Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
YOLOE:リアルタイム セイティング エニシング
YOLOE:リアルタイム セイティング エニシング
Ao Wang Lihao Liu Hui Chen Zijia Lin Jungong Han Guiguang Ding
概要
オブジェクト検出とセグメンテーションは、コンピュータビジョンの応用分野で広く用いられているが、YOLOシリーズなど従来のモデルは効率的かつ高精度である一方で、事前に定義されたカテゴリに制限されており、オープンな状況下での柔軟な適応が困難である。近年のオープンセット手法は、テキストプロンプトや視覚的ヒント、あるいはプロンプトフリーな枠組みを活用してこの課題に取り組んできたが、計算負荷の高さやデプロイの複雑さにより、性能と効率の間に妥協を強いられることが多かった。本研究では、単一の極めて効率的なモデル内に、多様なオープンプロンプト機構を統合したYOLOEを提案する。これにより、リアルタイムで「何でも見られる」(seeing anything)能力を実現した。テキストプロンプトに対しては、再パラメータ化可能な領域-テキストアライメント(RepRTA)戦略を提案する。この戦略は、再パラメータ化可能な軽量補助ネットワークを用いて事前学習済みのテキスト埋め込みを精緻化し、推論時および転送時にオーバーヘッドをゼロに保ちながら、視覚的・テキスト的アライメントを強化する。視覚プロンプトに対しては、セマンティック活性化型視覚プロンプトエンコーダ(SAVPE)を導入する。このアーキテクチャは、セマンティックと活性化の分離されたブランチを採用することで、最小限の計算複雑さでより優れた視覚的埋め込みと精度を達成する。また、プロンプトフリーな状況では、ラジ・リージョンプロンプトコントラスト(LRPC)戦略を提案する。この戦略は、内蔵された大規模語彙と専用の埋め込みを活用し、すべてのオブジェクトを識別するが、高コストな言語モデルへの依存を回避する。広範な実験により、YOLOEが極めて優れたゼロショット性能と転移性を示し、高い推論効率と低コストな学習を実現していることが確認された。特にLVISデータセットにおいて、学習コストを3倍低減し、推論速度を1.4倍向上させたYOLOE-v8-Sは、YOLO-Worldv2-Sを3.5 APの差で上回った。また、COCOへの転移学習においては、閉集合学習モデルであるYOLOv8-Lと比較して、YOLOE-v8-Lが0.6 APᵇおよび0.4 APᵐの向上を達成しつつ、学習時間はほぼ4倍短縮された。コードとモデルは、https://github.com/THU-MIG/yoloe にて公開されている。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Tsinghua University propose YOLOE, a highly efficient unified model for open-set object detection and segmentation, integrating Re-parameterizable Region-Text Alignment, Semantic-Activated Visual Prompt Encoder, and Lazy Region-Prompt Contrast to enable real-time performance across text, visual, and prompt-free scenarios with minimal overhead, outperforming prior methods in zero-shot accuracy and training efficiency.
Key Contributions
- YOLOE addresses the limitation of closed-set object detection and segmentation models by enabling real-time, unified detection and segmentation across diverse open prompt mechanisms—text, visual, and prompt-free—without sacrificing efficiency or accuracy.
- It introduces three novel components: RepRTA for efficient text prompt alignment via a re-parameterizable lightweight network, SAVPE for low-complexity visual prompt encoding with decoupled semantic and activation branches, and LRPC for prompt-free detection using a built-in large vocabulary and specialized embedding.
- Extensive evaluations show YOLOE achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on LVIS and COCO, surpassing YOLO-Worldv2 and YOLOv8 with up to 3.5 AP gain, 1.4× faster inference, and 4× less training time, while maintaining minimal model overhead.
Introduction
The authors address the growing need for real-time, flexible object detection and segmentation in open-world scenarios where models must respond to diverse prompts—text, visual, or none—without relying on predefined categories. While prior work has made progress in open-vocabulary detection, existing solutions often specialize in one prompt type, leading to inefficiencies: text-prompted methods suffer from high computational costs due to cross-modal fusion, visual-prompted approaches rely on heavy transformers or external encoders, and prompt-free methods depend on large language models, increasing latency and memory usage. The authors introduce YOLOE, a unified, efficient model that supports all three prompt types within a single architecture. They propose three key innovations: a re-parameterizable region-text alignment module that enhances text prompt performance with zero inference overhead, a lightweight semantic-activated visual prompt encoder that generates prompt-aware features with minimal complexity, and a lazy region-prompt contrast strategy that enables prompt-free detection without language models. As a result, YOLOE achieves state-of-the-art performance across all prompt types while significantly reducing training cost and inference latency—outperforming YOLO-Worldv2 and T-Rex2 with up to 3.5 AP gain and 1.4× faster inference on edge devices.
Dataset
- The dataset for YOLOE training combines Objects365, GoldG (which includes GQA and Flickr30k), providing diverse and large-scale image data for object detection and segmentation tasks.
- Objects365 contributes general-purpose object instances, while GoldG enhances visual-linguistic understanding through image-caption pairs from GQA and Flickr30k.
- High-quality segmentation masks are generated using SAM-2.1-Hiera-Large with ground truth bounding boxes as prompts; masks with insufficient area are filtered out to ensure quality.
- Mask smoothing is applied using a 3×3 Gaussian kernel for small masks and a 7×7 kernel for large ones to improve edge continuity.
- Mask refinement follows a method from prior work, iteratively simplifying contours to reduce noise while preserving the overall shape and structure.
- The training pipeline uses AdamW optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.002, batch size of 128, and weight decay of 0.025.
- Data augmentation includes color jittering, random affine transformations, random horizontal flipping, and mosaic augmentation to improve model robustness.
- During transfer to COCO for linear probing and full tuning, the same optimizer and hyperparameters are used, but with a reduced learning rate of 0.001.
Method
The authors leverage a unified YOLO-based architecture to integrate object detection and segmentation under diverse open prompt mechanisms. As shown in the framework diagram, the model begins with a backbone network that processes the input image, followed by a PAN (Path Aggregation Network) to generate multi-scale feature maps at different levels (P3, P4, P5). These features are then fed into three parallel heads: a regression head for bounding box prediction, a segmentation head for producing prototype and mask coefficients, and an embedding head for generating object embeddings. The embedding head is adapted from the classification head in standard YOLOs, with its final convolution layer's output channel count adjusted to match the embedding dimension instead of the class count in closed-set scenarios.
For text prompts, the model employs a Re-parameterizable Region-Text Alignment (RepRTA) strategy. This involves using a pretrained text encoder to obtain textual embeddings, which are then refined during training by a lightweight auxiliary network. This network, as illustrated in the figure below, consists of a single feed-forward block and is designed to enhance the textual embeddings without introducing significant computational overhead. The refined embeddings serve as classification weights, which are contrasted with the object embeddings from the anchor points to determine category labels. The process is formalized as Label=O⋅PT, where O represents the object embeddings and P represents the prompt embeddings.
For visual prompts, the model introduces a Semantic-Activated Visual Prompt Encoder (SAVPE). This encoder features two decoupled branches: a semantic branch and an activation branch. The semantic branch processes the multi-scale features from the PAN to generate prompt-agnostic semantic features. The activation branch, as shown in the figure below, takes the visual prompt (e.g., a mask) and image features, processes them through convolutions, and outputs prompt-aware weights. These weights are then used to modulate the semantic features, and their aggregation produces the final visual prompt embedding. This design allows for efficient processing of visual cues with minimal complexity.
In the prompt-free scenario, the model utilizes a Lazy Region-Prompt Contrast (LRPC) strategy. This approach reformulates the task as a retrieval problem. A specialized prompt embedding is trained to identify anchor points corresponding to objects. Only these identified points are then matched against a built-in large vocabulary to retrieve category names, bypassing the costly computation for irrelevant points. This lazy retrieval mechanism ensures high efficiency without sacrificing performance. The overall framework is designed to support all three prompt types within a single, highly efficient model, enabling real-time performance across various open-set scenarios.
Experiment
- YOLOE validates superior zero-shot detection and segmentation performance on LVIS, achieving 33.0% AP with YOLOE-v8-L, outperforming YOLOv8-Worldv2 by 3.5–0.4 AP across scales, with 1.2–1.6× faster inference on T4 and iPhone 12.
- YOLOE-v8-M / L achieves 20.8 / 23.5 AP^m in zero-shot segmentation, surpassing fine-tuned YOLO-Worldv2-M / L by 3.0 / 3.7 AP^m, demonstrating strong generalization without LVIS data.
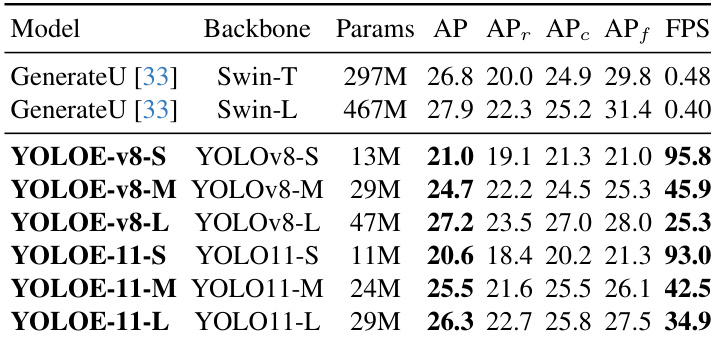
- In prompt-free evaluation, YOLOE-v8-L achieves 27.2 AP and 23.5 AP_r, outperforming GenerateU with Swin-T by 0.4 AP and 3.5 AP_r, while using 6.3× fewer parameters and 53× faster inference.
- YOLOE exhibits strong transferability to COCO: with less than 2% training time, YOLOE-11-M / L reaches over 80% of YOLO11-M / L performance in linear probing, and with 3× less training time, YOLOE-v8-S outperforms YOLOv8-S in both detection and segmentation.
- Ablation studies confirm the effectiveness of SAVPE (1.5 AP gain over mask pooling) and LRPC (1.7× speedup with minimal AP drop), while multi-task learning enables segmentation at the cost of minor detection performance loss.
- Visualizations across zero-shot, text prompt, visual prompt, and prompt-free settings demonstrate YOLOE’s robustness and versatility in diverse real-world scenarios.
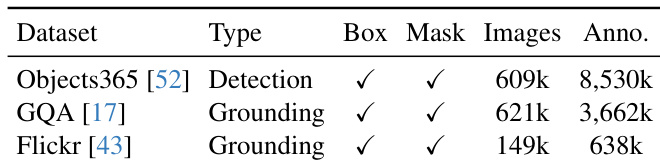
The authors use a multi-dataset evaluation to demonstrate YOLOE's capability in both detection and segmentation tasks, showing that it supports both box and mask outputs across different datasets. The results indicate that YOLOE can effectively handle diverse data types, including detection and grounding tasks, with varying image and annotation counts.
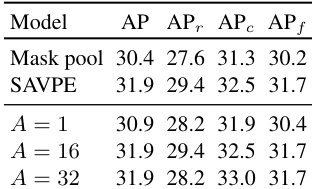
The authors evaluate the effectiveness of SAVPE by varying the number of groups in the activation branch, showing that performance remains stable across different group counts. Specifically, increasing the group number from 1 to 16 leads to a marginal improvement in AP, with the model achieving 31.9 AP at A = 16, indicating a favorable balance between performance and complexity.
Results show that YOLOE-v8-S achieves 21.0 AP and 95.8 FPS, outperforming GenerateU-Swin-T in AP while using significantly fewer parameters and achieving much higher inference speed. YOLOE-11-L achieves 26.3 AP and 34.9 FPS, demonstrating strong performance with a more efficient backbone compared to YOLOE-v8-L.
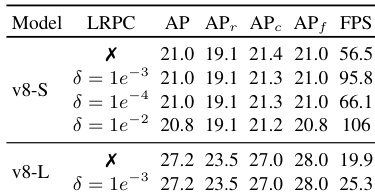
Results show that the inclusion of LRPC significantly improves inference speed without compromising performance, as demonstrated by the 1.7× and 1.3× speedups on T4 and iPhone 12 for YOLOE-v8-S and YOLOE-v8-L, respectively, while maintaining comparable AP and APf values. The effectiveness of LRPC is further confirmed by the substantial reduction in the number of retained anchor points with increasing threshold δ, which lowers computational overhead.
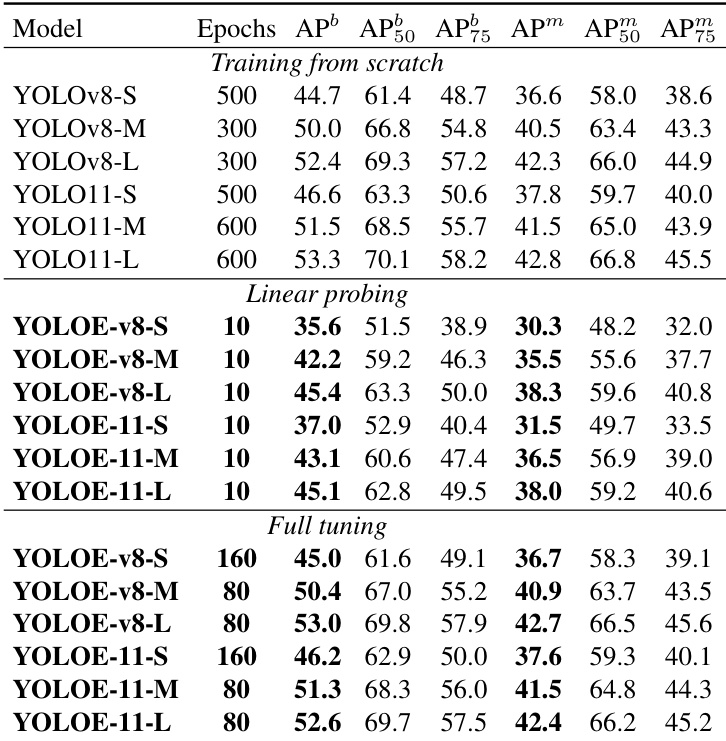
The authors use a table to compare the performance of YOLOE models with YOLOv8 and YOLO11 under different training strategies, including training from scratch, linear probing, and full tuning. Results show that YOLOE achieves competitive or superior performance across all settings, with YOLOE-v8-L and YOLOE-11-L achieving the highest AP and APm values in full tuning, while also demonstrating significant inference speedups compared to YOLOv8 and YOLO11 models.