Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
任意の深度に蒸留:蒸留によって強力な単眼深度推定器が構築される
任意の深度に蒸留:蒸留によって強力な単眼深度推定器が構築される
Xiankang He Dongyan Guo Hongji Li Ruibo Li Ying Cui Chi Zhang
概要
最近のゼロショット単眼深度推定(Monocular Depth Estimation, MDE)の進展により、正規化された深度表現を用いた深度分布の統一と、大規模なラベルなしデータを活用した疑似ラベル蒸留(pseudo-label distillation)によって、一般化性能が著しく向上している。しかし、従来の手法ではグローバルな深度正規化に依存しており、すべての深度値を同等に扱うため、疑似ラベル内のノイズが強調され、蒸留効果が低下する傾向がある。本論文では、疑似ラベル蒸留の文脈における深度正規化戦略について体系的な分析を行う。我々の調査結果から、最近の蒸留フレームワーク(例えば、共有コンテキスト蒸留)では、正規化を省略することでノイズの多い教師信号の影響を軽減でき、正規化が必ずしも必要ではないことが明らかになった。さらに、深度情報の表現方法にのみ注目するのではなく、グローバルかつローカルな深度ヒントを統合することで疑似ラベルの品質を向上させる「クロスコンテキスト蒸留(Cross-Context Distillation)」を提案する。また、拡散モデルに基づく教師モデルから得られる補完的な深度事前知識を活用するアシスタントガイド付き蒸留戦略を導入し、教師信号の多様性と耐障害性を強化した。ベンチマークデータセットにおける広範な実験により、本手法が定量的・定性的に、最先端手法を顕著に上回ることを示した。
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Zhejiang University of Technology, Westlake University, Lanzhou University, and Nanyang Technological University propose Cross-Context Distillation with assistant-guided supervision, a novel framework that improves zero-shot monocular depth estimation by integrating global and local depth cues and leveraging complementary priors from a diffusion-based teacher, thereby enhancing pseudo-label quality and robustness beyond prior methods relying on global depth normalization.
Key Contributions
- Existing zero-shot monocular depth estimation methods rely on global depth normalization (e.g., scale-and-shift invariant representations) to unify depth distributions across diverse datasets, but this approach amplifies noise in pseudo-labels by coupling local predictions with global statistics, degrading distillation quality.
- The paper introduces Cross-Context Distillation, a novel framework that jointly leverages local and global depth cues during pseudo-label generation, improving fine-grained detail preservation while maintaining scene-wide consistency, and proposes an assistant-guided distillation strategy using a diffusion-based teacher to inject complementary depth priors.
- Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both quantitative metrics (e.g., RMSE, δ1) and qualitative depth detail, outperforming prior approaches by effectively mitigating noise and enhancing supervision diversity.
Introduction
Monocular depth estimation (MDE) enables depth prediction from single RGB images, crucial for applications like autonomous driving and robotics, where stereo or multi-view setups are impractical. Recent zero-shot MDE methods leverage large-scale unlabeled data via pseudo-label distillation, using scale-and-shift invariant (SSI) representations to unify depth distributions across diverse datasets. However, global normalization in SSI distillation inadvertently propagates noise from inaccurate regions to the entire depth map, degrading local detail and distillation quality. The authors conduct a systematic analysis of depth normalization strategies and find that omitting global normalization or using localized normalization improves robustness. Their key contribution is Cross-Context Distillation, a hybrid framework that jointly leverages local fine-grained depth cues and global contextual relationships to generate higher-quality pseudo-labels. They further introduce an assistant-guided distillation strategy using a diffusion-based teacher model to inject complementary depth priors, enhancing supervision diversity. Experiments show their method significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches in both quantitative metrics and qualitative depth detail on in-the-wild images.
Dataset
-
The dataset is composed of 200,000 unlabeled images selected from SA-1B, a large-scale collection of high-quality RGB images featuring diverse indoor and outdoor scenes. SA-1B is also used in DepthAnythingv2 and provides high-fidelity imagery that supports detailed pseudo-label generation for robust depth estimation.
-
The training subset is drawn from SA-1B and used to generate pseudo-labels via teacher models in a distillation framework. For evaluation, the model is tested on five established monocular depth estimation benchmarks: NYUv2 (654 test images), KITTI (697 test images), ETH3D (454 test images), ScanNet (1,000 test images), and DIODE (full test set, with noted depth artifacts near object boundaries).
-
The authors use a shared-context distillation strategy where both teacher and student models process the same global region, extracted via random cropping. Crops maintain a 1:1 aspect ratio and are sampled from a range of 644 pixels up to the shortest image side, then resized to 560×560. In global-local distillation, the global crop is split into overlapping 560×560 local patches for the teacher. For assistant-guided distillation, the primary teacher and assistant are selected in a 7:3 ratio using probabilistic sampling.
-
All models are trained using only RGB inputs, with pseudo-labels generated by state-of-the-art teacher models. The best student model is trained for 20,000 iterations on a single NVIDIA V100 GPU with a batch size of 8, initialized from pre-trained DAv2-Large weights. The learning rate is tuned per student model, with a decoder learning rate of 5×10⁻⁵ for DAv2. The total loss uses weights λ₁ = 0.5, λ₂ = 1.0, and λ₃ = 2.0. Predictions are aligned with ground truth in scale and shift before evaluation using AbsRel and δ₁ metrics.
Method
The authors leverage a novel distillation framework to enhance zero-shot monocular depth estimation using unlabeled images. The overall architecture integrates two primary strategies: cross-context distillation and assistant-guided distillation, designed to improve the quality and robustness of pseudo-label supervision. The framework is structured to enable the student model to learn from both local fine-grained details and global scene structure, while also benefiting from diverse supervision sources.
Refer to the framework diagram 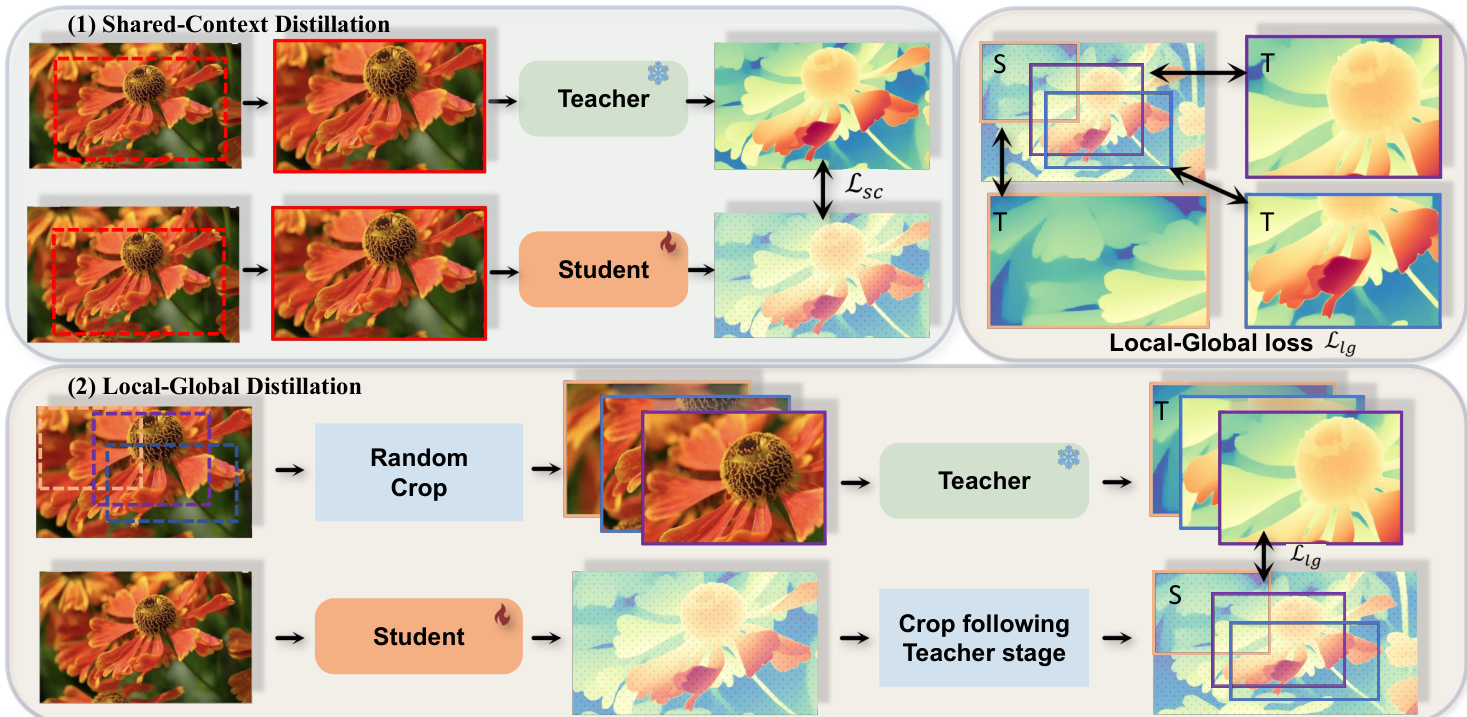 . The cross-context distillation strategy consists of two complementary approaches. In the first, shared-context distillation, both the teacher and student models are fed the same randomly sampled local crop of an image. This setup encourages the student to learn fine-grained details by directly aligning its predictions with the teacher's outputs at local scales. The loss for this component, denoted as Lsc, is computed as the average absolute difference between the normalized depth predictions of the student and the teacher for the local region.
. The cross-context distillation strategy consists of two complementary approaches. In the first, shared-context distillation, both the teacher and student models are fed the same randomly sampled local crop of an image. This setup encourages the student to learn fine-grained details by directly aligning its predictions with the teacher's outputs at local scales. The loss for this component, denoted as Lsc, is computed as the average absolute difference between the normalized depth predictions of the student and the teacher for the local region.
The second component, local-global distillation, operates on different input contexts. Here, the teacher model processes multiple local cropped regions to generate fine-grained depth predictions, while the student model predicts a global depth map from the full image. To transfer knowledge, the loss Llg is computed only over the overlapping regions between the teacher's local predictions and the corresponding areas in the student's global depth map. This ensures the student integrates detailed local information into its holistic depth estimation. The total loss function combines these components with additional constraints, such as feature alignment and gradient preservation, to balance the different sources of supervision.
The authors also introduce an assistant-guided distillation scheme to further enhance the quality of pseudo-labels. This approach pairs a primary teacher model with an auxiliary assistant model, which is a diffusion-based depth estimator. The assistant model provides complementary supervision by leveraging generative priors, offering fine-grained depth cues that differ from the primary teacher's global consistency. A probabilistic sampling mechanism determines whether supervision for each training iteration is drawn from the primary teacher or the assistant, encouraging the student to adapt to diverse supervision styles and fostering more generalizable depth representations.
Depth normalization is a crucial component of the framework, as it adjusts the pseudo-depth labels from the teacher and the depth predictions from the student for effective loss computation. The authors systematically analyze several normalization techniques. Global normalization adjusts depth predictions using global statistics of the entire depth map, ensuring scale-and-shift invariance by normalizing based on the median and mean absolute deviation. Hybrid normalization integrates both global and local depth information by dividing the depth range into multiple segments, allowing for a balance between global coherence and local adaptability. Local normalization focuses exclusively on the finest-scale groups, emphasizing the preservation of fine-grained depth details. As a baseline, a direct depth regression approach with no explicit normalization is also considered, which uses the absolute difference between raw student predictions and teacher pseudo-labels.
Refer to the normalization strategies diagram 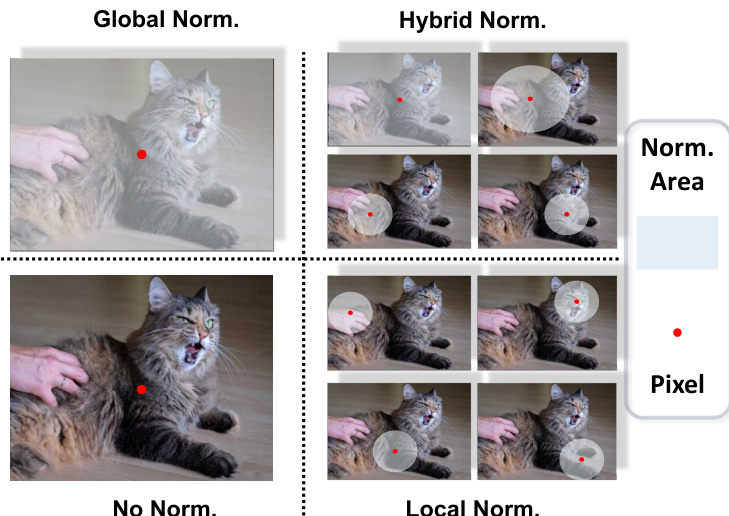 . The diagram visually illustrates how each strategy processes pixels within the normalization region. The red dot represents any pixel within the region, and the different normalization areas are shown for global, hybrid, and local normalization. The figure also includes a "No Norm." case, which serves as a baseline for comparison. The authors' analysis of these strategies provides insight into the effectiveness of normalization in distillation and helps to determine the optimal approach for their framework.
. The diagram visually illustrates how each strategy processes pixels within the normalization region. The red dot represents any pixel within the region, and the different normalization areas are shown for global, hybrid, and local normalization. The figure also includes a "No Norm." case, which serves as a baseline for comparison. The authors' analysis of these strategies provides insight into the effectiveness of normalization in distillation and helps to determine the optimal approach for their framework.
Experiment
- Ablation study on Cross-Context Distillation validates that combining Shared-Context and Local-Global Distillation with hybrid normalization significantly improves depth estimation accuracy, with hybrid normalization outperforming global and local normalization across both DIODE and ETH3D benchmarks.
- On DIODE and ETH3D datasets, the proposed hybrid normalization strategy achieves superior performance compared to global normalization, particularly in preserving local depth details and global structural coherence.
- Cross-Architecture Distillation experiments demonstrate consistent improvements over prior methods across diverse architectures (MiDaS and DepthAnythingv2), confirming the generalizability and effectiveness of the proposed distillation framework.
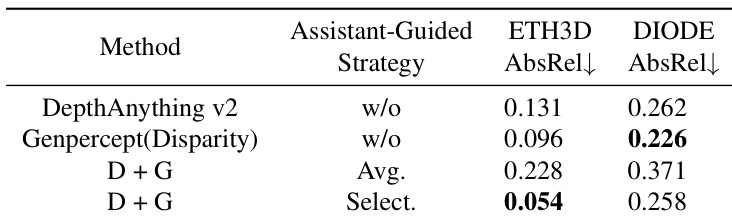
- Assistant-Guided Distillation using a diffusion-based model (GenPercept) as an assistant outperforms single-teacher distillation, with the selection-based strategy for combining pseudo-labels achieving the best results on ETH3D.
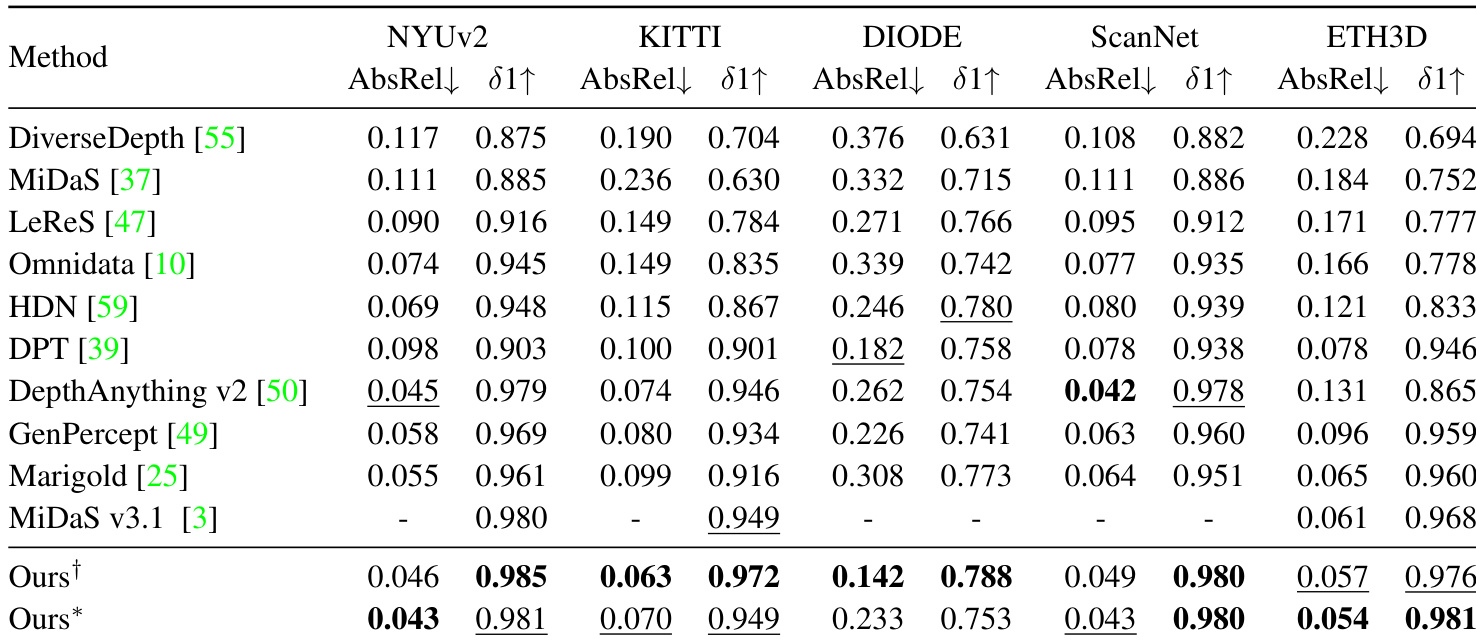
- Quantitative evaluation on zero-shot benchmarks (NYUv2, ScanNet, KITTI, DIODE, ETH3D) shows the method achieves state-of-the-art performance, with improvements in AbsRel and δ₁ accuracy across both DepthAnythingv2 and MiDaS architectures.
- On DIODE and ETH3D, the student model surpasses its teacher in accuracy and generalization, demonstrating the effectiveness of the distillation framework in transferring knowledge and enhancing performance.
- Data scaling experiments show that the proposed method consistently outperforms the SSI Loss baseline, with the performance gap increasing as training data size grows, indicating superior data efficiency.
- Distillation from generative models (GenPercept) enables the student to achieve significantly enhanced fine-detail prediction compared to distillation from encoder-decoder models.
- Qualitative results on diverse real-world, synthetic, and abstract inputs (e.g., anime, sketches, game renders) demonstrate robust depth estimation with high structural fidelity and semantic coherence, enabling effective 3D reconstruction in unconstrained environments.
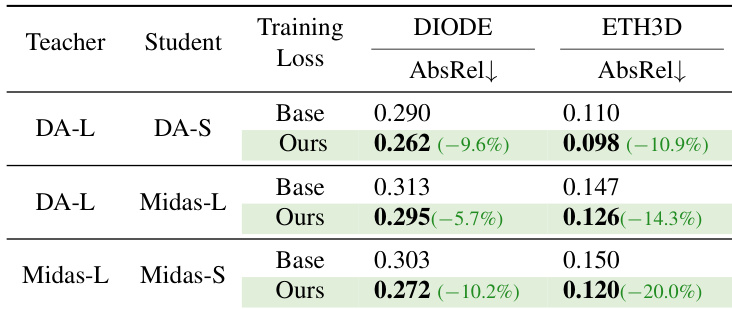
The authors use a distillation framework to compare the performance of different teacher-student model pairs on the DIODE and ETH3D benchmarks, evaluating the impact of their proposed training loss. Results show that their method consistently reduces the absolute relative error (AbsRel) across all configurations, with the largest improvements observed on ETH3D, indicating enhanced depth estimation accuracy and robustness.
Results show that hybrid normalization achieves the best performance in both Shared-Context and Local-Global distillation, with the lowest AbsRel on ETH3D and DIODE. In Shared-Context Distillation, no normalization also performs well, indicating that consistent supervision reduces the need for normalization, while in Local-Global Distillation, hybrid normalization is most effective due to its ability to balance local and global depth consistency.

Results show that combining both Shared-Context and Local-Global Distillation significantly improves depth estimation accuracy on both ETH3D and DIODE benchmarks, with the best performance achieved when both components are enabled, reducing AbsRel by 25.3% and 14.1% respectively.

Results show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks, outperforming existing affine-invariant depth estimators in most cases. The model consistently improves upon both DepthAnything v2 and MiDaS architectures, demonstrating superior accuracy and generalization in zero-shot depth estimation tasks.
Results show that the assistant-guided distillation strategy significantly improves depth estimation accuracy, with the "Select." method achieving the lowest AbsRel on both ETH3D and DIODE benchmarks. The combination of DepthAnything v2 and Genpercept outperforms individual models, demonstrating the effectiveness of selecting supervision signals from complementary teachers.