Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Mindscape-Aware Retrieval Augmented Generation for Improved Long Context Understanding
Mindscape-Aware Retrieval Augmented Generation for Improved Long Context Understanding
Yuqing Li Jiangnan Li Zheng Lin Ziyan Zhou Junjie Wu Weiping Wang Jie Zhou Mo Yu
Abstract
Humans understand long and complex texts by relying on a holistic semantic representation of the content. This global view helps organize prior knowledge, interpret new information, and integrate evidence dispersed across a document, as revealed by the Mindscape-Aware Capability of humans in psychology. Current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems lack such guidance and therefore struggle with long-context tasks. In this paper, we propose Mindscape-Aware RAG (MiA-RAG), the first approach that equips LLM-based RAG systems with explicit global context awareness. MiA-RAG builds a mindscape through hierarchical summarization and conditions both retrieval and generation on this global semantic representation. This enables the retriever to form enriched query embeddings and the generator to reason over retrieved evidence within a coherent global context. We evaluate MiA-RAG across diverse long-context and bilingual benchmarks for evidence-based understanding and global sense-making. It consistently surpasses baselines, and further analysis shows that it aligns local details with a coherent global representation, enabling more human-like long-context retrieval and reasoning.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from the Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tencent WeChat AI, and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology propose MiA-RAG, a novel RAG framework that introduces explicit global context awareness via hierarchical summarization to guide both retrieval and generation, enabling more human-like long-context reasoning by aligning local evidence with a coherent global mindscape, outperforming baselines on diverse long-context and bilingual benchmarks.
Key Contributions
- Current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems lack global context awareness, relying solely on local evidence signals and struggling with long-context understanding, whereas humans naturally use a holistic "mindscape" to organize knowledge, interpret information, and guide reasoning across complex texts.
- MiA-RAG introduces the first computational framework that equips LLM-based RAG with explicit global context awareness by building a hierarchical summary as an external mindscape, which conditions both retrieval (via enriched query embeddings) and generation (via context-aware reasoning) to align local details with a coherent global representation.
- Evaluated across diverse long-context and bilingual benchmarks—including government reports, narratives, and multiple task formats—MiA-RAG consistently outperforms baselines, with ablation and analysis confirming that the mindscape reshapes query embeddings and guides attention, enabling more human-like sense-making and integrative reasoning.
Introduction
Long-context understanding remains a critical challenge for large language models (LLMs), particularly when reasoning over extended documents with dispersed evidence. Current Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems rely heavily on local, evidence-level signals, lacking a mechanism to maintain a global semantic context—akin to the human "mindscape"—which guides selective retrieval, enriches interpretation, and enables coherent reasoning. This limitation leads to fragmented understanding, poor generalization across topics, and suboptimal performance on complex, multi-step tasks. The authors introduce Mindscape-Aware RAG (MiA-RAG), the first framework to explicitly model a global semantic representation through hierarchical summarization, serving as an external mindscape. This summary is used to condition both retrieval and generation: it enriches query embeddings for selective, context-aware retrieval and guides the generator to interpret retrieved evidence within a unified global context. Evaluated across diverse long-context benchmarks in English and Chinese, MiA-RAG consistently outperforms baselines, including larger vanilla models, and demonstrates improved alignment between local details and global meaning. Analysis confirms that the mindscape reshapes query representations into a coherent semantic space and acts as a scaffold for attention, validating its role in enabling human-like reasoning.
Dataset
- The dataset, denoted as D~emb, is constructed by automatically extending NarrativeQA to provide silver-standard query-evidence alignments at both chunk and node levels, addressing the lack of fine-grained supervision in existing long-narrative datasets.
- It comprises 27,117 questions, with an average of 2.3 silver chunks and 2.9 silver nodes per question, derived from a combination of NarrativeQA and synthetic data from CLIPPER.
- For chunk-level evidence, silver chunks are identified through a multi-step process: query augmentation, majority-vote ensemble retrieval, and LLM-based filtering (Algorithm 1), ensuring high-quality, contextually relevant evidence.
- Node-level evidence is built by constructing a knowledge graph from each document: key entities are extracted using GPT-4o, and concise descriptions are generated to form nodes; relevant nodes per query are then identified via the same algorithmic pipeline.
- The dataset is used to train the MiA-Emb model, which generates retrieval contexts C^ret by mixing silver chunks with irrelevant ones, simulating realistic retrieval noise and varying context lengths.
- The final supervised fine-tuning dataset Dgen for the MiA-Gen model combines NarrativeQA and CLIPPER data, formatted with instruction, context, retrieved evidence, and query, enabling training under realistic retrieval conditions.
- For CLIPPER, retrieval results from the MiA-Emb model are directly used to form C^ret, ensuring consistency between retrieval and generation training.
- The MiA-Gen model is optimized using autoregressive cross-entropy loss over D~gen, with the full input context including the instruction, source text, retrieved evidence, and query serving as input to generate answers.
Method
The authors leverage a hierarchical framework to construct a global semantic scaffold, termed the Mindscape, which serves as a document-level abstraction to guide both retrieval and generation in long-document understanding tasks. This Mindscape is built through a two-stage summarization process. First, each document chunk ci is independently summarized by a large language model, resulting in a set of chunk-level summaries {si}. These summaries are then concatenated and processed through a second summarization step to produce a single, coherent global representation S, which encapsulates the overarching narrative and key themes of the document. This hierarchical construction ensures that the global context is preserved and accessible for downstream tasks.
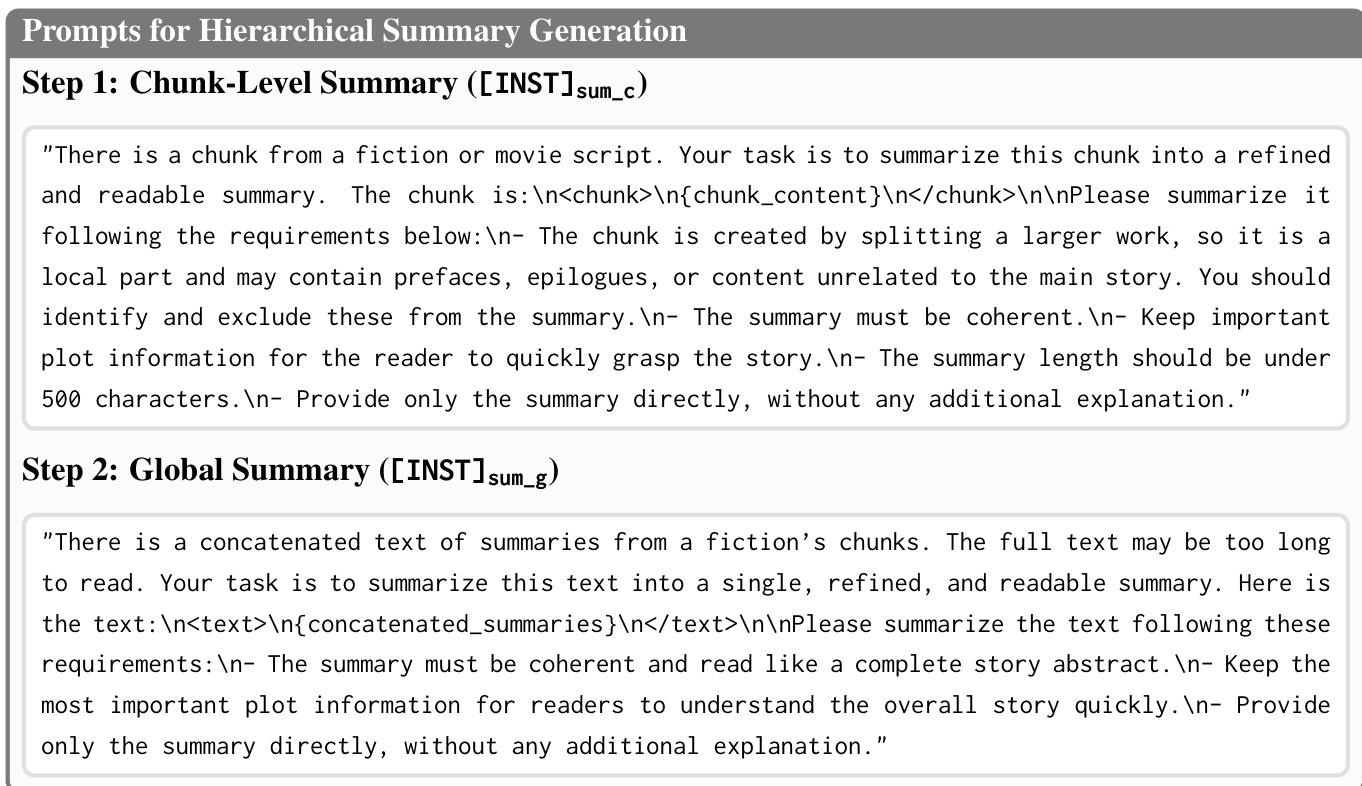
The framework, named Mindscape-Aware RAG (MiA-RAG), integrates this Mindscape into a retrieval-augmented generation pipeline. The core innovation lies in the Mindscape-Aware Retriever (MiA-Emb), which is trained to condition query representations on the global context. The model is fine-tuned on a pre-trained embedding model, with its input sequence explicitly structured to incorporate both the query and the Mindscape. The input format is defined as Q=[[INST]emb;qi;dq;S;dn;dc], where qi is the query, S is the Mindscape summary, and dq, dn, and dc are special tokens that mark the end of the query and activate node- and chunk-retrieval modes, respectively. This design enables the model to perceive both local query intent and global document context simultaneously.

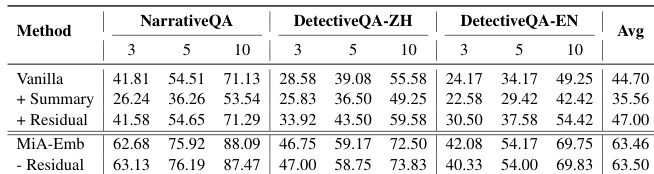
To balance the influence of the original query and the global guidance, the model employs a residual integration mechanism. The final enriched query representation q~t is computed as a weighted combination of the hidden state at the query delimiter (hq) and the hidden state at the task delimiter (ht), using a hyperparameter δ to control the balance. This ensures that the model's retrieval decisions are informed by the global context without losing the specificity of the query. The training objective is a joint contrastive loss over both chunk and node retrieval tasks, which is optimized using the InfoNCE loss. This objective requires the model to distinguish between positive evidence (silver chunks) and negative samples, which are constructed from both hard negatives (semantically similar but irrelevant) and simple negatives (clearly irrelevant).

The Mindscape-Aware Generator (MiA-Gen) is a fully fine-tuned large language model that leverages the retrieved chunks and the Mindscape to produce answers. The generator's input is structured to include the book summary, the retrieved chunks, and the query, allowing it to ground its responses in both local evidence and the global narrative. The framework is evaluated on a diverse set of long-narrative understanding benchmarks, including NarrativeQA, ∞Bench, DetectiveQA, and NoCha, demonstrating its effectiveness in handling complex, long-context tasks.
Experiment
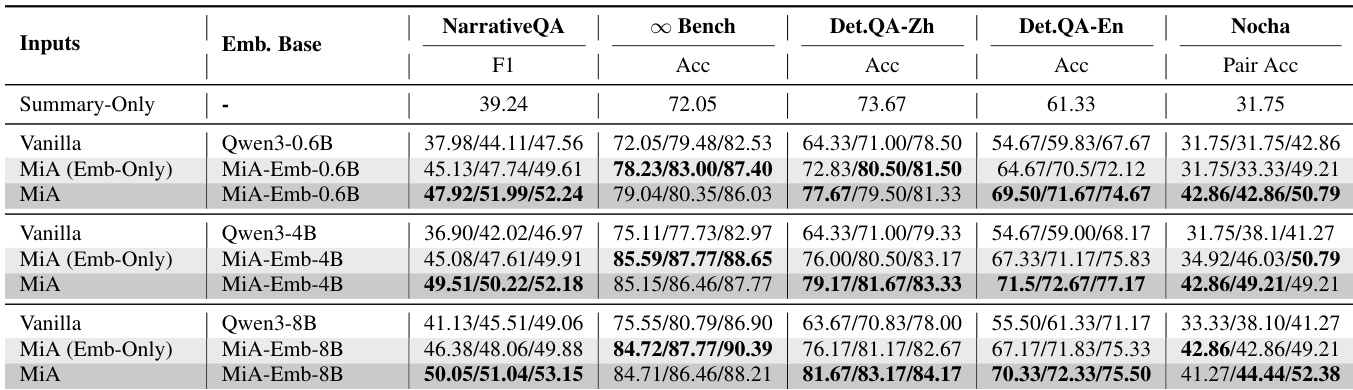
- MiA-Emb consistently outperforms all baselines on retrieval tasks, achieving superior Answer Recall on in-domain NarrativeQA and out-of-domain bilingual DetectiveQA, with gains over state-of-the-art Sit-Emb (Wu et al., 2025) and strong performance even with small models (e.g., MiA-Emb-0.6B surpasses Vanilla 8B).
- MiA-RAG achieves the best overall results across five long-context benchmarks (English and Chinese, diverse domains), with +16.18% gain over vanilla 14B and +8.63% over 72B, demonstrating that mindscape-aware alignment is more effective than scaling model size.
- Ablation studies confirm that removing the summary (w/o Summary) causes substantial performance degradation in both retrieval and generation, underscoring the essential role of mindscape representation in guiding query semantics and evidence integration.
- Mindscape-aware retrieval (MiA-Emb) improves average scores by 6.95% (72B) and 7.55% (14B) over vanilla retrievers, while mindscape-conditioned generation (MiA-Gen-14B) achieves +11.16% gain over vanilla, showing that global context enhances both retrieval and reasoning.
- MiA-GraphRAG achieves clear gains in global sense-making QA by retrieving semantically coherent graph nodes, with MiA-Emb outperforming SFT-Emb and vanilla Qwen3-Embedding across all evaluation dimensions (Comprehensiveness, Diversity, Empowerment).
- MiA-Emb demonstrates robustness to summary quality: performance remains stable even when using summaries from smaller open-source models (Qwen2.5-7B to 32B), with results close to GPT-4o-generated summaries.
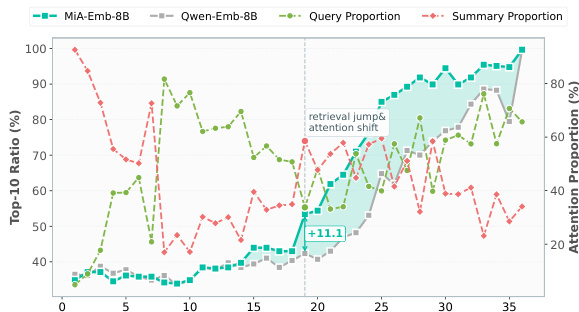
- Geometric analysis shows MiA-Emb queries are better aligned with document semantic subspaces (37.1° vs. 43.5°), enabling more selective retrieval, and attention analysis confirms that MiA-Emb progressively integrates summary cues at key layers to enrich query representations.
- MiA-Gen exhibits stronger integrative reasoning, as measured by higher Mindscape-Coherent Evidence Alignment (MCEA) scores, with attention focused on chunks consistent with the summary, especially in middle and late layers, and sensitivity to summary perturbations confirming genuine mindscape-driven reasoning.
- MiA-Emb and MiA-Gen scale effectively across model sizes, with MiA-Gen-14B matching or exceeding 72B vanilla models, and MiA-Emb-0.6B outperforming Vanilla 8B, indicating that global semantics are more impactful than model size alone.
The authors evaluate the MiA-RAG framework across multiple long-context benchmarks, showing that MiA-Gen consistently outperforms vanilla generators across model scales, with the 14B variant matching or exceeding the 72B model. Results demonstrate that integrating mindscape-aware retrieval and generation leads to significant gains in both retrieval and generation tasks, with performance improving as model size increases, particularly when the global summary is used to guide both stages.
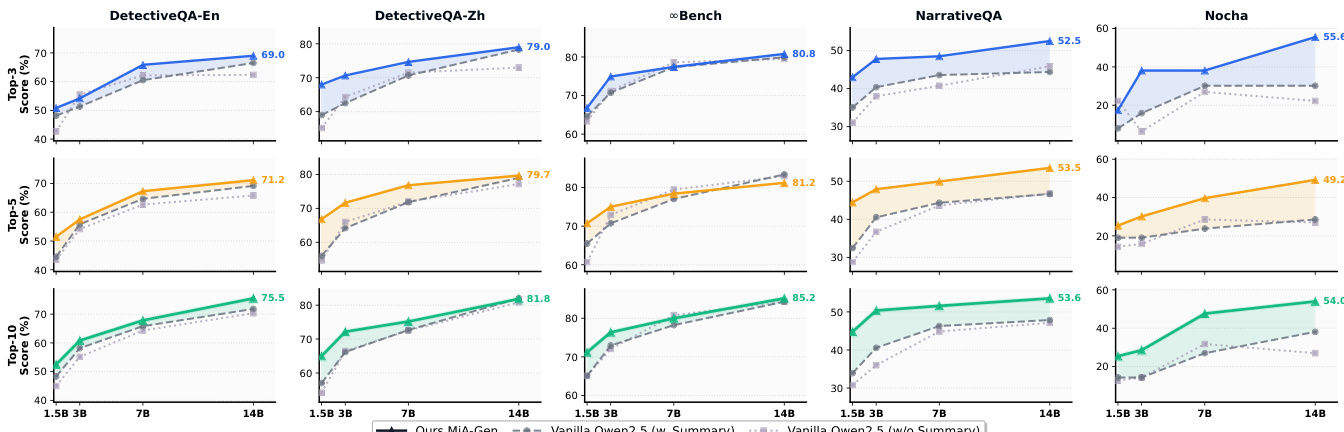
The authors use a retrieval model called MiA-Emb, which incorporates a global summary to guide query representations, and compare it against vanilla and summary-augmented baselines. Results show that MiA-Emb achieves the highest average performance across all benchmarks, with significant gains in Answer Recall on both in-domain NarrativeQA and out-of-domain DetectiveQA, demonstrating the effectiveness of mindscape-aware retrieval.
The authors use the MiA-Emb and MiA-Gen models with specific training configurations, where MiA-Emb employs LoRA with a learning rate of 1 × 10⁻⁴ and a LoRA rank of 128, while MiA-Gen uses a lower learning rate of 1 × 10⁻⁵ and a batch size of 2. Results show that MiA-Emb achieves superior retrieval performance across benchmarks, and MiA-Gen demonstrates strong generation capabilities, particularly when integrated with mindscape-conditioned retrieval.
The authors use a visual analysis to show that MiA-Emb-8B achieves a higher top-10 retrieval ratio compared to Qwen-Emb-8B, with a notable improvement of +11.1% at the 20th layer. The results indicate that MiA-Emb-8B maintains a more stable attention proportion on the query and summary, suggesting better alignment of query representations with the document's semantic subspace.
The authors use MiA-Emb, a mindscape-aware embedding model, to improve retrieval performance across multiple long-context benchmarks. Results show that MiA-Emb consistently outperforms baseline models, achieving higher recall and better end-task performance, with the best results observed when the mindscape summary is incorporated during retrieval.