Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
HiF-VLA:視覚・言語・行動モデルにおける運動表現を用いた後知恵、洞察、先見性
HiF-VLA:視覚・言語・行動モデルにおける運動表現を用いた後知恵、洞察、先見性
Minghui Lin Pengxiang Ding Shu Wang Zifeng Zhuang Yang Liu Xinyang Tong Wenxuan Song Shangke Lyu Siteng Huang Donglin Wang
概要
視覚・言語・行動(Vision-Language-Action: VLA)モデルは、視覚的および言語的手がかりを行動に具現化することにより、ロボット操作の分野で近年顕著な進展を遂げている。しかしながら、大多数のVLAモデルはマルコフ性を仮定しており、現在の観測値のみに依存するため、時間的連続性の欠如(temporal myopia)に起因する長時間スケールの整合性の低下という課題に直面している。本研究では、時間的文脈や世界の動的変化をよりコンパクトかつ情報量の多い表現として運動(motion)に着目し、状態間の変化を捉えつつ、静的なピクセルレベルのノイズを効果的に除去する可能性を示す。この知見を基盤として、未来の予測(foresight)、過去の再考(hindsight)、そして両者の統合(insight)を可能にする統一的枠組み「HiF-VLA(Hindsight, Insight, and Foresight for VLAs)」を提案する。HiF-VLAは、過去の動的状態を「後知恵的事前知識(hindsight priors)」として符号化し、未来の運動を「予見的推論(foresight reasoning)」によって予測することで、両者を「後知恵制御型統合エキスパート(hindsight-modulated joint expert)」により統合し、「行動しながら思考する(think-while-acting)」という新たなアプローチを実現する。その結果、HiF-VLAはLIBERO-LongおよびCALVIN ABC-Dベンチマークにおいて強力なベースラインを上回りつつ、追加の推論遅延は極めて小さく抑えられた。さらに、実世界における長時間スケールのロボット操作タスクにおいても顕著な性能向上を達成し、実用的なロボットシステムにおける広範な有効性を実証した。
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Westlake University, Zhejiang University, and HKUST(GZ) propose HiF-VLA, a unified Vision-Language-Action framework that leverages motion for bidirectional temporal reasoning, enabling hindsight and foresight capabilities to improve long-horizon robotic manipulation with minimal latency and strong real-world performance.
Key Contributions
- HiF-VLA addresses temporal myopia in Vision-Language-Action models by using motion as a compact, low-dimensional representation of temporal dynamics, enabling efficient and structured bidirectional reasoning through hindsight and foresight mechanisms.
- The framework introduces a hindsight-modulated joint expert that integrates past motion priors with future motion anticipation, allowing for a "think-while-acting" paradigm that improves causal consistency and temporal coherence in long-horizon manipulation.
- HiF-VLA achieves state-of-the-art performance on the LIBERO-Long and CALVIN ABC-D benchmarks and demonstrates significant improvements in real-world robotic tasks, all with negligible increase in inference latency compared to baseline methods.
Introduction
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models enable robots to interpret language and visual inputs to generate control actions, but most assume the Markov property—relying only on the current observation—leading to temporal myopia that undermines performance in long-horizon tasks. Prior approaches attempt to incorporate temporal context by stacking past frames or predicting future subgoals, but these methods suffer from high computational cost, pixel-level redundancy, and limited ability to model bidirectional temporal dynamics. The authors leverage motion as a compact, low-dimensional representation of temporal change, proposing HiF-VLA—a framework that enables bidirectional reasoning through hindsight (encoding past dynamics), foresight (anticipating future motion), and insight (interpreting current task context). Their key contribution is a hindsight-modulated joint expert that integrates these cues in a unified space, enabling a "think-while-acting" paradigm that improves temporal coherence and causal consistency with minimal latency overhead.
Method
The authors leverage a unified framework called HiF-VLA, which extends vanilla vision-language-action (VLA) models by integrating structured historical priors and foresight reasoning to enhance temporal consistency and causal coherence in action prediction. The architecture is designed to jointly predict future motion and actions conditioned on the current observation, task instruction, and a compressed historical motion prior, enabling more robust decision-making under sparse or occluded visual inputs.
The framework operates in three primary stages: hindsight prior acquisition, foresight reasoning with insight, and hindsight-modulated joint expert fusion. In the first stage, historical visual dynamics are encoded into compact motion vectors (MVs) using MPEG-4 video encoding standards. These MVs, derived from macroblock displacements between consecutive frames, form a structured, low-redundancy representation of past manipulator motion. A lightweight ViT-based encoder, augmented with shallow 3D convolutions, processes this MV stream into compact hindsight tokens Mh∈RKh×d, which serve as a temporal prior without disrupting the VLM’s modality alignment.
As shown in the figure below, the second stage employs the VLM to perform parallel reasoning over future visual dynamics and action generation. The model introduces learnable foresight query tokens and empty action tokens into the VLM embedding space, concatenated with the current observation and task instruction. The VLM then outputs foresight motion tokens Mf∈RKf×d and action latent tokens Af∈RKa×d, enabling the model to reason about visual consequences and motor commands simultaneously. This design avoids pixel-level future frame prediction, which is prone to distortion and semantic drift, and instead leverages MVs as structured spatiotemporal targets.
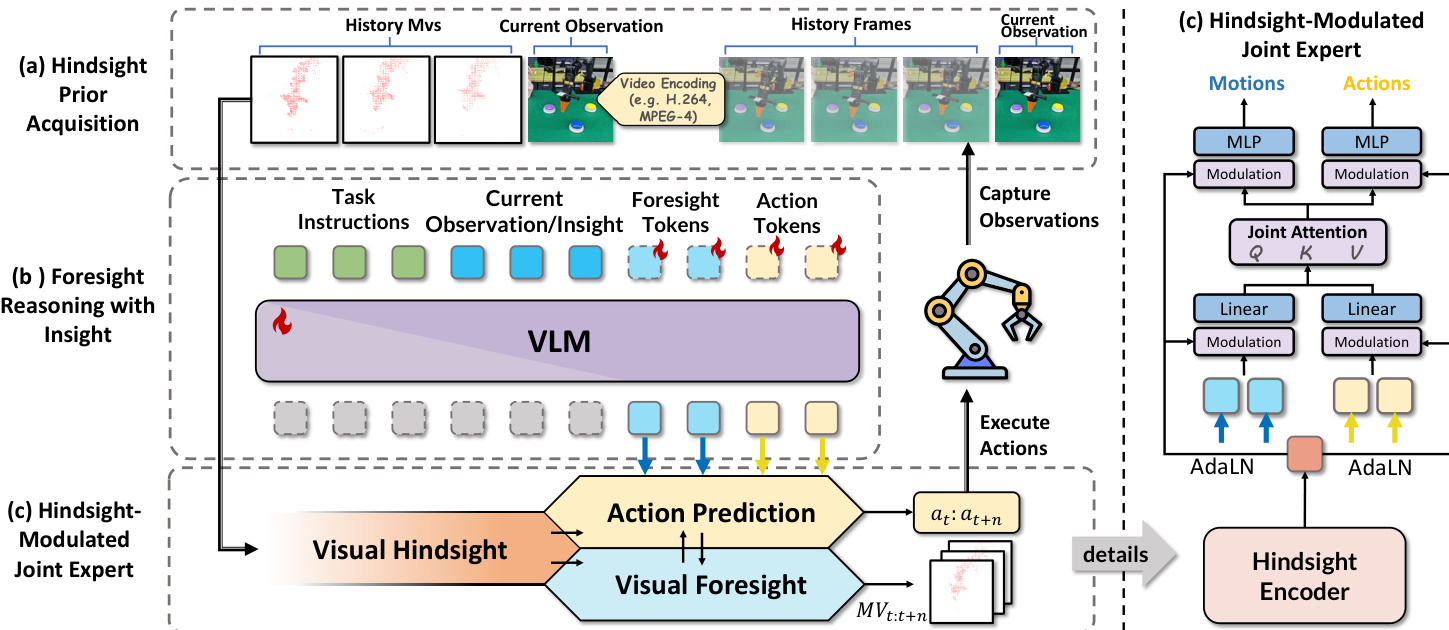
The final stage, the hindsight-modulated joint expert, fuses the foresight motion and action representations under the guidance of the historical prior. Rather than injecting historical tokens directly into the VLM, which risks misalignment, the model projects Mh into a conditioning vector hc and applies Adaptive Layer Normalization (AdaLN) to modulate both motion and action streams. The joint expert employs non-causal self-attention over a concatenated sequence of Mf and Af, allowing cross-stream interaction while preserving disentangled representations through separate feed-forward networks. Positional information is encoded via Rotary Positional Embedding (RoPE) to maintain spatiotemporal ordering. The modulated representations are then projected through respective heads to generate the final predicted motion m~t:t+n and action a~t:t+n sequences.
During training, the model is optimized with a combined L1 loss that jointly penalizes deviations in both action and motion predictions:
Lall=LA+λ⋅LMV,where λ=0.01 balances the contribution of motion reconstruction against action accuracy. This dual-objective training ensures that the model learns to generate physically plausible and semantically aligned behaviors. At inference time, motion decoding is optional, allowing flexibility for downstream applications that may not require explicit motion prediction.
The overall architecture enables the model to reason about past dynamics, anticipate future consequences, and generate temporally consistent actions—all within a unified latent space that preserves modality alignment and avoids redundancy.
Experiment
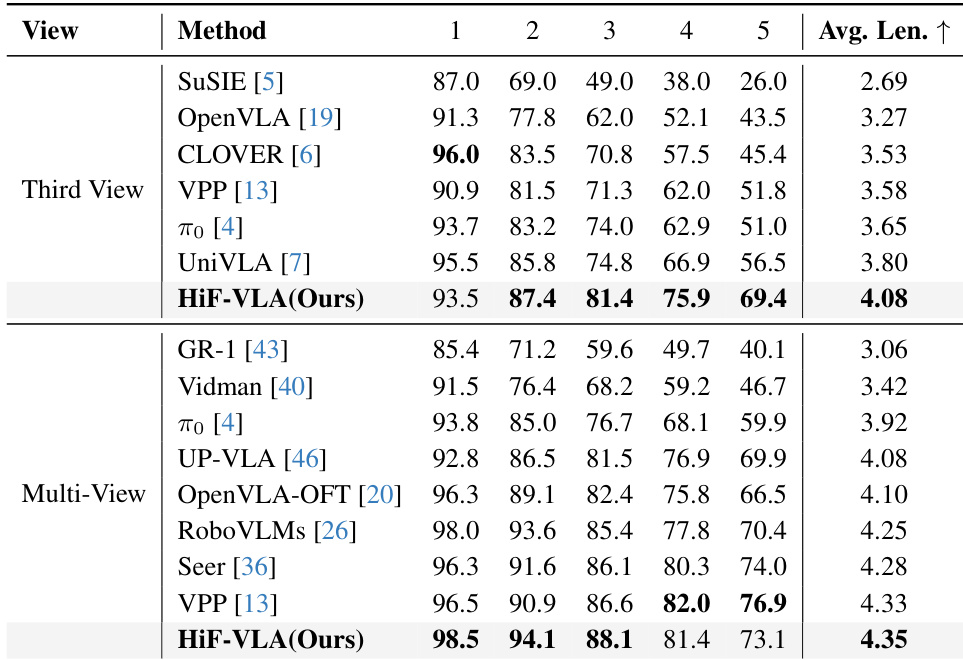
- Evaluated on LIBERO-Long and CALVIN ABC-D benchmarks, HiF-VLA achieves 96.4% success rate (multi-view) and 4.35 average task length on CALVIN, surpassing prior state-of-the-art methods including Seer, VPP, and OpenVLA-OFT.
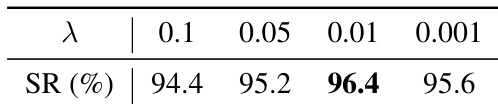
- On the full LIBERO benchmark (four suites), HiF-VLA achieves 98.0% average success rate, outperforming existing approaches such as OpenVLA-OFT (97.1%) and MemoryVLA (96.5%).
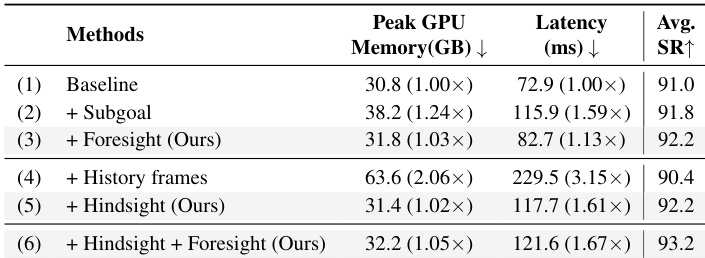
- Ablation studies show that hindsight length of 8 and expert-conditioned embedding yield optimal performance, with 96.4% success on LIBERO-Long.
- HiF-VLA maintains low inference latency (1.67× baseline) and scalable computation as context length increases, significantly outperforming multi-frame baselines that suffer from linear latency growth.
- Replaces redundant RGB history with motion-based representations, reducing GPU memory usage and improving efficiency while increasing success rate by 2.2% over baseline on LIBERO-Long.
- Validated on real-world AgileX Piper robot across long-horizon tasks (e.g., stacking, covering, button pressing), achieving high success rates where baseline (OpenVLA-OFT) fails, e.g., robust performance on visually subtle state transitions like button presses.
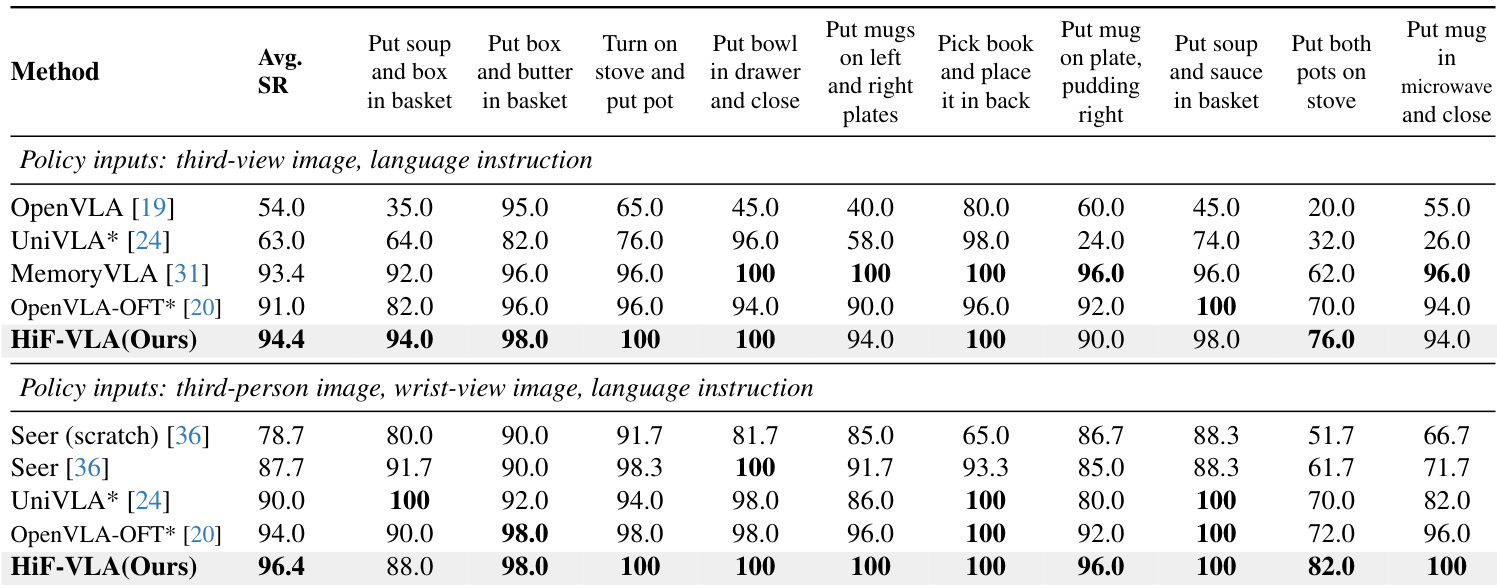
HiF-VLA achieves the highest average performance across all four LIBERO benchmark suites, with particularly strong results on the challenging LIBERO-Long tasks. The model outperforms prior state-of-the-art methods in LIBERO-Spatial and LIBERO-Object, while matching or exceeding top performers in LIBERO-Goal and LIBERO-Long. This demonstrates HiF-VLA’s robust generalization and effectiveness in handling diverse long-horizon manipulation tasks.
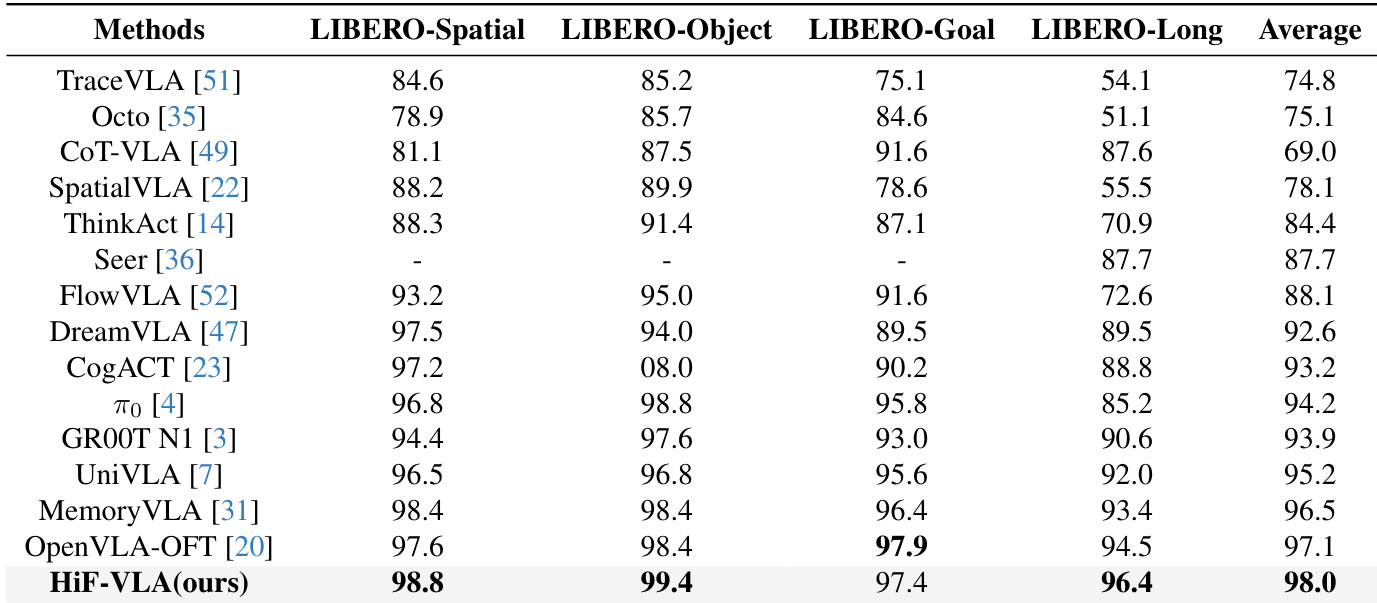
The authors evaluate the impact of the foresight motion loss weight λ on task success rate, finding that λ = 0.01 yields the highest performance at 96.4%. Results show that moderate weighting of motion prediction enhances planning without destabilizing the model, while higher or lower values reduce effectiveness.
The authors use HiF-VLA to evaluate efficiency and redundancy by comparing variants that incorporate subgoal, foresight, or historical frame inputs. Results show that adding foresight or hindsight individually improves success rates with minimal latency overhead, while combining both yields the highest performance at 93.2% with only a 1.67× latency increase over the baseline. In contrast, dense history frames significantly increase latency and degrade performance, highlighting HiF-VLA’s advantage in using compact motion representations to avoid redundancy.
HiF-VLA outperforms all compared methods on the CALVIN ABC-D benchmark under both third-view and multi-view settings, achieving the highest average task length of 4.08 and 4.35 respectively. The model demonstrates superior generalization to unseen environments and maintains consistent performance gains across consecutive task steps, particularly excelling in later stages where long-horizon reasoning is critical. These results confirm HiF-VLA’s effectiveness in handling complex, temporally extended robotic tasks through its bidirectional temporal modeling architecture.
HiF-VLA achieves the highest average success rate on the LIBERO-Long benchmark under both third-view and multi-view settings, outperforming prior state-of-the-art methods including OpenVLA-OFT and UniVLA. The model demonstrates consistent superiority across individual long-horizon tasks, particularly in complex sequences requiring temporal coherence such as stacking, covering, and ordered button pressing. Its performance under third-view input matches or exceeds multi-view baselines, highlighting its strong temporal reasoning without relying on additional camera streams.