Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
プロンプトエンハンサー:チェーン・オブ・シンキングによるプロンプト再書き換えを活用したテキストto画像モデルの強化のためのシンプルなアプローチ
プロンプトエンハンサー:チェーン・オブ・シンキングによるプロンプト再書き換えを活用したテキストto画像モデルの強化のためのシンプルなアプローチ
概要
テキストから画像(T2I)への拡散モデルの最近の進展は、高忠実度の画像生成において顕著な能力を示している。しかし、これらのモデルは、属性の結合、否定、構成的関係といった複雑なユーザーのプロンプトを忠実に再現する点でしばしば困難に直面しており、結果としてユーザーの意図と生成結果との間に大きな乖離が生じる。この課題に対処するため、本研究では、事前学習済みT2Iモデルの重みを変更することなく、あらゆるモデルに適用可能な普遍的なプロンプト再構成フレームワーク「PromptEnhancer」を提案する。従来のモデル固有のファインチューニングや画像報酬スコアのような暗黙的な報酬信号に依存する手法とは異なり、本フレームワークは再構成器(rewriter)と生成器(generator)を分離する。この目的を達成するために、Chain-of-Thought(CoT)形式の再構成器を強化学習により訓練し、専用の報酬モデル「AlignEvaluator」によってガイドする。AlignEvaluatorは、T2Iモデルの典型的な失敗モードを包括的に分析した上で導き出された24項目からなる体系的な分類体系に基づき、明示的かつ細分化されたフィードバックを提供するように学習されている。本フレームワークは、AlignEvaluatorからの報酬を最大化するようにCoT再構成器を最適化することで、T2Iモデルによってより正確に解釈可能なプロンプトを生成する能力を学習する。HunyuanImage 2.1モデルを用いた広範な実験により、PromptEnhancerが多様な意味的・構成的課題において画像とテキストの整合性を顕著に向上させることを実証した。さらに、今後の研究を促進するため、高品質な人間の好み評価ベンチマークを新たに提案した。
One-sentence Summary
The authors propose PromptEnhancer, a universal prompt rewriting framework developed by Tencent Hunyuan that enhances text-to-image generation by decoupling a Chain-of-Thought rewriter from pretrained models via reinforcement learning guided by a fine-grained AlignEvaluator reward model, which provides explicit feedback on 24 failure modes to improve attribute binding, negation, and compositional accuracy, significantly boosting alignment on HunyuanImage 2.1 and enabling more faithful interpretation of complex user prompts.
Key Contributions
- Many text-to-image diffusion models fail to accurately interpret complex user prompts due to issues like attribute binding, negation, and compositional relationships, leading to a significant gap between user intent and generated output.
- PromptEnhancer introduces a universal, model-agnostic prompt rewriting framework that decouples prompt refinement from image generation by training a Chain-of-Thought rewriter via reinforcement learning, guided by a novel AlignEvaluator reward model.
- The AlignEvaluator provides fine-grained feedback across 24 key points organized into six categories, enabling precise alignment with human intent; experiments on HunyuanImage 2.1 show substantial improvements in image-text alignment, supported by a new high-quality human preference benchmark.
Introduction
Text-to-image diffusion models have achieved impressive photorealism and diversity, but they often fail to accurately interpret complex user prompts—struggling with attribute binding, negation, and compositional relationships—leading to a persistent gap between user intent and generated output. Prior prompt rewriting methods are limited by their reliance on model-specific fine-tuning or coarse, implicit rewards like CLIP scores, which lack the precision to correct nuanced errors and hinder adaptability across different models. The authors introduce PromptEnhancer, a universal, model-agnostic framework that decouples prompt rewriting from image generation. It employs a Chain-of-Thought rewriter trained via reinforcement learning using a novel reward model called AlignEvaluator, which provides fine-grained feedback across 24 specific dimensions of image-text alignment. This enables the rewriter to systematically enhance prompts with explicit, structured details, significantly improving fidelity and compositional accuracy across diverse domains without modifying the underlying T2I model.
Dataset
- The dataset is constructed through a multi-stage curation pipeline to support both Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) and policy alignment via reinforcement learning.
- The SFT dataset comprises 485,119 high-quality (user prompt, Chain-of-Thought, reprompt) triplets, generated from a pool of 3.26 million images—1.53 million Chinese-centric and 1.73 million English-centric.
- User prompts are simulated using an image captioning model, producing 2.26 million proxy prompts that reflect naturalistic, concise user queries.
- For each prompt, Gemini-2.5-Pro generates a detailed Chain-of-Thought reasoning path and multiple reprompt candidates, enabling diverse rewriting exploration.
- An automated filtering step using Gemini-2.5-Pro removes instances with semantic deviation, information loss, or incoherence, reducing the dataset from 1 million to 611,921 triplets.
- A human-in-the-loop selection process evaluates reprompt candidates by generating corresponding images via the Hunyuan Text-to-Image model; professional annotators select the reprompt that best aligns with intent and produces the highest visual quality.
- The final SFT dataset is thematically distributed as: Design (27%), Art (23%), Film & Story (22%), Illustration (18%), and Creative tasks (10%), with detailed sub-category breakdowns shown in Figure 4.
- For policy alignment, a separate set of approximately 50,000 prompts is created using the same image simulation method but from a disjoint image pool to prevent data leakage.
- This RL prompt set lacks ground-truth CoTs or reprompts; instead, the AlignEvaluator provides dynamic feedback during training to guide policy optimization.
- The thematic distribution of the RL prompt set mirrors that of the SFT data to ensure consistent training dynamics.
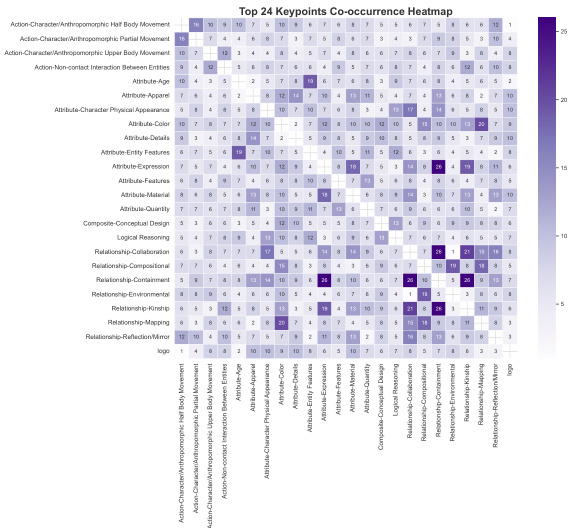
- A complementary evaluation benchmark, T2I-Keypoints-Align, includes 6,687 prompts—44.9% English and 55.1% Chinese—each annotated with fine-grained semantic keypoints (e.g., actions, attributes, relationships) for detailed model assessment.
- Chinese prompts are more concise (mean ~100 characters) and exhibit higher keypoint density (peaking at 4 keypoints per prompt), while English prompts show greater variation in length and structure.
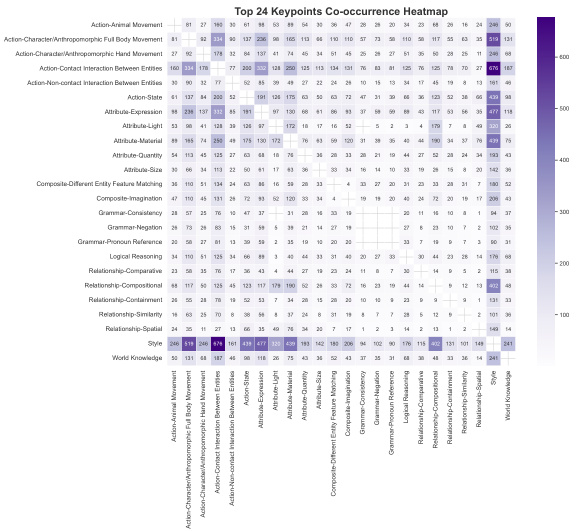
- The benchmark enables granular evaluation across 24 fine-grained KeyPoints and six Super-Categories, with performance visualized in Figure 5 and Figure 8.
Method
The authors leverage a two-stage training framework for PromptEnhancer, a universal prompt rewriting system designed to enhance the performance of pretrained Text-to-Image (T2I) models without modifying their weights. The core of this framework consists of a CoT Rewriter, a policy model based on a large vision-language model, and a specialized reward model called the AlignEvaluator. The primary objective is to train the CoT Rewriter to transform a user's initial prompt into a more detailed and structured instruction that better aligns with the user's intent, thereby improving the quality of the generated images.
As shown in the figure below, the framework operates in two distinct stages. The first stage, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), initializes the CoT Rewriter. This stage uses a dataset of (user prompt, reprompt) pairs, where the reprompt is a detailed, chain-of-thought (CoT) enriched version of the original prompt. The dataset is generated by distilling knowledge from a powerful proprietary large model, such as Gemini-2.5-Pro or DeepSeekV3, which acts as a "teacher" to analyze the prompt's elements, identify ambiguities, and synthesize a comprehensive, structured instruction. The CoT Rewriter is fine-tuned on this dataset using a standard next-token prediction loss, which teaches it to generate responses in the desired CoT format and establishes a strong foundation for the subsequent refinement stage.
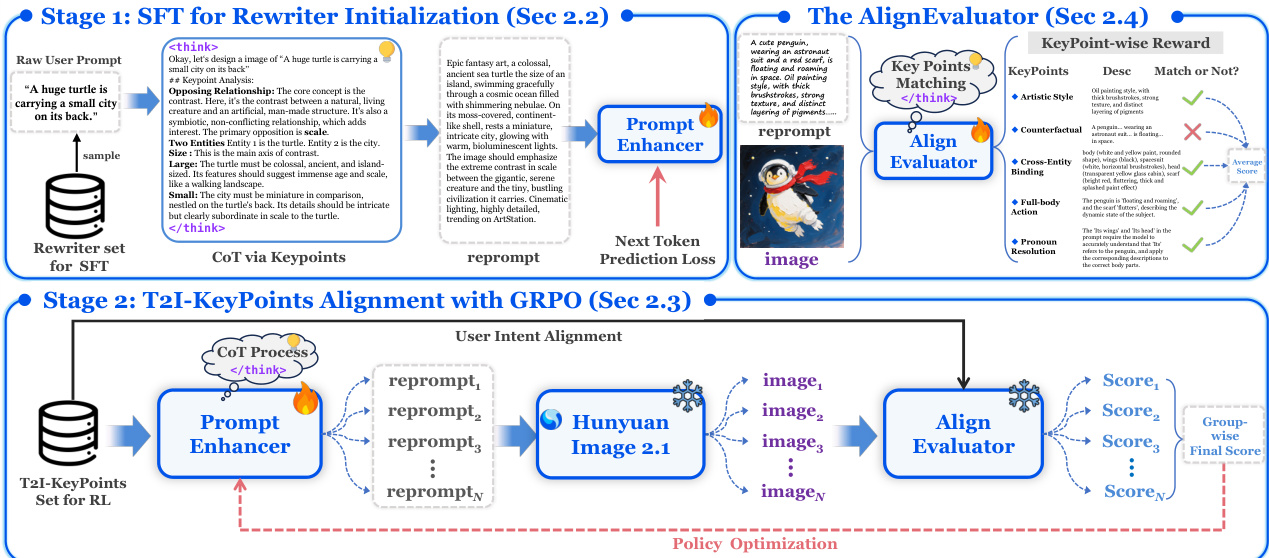
The second stage, Policy Alignment, refines the initialized rewriter using reinforcement learning. This stage employs Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to align the rewriter's output with the fine-grained preferences captured by the AlignEvaluator. The process is iterative: for a given user prompt, the CoT Rewriter generates multiple candidate rewritten prompts. Each candidate is fed into a frozen T2I model (e.g., Hunyuan Image 2.1) to generate a corresponding image. The pre-trained AlignEvaluator then assesses each (image, user prompt) pair and provides a scalar reward based on a taxonomy of 24 fine-grained key points, which are organized into six categories. These categories include attributes like Artistic Style, Counterfactual, and Cross-Entity Binding, as detailed in the accompanying heatmap. The rewards are used to update the rewriter's policy, creating a preference ranking that encourages the generation of prompts leading to higher rewards, thus optimizing the alignment between the user's intent and the final image output. The AlignEvaluator is central to this process, providing a robust and nuanced reward signal that guides the rewriter's policy optimization.
Experiment
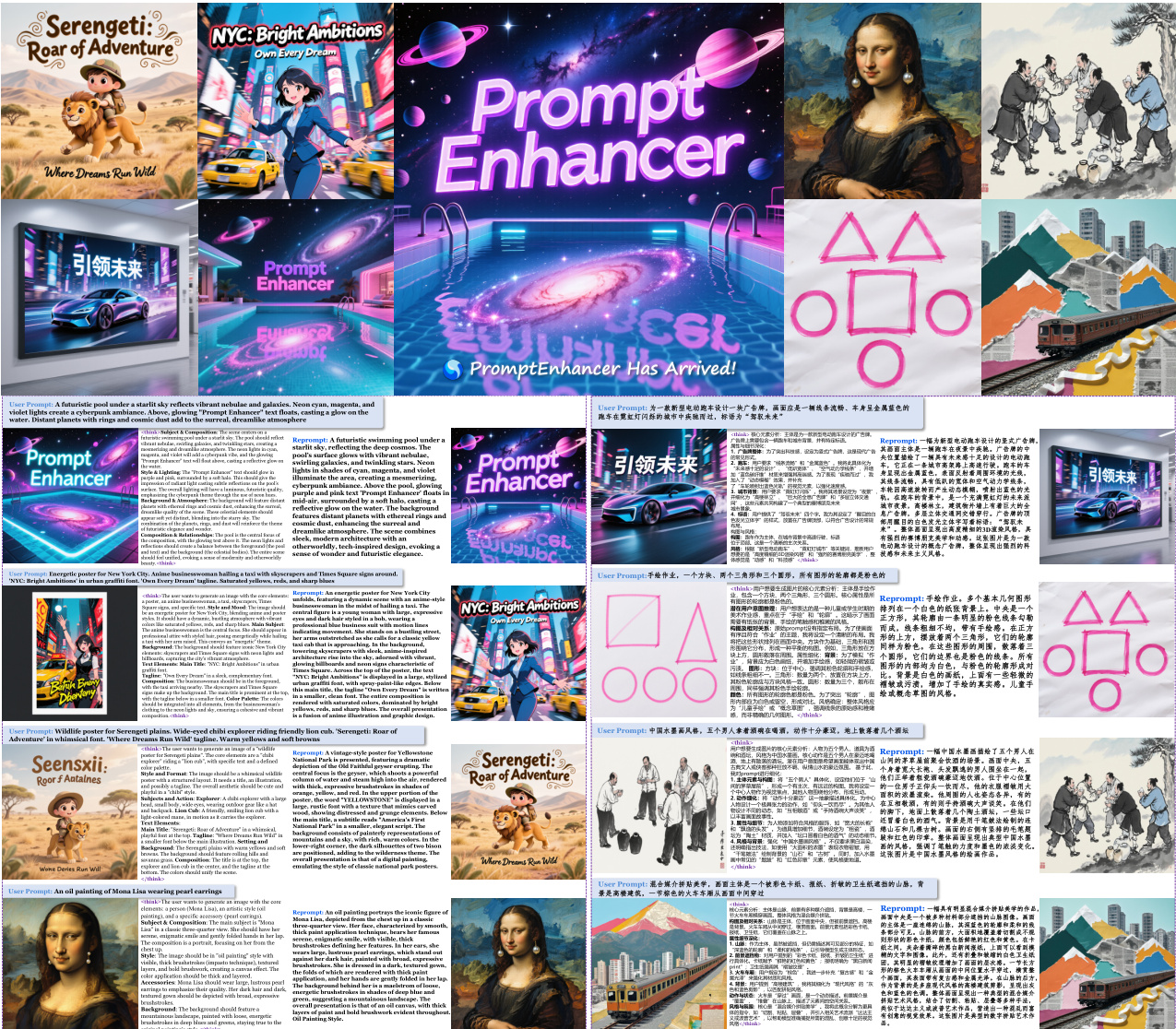
- PromptEnhancer significantly improves text-to-image models' ability to follow complex prompts by generating enriched, detailed prompts that enhance visual fidelity and stylistic accuracy, as demonstrated in qualitative comparisons (Figure 6).
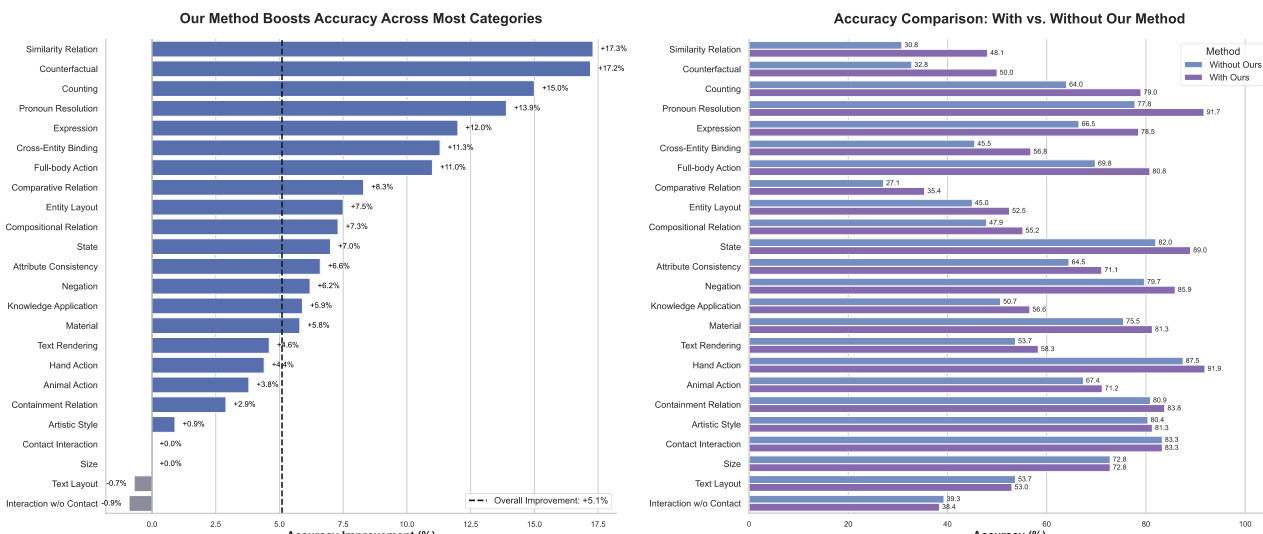
- On the proposed benchmark, PromptEnhancer achieves an average +5.1% improvement in prompt-following accuracy across 24 semantic categories, with 20 out of 24 categories showing performance gains.
- Notable improvements include +17.3% in Similarity Relation, +17.2% in Counterfactual Reasoning, +15.0% in Counting, +13.9% in Pronoun Resolution, +12.0% in Facial Expression, and +11.3% in Cross-Entity Binding.
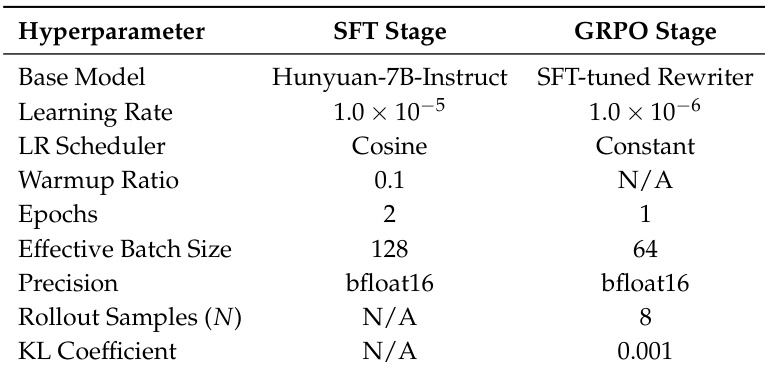
- The framework is evaluated on HunyuanImage 2.1 with a plug-and-play design, using supervised fine-tuning and GRPO-based policy alignment on 8 H800 GPUs, with training conducted via bfloat16 mixed precision.
- Minor regressions in Text Layout (-0.7%) and Interaction w/o Contact (-0.9%) are observed, but these are outweighed by broad gains, confirming the robustness and effectiveness of the approach.
The authors use PromptEnhancer to improve a text-to-image model's ability to follow complex prompts, evaluating its impact across 24 semantic categories. Results show that PromptEnhancer significantly boosts accuracy, with an average improvement of +5.1% across all categories, particularly in complex reasoning tasks such as similarity relation, counterfactual reasoning, and counting.
The authors use the Hunyuan-7B-Instruct model as the base model for the SFT stage and fine-tune it with a learning rate of 1.0×10−5, a cosine scheduler, and a warmup ratio of 0.1 over 2 epochs, achieving an effective batch size of 128 using bfloat16 precision. For the GRPO stage, the SFT-tuned rewriter is further optimized with a reduced learning rate of 1.0×10−6, a constant scheduler, and 1 epoch, using 8 rollout samples and a KL coefficient of 0.001 to stabilize policy updates.
The authors use the PromptEnhancer framework to improve text-to-image models' ability to follow complex prompts, evaluating its impact across 24 semantic categories. Results show that PromptEnhancer significantly boosts prompt-following accuracy, achieving an average improvement of +5.1% across all categories, with substantial gains in complex reasoning tasks such as similarity relations, counterfactual reasoning, and counting.
The authors use PromptEnhancer to improve a text-to-image model's ability to follow complex prompts, evaluating its performance on a benchmark with 24 semantic categories. Results show that PromptEnhancer significantly boosts prompt-following accuracy, increasing the average performance by 5.1% across all categories, with substantial gains in complex reasoning tasks such as similarity relations, counterfactual reasoning, and counting.