Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
ネイティブ並列推論者:自己蒸留強化学習を用いた並列推論
ネイティブ並列推論者:自己蒸留強化学習を用いた並列推論
Tong Wu Yang Liu Jun Bai Zixia Jia Shuyi Zhang Ziyong Lin Yanting Wang Song-Chun Zhu Zilong Zheng
概要
我々は、大規模言語モデル(LLM)が自己進化によって本質的な並列推論能力を獲得できる、教師不要のフレームワーク「ネイティブ並列推論器(Native Parallel Reasoner, NPR)」を提案する。NPRは、以下の3つの革新的な手法により、モデルの推論方式を従来の逐次的模倣から「本質的な並列認知」へと変革する。第一に、外部教師信号を必要とせずに「コールドスタート」形式の発見から厳格なトポロジカル制約への移行を実現する、自己蒸留型の段階的学習枠組み。第二に、実行グラフ内において分岐方策を直接最適化する新規の「並列認識型方策最適化(Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization, PAPO)」アルゴリズムにより、モデルが試行錯誤を通じて適応的な問題分解を学習可能となる。第三に、SGLangのメモリ管理およびフロー制御を再構築した堅牢なNPRエンジンを採用し、安定的かつ大規模な並列強化学習(RL)訓練を実現。8つの推論ベンチマークにおいて、Qwen3-4Bを用いたNPRの学習は、最大24.5%の性能向上と最大4.6倍の推論速度向上を達成した。従来のベースラインがしばしば逐次的生成(autoregressive decoding)に依存するのに対し、NPRは100%の本質的な並列実行を実現し、自己進化型で効率的かつスケーラブルなエージェント推論の新たな基準を確立した。
Summarization
Researchers from NLCo Lab at Beijing Institute for General Artificial Intelligence (BIGAI) propose Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR), a teacher-free framework enabling LLMs to self-evolve true parallel reasoning via self-distilled training, Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO), and an enhanced NPR Engine, achieving up to 24.5% gains and 4.6× speedup on reasoning tasks with 100% genuine parallel execution.
Key Contributions
- Introduces a self-distilled progressive training paradigm that transitions from cold-start format discovery to native parallelism, enabling models to learn adaptive decomposition strategies through trial and error without relying on external supervision.
- Proposes a novel parallel-aware policy optimization algorithm leveraging rejection sampling to refine reasoning paths, outperforming prior methods by eliminating reward hacking and enhancing execution efficiency across diverse trajectories.
- Demonstrates 100% genuine parallelism through comprehensive evaluation of eight reasoning benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art performance with supervised learning from human feedback data.
Introduction
The authors leverage a novel framework called Native Parallel Reasoner (NPR) to enable large language models to self-evolve parallel reasoning capabilities without relying on external supervision. This advancement addresses the limitations of prior work, which often depended on hand-crafted parallel structures or required supervised distillation from stronger models—restricting the emergence of genuine parallel intelligence.
Technical and application context matters because complex problem-solving in real-world scenarios demands models that can explore multiple reasoning trajectories simultaneously. Prior work in this domain typically used sequential reasoning, where models are prompted to solve problems step-by-step. In contrast, NPR internalizes parallelism by training the model to generate valid parallel reasoning paths natively, allowing it to learn adaptive decomposition strategies through trial and error.
The authors’ main contribution is a three-stage progressive training paradigm that transitions models from sequential emulation to genuine parallel cognition. This approach enables collision-free parallel rollouts and optimizes branching policies directly within the parallel execution graph.
Key innovations and advantages include:
- A unified framework for self-distilled data construction that eliminates reliance on external supervision
- Collision-free parallel rollouts using a novel Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO) algorithm
- Task-agnostic parallelism that achieves 100% genuine parallel reasoning with no instances of pseudo-parallel behavior across diverse benchmarks
Dataset
- The authors use the ORZ dataset, which contains 57k problem–answer pairs, as the foundation for their experiments, sampling a fixed subset of 8k examples for use across all training stages.
- The 8k-example subset is consistently used in Stage 1, Stage 2, and Stage 3 of the pipeline, ensuring uniformity throughout the training process.
- The dataset is derived from ORZ, and the models used are based on Qwen3-4B-Instruct and Qwen3-7B, with no modifications applied during training.
- For training, the authors use Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 and Qwen3-4B, avoiding the thinking-mode variant due to incompatibility with standard supervised fine-tuning.
- In Stage 1, the authors follow the DAPO setup with a maximum generation length of 30,000 tokens.
- Stage 2 begins with a learning rate of 1e-6, decaying to 5e-7, and applies a weight decay of 0.1.
- In Stage 3, the authors employ PAPO with the NPR engine, maintaining a maximum generation length of 30,000 tokens and setting the learning rate to 1e-7.
Method
The authors leverage a three-stage curriculum to train language models for native parallel reasoning (NPR), progressively inducing, grounding, and amplifying the ability to generate and evaluate multiple reasoning branches concurrently. The overall framework, as shown in the figure below, begins with a base instruction-tuned model and culminates in a fully optimized parallel reasoner capable of structured, parallel inference without external teacher models.
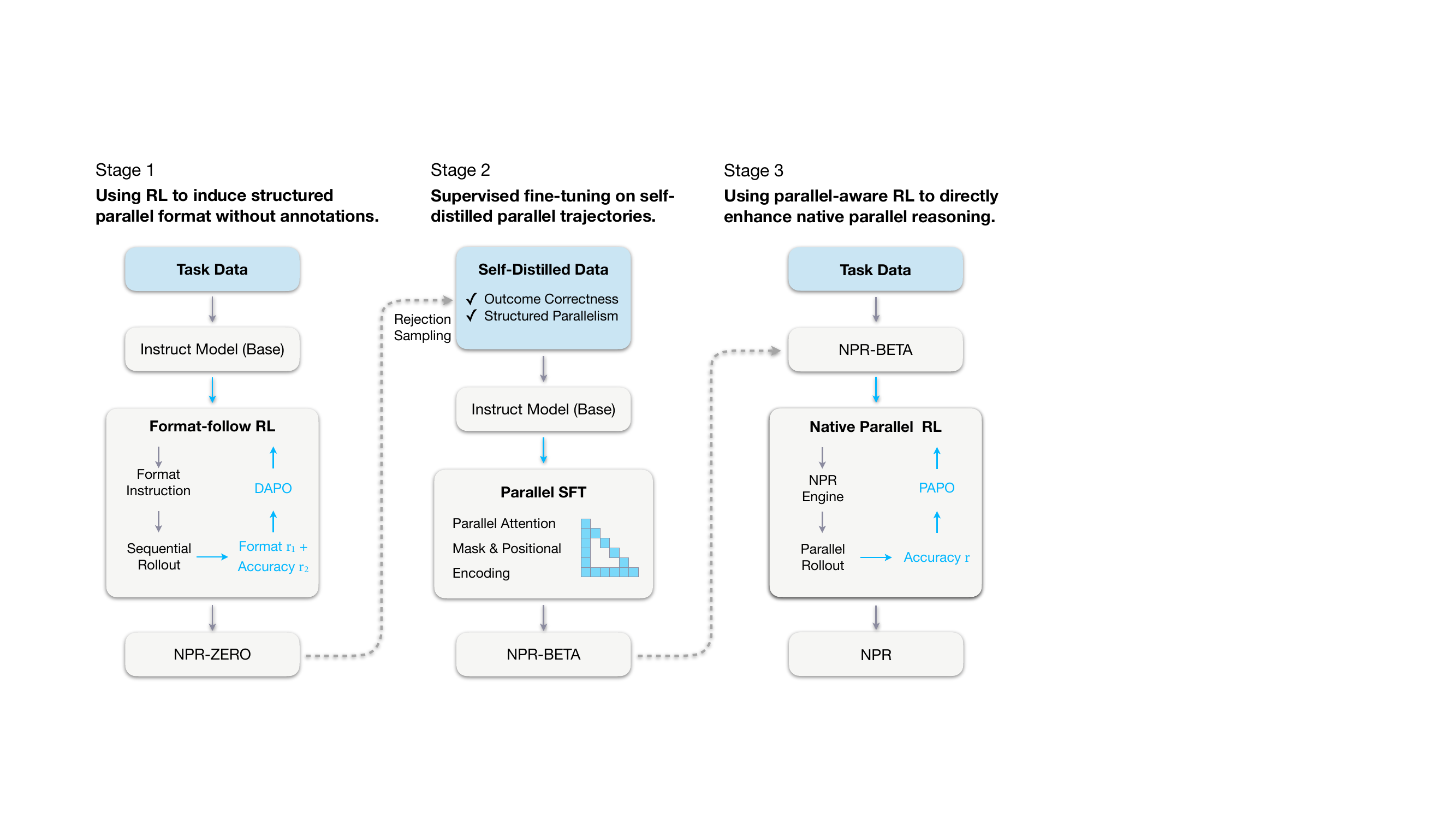
In Stage 1, the authors induce a structured parallel generation format using reinforcement learning without paired supervision. They adopt a simplified “Map–Process–Reduce” schema, where each parallel block is enclosed in explicit tags: <guideline> for planning, <step> for independent subtask execution, and <takeaway> for final aggregation. The model is trained via DAPO, with a reward function combining format compliance (0.0 for valid, penalty for invalid) and answer accuracy (+1.0 for correct, -1.0 for incorrect). This yields the NPR-Zero checkpoint, which serves as a generator for self-distilled training data.
Stage 2 performs supervised fine-tuning on the self-distilled dataset, which is constructed via rejection sampling: only trajectories that satisfy both outcome correctness and structural format compliance are retained. To enable parallel generation, the authors integrate Multiverse-style parallel attention masks and positional encodings, which allow multiple reasoning paths to coexist within a single forward pass while enabling efficient KV-cache reuse. The model is trained via standard negative log-likelihood on this curated dataset, producing NPR-Beta—a stable initialization for the final RL stage.
Stage 3 introduces Native Parallel RL, which directly optimizes the model’s parallel reasoning capability using a modified policy objective called Parallel-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO). To ensure structural fidelity, rollouts are generated using the NPR-Engine, a hardened inference engine that enforces strict parallel semantics and prevents malformed trajectories. During training, schema-level filtering is applied using the SFT-constructed attention mask and position IDs, eliminating the need for format rewards and reducing the reward signal to accuracy alone. The authors replace group-level advantage normalization with batch-level normalization to stabilize training, and they preserve gradients on special tokens that control parallel branching to maintain structural integrity. Crucially, they eliminate importance sampling and adopt a strict on-policy objective, replacing the clipped probability ratio with a stop-gradient fraction to avoid unstable reweighting. The resulting PAPO objective is:
J(θ)=E(q,y)∼D,{y^i}i=1G∼πθ(⋅∣q)−∑i=1G∣y^i∣1i=1∑Gt=1∑∣y^i∣sg[πθ(y^i,t∣q,y^i,<t)]πθ(y^i,t∣q,y^i,<t)A^i,t.As shown in the figure below, this approach contrasts with GRPO-style RL by replacing group normalization with batch normalization and eliminating the reference model and KL penalty, while enforcing parallel structure via the inference engine and structural filtering.
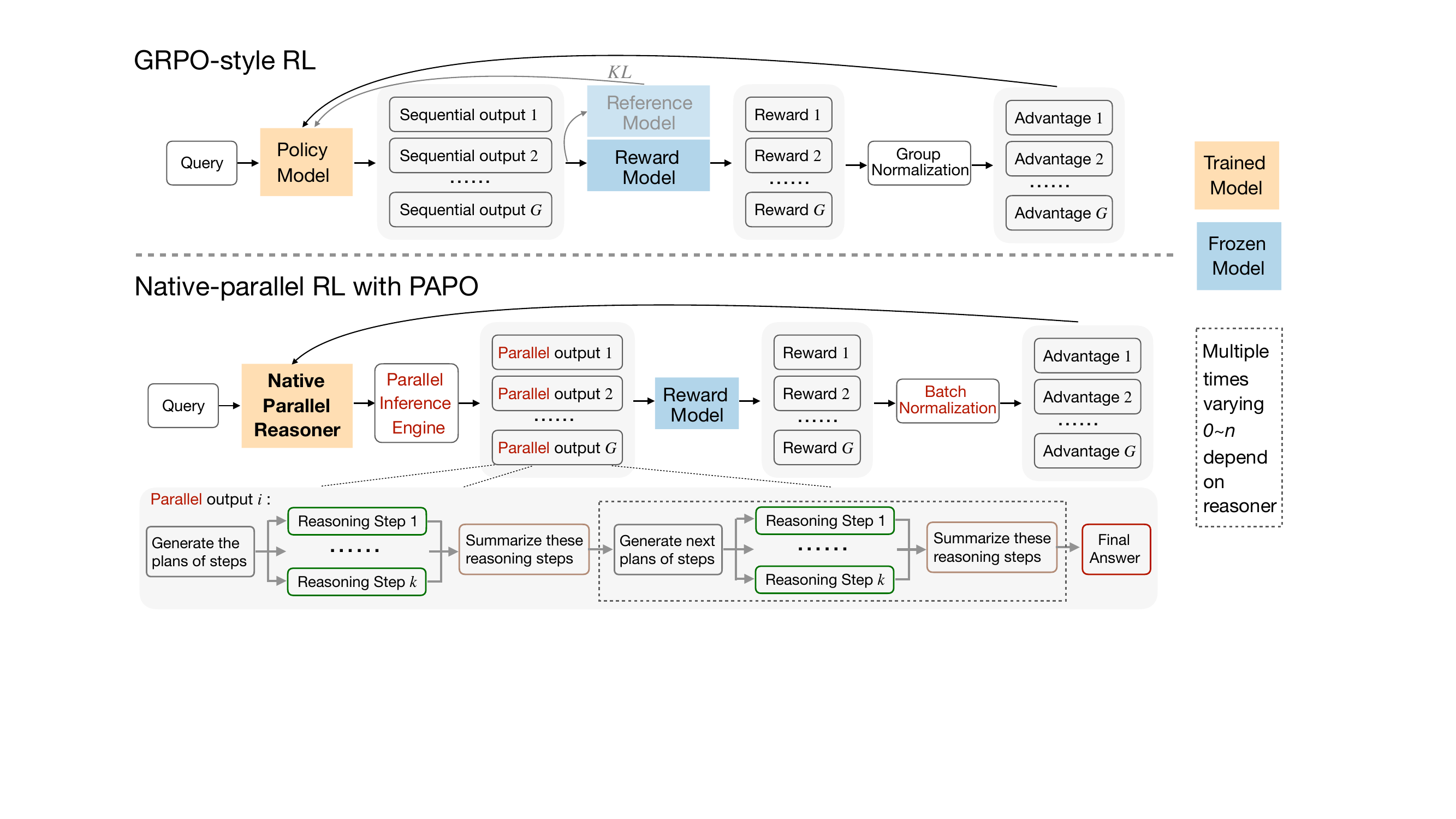
The NPR-Engine, a critical component enabling stable parallel rollouts, addresses several engineering challenges including KV-cache double-free, underestimated token budgets, undefined states from illegal schemas, and local repetition within step blocks. These fixes ensure deterministic behavior, memory safety, and correct length accounting under high-throughput parallel decoding, making large-scale RL feasible. The final NPR model exhibits genuine parallelism, token acceleration, and improved reasoning accuracy over autoregressive baselines, as demonstrated on benchmarks such as AIME25.
Experiment
- Evaluated NPR across eight reasoning benchmarks, showing consistent improvements over Multiverse, autoregressive training, and direct RL baselines
- Achieved 76.7% accuracy on AIME25, surpassing Multiverse-32B (72.8%) and Qwen3-4B-Instruct (60.1%)
- Demonstrated strong test-time scalability and inference acceleration due to native parallel reasoning architecture
- Eliminated pseudo-parallel behavior through clean template design and self-distilled parallel SFT
- Showed adaptive parallelism in case studies, with model adjusting branching depth based on problem difficulty
- NPR outperformed sequential models by enabling diverse subproblem exploration and robust verification via lightweight consistency checks
The authors use a self-distilled dataset and parallel training methods to develop NPR, which consistently outperforms baselines including Multiverse and sequential variants across multiple reasoning benchmarks. Results show that replacing sequential training with parallel SFT and RL yields measurable gains, with NPR achieving the highest average score of 65.0 and 100% parallel reasoning trigger rate across all evaluated datasets. The improvements are most pronounced on harder tasks, where parallel exploration and verification mechanisms enhance both accuracy and inference efficiency.
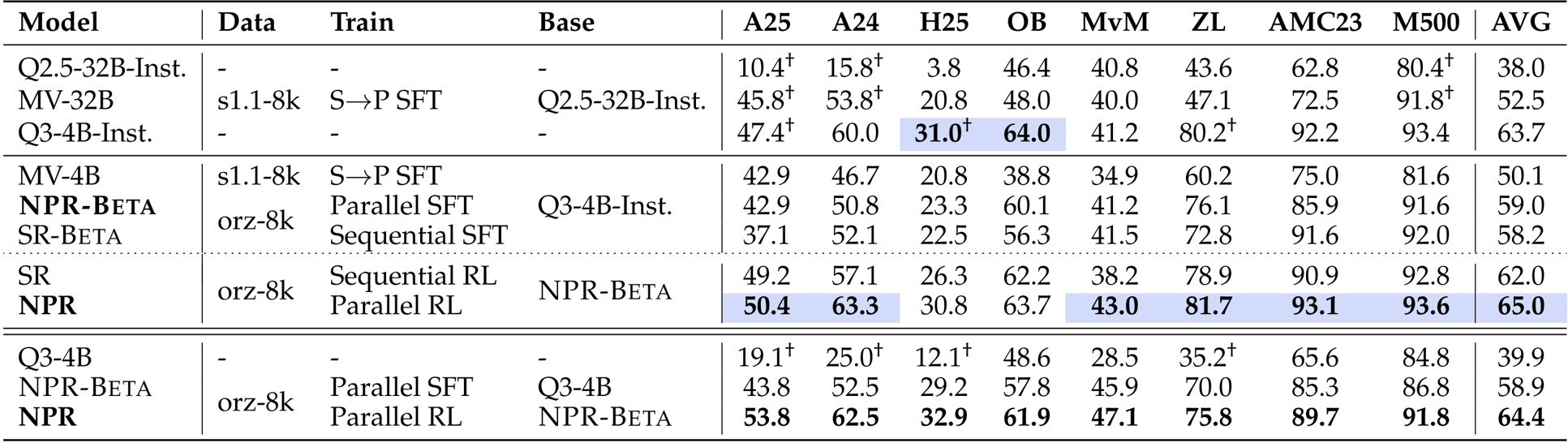
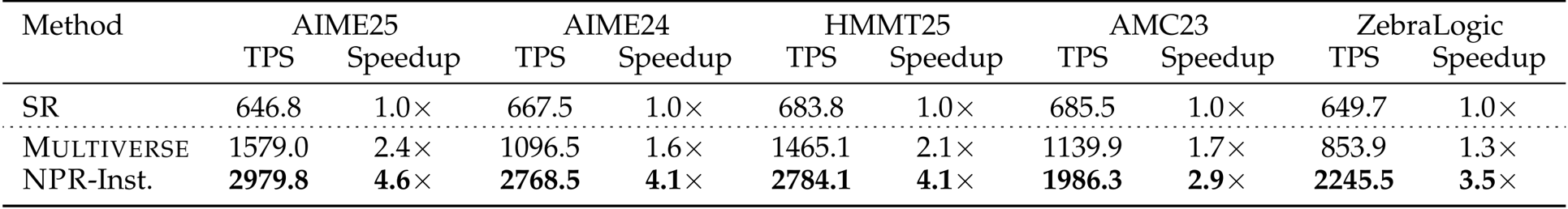
The authors evaluate inference efficiency by comparing token throughput and speedup across three methods: SR, Multiverse, and NPR-Inst. Results show NPR-Inst achieves the highest TPS and speedup on all five benchmarks, with gains ranging from 2.9x to 4.6x over SR and consistently outperforming Multiverse. The speedup scales with task difficulty, indicating NPR-Inst becomes more efficient as problems require deeper parallel exploration.
The authors use the parallel reasoning trigger rate to measure how consistently models adopt parallel reasoning across datasets. Results show that NPR-Inst. achieves a 100.0% trigger rate on all eight benchmarks, while MV-32B exhibits highly variable rates, indicating NPR’s training pipeline institutionalizes parallel reasoning as a default mode regardless of task domain.

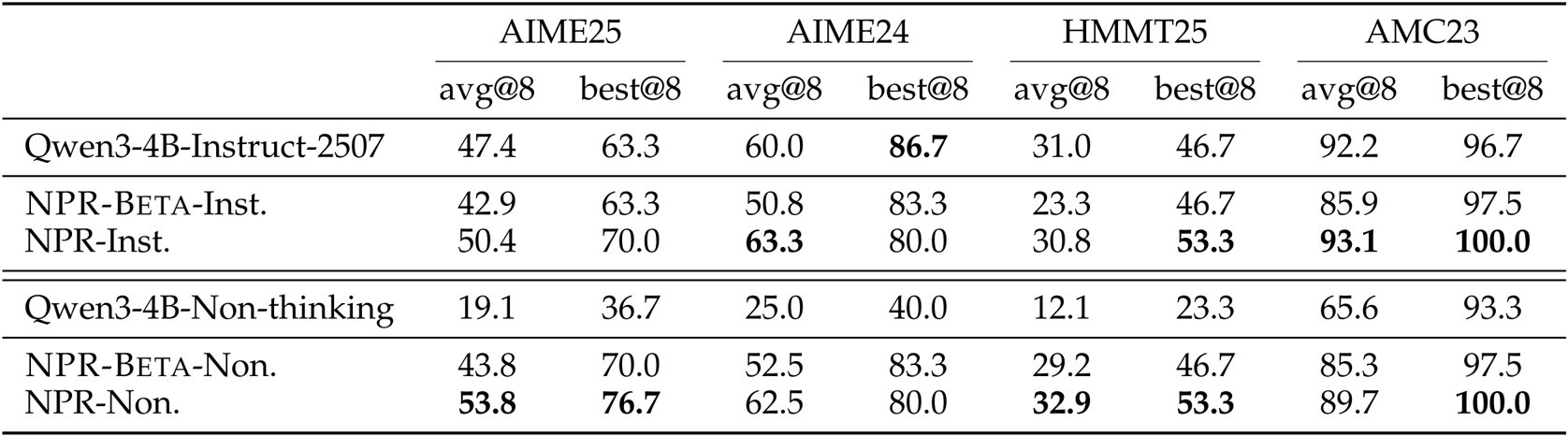
The authors evaluate NPR against Qwen3-4B baselines on four math benchmarks using avg@8 and best@8 metrics, showing that NPR consistently improves both average and best-case performance across all datasets. NPR-Inst. and NPR-Non. outperform their respective baselines, with the largest gains seen in best@8 scores, indicating stronger test-time scalability and oracle coverage. These results confirm that NPR’s parallel training pipeline enhances solution diversity and robustness compared to sequential or non-thinking models.