Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
HiStream:冗長性除去ストリーミングを用いた効率的な高解像度ビデオ生成
HiStream:冗長性除去ストリーミングを用いた効率的な高解像度ビデオ生成
概要
高解像度動画生成は、デジタルメディアや映画分野において極めて重要であるが、拡散モデルの二次時間計算量に起因する計算上のボトルネックにより、実用的な推論が困難である。この課題に対処するため、本研究では、空間、時間、時刻の3軸にわたり冗長性を体系的に低減する効率的な自己回帰型フレームワーク「HiStream」を提案する。具体的には、(i) 空間的圧縮:高解像度での精緻化の前に低解像度でノイズ除去を行い、キャッシュされた特徴量を活用する;(ii) 時間的圧縮:固定サイズのアンカー・キャッシュを用いたチャンク単位の戦略により、推論速度の安定性を確保する;(iii) 時刻的圧縮:キャッシュ条件付きの後続チャンクに対して、少ないノイズ除去ステップを適用する。1080pベンチマークにおいて、本研究の主なHiStreamモデル(i+ii)は最先端の視覚品質を達成しつつ、Wan2.1ベースラインと比較してノイズ除去が最大76.2倍高速化され、品質の低下は無視できる程度にとどまる。さらに高速なバージョンであるHiStream+は、3つの最適化(i+ii+iii)を統合し、ベースライン比で107.5倍の加速を実現。速度と品質のバランスが優れており、高解像度動画生成の実用性とスケーラビリティを両立させるものである。
One-sentence Summary
Meta AI and Nanyang Technological University researchers propose HiStream, an efficient autoregressive framework that reduces computational redundancy in high-resolution video generation across spatial (dual-resolution caching), temporal (anchor-guided sliding window), and timestep (asymmetric denoising) axes, achieving 76.2-107.5× faster denoising than Wan2.1 while maintaining state-of-the-art visual quality for practical 1080p video synthesis.
Key Contributions
- Existing DiT-based video generation models suffer from computational bottlenecks at high resolutions due to misaligned positional encodings causing blurriness, unlike UNet-based approaches that face receptive-field limitations.
- HiStream introduces an anchor-guided sliding window for temporal processing and dual-resolution caching with asymmetric denoising, enabling fixed-size KV cache usage and spatially consistent chunk-based generation without additional training.
- The framework leverages consistency distillation via Flow Matching on a DiT-based autoregressive baseline (WAN-2.1), adapting techniques like persistent content anchors to maintain efficiency and quality during high-resolution video synthesis.
Introduction
Video diffusion models have shifted from UNet-based architectures to scalable Diffusion Transformers (DiTs) for improved video generation, yet high-resolution synthesis remains challenging due to data scarcity and computational costs. Prior tuning-free methods primarily target UNet limitations like receptive-field artifacts but fail to address DiT-specific issues such as positional encoding misalignment causing blurriness at high resolutions, while two-stage super-resolution pipelines often sacrifice detail fidelity. Additionally, slow inference speeds persist despite KV caching techniques adapted from LLMs for temporal attention. The authors leverage attention sink properties and causal reformulation to develop HiStream, a tuning-free framework that enables efficient high-resolution video generation directly within DiT architectures by maintaining stable KV caches without additional training data.
Method
The authors leverage HiStream, an optimized autoregressive video diffusion framework, to address the computational inefficiencies inherent in high-resolution video generation. The core innovation lies in a synergistic combination of three efficiency mechanisms: Anchor-Guided Sliding Window for temporal compression, Dual-Resolution Caching with Asymmetric Denoising for spatial and timestep compression, and a progressive denoising trajectory that exploits redundancy across resolution and time.
The framework operates on a baseline autoregressive diffusion model that factorizes the joint distribution of N video frames as p(x1:N)=∏i=1Np(xi∣x<i). Generation proceeds chunk-wise rather than frame-by-frame, with each chunk conditioned on prior context. The model is trained using a standard diffusion loss LDM(θ)=Ex,t,ϵ[∥ϵ^θ(xt,t,c)−ϵ∥22], and further optimized via consistency distillation using Flow Matching, which trains a student model fϕ to directly map noisy inputs to clean data via the objective LFM(ϕ)=Ep0(x0),pt(xt)[∥fϕ(xt,t,c)−(x0−xt)∥22].
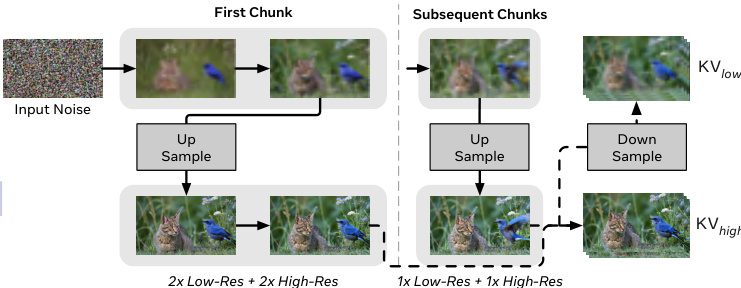
To manage spatial complexity, HiStream introduces Dual-Resolution Caching (DRC). The denoising process is restructured into a two-stage trajectory: the first two steps operate at low resolution to establish global structure, followed by upsampling and two high-resolution refinement steps to recover fine details. This design is empirically justified by the observation that early denoising steps contribute minimally to final quality when followed by high-resolution refinement. To support this resolution shift within a single network, the authors integrate Rotary Positional Embeddings with NTK-inspired scaling, enabling positional generalization across scales.
Refer to the framework diagram illustrating the dual-resolution denoising process. The first chunk undergoes a full 2x low-res + 2x high-res denoising path, while subsequent chunks use an accelerated 1x low-res + 1x high-res path. Crucially, after high-resolution refinement, the output is downsampled and used to update the low-resolution KV cache, ensuring spatial consistency for the next chunk. This dual KV caching mechanism prevents misalignment between cached features and the final high-resolution output, preserving spatio-temporal coherence.
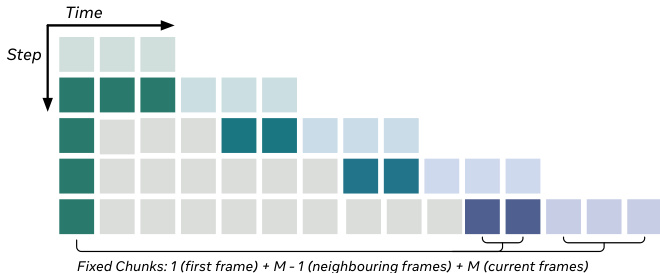
For temporal efficiency, HiStream employs Anchor-Guided Sliding Window (AGSW). Instead of attending to the entire history, each chunk’s generation is conditioned on a fixed-size context: the current chunk (M frames), a local history of M-1 neighboring frames, and a global anchor—the first frame. This limits the maximum attention context to 2M frames, preventing unbounded KV cache growth. The local history provides short-range motion cues, while the first frame acts as a “temporal attention sink,” maintaining long-range scene consistency without requiring full-history attention.
As shown in the figure below, the attention window is composed of a fixed anchor (first frame), recent local context, and the current chunk, ensuring constant computational cost per generation step.
Finally, the authors introduce Asymmetric Denoising to exploit timestep redundancy. The first chunk undergoes the full 4-step denoising process to establish a high-quality anchor cache. Subsequent chunks, benefiting from this cached context, require only 2 steps to reach near-final quality. This aggressive acceleration is implemented as an optional variant, HiStream+, and is enabled by the observation that later chunks inherit sufficient structural information from the fully denoised prior chunk, making full denoising redundant.
Experiment
- Evaluated HiStream (spatial and temporal compression) on 1080p video generation, achieving state-of-the-art VBench scores with 76.2× faster denoising than Wan2.1 baseline while maintaining visual quality.
- Tested HiStream+ variant (adding timestep compression), reaching 107.5× speedup over Wan2.1 with minimal quality degradation, enabling near real-time generation at 4.8 FPS on H100 GPU.
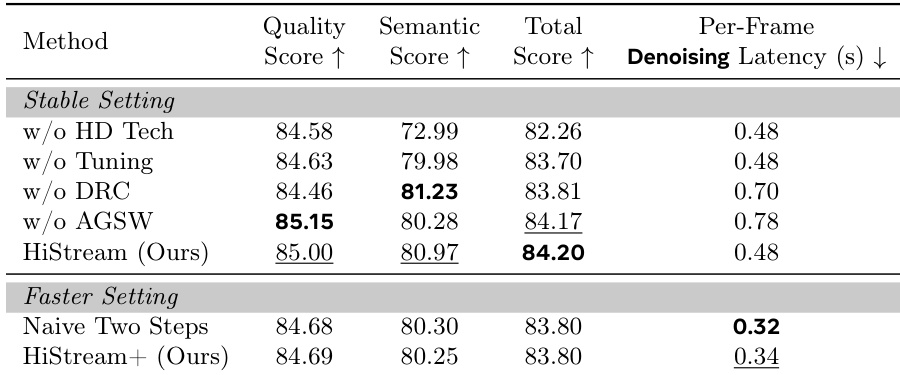
- Ablation studies confirmed Dual-Resolution Caching and Anchor-Guided Sliding Window reduced latency to 0.48s per frame; user studies showed HiStream outperformed baselines in quality, alignment, and detail fidelity.
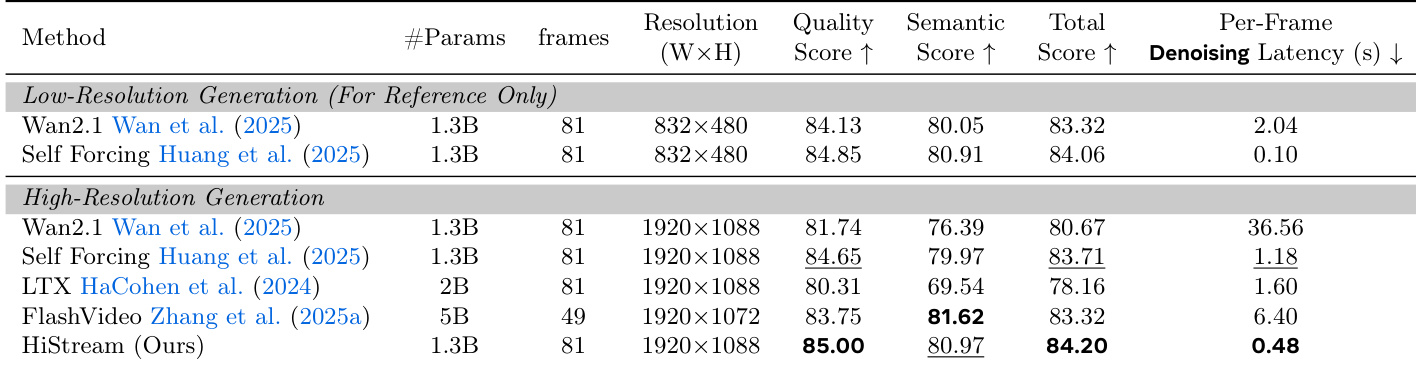
The authors evaluate HiStream’s ablation variants and find that removing Dual-Resolution Caching or Anchor-Guided Sliding Window increases latency to 0.70s and 0.78s respectively, while maintaining the full HiStream configuration achieves the highest total score of 84.20 at 0.48s per frame. In the faster setting, HiStream+ reduces latency to 0.34s with minimal quality loss compared to a naive two-step approach, which achieves 0.32s but lacks the asymmetric denoising strategy that preserves initial chunk fidelity.
HiStream achieves a higher Quality Score and Total Score compared to the two-stage super-resolution approach of Self Forcing combined with FlashVSR, demonstrating superior detail fidelity in native high-resolution generation. The Semantic Score remains competitive, indicating strong alignment with input prompts despite the absence of dedicated super-resolution post-processing.

The authors use HiStream to generate high-resolution videos at 1920×1088, achieving the highest Quality Score (85.00) and Total Score (84.20) among compared methods while maintaining the lowest per-frame denoising latency of 0.48 seconds. Results show HiStream outperforms baselines including Wan2.1, Self Forcing, LTX, and FlashVideo in both visual fidelity and efficiency, with its latency representing a 76.2× speedup over Wan2.1. The model also achieves the best Semantic Score (80.97), indicating strong alignment between generated content and input prompts.
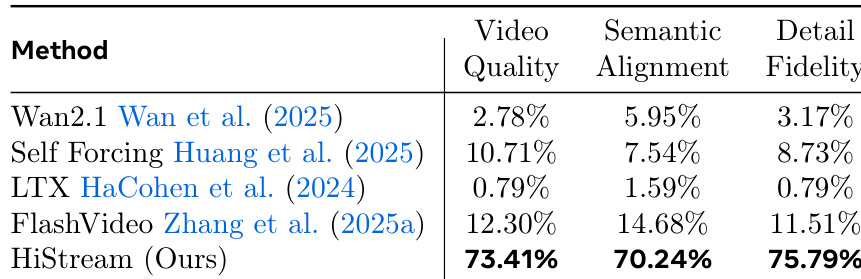
The authors use HiStream to generate high-resolution videos and evaluate it against several baselines using user preference metrics. Results show HiStream receives 73.41% of votes for video quality, 70.24% for semantic alignment, and 75.79% for detail fidelity, significantly outperforming all compared methods. This indicates HiStream produces videos that users perceive as higher quality, more semantically accurate, and richer in fine detail.