Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
SurgWorld:ワールドモデリングを用いた動画からの外科ロボット方策学習
SurgWorld:ワールドモデリングを用いた動画からの外科ロボット方策学習
概要
データの不足は、完全に自律的な手術ロボットの実現に向けた根本的な障壁のままです。大規模な視覚言語行動(VLA)モデルは、多様な領域から得られた対応する動画と行動データを活用することで、家庭内および産業用の操作タスクにおいて優れた汎化性能を示していますが、手術ロボティクス分野では、視覚的観測と正確なロボット運動学データを両方含むデータセットが極めて乏しいという課題に直面しています。一方で、膨大な数の手術動画が存在する一方、それらには対応する行動ラベルが付与されておらず、模倣学習やVLAモデルの訓練を直接行うことが困難です。本研究では、手術用物理AI向けに設計された「SurgWorld」という世界モデルを用いて、ポリシーモデルの学習に取り組み、この課題の緩和を目指します。具体的には、手術ロボット専用に詳細な行動記述を含む「Surgical Action Text Alignment(SATA)」データセットを構築しました。さらに、最新の物理AI世界モデルとSATAデータセットを基に「SurgeWorld」を構築し、多様で汎化性に富み、現実的な手術動画の生成が可能になりました。また、本研究では、合成手術動画から仮想運動学(pseudokinematics)を逆動力学モデルを用いて推定するという、初めてのアプローチを採用し、合成された対応する動画・行動データを生成しました。実験の結果、これらの拡張データを用いて訓練された手術用VLAポリシーは、実際の手術ロボットプラットフォーム上で、実データのみで訓練されたモデルと比較して顕著に優れた性能を示しました。本研究のアプローチは、ラベルの付与されていない手術動画の豊富な蓄積と生成型世界モデリングを活用することで、自律的で汎化性に富み、データ効率の高い手術ロボットポリシーの実現に向けたスケーラブルな道筋を提示しています。
One-sentence Summary
The authors, from NVIDIA, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sung Kyun Kwan University, Wenzhou Medical University, National University of Singapore, and Ruijin Hospital, propose SurgWorld—a novel framework that leverages a large-scale surgical world model trained on the curated SATA dataset to generate high-fidelity synthetic video-action pairs via inverse dynamics modeling, enabling data-efficient and generalizable training of vision-language-action policies for surgical robots, significantly improving performance over real-data-only baselines in needle manipulation tasks.
Key Contributions
- Data scarcity in surgical robotics, particularly the lack of paired video-kinematic data, hinders the training of generalizable robot policies, despite the abundance of unlabeled surgical videos.
- The authors introduce SurgWorld, a diffusion-based world model trained on the curated SATA dataset, which generates photorealistic, task-consistent surgical videos and enables the first use of inverse dynamics models to infer pseudo-kinematics from synthetic video rollouts.
- Evaluations on a real surgical robot show that a VLA policy trained with both real and synthetic data from SurgWorld achieves significantly lower trajectory prediction error and superior performance compared to models trained only on real demonstrations.
Introduction
The authors address the critical challenge of data scarcity in autonomous surgical robotics, where high-fidelity paired video-kinematic data is extremely limited due to ethical, logistical, and safety constraints. While vision-language-action (VLA) models have enabled generalizable manipulation in household and industrial settings, their application in surgery is hindered by the lack of large-scale, annotated datasets that link visual observations with precise robot actions. Prior efforts to generate synthetic data through physics-based simulators suffer from significant visual and dynamic domain gaps, while existing surgical video generation models are often task-specific and lack robust text-action alignment. To overcome these limitations, the authors introduce SurgWorld, a surgical world model built on a curated, expert-annotated dataset called SATA, which contains 2,447 video clips with detailed action descriptions across 8 procedures. They leverage this model to generate photorealistic, task-consistent surgical videos and, for the first time, use an inverse dynamics model to infer pseudo-kinematics from synthetic video rollouts, creating augmented paired video-action data. This synthetic data enables training of a surgical VLA policy that significantly outperforms models trained only on real demonstrations, demonstrating a scalable, data-efficient path toward autonomous surgical skill acquisition by bridging the gap between abundant unlabeled surgical videos and robot control.
Dataset
- The SATA dataset consists of 2,447 expert-annotated video clips totaling over 300,000 frames, spanning 8 surgery types and four fundamental surgical actions: needle grasping (689 clips), needle puncture (989 clips), suture pulling (475 clips), and knotting (294 clips).
- Data is sourced from credentialed YouTube surgical channels and public datasets including GraSP, SAR-RARP50, Multiypass140, SurgicalActions160, Auto-Laparo, and HeiCo, with annotations re-processed to ensure consistency and granularity.
- Each clip is paired with a detailed textual description capturing spatial relationships between instruments, anatomical structures, and instrument-tissue interactions—e.g., "The left needle driver punctures the right side of the patient's dorsal venous complex."
- The dataset is designed for physical AI, emphasizing fine-grained action labels and precise descriptions of tool-tissue dynamics, distinguishing it from semantic-focused datasets like SurgVLM-DB.
- For model training, SATA is used as a primary source for aligning video and text, with a mixture ratio that balances the four action categories to ensure representative coverage during training.
- The authors apply a cropping strategy to focus on the region of interest around the surgical site, ensuring consistent visual context across clips.
- Metadata is constructed to include action labels, anatomical context, instrument types, and interaction types, enabling structured learning of surgical procedures.
- Real-world trajectory data includes 60 successful human-teleoperated demonstrations of the "Needle Pickup and Hand-Over" task on a rubber pad, with synchronized endoscopic video (avg. 217 frames) and 20-dimensional action kinematics.
- Action kinematics are represented as a 20D vector encoding position, orientation (6D rotation), and gripper state for both left and right robotic arms, all relative to the endoscope frame for view consistency.
- An additional 66 out-of-domain episodes (approx. 60k frames) of general robot movements are used to pretrain a foundational inverse dynamics model (IDM), enabling transferable motion understanding across tasks.
- The IDM and the vision-language action model (GR00T N1.5) share a similar architecture, but the IDM operates without text prompts or robot state inputs, focusing solely on motion prediction from visual input.
Method
The authors leverage the Cosmos-Predict2.5 model, a large-scale video world model pretrained on diverse robotic and embodied datasets, as the foundation for their surgical world model, SurgWorld. This model employs a diffusion-based latent video prediction framework with a transformer backbone to simulate high-fidelity spatiotemporal dynamics. To adapt it to the surgical domain, the model is fine-tuned on the SATA dataset, which includes real-world surgical trajectories and detailed annotations. The adaptation process conditions the model solely on the initial observed frame I0 and a text prompt, enabling it to predict future trajectories that capture the temporal evolution of the surgical scene. This includes modeling instrument-tissue interactions, limited field-of-view motion, and constrained articulation patterns unique to endoscopic surgery. To ensure parameter efficiency and preserve the model's general video modeling capabilities, Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is applied by inserting modules into the transformer's attention and feed-forward layers. The resulting model, denoted as Wθ, generates video rollouts I^1:T=Wθ(I0), where a spatiotemporal encoder processes the initial frame, a transformer-based latent dynamics module models temporal evolution, and a decoder reconstructs the predicted frames.

The training of the surgical video world model is conducted using the Flow Matching (FM) formulation, which provides a direct and stable training signal in latent space. The method defines a velocity-based target by interpolating between the original data sample I and a noise vector ϵ at a timestep t, resulting in the interpolated latent It=(1−t)I+tϵ. The corresponding ground-truth velocity is vt=ϵ−I. The model predicts this velocity via a network uθ(It,t,c), where c represents the conditioning frame I0 and the text prompt. The training objective is the mean squared error (MSE) between the predicted and ground-truth velocities, formulated as L(θ)=EI,ϵ,c,t∥uθ(It,t,c)−vt∥Q2. This approach enhances optimization stability and sample quality.

To bridge the gap between the world model and the specific robot embodiment, an inverse dynamic model (IDM) is constructed. The IDM takes two frames from the same video, separated by 16 frames, as input and predicts the robot actions for every frame between them. This model is trained to label the synthetic video rollouts generated by the world model with pseudo action kinematics. The IDM architecture, as shown in the figure below, consists of a diffusion transformer with a SigLIP-2 vision encoder, an action encoder, and an action decoder. The model processes the two input frames and the corresponding noisy actions to predict the intermediate actions.

The final policy for the robot is learned using the GR00T Vision Language Action Model, which is also based on a diffusion transformer. This model takes the current frame, a text prompt, and the robot state as inputs to predict future actions. The architecture includes a vision language model, a state encoder, and an action encoder, all feeding into the diffusion transformer to generate the predicted actions. The IDM and the GR00T policy model share a similar backbone but differ in their inputs and outputs, with the IDM focusing on action prediction from video frames and the GR00T model incorporating robot state for policy learning. The synthetic videos and pseudo kinematics generated by the world model and IDM are used to train the GR00T policy, enabling it to learn from both real and synthetic data.
Experiment
- Evaluated SurgWorld on video generation quality using the curated SATA dataset, demonstrating superior perceptual fidelity and semantic coherence over zero-shot and coarse-prompt baselines, achieving the lowest FVD and highest VBench scores (DD, IQ, OC), with qualitative results showing correct tool and action generation even in challenging scenarios.
- Validated new behavior generalization by generating diverse surgical sequences (e.g., multi-time needle handover) from novel textual prompts, showing strong text–video alignment and anatomically plausible, temporally consistent motions despite no explicit training on such compositions.
- Human expert evaluation confirmed SurgWorld’s clinical realism, achieving the highest ratings across text-video alignment, tool consistency, and anatomical plausibility, outperforming zero-shot and action-category variants in surgical fidelity.
- Demonstrated effective few-shot adaptation on 5 real surgical trajectories, where SurgWorld pretrained on SATA achieved a 73.2% task success rate and lowest FVD, significantly outperforming direct finetuning from the original model, highlighting improved data efficiency and robustness.
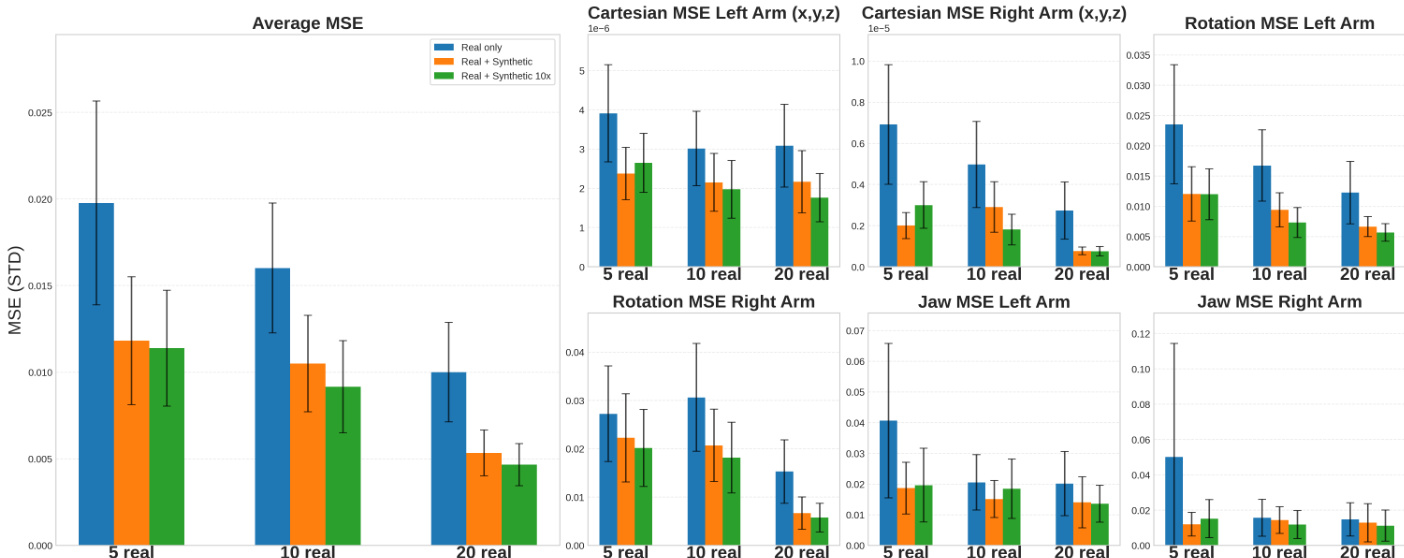
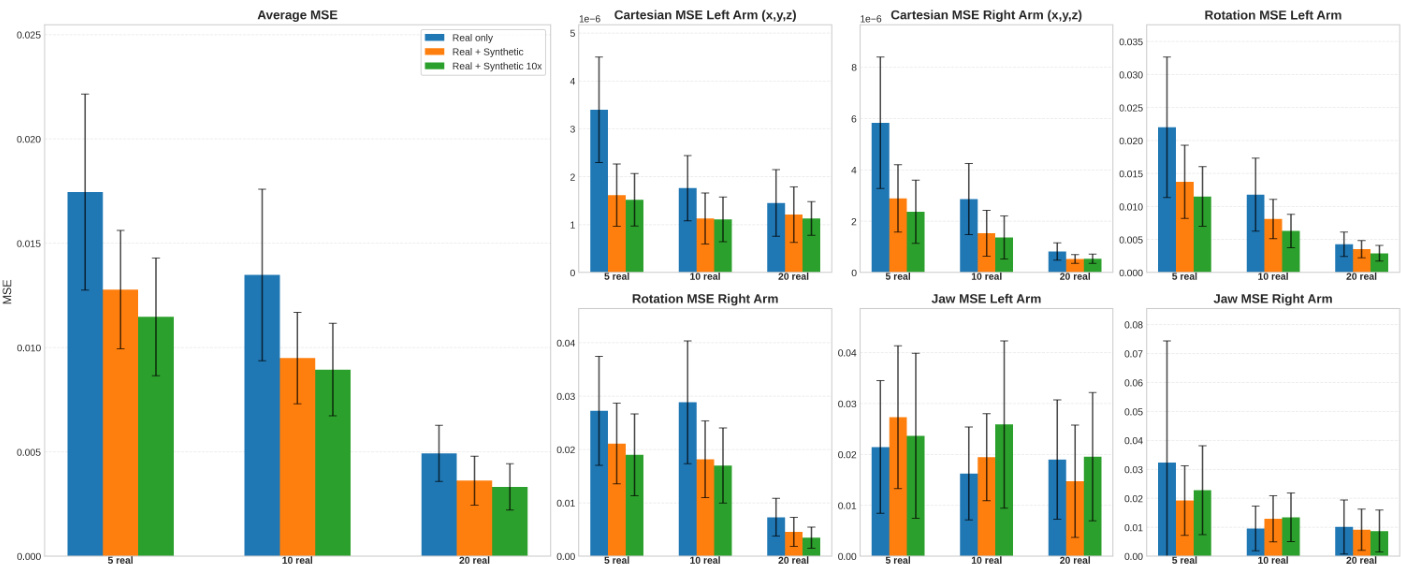
- Showed that synthetic data from SurgWorld enhances downstream robotic policy learning: using 56 or 560 synthetic videos reduced trajectory MSE across cartesian, rotation, and jaw actions compared to real-only training, with consistent improvements across varying real data sizes and policy models (GR00T, π₀.₅).
- Confirmed that single-view synthetic videos from SurgWorld improve multi-view policy performance even when real data includes multiple camera views, and that benefits persist across different training hyperparameters and VLA architectures.
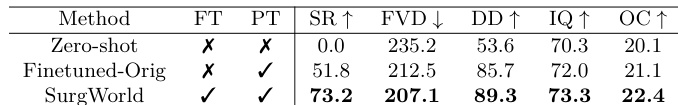
The authors evaluate three variants of the Surgical World Model on the SATA dataset, comparing Zero-Shot, Finetuned-Orig, and SurgWorld. Results show that SurgWorld achieves the highest task success rate, lowest FVD, and best scores across all VBench metrics, indicating superior video quality and task performance.
The authors use the table to show the distribution of video clips across different surgical actions in the SATA dataset, highlighting that the dataset is heavily skewed toward certain procedures like Needle Grasping and Suture Pulling. This imbalance reflects the focus on specific surgical tasks in the data collection process, with some actions such as Knotting and Needle Puncture being less represented.

The authors evaluate the impact of synthetic data on robotic policy performance by comparing trajectory prediction errors across different training configurations. Results show that incorporating synthetic videos significantly reduces mean squared error (MSE) across all action components—cartesian, rotation, and jaw—compared to training with real data alone, with the largest improvements observed when using 10× more synthetic data. This demonstrates that synthetic data enhances policy learning, particularly with limited real-world demonstrations.
The authors evaluate the impact of synthetic data on robotic policy performance by comparing trajectory prediction errors across different training configurations. Results show that incorporating synthetic videos significantly reduces the mean squared error (MSE) for both Cartesian and rotational actions, with the best performance achieved when using 560 synthetic videos (Real + Synthetic 10x), particularly with 5 real trajectories. This improvement holds across varying numbers of real training data and different finetuning steps, demonstrating that synthetic data enhances policy learning even with limited real-world examples.
Results show that the SurgWorld model achieves the best performance across all metrics, with the lowest FVD and highest scores in dynamic degree, imaging quality, and overall consistency compared to the zero-shot and action-category baselines. This indicates that fine-grained, expert-curated textual prompts significantly improve perceptual realism and semantic coherence in surgical video generation.
