Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
DreaMontage:任意フレームガイド付きワンショット動画生成
DreaMontage:任意フレームガイド付きワンショット動画生成
概要
「ワンショット」技法は、映画制作における明確かつ洗練された美学的表現を特徴とする。しかし、その実現はしばしば高コストと現実世界における複雑な制約によって阻まれる。近年、登場したビデオ生成モデルは仮想的な代替手段を提供しているが、従来のアプローチは単純なクリップ連結に依存しており、視覚的な滑らかさや時間的整合性を維持することができないことが頻発する。本論文では、多様なユーザー入力から、滑らかで表現力豊かかつ長時間にわたるワンショット動画を合成可能な、任意のフレームをガイドとして用いるための包括的フレームワーク「DreaMontage」を提案する。本研究では、この課題に三つの主要なアプローチで対応する。(i) DiT(Diffusion Transformer)アーキテクチャに軽量な中間条件制御機構を統合。ベース学習データを効果的に活用する「アダプティブチューニング」戦略を採用することで、任意のフレームに対する強力な制御能力を実現。(ii) 視覚的精細度と映画的表現力の向上のため、高品質なデータセットを構築し、Visual Expression SFT(Supervised Fine-Tuning)段階を導入。被写体の運動の妥当性や遷移の滑らかさといった重要な課題に対処するため、特化型のDPO(Direct Preference Optimization)スキームを適用。これにより、生成コンテンツの成功確率と実用性が顕著に向上した。(iii) 長時間のシーケンス生成を可能にするため、メモリ効率の高い「セグメント単位の自己回帰(Segment-wise Auto-Regressive, SAR)推論戦略」を設計。広範な実験により、本手法が視覚的にインパクトがあり、滑らかで一貫性のあるワンショット効果を実現しつつ、計算効率を維持することを示した。これにより、ユーザーは断片的な視覚素材を、鮮明で統一感のあるワンショット映画体験へと変換できる。
One-sentence Summary
ByteDance researchers propose DreaMontage, a framework for seamless one-shot video generation that overcomes prior clip concatenation limitations through adaptive tuning within DiT architecture and segment-wise autoregressive inference, enabling cinematic-quality long sequences from fragmented inputs via visual expression refinement and tailored optimization.
Key Contributions
- The one-shot filmmaking technique faces prohibitive real-world costs and constraints, while existing video generation methods rely on naive clip concatenation that fails to ensure visual smoothness and temporal coherence across transitions. DreaMontage introduces a lightweight intermediate-conditioning mechanism integrated into the DiT architecture, using an Adaptive Tuning strategy to leverage base training data for robust arbitrary-frame control capabilities.
- To address critical issues like subject motion rationality and transition smoothness in generated content, the framework curates a high-quality dataset and implements a Visual Expression Supervised Fine-Tuning stage followed by a Tailored DPO scheme. This pipeline significantly improves cinematic expressiveness and the success rate of seamless one-shot video synthesis.
- For generating extended one-shot sequences under memory constraints, DreaMontage designs a Segment-wise Auto-Regressive inference strategy that enables long-duration production while maintaining computational efficiency. Extensive experiments confirm the approach achieves visually striking, temporally coherent results that transform fragmented inputs into cohesive cinematic experiences.
Introduction
The authors address the challenge of generating seamless "one-shot" long videos, which are highly valued in filmmaking for immersive storytelling but traditionally require costly production and physical constraints. While recent video diffusion models offer potential, prior approaches relying on first-last frame conditioning fail to ensure temporal coherence, often producing disjointed transitions due to limitations in latent space representation of intermediate frames, semantic shifts between keyframes, and prohibitive computational demands for extended durations. To overcome these, the authors introduce DreaMontage, which implements three key innovations: an intermediate-conditioning mechanism with Shared-RoPE and Adaptive Training for precise frame-level control, Supervised Fine-Tuning with Differentiable Prompt Optimization on curated datasets to enhance visual continuity and reduce abrupt cuts, and a Segment-wise Auto-Regressive inference strategy that enables memory-efficient long-video generation while maintaining narrative integrity.
Dataset
The authors describe their Visual Expression SFT dataset as follows:
- Composition and sources: The dataset comprises newly collected, category-balanced video samples specifically targeting model weaknesses. It originates from a fine-grained analysis of underperforming cases, structured using a hierarchical taxonomy.
- Key subset details: The data spans five major classes (Camera Shots, Visual Effects, Sport, Spatial Perception, Advanced Transitions), each divided into precise subclasses (e.g., "Basic Camera Movements – Dolly In" under Camera Shots; "Generation – Light" under Visual Effects). It is a small-scale collection where videos per subclass were carefully selected for core scenario characteristics and high motion dynamics. Videos are longer (up to 20 seconds) and feature more seamless scene transitions compared to prior adaptive tuning data.
- Usage in training: The authors apply Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) using this dataset directly on the model weights obtained from the previous adaptive tuning stage. They reuse similar training strategies and random condition settings from that prior stage.
- Processing details: The primary processing distinction is the intentional collection of longer-duration videos emphasizing motion dynamics and transitions. No specific cropping strategies or metadata construction beyond the hierarchical classification and selection criteria are mentioned.
Method
The authors leverage a DiT-based video generation framework, extending it with a novel intermediate-conditioning mechanism and a progressive training pipeline to enable arbitrary-frame guided synthesis of long, cinematic one-shot videos. The overall architecture, as shown in the figure below, is structured around two core components: a training pipeline that incrementally refines the model’s capabilities, and an inference pipeline that supports flexible, memory-efficient generation.
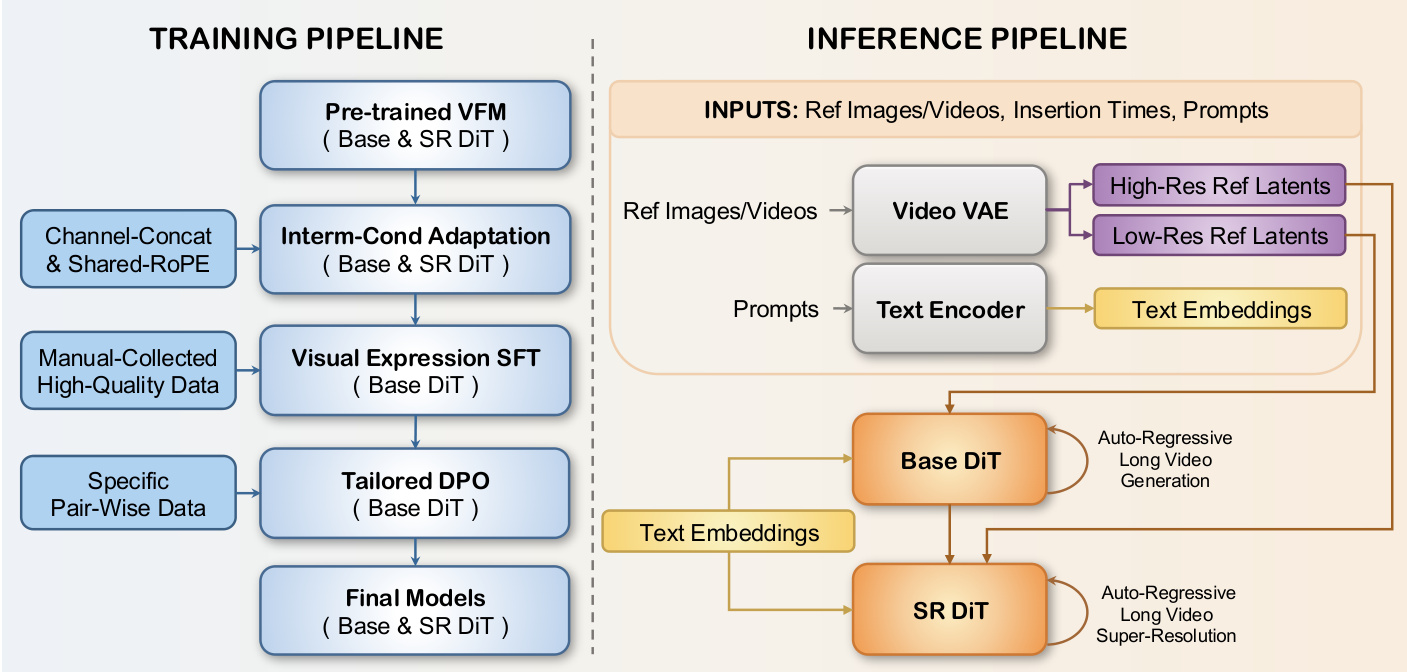
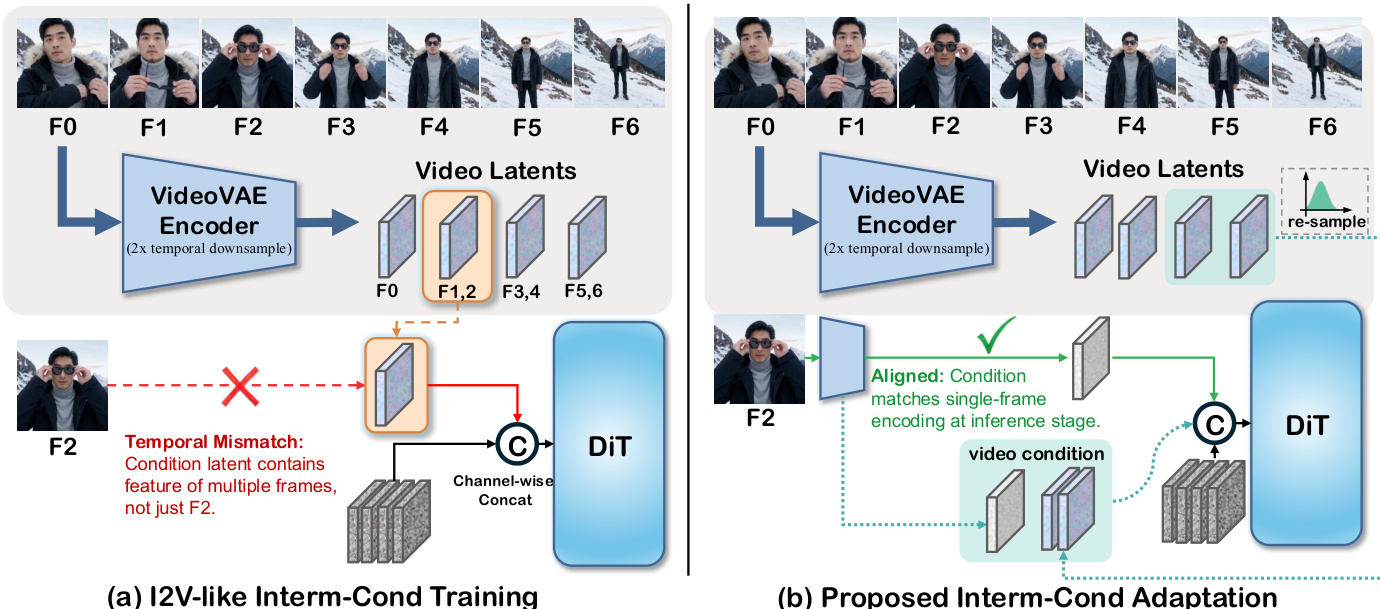
At the core of the framework is the Interm-Cond Adaptation strategy, which addresses the temporal misalignment inherent in conditioning on arbitrary frames. The VideoVAE encoder performs 2x temporal downsampling, meaning a single frame’s latent representation corresponds to multiple generated frames, leading to imprecise conditioning. As shown in the figure below, the authors resolve this by aligning the training distribution with inference: for single-frame conditions, the frame is re-encoded; for video conditions, subsequent frames are re-sampled from the latent distribution to match the temporal granularity of the target video. This lightweight tuning enables robust arbitrary-frame control without architectural overhaul.
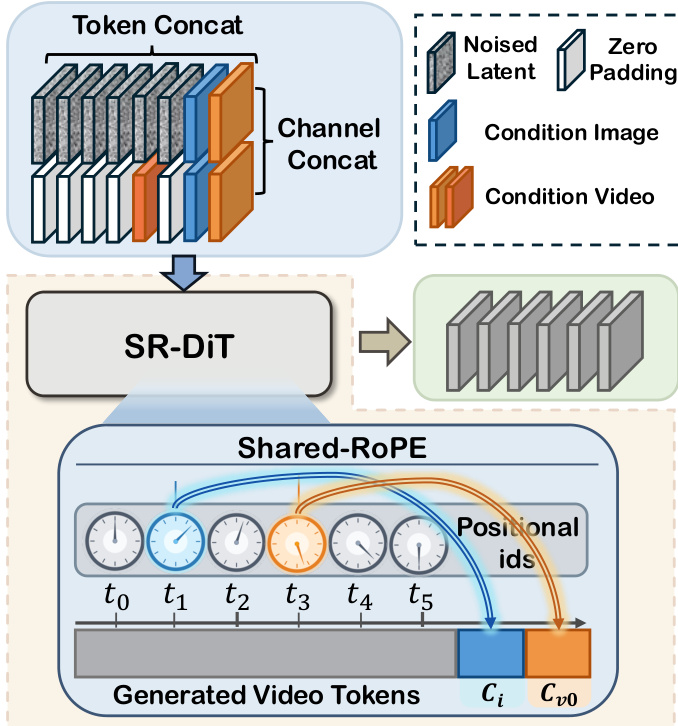
For super-resolution, the authors introduce Shared-RoPE to mitigate flickering and color shifts caused by channel-wise concatenation of conditioning signals. As depicted in the figure below, in addition to channel-wise conditioning, the VAE latent of each reference image is concatenated along the token sequence dimension, with its Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) set to match the corresponding temporal position. This sequence-wise conditioning ensures spatial-temporal alignment, particularly critical for maintaining fidelity at higher resolutions. For video conditions, Shared-RoPE is applied only to the first frame to avoid computational overhead.
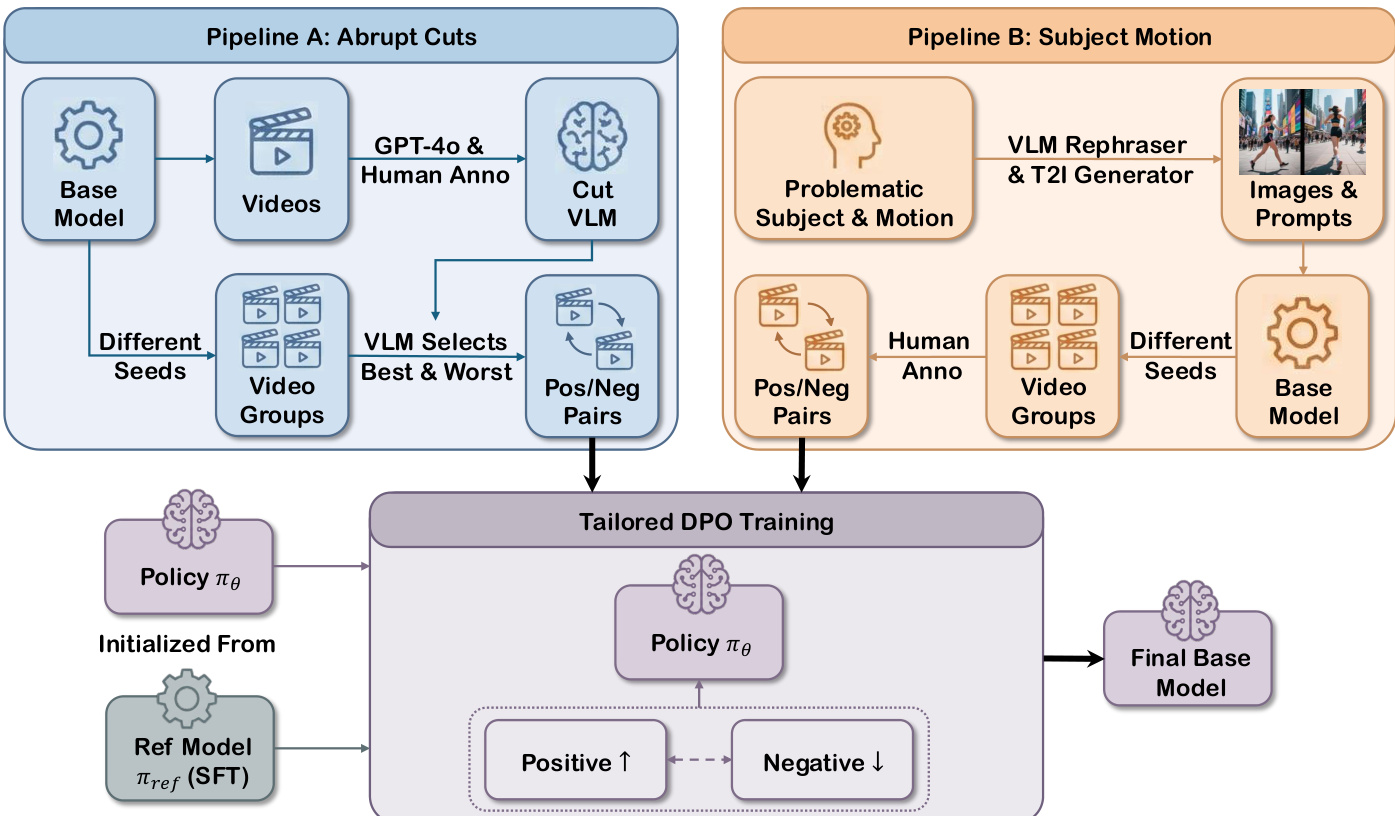
To enhance visual expressiveness and temporal coherence, the authors implement a Visual Expression SFT stage using a manually curated high-quality dataset. This is followed by a Tailored DPO training phase, which targets two specific failure modes: abrupt cuts and physically implausible subject motion. As shown in the figure below, two distinct pipelines generate contrastive preference pairs. Pipeline A uses a trained VLM discriminator to automatically select “best” and “worst” videos from groups generated with the same prompt but different seeds, focusing on cut severity. Pipeline B relies on human annotation to identify problematic subject motions, generating pairs that guide the model toward physically plausible dynamics. The DPO objective directly optimizes the policy πθ against a reference model πref:
LDPO=−E(c,vw,vl)∼D[logσ(βlogπref(vw∣c)πθ(vw∣c)−βlogπref(vl∣c)πθ(vl∣c))]where c denotes the conditioning inputs, and β controls the deviation from the reference policy.
For long-form generation, the authors design a Segment-wise Auto-Regressive (SAR) inference strategy. The target video is partitioned into consecutive segments using a sliding window in the latent space, with user-provided conditions acting as candidate boundaries. Each segment sn is generated conditionally on the tail latents of the previous segment τ(sn−1) and the local conditions Cn:
sn=Gθ(τ(sn−1),Cn)where Cn={cn(1),…,cn(m)} represents the heterogeneous conditions within the current window. This auto-regressive mechanism ensures pixel-level continuity across segment boundaries. Overlapping latents are fused before decoding, yielding a temporally coherent long video. The entire process operates in the latent space, avoiding pixel-level artifacts and leveraging the model’s learned consistency from prior training stages.
Experiment
- Demonstrated arbitrary frame-guided one-shot video generation through qualitative examples, showing coherent narrative transitions across complex scenarios like train-to-cyberpunk shifts and eye-to-meadow sequences without morphing artifacts.
- In multi-keyframe conditioning, achieved 15.79% higher overall preference than Vidu Q2 and 28.95% over Pixverse V5, with significant gains in prompt following (+23.68%) while maintaining competitive motion and visual quality.
- In first-last frame conditioning, surpassed Kling 2.5 by 3.97% in overall preference with consistent improvements in motion effects and prompt following (+4.64% each), matching visual fidelity of top-tier models.
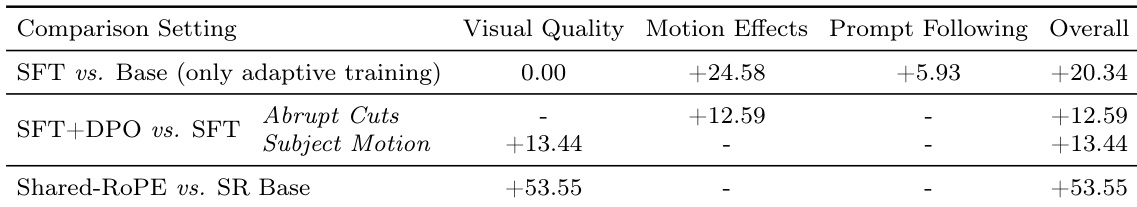
The authors use ablation studies to isolate the impact of key optimizations in DreaMontage, showing that combining SFT with DPO improves motion handling and overall performance, while Shared-RoPE delivers the largest gain in visual quality. Results show that adaptive training alone boosts motion and prompt following without affecting visual fidelity, and Shared-RoPE significantly enhances visual quality over its base variant. The cumulative effect of these optimizations leads to substantial overall performance gains across multiple metrics.