Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
140万件のオープンソース分散推論データセットが大規模言語モデルの訓練を強化
140万件のオープンソース分散推論データセットが大規模言語モデルの訓練を強化
Han Zhao Haotian Wang Yiping Peng Sitong Zhao Xiaoyu Tian Shuaiting Chen Yunjie Ji Xiangang Li
概要
AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilledは、一般推論タスク向けに設計された大規模なデータセットであり、高品質かつ挑戦的な推論問題から構成されています。これらの問題は多数のオープンソースデータセットから収集され、意味的重複除去および細心のクリーニング処理が施されており、テストセットの汚染を排除しています。データセット内のすべての回答は、主にDeepSeek-R1を含む推論モデルから蒸留(distillation)されたものであり、厳格な検証プロセスを経ています。数学問題については参照解答との照合により検証され、コード問題はテストケースを用いて検証され、その他のタスクは報酬モデル(reward model)を活用して評価されています。本データセットを用いて単純な教師あり微調整(Supervised Fine-Tuning: SFT)のみで訓練されたAM-Distill-Qwen-32Bモデルは、AIME2024、MATH-500、GPQA-Diamond、LiveCodeBenchの4つのベンチマークにおいて、DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32Bモデルを上回る性能を示しました。さらに、AM-Distill-Qwen-72BモデルはすべてのベンチマークでDeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70Bモデルを上回りました。本研究チームは、強力な推論指向の大規模言語モデル(LLM)の開発を促進することを目的として、この140万件の問題および対応する回答を研究コミュニティに公開します。データセットは以下のリンクより公開されています:\href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M}{https://huggingface.co/datasets/a-m-team/AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M}。
One-sentence Summary
The authors, affiliated with a-m-team, introduce AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled, a 1.4M problem dataset with verified reasoning traces distilled from DeepSeek-R1, enabling SFT-trained AM-Distill-Qwen models to outperform larger predecessors on key benchmarks, advancing reasoning-capable LLM development.
Key Contributions
- The AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled dataset addresses the need for high-quality, large-scale reasoning data by compiling 1.4 million curated problems from diverse open-source sources, with rigorous semantic deduplication and contamination removal to ensure data purity and challenge.
- The dataset features reasoning traces distilled from DeepSeek-R1 and verified through multiple methods—answer checking for math, test cases for code, and reward models for other tasks—ensuring high accuracy and reliability for training.
- Models trained on this dataset via simple Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), such as AM-Distill-Qwen-32B and AM-Distill-Qwen-72B, outperform their DeepSeek-R1 counterparts on four major benchmarks, demonstrating the dataset’s effectiveness in enhancing reasoning capabilities.
Introduction
The authors leverage a newly released open-source dataset of 1.4 million distilled reasoning examples to enhance large language model training, particularly for tasks requiring structured reasoning and intent understanding. This dataset is designed to support instruction tuning by providing high-quality, difficulty-rated queries that reflect a spectrum of cognitive demands, from basic factual recall to expert-level problem solving. Prior work in this space often relied on limited or proprietary datasets with inconsistent difficulty annotations, which hindered model generalization and reliable evaluation. The main contribution is the creation of a large-scale, publicly available dataset with fine-grained difficulty labeling, enabling more precise training and benchmarking of reasoning capabilities in LLMs.
Dataset
- The AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled dataset comprises 1.4 million high-quality reasoning problem-response pairs, sourced from a combination of open-source datasets and model-distilled content.
- Of these, 500,000 entries are fully derived from open-source datasets, including math, code, science QA, and general chat data, while 900,000 entries have instructions sourced from open-source materials and responses distilled from DeepSeek-R1.
- Data sources include high-quality benchmarks such as NuminaMath, MetaMathQA, OpenCoder, Omni-MATH, PRIME, CodeIO, MATH-lighteval, and community-provided datasets like OpenThoughts, OpenR1Math, KodCode, and Dolphin-R1. General chat data comes from InfinityInstruct and Orca.
- The dataset is categorized into four primary types—math, code, science QA, and general chat—with additional fine-grained labels (e.g., creative writing, instruction following) generated using Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct to enhance diversity and usability.
- To ensure quality and challenge, the authors used a large language model to score instruction difficulty and downsampled easy and medium-difficulty examples, focusing on more complex reasoning tasks.
- Strict semantic deduplication was applied using embeddings and similarity thresholds, with priority rules to retain only one representative entry per cluster, ensuring uniqueness and diversity.
- All responses underwent multi-stage verification: mathematical problems were validated via rule-based checks (math-verify) and LLM evaluation; code problems were tested in sandbox environments using test cases; and non-code/math tasks were assessed using a reward model (Decision-Tree-Reward-Llama-3.1-8B) and Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct, with scores above a threshold retained.
- Rule-based checks ensured format compliance (e.g., proper and tags) and eliminated responses with excessive n-gram repetition.
- Each entry includes rich metadata: language (English, Chinese, or other), token/word count, category, difficulty score, and reference answers or test cases.
- The dataset uses a unified, standardized format to support easy integration into training pipelines.
- The authors used this dataset for Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) of the AM-Distill-Qwen-32B and AM-Distill-Qwen-72B models, achieving state-of-the-art performance on AIME2024, MATH-500, GPQA-Diamond, and LiveCodeBench.
- Training leveraged a mixture of the 1.4 million entries with no explicit split, but the data’s high difficulty and long reasoning chains were designed to support extended Chain-of-Thought training.
- The dataset is released on Hugging Face under a research-only license, with warnings about potential inaccuracies in model-generated responses and the need for careful review before use.
Experiment
- Evaluated AM-Distill-Qwen-32B and AM-Distill-Qwen-72B models on multiple benchmarks using consistent generation settings: max length 32,768 tokens, temperature 0.6, top-p 0.95, with 16 samples for AIME 2024 and 4 samples for other benchmarks to estimate pass@1.
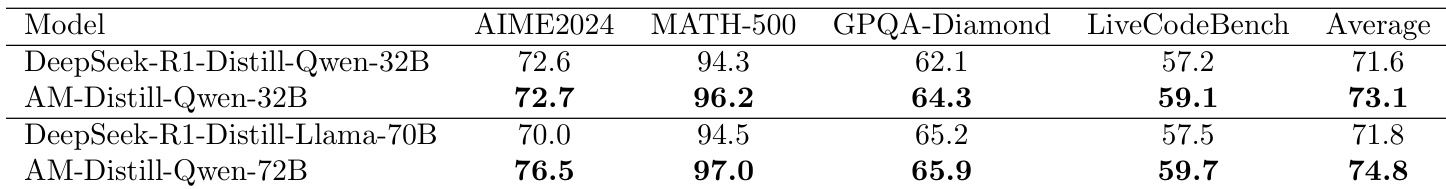
- AM-Distill-Qwen-32B achieved improved accuracy over DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B: AIME2024 (72.7% vs. 72.6%), MATH-500 (96.2% vs. 94.3%), GPQA Diamond (64.3% vs. 62.1%), LiveCodeBench (59.1% vs. 57.2%), with overall average accuracy increasing from 71.6% to 73.1%.
- AM-Distill-Qwen-72B outperformed DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B: AIME2024 (76.5% vs. 70.0%), MATH-500 (97.0% vs. 94.5%), GPQA Diamond (65.9% vs. 65.2%), LiveCodeBench (59.7% vs. 57.5%).
- Results validate that training on the AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M dataset significantly enhances reasoning capabilities across diverse benchmarks.
- Dataset difficulty distribution shows 51.8% Medium and 25.7% Hard entries, indicating a focus on challenging reasoning tasks.
The authors use the AM-Distill-Qwen-32B and AM-Distill-Qwen-72B models to evaluate performance on four benchmarks, showing improvements over baseline models. Results show that AM-Distill-Qwen-32B achieves higher accuracy than DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B across all benchmarks, with notable gains on MATH-500 (96.2% vs. 94.3%) and GPQA Diamond (65.9% vs. 62.1%), while AM-Distill-Qwen-72B outperforms DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B, particularly on AIME 2024 (76.5% vs. 70.0%) and MATH-500 (97.0% vs. 94.5%).
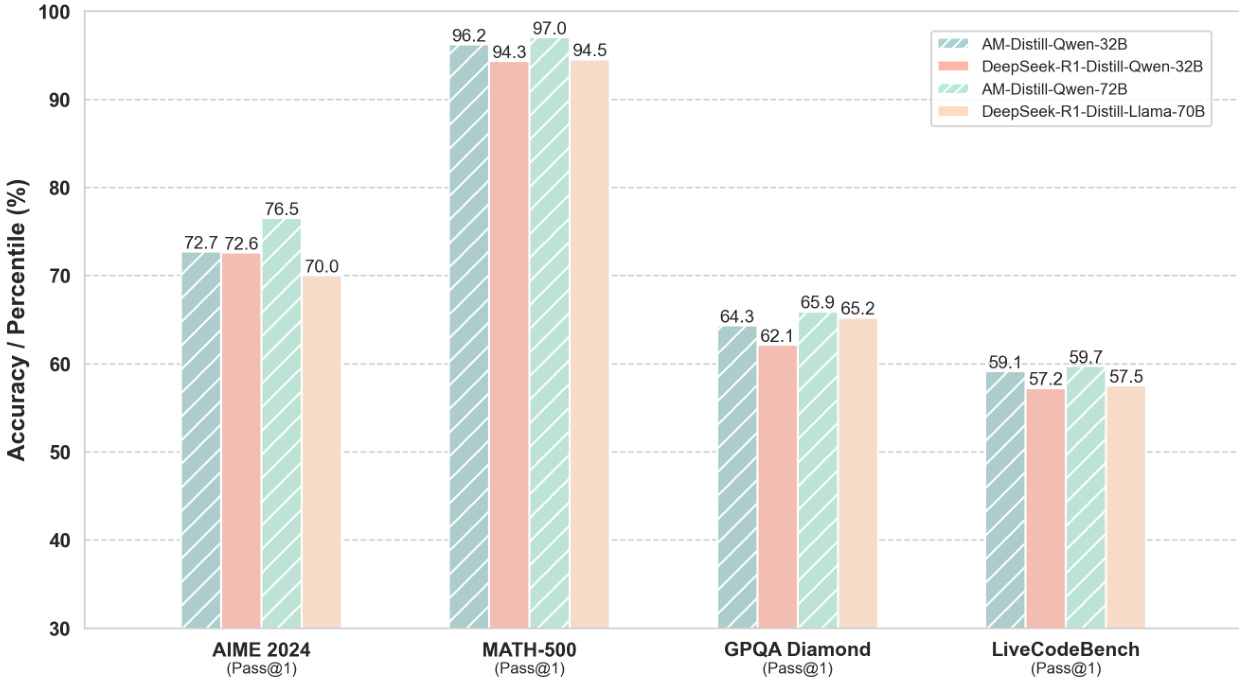
The authors use the AM-Distill-Qwen-32B model, trained on their AM-DeepSeek-R1-Distilled-1.4M dataset, to achieve improved performance over DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-32B across all benchmarks, with accuracy increases from 71.6% to 73.1% on average. Results show that the AM-Distill-Qwen-72B model further improves performance, achieving an average accuracy of 74.8%, outperforming DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-70B on all evaluated tasks.