Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
LiveTalk:改善されたオンポリシー蒸留を用いたリアルタイムマルチモーダル相互作用型ビデオディフュージョン
LiveTalk:改善されたオンポリシー蒸留を用いたリアルタイムマルチモーダル相互作用型ビデオディフュージョン
Ethan Chern Zhulin Hu Bohao Tang Jiadi Su Steffi Chern Zhijie Deng Pengfei Liu
概要
拡散モデルを用いたリアルタイム動画生成は、汎用的なマルチモーダル相互作用型AIシステムの構築にとって不可欠である。しかし、拡散モデルにおける反復プロセスにより、双方向アテンションを用いてすべての動画フレームを同時にノイズ除去する手法は、リアルタイム相互作用を妨げる。既存の知識蒸留(distillation)手法はモデルを自己回帰型にし、サンプリングステップ数を削減することでこの問題を緩和しているが、主にテキストから動画生成に焦点を当てており、人間とAIの相互作用が自然でない、かつ効率的でないという課題が残っている。本論文では、テキスト、画像、音声を含むマルチモーダルなコンテキスト条件下でリアルタイムな相互作用型動画拡散を実現することを目的としている。特に、最先端のオンポリシー蒸留手法であるSelf Forcingが、マルチモーダル条件付き入力において課題(フレッシャー、黒フレーム、品質低下などの視覚的アーティファクト)に直面することに着目し、オンポリシー最適化における条件入力の品質、初期化、スケジュールの改善に重点を置いた新たな蒸留手法を提案する。HDTF、AVSpeech、CelebV-HQといったマルチモーダル条件付き(音声、画像、テキスト)アバター動画生成ベンチマークにおいて、提案手法は、サイズが同程度またはそれ以上である双方向ベースラインと同等またはそれ以上の視覚品質を達成しつつ、推論コストとレイテンシを20倍削減した。さらに、本モデルを音声言語モデルおよび長時間動画推論技術であるAnchor-Heavy Identity Sinksと統合し、リアルタイムマルチモーダル相互作用型アバターシステム「LiveTalk」を構築した。独自に構築した複数ターン相互作用ベンチマークにおけるシステムレベル評価では、LiveTalkは最先端モデル(Sora2、Veo3)を上回る複数ターン動画の整合性とコンテンツ品質を実現するとともに、応答レイテンシを1〜2分からリアルタイム生成にまで短縮し、人間とAIのシームレスなマルチモーダル相互作用を可能にした。
One-sentence Summary
The authors, affiliated with SII, SJTU, and GAIR, propose a distilled multimodal diffusion model enabling real-time interactive video generation conditioned on text, image, and audio, achieving 20× faster inference than bidirectional baselines while maintaining high visual quality through improved on-policy distillation with better input conditioning and optimization scheduling; integrated into LiveTalk, the system enables seamless, low-latency, multi-turn human-AI interaction with superior coherence and content quality compared to Sora2 and Veo3.
Key Contributions
-
The paper addresses the challenge of real-time interactive video generation by enabling multimodal-conditioned diffusion models (text, image, audio) to operate efficiently in autoregressive mode, overcoming the high latency of bidirectional, many-step diffusion models that hinder real-time human-AI interaction.
-
It introduces an improved distillation framework that stabilizes on-policy training under complex multimodal conditions through refined input conditioning, converged ODE initialization, and an aggressive optimization schedule, significantly reducing visual artifacts like flickering and black frames while preserving high-fidelity output.
-
Evaluated on HDTF, AVSpeech, and CelebV-HQ benchmarks, the distilled model achieves 20× faster inference and sub-second latency compared to bidirectional baselines, and when integrated into the LiveTalk system with Anchor-Heavy Identity Sinks, it enables real-time, long-form, coherent multi-turn avatar interactions outperforming Sora2 and Veo3 in both quality and responsiveness.
Introduction
Real-time multimodal interactive video generation is critical for building natural, responsive AI avatars capable of engaging in dynamic conversations using text, image, and audio inputs. However, standard diffusion models rely on computationally expensive, bidirectional denoising across all frames, leading to latencies of 1–2 minutes—prohibitive for real-time interaction. While prior distillation methods enable faster autoregressive generation, they primarily target text-to-video and struggle with multimodal conditioning, resulting in visual artifacts like flickering and degraded quality. The authors address this by introducing an improved on-policy distillation framework that stabilizes training under complex multimodal conditions through three key enhancements: high-quality, motion-focused multimodal conditioning; converged ODE initialization before on-policy training; and aggressive optimization schedules with tuned classifier guidance. Their distilled model achieves 20× faster inference with sub-second latency while matching or exceeding the visual quality of larger, bidirectional baselines. Building on this, they develop LiveTalk, a real-time interactive avatar system that integrates audio language models and a novel Anchor-Heavy Identity Sinks technique to maintain long-term visual consistency. System evaluations show LiveTalk outperforms Sora2 and Veo3 in multi-turn coherence, content quality, and response latency, enabling seamless, human-like multimodal interaction.
Dataset
- The dataset is composed of nine distinct evaluation dimensions designed to assess visual interaction performance and interaction content quality in multimodal models.
- Each dimension is evaluated using structured prompts tailored to specific scoring criteria, enabling consistent and measurable assessment across tasks.
- The evaluation framework is implemented through a multi-round protocol, where a Vision-Language Model (VLM) processes each prompt and generates responses for scoring.
- The dataset supports both qualitative and quantitative analysis, with detailed implementation guidelines provided for reproducibility.
- The data is used in the model training and evaluation pipeline to refine interaction capabilities, with mixture ratios and split configurations optimized for balanced representation across dimensions.
- No explicit cropping or metadata construction is applied; instead, the focus is on prompt engineering and response alignment to ensure high-fidelity assessment of interaction dynamics.
Method
The authors leverage a two-stage distillation framework to transform a bidirectional, many-step diffusion model into a causal, few-step autoregressive (AR) model suitable for real-time video generation. The overall architecture, as illustrated in the figure below, integrates a distilled video diffusion model with a large language model to form a complete real-time multimodal interactive system. The core of the method involves an ODE initialization stage followed by on-policy distillation using distribution matching distillation (DMD).
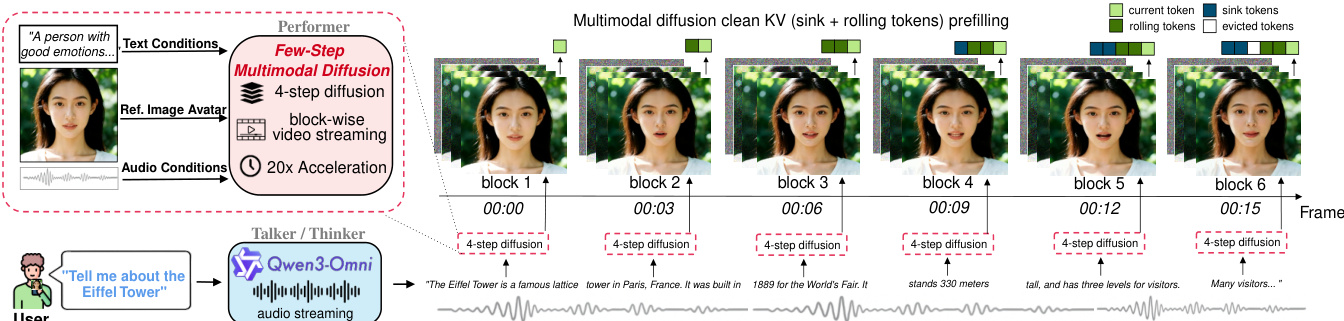
During ODE initialization, the student model is trained to predict the clean latent frames x0 from a few sampled timesteps of the teacher's denoising trajectory. This is achieved by minimizing the trajectory distillation loss, which encourages the student to match the teacher's output at specific time steps. The student model is designed to generate video in a block-wise manner, where each block consists of multiple latent frames, enabling efficient streaming. The architecture supports causal attention and key-value (KV) cache for autoregressive generation, allowing the model to maintain visual consistency across blocks by prefiling clean KV cache from previous blocks.
Following ODE initialization, the model undergoes on-policy distillation with DMD to mitigate exposure bias. This stage involves a generator gϕ and a trainable critic sψ, with a frozen teacher score network sθ. The critic learns to track the generator's evolving distribution by minimizing a denoising objective, while the generator is updated to align its output with the teacher's score. The gradient update for the generator incorporates the difference between the teacher and critic scores, ensuring the generator learns to produce outputs that match the teacher's distribution. This process is conducted using self-generated rollouts, where the model generates sequences that are then used for training.
The system further incorporates several improvements to enhance the distillation process. Multimodal conditions are refined to provide high-quality training signals, with specific curation strategies applied to image and text inputs based on dataset characteristics. ODE initialization is trained to convergence to establish a robust starting point, and an aggressive learning rate schedule is employed during DMD to maximize learning within the limited effective window. These enhancements ensure strong audio-visual alignment and high visual quality in the generated videos.
The distilled model is integrated into a real-time interactive system, where it functions as the performer module, rendering synchronized talking avatars. The system uses overlapped windowing for audio conditioning to provide rich acoustic context while maintaining real-time responsiveness. To preserve speaker identity over long video streams, a training-free method called Anchor-Heavy Identity Sinks (AHIS) is employed, which allocates a portion of the KV cache as identity anchors to store high-fidelity early frames. Additionally, pipeline parallelism is used to execute diffusion denoising and VAE decoding in parallel, reducing per-block latency and enabling non-stalling streaming.
Experiment
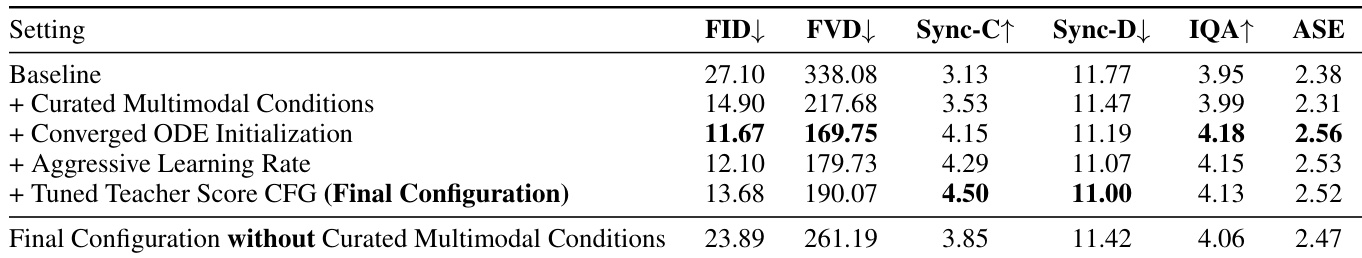
- Identified three key issues in existing distillation recipes: data quality problems due to low-quality reference images, insufficient ODE initialization leading to unstable training, and a limited learning window causing premature degradation in multimodal video diffusion distillation.
- Proposed and validated four improvements: curated high-quality multimodal conditions, converged ODE initialization (20k steps), aggressive learning rate scheduling, and tuned teacher score CFG guidance, which collectively eliminate visual degradation and improve stability.
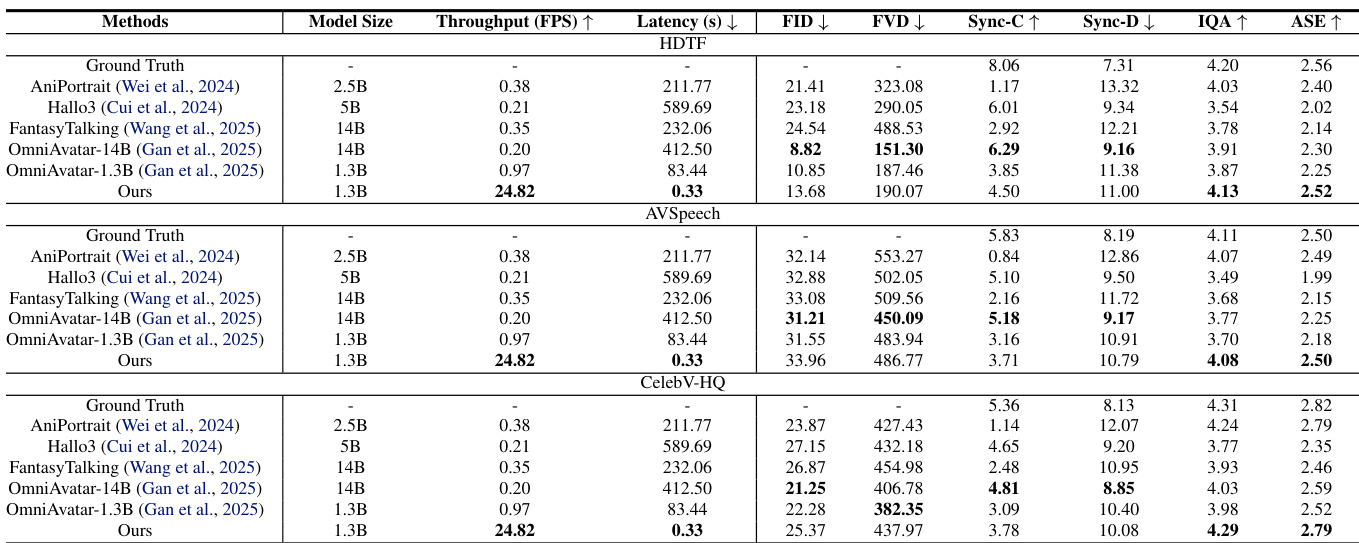
- On the HDTF, AVSpeech, and CelebV-HQ benchmarks, the distilled model achieves comparable or superior visual quality (FID, FVD, IQA, ASE), lip-sync accuracy (Sync-C/D), and conversational coherence to larger bidirectional models (e.g., OmniAvatar-1.3B, 14B), while delivering 25× higher throughput (24.82 FPS vs. 0.97 FPS) and 250× faster first-frame latency (0.33s vs. 83.44s).
- In multi-round interaction evaluation using a VLM-based benchmark, the model outperforms Veo3 and Sora2 in multi-video coherence and content quality, demonstrating superior temporal consistency and contextual awareness through AR generation with KV cache and Qwen3-Omni memory mechanisms.
- Ablation studies confirm that each proposed component contributes incrementally to performance, with curated data and converged ODE initialization being essential for stable and high-quality distillation.
The authors conduct an ablation study to evaluate the impact of four key improvements on distillation quality, showing that each component contributes incrementally to performance. The final configuration achieves the best results across all metrics, with the most significant improvements in FID, FVD, Sync-C, and Sync-D, while the absence of curated multimodal conditions leads to a substantial drop in quality, highlighting the critical role of data quality.
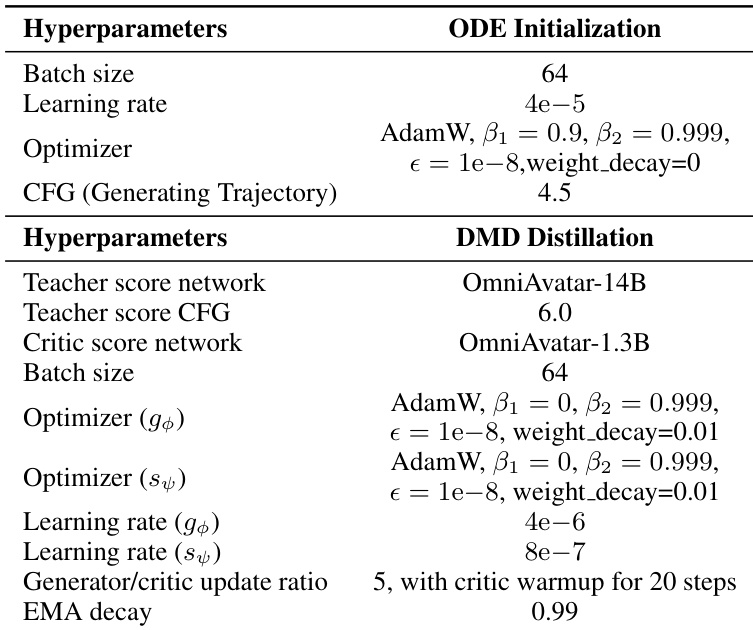
The authors use a two-stage distillation pipeline consisting of ODE initialization and DMD distillation, with distinct hyperparameters for each stage. Results show that the DMD distillation stage employs a 5:1 update ratio between the generator and critic networks, with the critic network updated for 20 steps before generator training begins, and uses an EMA decay of 0.99 from step 200 onward.
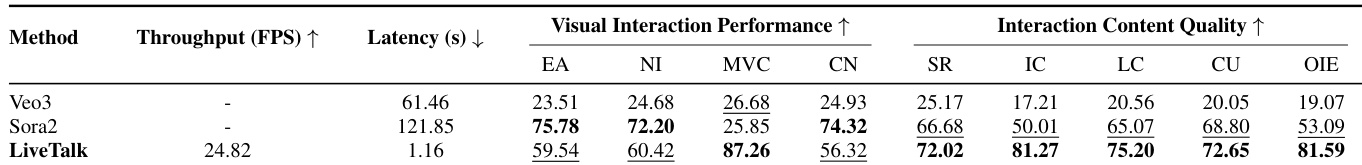
The authors evaluate their distilled model against baselines Veo3 and Sora2 on a multi-round interaction benchmark, showing that LiveTalk outperforms both in multi-video coherence and content quality metrics while maintaining competitive performance on other visual interaction dimensions. LiveTalk achieves this through AR generation with KV cache for visual memory and a Qwen3-Omni module for textual memory, enabling coherent multi-turn generation with significantly lower latency and higher throughput.
The authors use a distilled model to evaluate performance against several baselines on multimodal avatar generation benchmarks, achieving comparable or superior visual quality, aesthetics, and lip-sync accuracy to larger bidirectional models while significantly improving throughput and latency. Results show that the distilled model outperforms or matches the performance of models like OmniAvatar-1.3B and OmniAvatar-14B across in-domain and out-of-domain datasets, with a 25× speedup in throughput and over 250× faster first-frame latency.