintao Wang Hangyu Mao Pengfei Wan Ling Pan
概要
テキストから画像への対応を強化するため、オンライン強化学習(RL)を用いた拡散モデルの微調整は、大きな可能性を示している。しかし、視覚タスクにおける真の目的関数を正確に定義することが依然として困難なため、モデルは真の目的を部分的にしか捉えられない代理報酬(proxy reward)を用いて最適化されることが多く、この不一致は報酬の悪用(reward hacking)を引き起こすことがある。すなわち、代理報酬は上昇する一方で、実際の画像品質は低下し、生成の多様性が崩壊する現象が生じる。一般的な対策として、参照方策(reference policy)に対する正則化を導入することで報酬の悪用を抑制する手法が用いられるが、こうした手法はサンプル効率を低下させ、新たな高報酬領域の探索を妨げることがある。なぜなら、参照方策自体が通常は最適ではないためである。サンプル効率、有効な探索、報酬の悪用の緩和という相互に拮抗する要求に対応するため、本研究では「多様性認識型最適化を備えたゲート付き適応的正則化(Gated and Adaptive Regularization with Diversity-aware Optimization, GARDO)」という汎用性の高いフレームワークを提案する。本研究の核心的な洞察は、正則化をすべてのサンプルに均一に適用する必要はなく、むしろ高い不確実性を示すサンプルのサブセットに対して選択的にペナルティを課すことが極めて効果的である点にある。探索の課題に対処するため、GARDOは適応的正則化機構を導入し、オンライン方策の能力に応じて参照モデルを定期的に更新することで、関連性のある正則化目標を維持する。また、RLにおけるモード崩壊(mode collapse)の問題に対処するため、高品質かつ高多様性を示すサンプルに対して報酬を強調することで、モードのカバレッジを促進しつつ最適化プロセスの安定性を損なわないようにしている。さまざまな代理報酬および未知の評価指標を用いた広範な実験により、GARDOが報酬の悪用を抑制し、生成の多様性を向上させながらもサンプル効率や探索能力を損なわないことが一貫して確認された。これにより、本手法の有効性とロバスト性が明確に示された。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kuaishou Technology, CUHK MMLab, and the University of Edinburgh propose GARDO, a novel framework that strengthens diffusion models through reward-free training, avoiding reward hacking by leveraging self-supervised consistency regularization, enabling more reliable and robust image generation in real-world applications.
Key Contributions
-
Fine-tuning diffusion models with proxy rewards for text-to-image generation often leads to reward hacking, where models optimize unreliable reward signals at the expense of image quality and diversity, due to the inherent limitations of model-based and rule-based reward functions in capturing true human preferences.
-
GARDO introduces a gated regularization mechanism that selectively applies KL penalties only to high-uncertainty samples—identified via ensemble reward disagreement—while allowing the rest to explore freely, and an adaptive reference model that evolves with the policy to maintain effective exploration and avoid stagnation.
-
Experiments across multiple proxy rewards and unseen evaluation metrics show GARDO consistently mitigates reward hacking, improves generation diversity, and maintains high sample efficiency, demonstrating robust performance without compromising on exploration or stability.
Introduction
Fine-tuning diffusion models for text-to-image generation using reinforcement learning (RL) is critical for aligning outputs with human preferences, yet it faces a fundamental challenge: proxy reward models—whether learned from finite human feedback or rule-based—are imperfect approximations of true human judgment. This misalignment often leads to reward hacking, where models optimize for high proxy scores at the cost of degraded image quality and reduced diversity. Prior solutions rely on KL regularization against a static reference policy to prevent over-optimization, but this approach hampers sample efficiency and stifles exploration by constraining the policy to stay close to a suboptimal baseline. The authors propose GARDO, a framework that overcomes these limitations through three key innovations. First, it introduces gated regularization that applies penalties only to a small subset of high-uncertainty samples—identified via disagreement among an ensemble of reward models—allowing the majority of samples to be optimized freely. Second, it employs adaptive regularization by periodically updating the reference model to match the evolving online policy, maintaining a relevant and effective regularization target. Third, it incorporates diversity-aware advantage shaping to amplify rewards for high-quality, diverse samples, promoting mode coverage without destabilizing training. Experiments across multiple proxy rewards and unseen metrics demonstrate that GARDO effectively mitigates reward hacking while preserving sample efficiency, exploration, and diversity.
Method
The authors leverage a reinforcement learning (RL) framework to optimize diffusion-based generative models, treating the denoising process as a Markov Decision Process (MDP). The overall framework begins with a policy model πθ, which is conditioned on a textual prompt and generates images through a multi-step denoising process. At each step t, the state st is defined as (c,t,xt), where c is the prompt, t is the current time step, and xt is the noisy image. The policy πθ predicts the action at, which corresponds to the denoised image xt−1, effectively modeling the transition from xt to xt−1. The reward function R(st,at) is non-zero only at the final step t=0, where it evaluates the quality of the generated image x0 based on a proxy reward function r(x0,c). The transition dynamics are deterministic, and the initial state sT is sampled from a predefined distribution ρ0. The objective is to learn an optimal policy π∗ that maximizes the expected cumulative reward over the trajectory.

The policy optimization is performed using a variant of the Generalized Reward Policy Optimization (GRPO) algorithm. During each training iteration, a batch of prompts is sampled, and for each prompt, G images are generated by rolling out the policy from a random noise input. The reward for each generated image x0i is computed, and the advantage Ati is estimated within the group of G samples. The policy is updated using a surrogate objective that combines a clipped importance sampling ratio with a KL divergence regularization term. This objective is designed to ensure stable policy updates while preventing large deviations from the behavior policy used for data collection.

To address the issue of reward hacking and mode collapse, the authors introduce a gated KL regularization mechanism. This mechanism selectively applies the KL penalty only to samples that exhibit high uncertainty in their proxy reward. The uncertainty is quantified by comparing the win rate of a sample's proxy reward R~ against the average win rate of the same sample across an ensemble of auxiliary reward models {R^n}n=1K. This approach ensures that regularization is applied only to samples where the proxy reward is unreliable, thereby preventing unnecessary constraints on the policy. Furthermore, an adaptive KL regularization scheme is employed, where the reference policy πref is periodically reset to the current policy πθ to maintain its relevance and prevent the KL penalty from dominating the loss and stalling exploration.
To promote sample diversity, the authors propose a diversity-aware advantage shaping strategy. This strategy reshapes the advantage function by multiplying it with a diversity score di for each generated sample. The diversity score is computed as the cosine distance to the nearest neighbor in the semantic feature space, where features are extracted using the DINOv3 model. This reshaping is applied only to samples with positive advantages, ensuring that the model is rewarded for generating high-quality and novel images. The overall training process is summarized in Algorithm 1, which integrates the policy model, reward computation, uncertainty estimation, advantage computation, diversity estimation, and the adaptive KL regularization mechanism.
Experiment
- GARDO's multiplicative advantage reshaping within positive samples improves diversity and enables discovery of low-probability modes, such as a central cluster with 0.1× reference model density, demonstrating robust exploration.
- Removing standard deviation in advantage normalization mitigates reward hacking by preventing amplification of minor reward differences, improving stability and generalization without sacrificing sample efficiency.
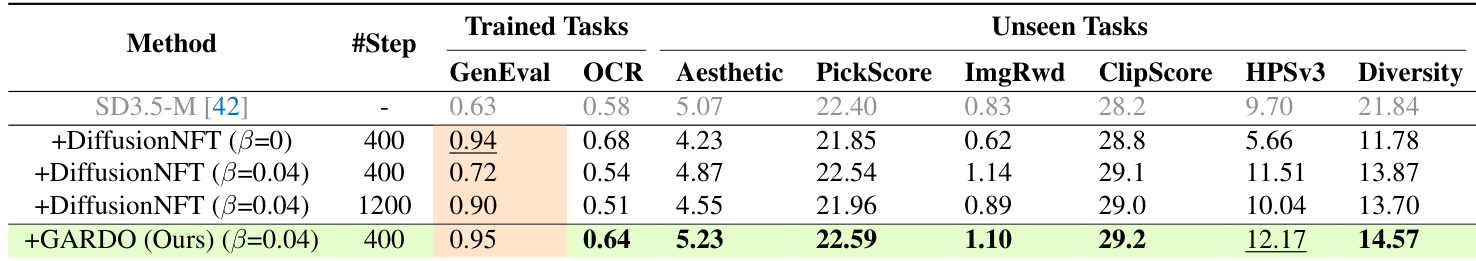
- On GenEval and OCR benchmarks, GARDO achieves proxy rewards comparable to KL-free baselines while significantly outperforming them on unseen metrics (Aesthetic, PickScore, HPSv3) and diversity, with diversity increasing from 19.98 to 24.95.
- GARDO’s gated and adaptive KL regularization enhances sample efficiency, matching KL-free baselines’ convergence speed while effectively suppressing reward hacking, with only ~10% of samples penalized.
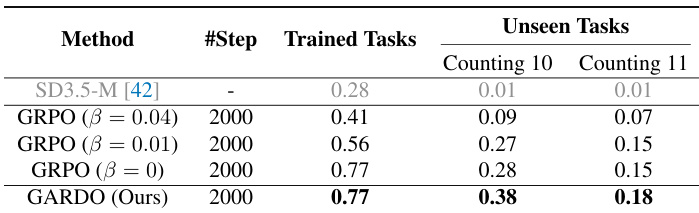
- On challenging counting tasks (10–11 objects), GARDO significantly improves accuracy over base models and vanilla GRPO, demonstrating emergence of novel behaviors beyond the pre-trained distribution.
- GARDO generalizes across different base models (Flux.1-dev, SD3.5-Medium) and RL algorithms (DiffusionNFT), consistently achieving superior trade-off between sample efficiency and o.o.d. generalization, outperforming multi-reward training methods in both proxy and unseen rewards.
The authors use a counting task to evaluate the ability of different methods to generate images with novel object counts beyond the training distribution. Results show that GARDO significantly improves counting accuracy for 10 and 11 objects compared to baseline GRPO methods, which fail to generalize to these unseen counts.
The authors use a table to compare the performance of their proposed method, GARDO, against various baselines on both proxy and unseen tasks. Results show that GARDO achieves the highest scores on both proxy rewards and unseen metrics, particularly excelling in diversity and generalization, while maintaining high sample efficiency. The method outperforms baselines that either suffer from reward hacking or are overly conservative due to strong regularization.
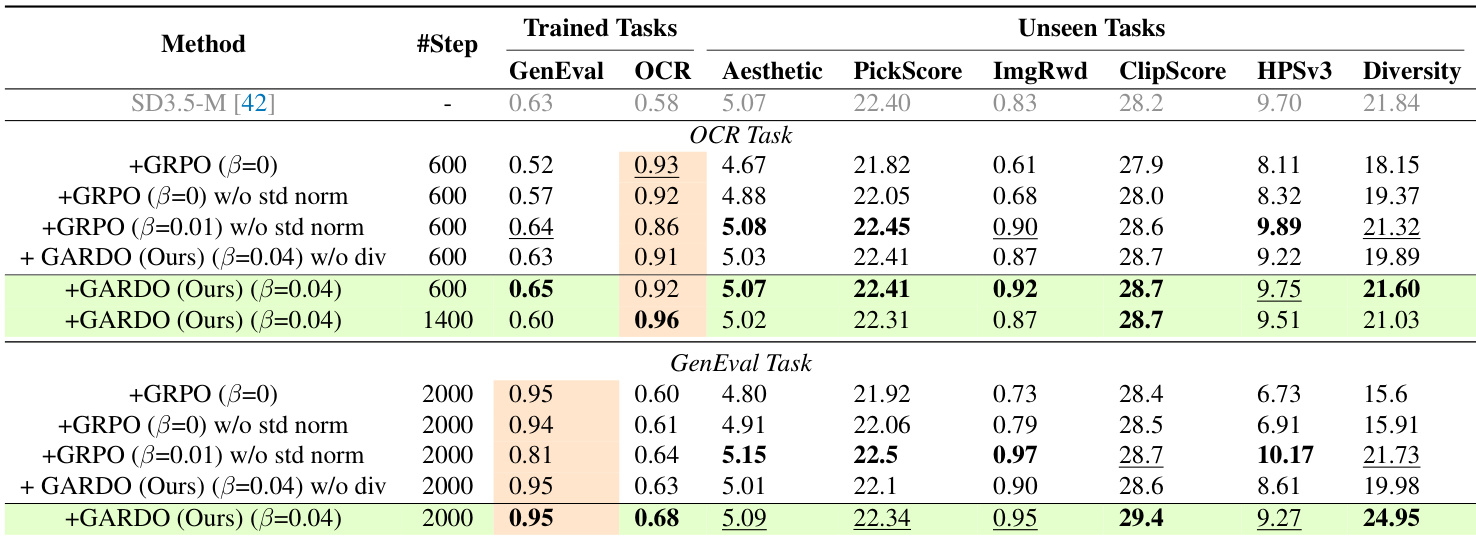
The authors use a table to compare the performance of their proposed method, GARDO, against several baselines across proxy and unseen tasks. Results show that GARDO achieves the highest scores on both proxy rewards and unseen metrics, including GenEval, OCR, Aesthetic, PickScore, and diversity, while maintaining high sample efficiency. This demonstrates that GARDO effectively mitigates reward hacking and improves generalization without sacrificing performance on the primary task.