Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Qwen-Image-Layered:レイヤー分解による本質的な編集可能性の実現へ
Qwen-Image-Layered:レイヤー分解による本質的な編集可能性の実現へ
概要
近年の視覚生成モデルは、ラスタ画像のすべての視覚的コンテンツが単一のキャンバスに混合されるという特徴上、画像編集における一貫性の維持に課題を抱えている。これに対して、プロフェッショナルなデザインツールではレイヤー構造を採用しており、各コンテンツを独立して編集しつつも全体の整合性を保つことが可能である。この点に着目し、本研究では、単一のRGB画像を意味的に分離された複数のRGBAレイヤーに分解するエンドツーエンドの拡散モデル「Qwen-Image-Layered」を提案する。本モデルは、各RGBAレイヤーを独立して操作可能にする「本質的な編集性(inherent editability)」を実現し、他のコンテンツに影響を与えることなく、個別に編集が行える。可変長の分解を可能とするため、以下の3つのキーコンポーネントを導入した:(1) RGB画像とRGBA画像の潜在表現を統一するRGBA-VAE;(2) 任意の数の画像レイヤーを分解可能なVLD-MMDiT(Variable Layers Decomposition MMDiT)アーキテクチャ;(3) 事前学習済みの画像生成モデルをマルチレイヤー画像分解器へ適応させるためのマルチステージ学習戦略。さらに、高品質なマルチレイヤー訓練画像の不足という課題に対応するため、Photoshopドキュメント(PSD)からマルチレイヤー画像を抽出・アノテーションするパイプラインを構築した。実験結果により、本手法が既存手法を大きく上回る分解品質を達成し、一貫性のある画像編集の新しいパラダイムを確立したことが示された。
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Alibaba and HKUST propose Qwen-Image-Layered, an end-to-end diffusion model that decomposes RGB images into semantically disentangled RGBA layers via novel RGBA-VAE and VLD-MMDiT components for variable-length decomposition. This enables consistent isolated edits without affecting other content, significantly outperforming prior methods in layered image quality using a PSD-derived training dataset for professional design applications.
Key Contributions
- Existing visual generative models face consistency issues during image editing because raster images fuse all content into a single entangled canvas, unlike professional layered design tools that enable isolated edits; Qwen-Image-Layered addresses this by decomposing a single RGB image into multiple semantically disentangled RGBA layers for inherent editability.
- The method introduces three key components: an RGBA-VAE to unify RGB and RGBA latent representations, a VLD-MMDiT architecture for variable-length layer decomposition, and a Multi-stage Training strategy to adapt pretrained models into multilayer decomposers, enabling end-to-end decomposition without recursive inference.
- To overcome multilayer training data scarcity, the authors built a pipeline extracting annotated images from Photoshop documents (PSD), and experiments demonstrate the approach significantly surpasses existing methods in decomposition quality across diverse images including text-containing examples.
Introduction
Image editing requires preserving consistency in unmodified regions during edits, which is critical for professional applications like digital content creation where unintended artifacts undermine usability. Prior global editing methods suffer from the inherent randomness of generative models, failing to maintain fidelity in untouched areas, while mask-guided local approaches struggle with occlusions and soft boundaries, leading to imprecise region identification and persistent consistency issues. Existing decomposition techniques rely on error-prone segmentation or recursive inference that propagates mistakes, especially with complex layouts or semi-transparent layers, resulting in low-fidelity outputs unsuitable for precise editing. The authors propose Qwen-Image-Layered, an end-to-end diffusion model that directly decomposes RGB images into semantically disentangled RGBA layers, enabling independent layer manipulation without affecting other content and fundamentally solving the consistency problem.
Dataset
The authors address multilayer image scarcity by building a dataset from real PSD files. Key details:
- Composition and sources: Sourced from real-world PSD files parsed using the psd-tools Python library, avoiding synthetic or simplistic design datasets.
- Subset processing:
- Filtered layers containing anomalous elements (e.g., blurred faces) and non-contributing layers that don’t affect the final composite.
- Merged spatially non-overlapping layers to reduce complexity, significantly lowering layer counts (from Fig. 5a).
- Used Qwen2.5-VL to generate text descriptions for composite images, enabling text-to-multilayer generation.
- Usage in the model:
- Trained exclusively for Text-to-Multi-RGBA and Image-to-Multi-RGBA tasks, with a maximum of 20 layers per image.
- Applied in three training stages (500K, 400K, and 400K optimization steps) using the Adam optimizer.
- Additional processing: No explicit cropping strategy was used; metadata consisted of generated text descriptions via Qwen2.5-VL. Layer merging was the primary structural adjustment to manage input complexity.
Method
The authors leverage a novel end-to-end diffusion framework, Qwen-Image-Layered, to decompose a single RGB input image I∈RH×W×3 into N semantically disentangled RGBA layers L∈RN×H×W×4, where each layer Li=[RGBi;αi] contains a color component and an alpha matte. The original image is reconstructed via sequential alpha blending:
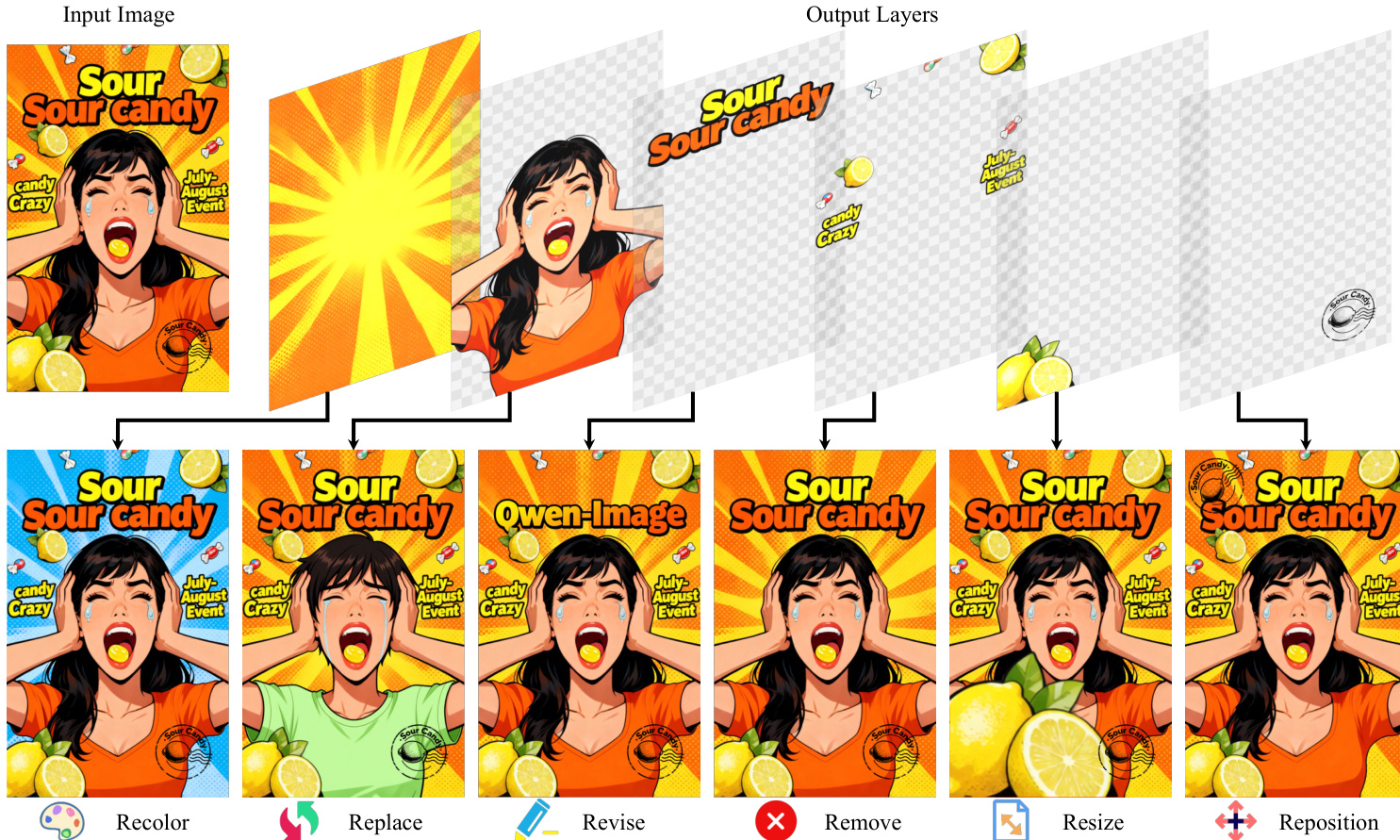
C0=0Ci=αi⋅RGBi+(1−αi)⋅Ci−1i=1,…,Nwhere CN=I. This decomposition enables inherent editability: each layer can be independently modified—recoloring, resizing, repositioning, or removing—without affecting other content, as demonstrated in the visual examples of layer manipulation.
To support this capability, the architecture integrates three core innovations. First, the authors introduce an RGBA-VAE that encodes both RGB inputs and RGBA layer outputs into a shared latent space, eliminating the distribution gap present in prior methods that used separate VAEs. The encoder and decoder are extended to four channels, with initialization preserving RGB reconstruction fidelity by copying pretrained weights into the first three channels and setting the alpha channel parameters to zero (except for the decoder bias, initialized to 1). The VAE is trained with a composite loss including reconstruction, perceptual, and regularization terms.
Second, the model employs a VLD-MMDiT (Variable Layers Decomposition MMDiT) architecture, which enables decomposition into a variable number of layers and supports multi-task training. The input RGB image and target RGBA layers are both encoded via the RGBA-VAE. During attention computation, their latent sequences are concatenated along the sequence dimension to model both intra-layer and inter-layer interactions. To handle variable layer counts, the authors introduce Layer3D RoPE, which extends positional encoding with an explicit layer dimension. The input image is assigned a layer index of -1, while target layers are indexed from 0 upward, ensuring clear separation during attention.
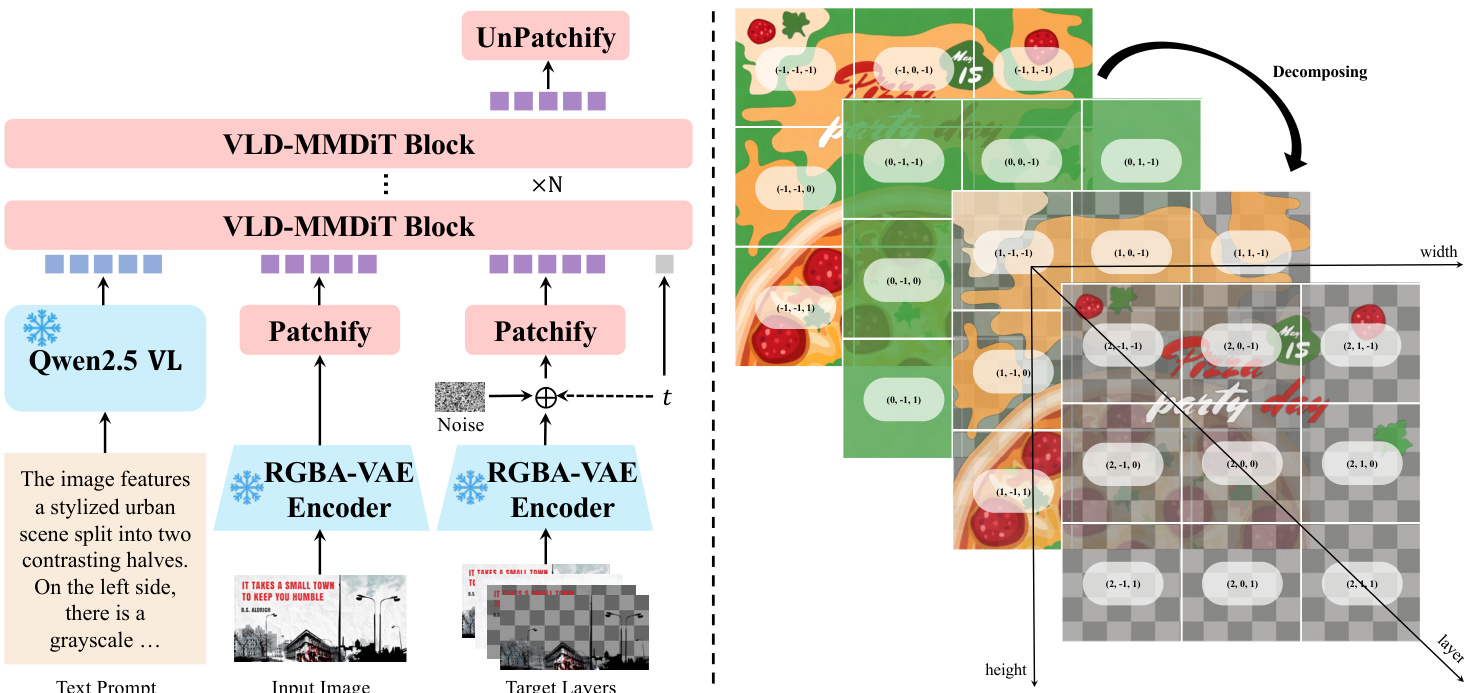
Training follows a multi-stage, multi-task strategy to progressively adapt a pretrained image generation model. Stage 1 adapts the MMDiT to the RGBA-VAE latent space by jointly training on text-to-RGB and text-to-RGBA generation. Stage 2 introduces text-to-multi-RGBA generation, where the model predicts both the final composite and its constituent transparent layers, enabling information flow between them. Stage 3 extends the model to image-to-multi-RGBA decomposition by conditioning on both the input RGB image and text prompt, using the Flow Matching objective. The model predicts the velocity vθ(xt,t,zI,h) of the intermediate state xt=tx0+(1−t)x1, where x0 is the latent target, x1 is noise, and zI is the encoded input image, minimizing the mean squared error against the ground truth velocity vt=x0−x1.
Experiment
- Image decomposition on Crello dataset achieved highest Alpha soft IoU and RGB L1 metrics, surpassing LayerD [36] with superior alpha channel fidelity and artifact-free layer generation.
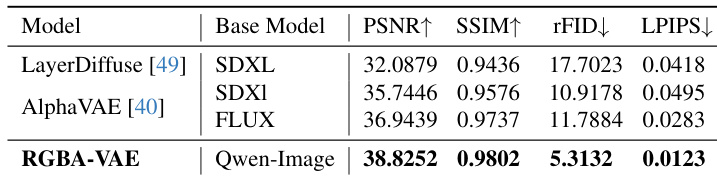
- RGBA image reconstruction on AIM-500 dataset outperformed LayerDiffuse and AlphaVAE across all metrics (PSNR, SSIM, rFID, LPIPS), demonstrating state-of-the-art reconstruction capability.
- Qualitative image editing showed consistent, high-fidelity resizing and repositioning without pixel-level shifts, unlike Qwen-Image-Edit-2509, by enabling precise per-layer modifications.
- Multilayer image synthesis produced semantically coherent layered compositions, with the combined text-to-image and decomposition pipeline enhancing visual aesthetics and semantic alignment.
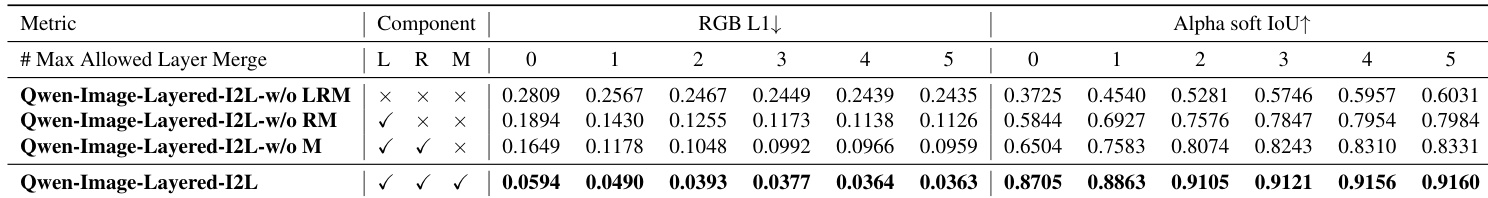
The authors evaluate image decomposition on the Crello dataset using RGB L1 and Alpha soft IoU metrics, allowing up to five adjacent layer merges to account for decomposition ambiguity. Results show Qwen-Image-Layered-I2L consistently outperforms LayerD and other baselines across all merge settings, achieving the lowest RGB L1 and highest Alpha soft IoU, indicating superior layer fidelity and alpha channel accuracy.

The authors evaluate their image decomposition model using RGB L1 and Alpha soft IoU metrics under varying layer merge constraints. Results show that including all components—Layer3D Rope, RGBA-VAE, and Multi-stage Training—yields the best performance, with the lowest RGB L1 and highest Alpha soft IoU across all merge settings. This indicates the full model achieves superior decomposition accuracy and alpha channel fidelity compared to ablated versions.
The authors evaluate RGBA image reconstruction on the AIM-500 dataset using PSNR, SSIM, rFID, and LPIPS metrics. Results show that RGBA-VAE outperforms LayerDiffuse and AlphaVAE across all metrics, achieving the highest PSNR and SSIM while reporting the lowest rFID and LPIPS, indicating superior reconstruction fidelity and perceptual quality.