Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Ministral 3
Ministral 3
Abstract
We introduce the Ministral 3 series, a family of parameter-efficient dense language models designed for compute and memory constrained applications, available in three model sizes: 3B, 8B, and 14B parameters. For each model size, we release three variants: a pretrained base model for general-purpose use, an instruction finetuned, and a reasoning model for complex problem-solving. In addition, we present our recipe to derive the Ministral 3 models through Cascade Distillation, an iterative pruning and continued training with distillation technique. Each model comes with image understanding capabilities, all under the Apache 2.0 license.
One-sentence Summary
The authors propose Ministral 3, a family of parameter-efficient dense language models (3B–14B) with image understanding, derived via Cascade Distillation for compute- and memory-constrained environments, offering pretrained, instruction-tuned, and reasoning variants under Apache 2.0.
Key Contributions
-
The Ministral 3 series introduces a family of 9 parameter-efficient dense language models—3B, 8B, and 14B in size—each available as a pretrained base, instruction-tuned, and reasoning variant, all supporting image understanding and up to 256k token context lengths, designed for deployment in compute and memory-constrained environments.
-
The models are derived through Cascade Distillation, an iterative pruning and distillation technique that progressively transfers knowledge from a strong 24B parent model (Mistral Small 3.1) to smaller children, enabling high performance with significantly reduced training compute and data requirements compared to models trained from scratch.
-
Evaluations show that Ministral 3 models achieve competitive performance on standard benchmarks, matching or exceeding similarly sized open models like Gemma 3 and Qwen 3, with the 14B Base model outperforming its larger parent in efficiency while maintaining strong reasoning and instruction-following capabilities.
Introduction
The research operates within the technical context of large language model development, where collaborative contributions from diverse experts are essential for advancing model capabilities, efficiency, and reliability. Prior work in this domain has often faced challenges related to inconsistent contributor attribution, fragmented knowledge sharing, and limited transparency in the roles and impact of individual contributors. The authors address these limitations by providing a comprehensive and structured list of core and contributing researchers, enabling clearer credit assignment, improved reproducibility, and better coordination in future collaborative efforts.
Method
The Ministral 3 models are constructed using a hierarchical training framework that begins with a large parent model and iteratively derives smaller, more efficient variants through a process termed Cascade Distillation. This approach enables the creation of three model sizes—3B, 8B, and 14B parameters—each available in base, instruction-following, and reasoning variants, all derived from the Mistral Small 3.1 model. The overall training pipeline consists of a pretraining phase followed by two distinct post-training stages for instruction-following and reasoning capabilities.
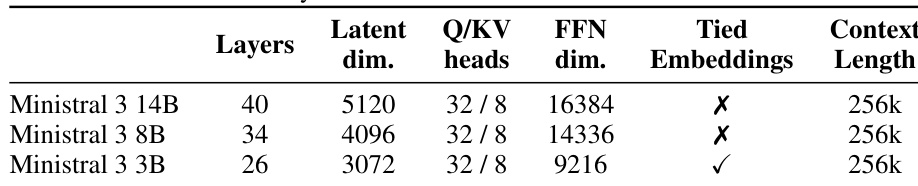
The core architecture of the Ministral 3 family is based on a decoder-only transformer, with all models sharing a common foundation while scaling in size. As detailed in the accompanying table, the 3B, 8B, and 14B models consist of 26, 34, and 40 layers, respectively. Key architectural components include Grouped Query Attention with 32 query heads and 8 key-value heads, RoPE positional embeddings, SwiGLU activation functions, and RMSNorm normalization. To support long-context processing, the models employ YaRN and position-based softmax temperature scaling. The 3B variant uses tied input-output embeddings to reduce parameter overhead, and all models operate with a vocabulary size of 131K tokens and support context lengths up to 256K tokens. For multimodal capabilities, each model incorporates a 410M-parameter ViT vision encoder, copied from Mistral Small 3.1 and kept frozen, with a new projection layer trained for each model to map visual features into the language model space.
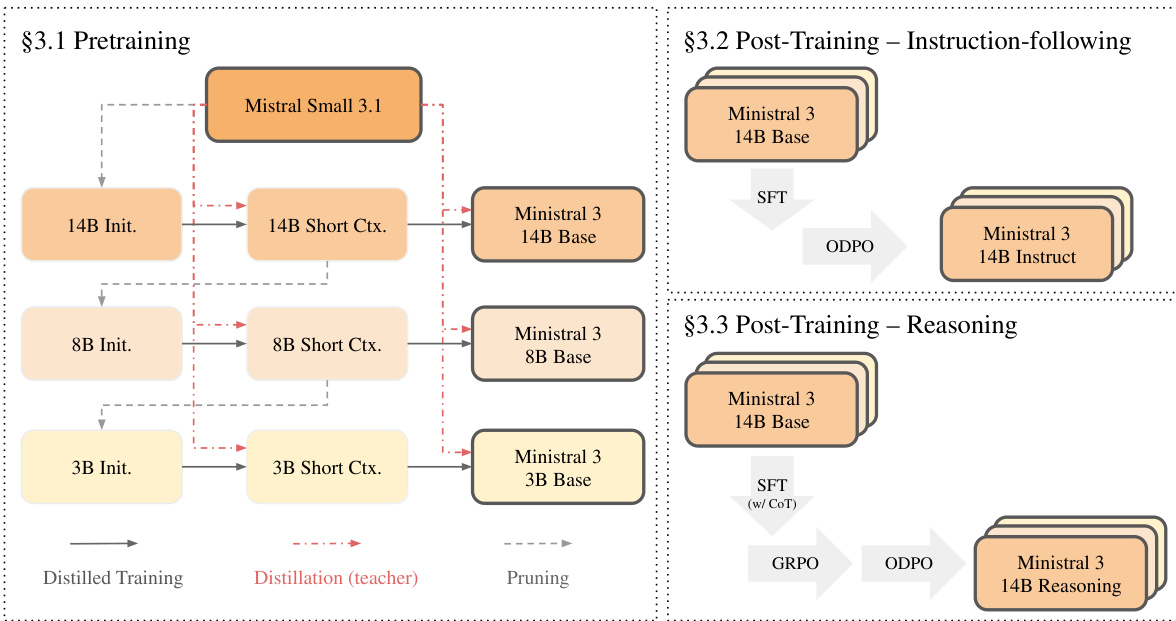
As shown in the figure below, the pretraining phase begins with the Mistral Small 3.1 model and proceeds through an iterative "prune-distill-repeat" cycle to generate the smaller models. The process starts by pruning the parent model to initialize a child model of the target size, followed by distillation training to recover performance. This sequence is repeated for each model size, with the output of one stage serving as the input to the next. Specifically, the 14B model is first pruned to create a 14B Init. model, which is then trained on short-context data with logit distillation from the parent model to produce the 14B Short Ctx. model. This model is further extended to a long-context version (14B Base) using a second distillation stage with longer context data. The 14B Short Ctx. model is then pruned to initialize the 8B Init. model, and the same process is repeated to derive the 8B Base model. The same pipeline is applied to generate the 3B Base model. This cascade structure ensures that each smaller model benefits from the knowledge of the larger parent, while avoiding redundant data processing across stages.
The pruning strategy employed in the initialization phase is designed to preserve the most critical components of the parent model. It involves three key techniques: layer pruning based on the ratio of input to output activation norms, hidden dimension pruning using Principal Component Analysis on concatenated activations from attention and feed-forward normalization layers, and feedforward dimension pruning for SwiGLU-based MLPs by selecting dimensions based on the averaged absolute values of the activation expressions. After pruning, the model undergoes distillation training using logit distillation from the parent model as the teacher. The pretraining phase consists of two stages: a short-context stage with a 16,384-token window, followed by a long-context stage that extends the context to 262,144 tokens using YaRN and position-based temperature scaling.
Following pretraining, each base model undergoes post-training to produce the instruction-following and reasoning variants. The instruction-following models are fine-tuned using a two-stage process: Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) followed by Online Direct Preference Optimization (ODPO). The reasoning models, in contrast, are trained from the pre-trained checkpoint using a three-stage pipeline: SFT with chain-of-thought data, Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), and ODPO. This structured approach ensures that each variant is optimized for its intended use case while maintaining the efficiency and performance characteristics of the underlying base model.
Experiment
- Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) with fp8 quantization and logit distillation from Mistral Medium 3 validates effective parameter-efficient training, with the vision encoder frozen and adapter trainable, enabling strong downstream performance.
- Reinforcement Learning via GRPO in two stages—STEM RL (math, code, visual reasoning) and General RL (instruction following, chat, open-ended reasoning)—validates improved reasoning and alignment, with longer generation length (up to 80K) enabling completion of complex reasoning chains and boosting performance.
- On MMLU, MATH, GPQA Diamond, and MMMU benchmarks, Ministral 3 14B outperforms Qwen 3 14B and significantly surpasses Gemma 12B, while Ministral 3 8B exceeds Gemma 12B on most tasks, demonstrating high parameter efficiency.
- Ministral 3 Instruct models achieve competitive results against Qwen 3 and Gemma 3 families across general, math, code, and multimodal benchmarks, with Ministral 3 Reasoning models matching or exceeding Qwen 3 counterparts on STEM tasks.
- Distillation from a post-trained, preference-tuned Mistral Small 3.1 teacher during pretraining yields stronger STEM and multimodal performance than using a larger but unrefined teacher, validating the importance of teacher quality over size.
- ODPO post-training on GRPO checkpoints significantly improves conversational quality of Ministral 3 14B and 8B models on alignment benchmarks, with the 3B model showing internal human evaluation gains despite limited public benchmark improvements.
The authors compare Ministral 3 Instruct models against Qwen 3 and Gemma 3 models on post-training benchmarks, showing that Ministral 3 14B outperforms Qwen 3 14B on AIME 2024 and AIME 2025, while also achieving competitive results on other tasks. At smaller scales, Ministral 3 8B and 3B models demonstrate strong performance relative to their Qwen 3 counterparts, with the 8B model matching or exceeding Qwen3-VL 8B on several benchmarks.
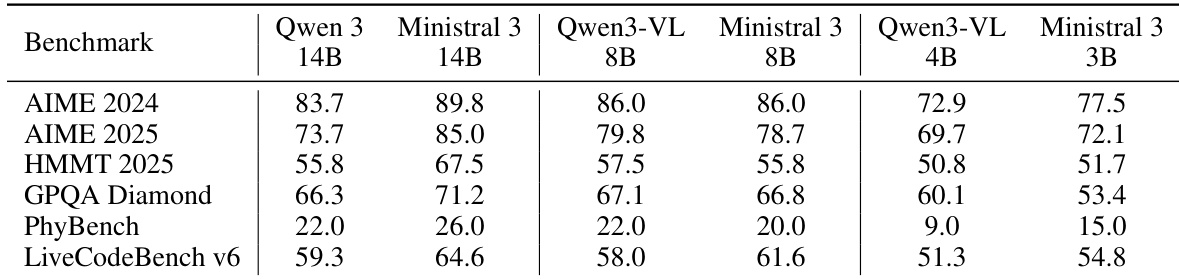
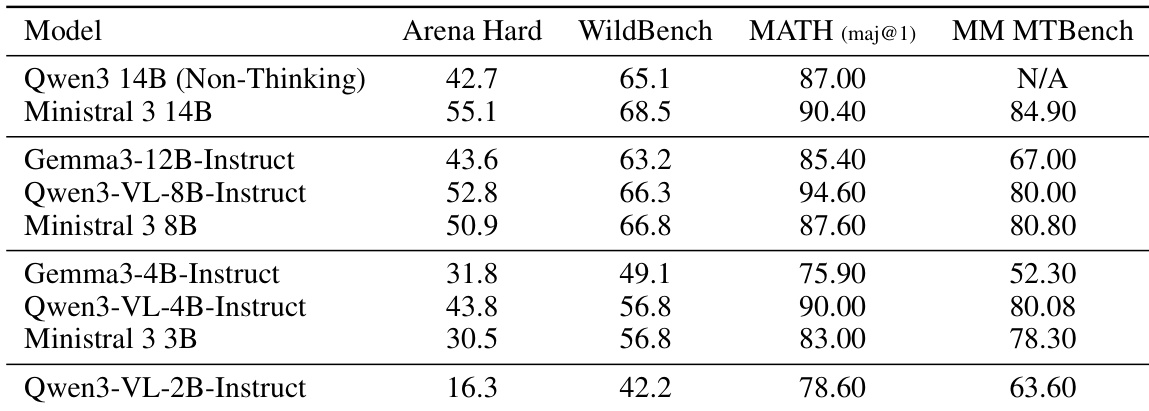
The authors compare Ministral 3 Instruct models to instruction-tuned baselines from the Qwen 3 and Gemma 3 families, showing that Ministral 3 14B outperforms Qwen3 14B (Non-Thinking) and Gemma3-12B-Instruct on Arena Hard, WildBench, and MATH, while also achieving higher scores than Qwen3-VL-8B-Instruct on most benchmarks. At smaller scales, Ministral 3 8B and 3B models are competitive with Qwen3-VL variants, demonstrating strong performance relative to their size, particularly on MATH and MM MTBench.
The authors compare Ministral 3 Base models against the teacher model Mistral Small 3.1 24B across various benchmarks, showing that performance scales smoothly with model size while the pruned Ministral 3 variants retain a large fraction of the teacher's capability despite substantial parameter reductions. The 14B model outperforms the 24B teacher on MMLU-Redux and ARC-Challenge, while the 8B and 3B models show competitive results on most general and math benchmarks, indicating strong parameter efficiency.
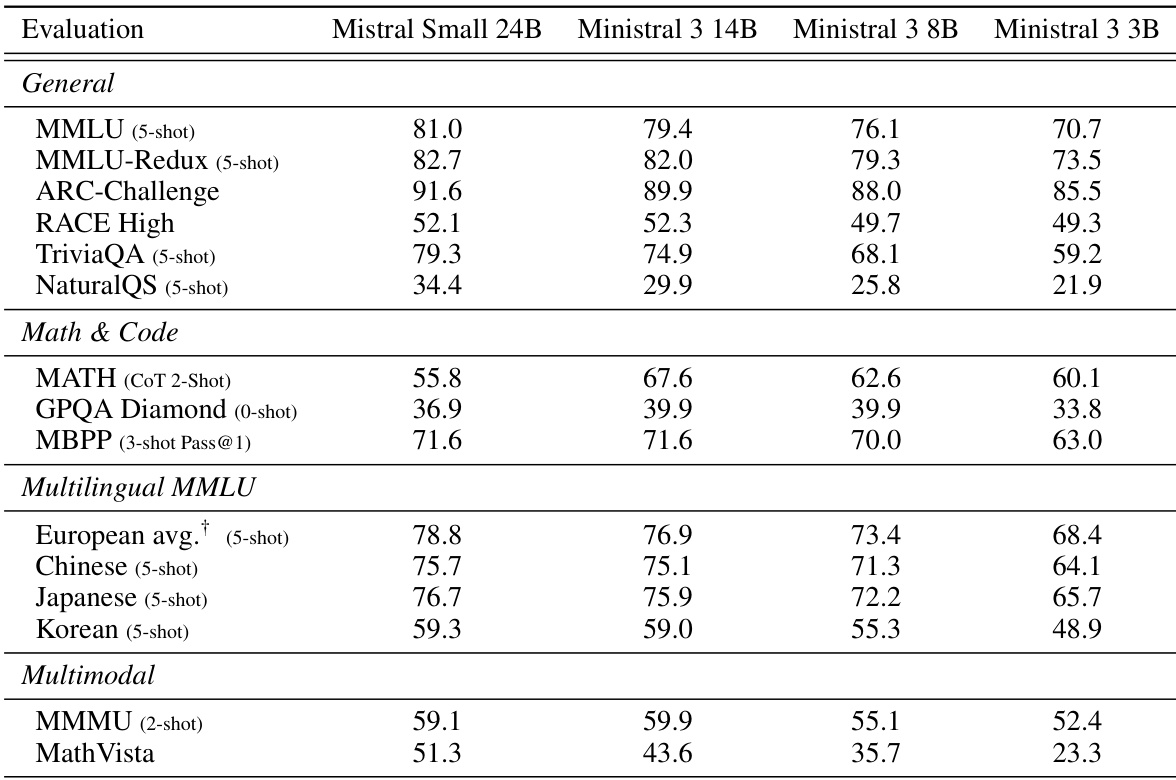
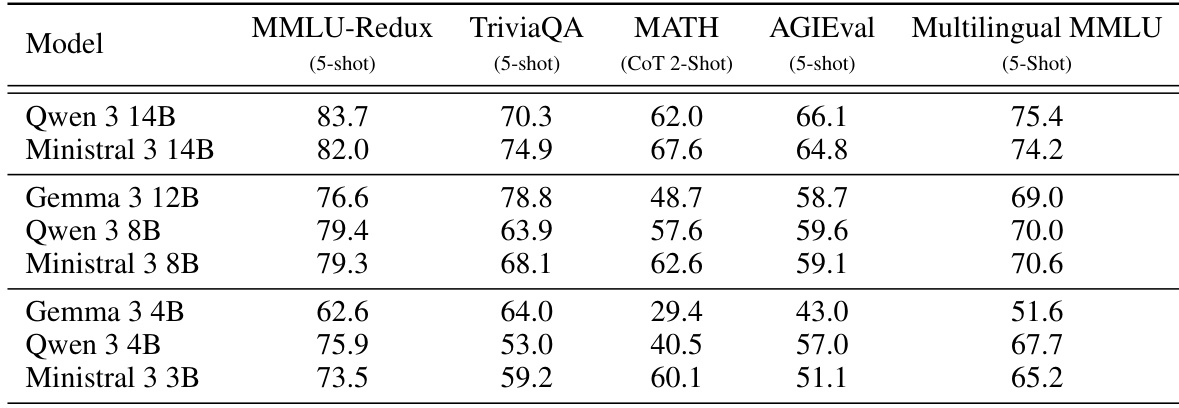
The authors compare Ministral 3 14B and 8B models against Qwen 3 and Gemma 3 models of similar size on pretraining benchmarks. Results show that Ministral 3 14B outperforms Qwen 3 14B on TriviaQA and MATH, while being competitive on other tasks, and Ministral 3 8B surpasses the larger Gemma 12B on most evaluations except TriviaQA.
The authors use a consistent architecture across Ministral 3 models, with varying numbers of layers, latent dimensions, and feed-forward network dimensions, while maintaining a fixed context length of 256k tokens. The 3B variant includes tied embeddings, which is not present in the larger 8B and 14B models, and all models share the same Q/KV head configuration of 32/8.