Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Generative Refocusing: Flexible Defocus Control from a Single Image
Generative Refocusing: Flexible Defocus Control from a Single Image
Chun-Wei Tuan Mu Jia-Bin Huang Yu-Lun Liu
Abstract
Depth-of-field control is essential in photography, but getting the perfect focus often takes several tries or special equipment. Single-image refocusing is still difficult. It involves recovering sharp content and creating realistic bokeh. Current methods have significant drawbacks. They need all-in-focus inputs, depend on synthetic data from simulators, and have limited control over aperture. We introduce Generative Refocusing, a two-step process that uses DeblurNet to recover all-in-focus images from various inputs and BokehNet for creating controllable bokeh. Our main innovation is semi-supervised training. This method combines synthetic paired data with unpaired real bokeh images, using EXIF metadata to capture real optical characteristics beyond what simulators can provide. Our experiments show we achieve top performance in defocus deblurring, bokeh synthesis, and refocusing benchmarks. Additionally, our Generative Refocusing allows text-guided adjustments and custom aperture shapes.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University and University of Maryland introduce Generative Refocusing, a DeblurNet-BokehNet system achieving state-of-the-art defocus deblurring and bokeh synthesis through semi-supervised training that leverages real EXIF metadata alongside synthetic data, overcoming prior reliance on simulators to enable text-guided depth-of-field control and custom aperture shapes like heart bokeh.
Key Contributions
- Current single-image refocusing methods require all-in-focus inputs, depend heavily on synthetic data from simulators, and provide limited aperture control, making practical depth-of-field adjustments difficult without specialized equipment or multiple capture attempts.
- The authors introduce Generative Refocusing, a two-stage pipeline using DeblurNet to recover all-in-focus images from diverse inputs and BokehNet for bokeh synthesis, with semi-supervised training that combines synthetic paired data and unpaired real bokeh images leveraging EXIF metadata to model authentic optical characteristics beyond simulator capabilities.
- Their approach achieves state-of-the-art results across defocus deblurring, bokeh synthesis, and refocusing benchmarks while enabling new capabilities like text-guided adjustments and custom aperture shapes for creative post-capture control.
Introduction
Diffusion models have advanced image restoration by leveraging generative priors, enabling tasks like deblurring and artifact removal through efficient latent-space approaches. However, existing methods for defocus deblurring often treat it as a standalone task, failing to integrate seamlessly with bokeh synthesis for controllable refocusing, while bokeh rendering typically requires pristine all-in-focus inputs and accurate depth maps—constraints impractical for real-world single-image applications. Prior solutions also struggle with spatially-varying blur artifacts and lack flexibility in handling defocused inputs or authentic lens characteristics.
The authors address this by introducing a two-stage pipeline that explicitly separates defocus deblurring from bokeh synthesis. Their method accepts either defocused or all-in-focus images, uses semi-supervised learning on mixed synthetic and unpaired real data to capture realistic optics, and enables precise control over focus plane, bokeh intensity, and aperture shape—achieving scene-consistent refocusing without specialized capture hardware or paired training data.
Dataset
The authors construct a multi-stage training pipeline using diverse datasets with specialized processing:
-
Composition and sources:
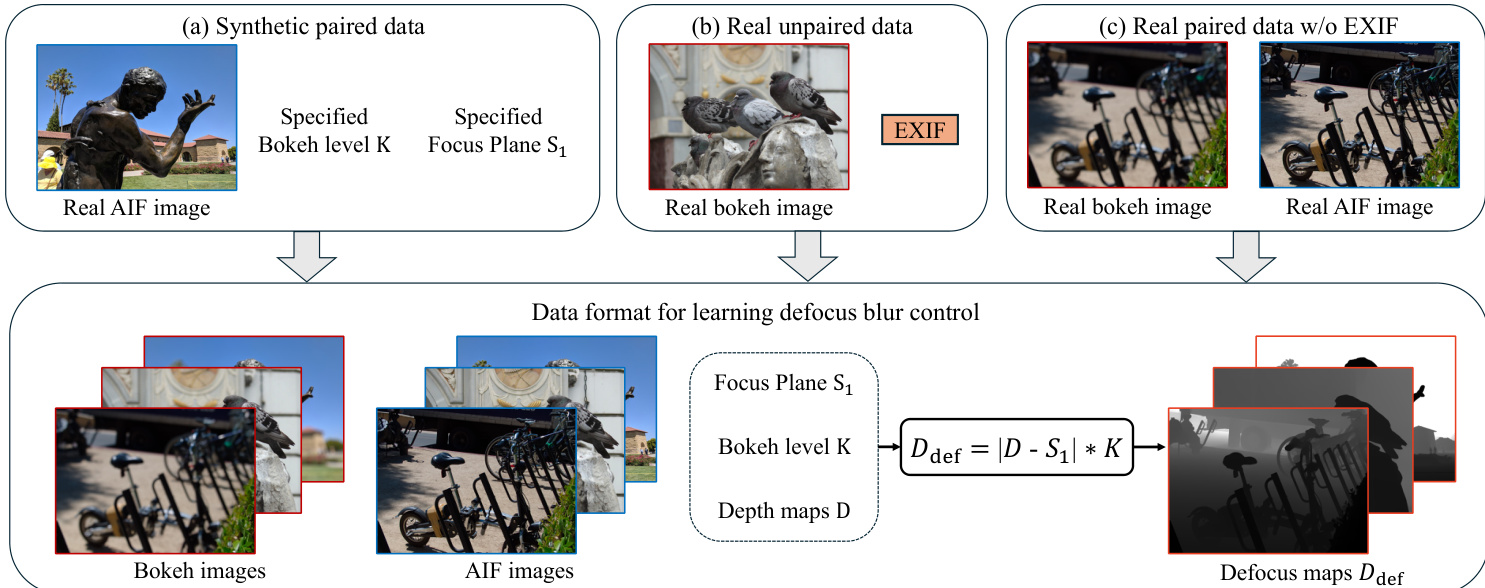
Combines synthetic pairs, real unpaired bokeh images with EXIF metadata, real paired bokeh images lacking metadata, and a custom PointLight-1K dataset. Sources include DPDD, REALBOKEH_3MP, BOKEHDIFFUSION, and Flickr-derived synthetic data. -
Key subset details:
- DeblurNet training: Uses DPDD’s official training split (paired defocused/AIF images) and REALBOKEH_3MP. Filters REALBOKEH_3MP via Laplacian variance, retaining the top 3,000 sharpest images.
- BokehNet synthetic pretraining: Renders bokeh from real AIF images (1.7k filtered via Laplacian variance from [82]/[30] collections) and estimated depth. Randomly samples focus plane S1 and bokeh level K using a simulator [48].
- Real unpaired data: Leverages BOKEHDIFFUSION with EXIF metadata. Estimates K via K≈2F(S1−f)f2S1×pixel_ratio. Uses DeblurNet outputs as AIF inputs and refines focus planes via BiRefNet-generated in-focus masks (human-filtered for errors).
- Real paired data without metadata (REALBOKEH_3MP): Calibrates pseudo K∗ via simulator-in-the-loop: K⋆=(Kmin,Kmax)argmax SSIM(B(Iaif,D;S1,K),Ireal).
- PointLight-1K: Curates 1k night-scene images via Flickr keyword mining (e.g., "night," "bokeh"), GPT-4o prompt expansion, FLUX.1-Dev image generation (fine-tuned for sharpness), and DeblurNet refinement to eliminate residual blur.
-
Usage in training:
- DeblurNet trains exclusively on DPDD and filtered REALBOKEH_3MP for AIF reconstruction.
- BokehNet uses synthetic pairs for initial pretraining, then refines with real unpaired/paired data. Real data dominates the final training to overcome renderer bias.
- PointLight-1K enables shape-aware synthesis: the base BokehNet (trained without shape control) is fine-tuned with a frozen backbone, adding a shape-conditioning branch fed by binary/raster PSF kernels.
-
Processing specifics:
- All AIF candidates undergo Laplacian variance filtering to exclude blurry images.
- Defocus maps derive from estimated depth and focus-plane proxies (S1), with real data using BiRefNet masks (expert-verified) for reliable S1.
- EXIF metadata gaps in REALBOKEH_3MP are resolved via SSIM-based K⋆ optimization against rendered outputs.
- PointLight-1K generation includes DeblurNet post-processing to ensure minimal residual blur for strong point-light cues.
Method
The authors leverage a two-stage architecture—DeblurNet followed by BokehNet—to enable flexible, post-capture depth-of-field control from a single input image. This decomposition allows the system to first recover a sharp, all-in-focus representation and then synthesize user-controllable bokeh effects, addressing the limitations of prior methods that often require all-in-focus inputs or lack aperture shape control.
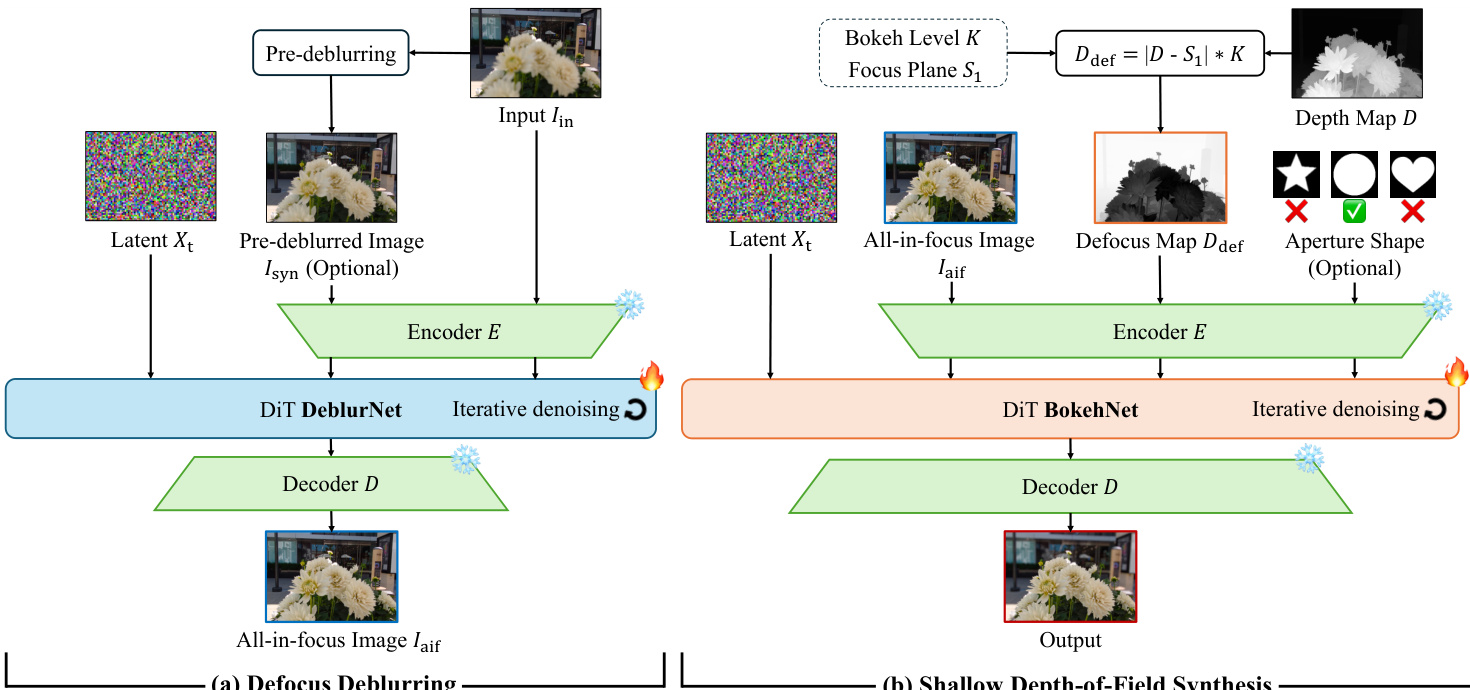
In the first stage, DeblurNet operates on an input image Iin and optionally a pre-deblurred image Ipd generated by an off-the-shelf deblurring model. The network is built upon a diffusion-based framework, specifically a DiT (Diffusion Transformer) architecture, which iteratively denoises a latent representation Xt to produce the all-in-focus output Iaif. To ensure robustness against artifacts in the pre-deblurred input, the authors introduce dual conditioning mechanisms. First, positional disentanglement encodes Iin and Ipd using spatially offset 2D positional grids, allowing the model to treat the pre-deblurred image as a low-frequency anchor while extracting high-frequency details from the original input. Second, pre-deblur dropout stochastically replaces Ipd with a zero tensor during training, forcing the model to remain effective even when the auxiliary input is absent or unreliable—enabling single-input inference at test time.
As shown in the figure below, the second stage, BokehNet, takes the all-in-focus image Iaif and synthesizes a refocused output based on user-specified parameters: focus plane S1, bokeh intensity K, and optional aperture shape. A defocus map Ddef is computed as Ddef=∣D−S1∣K, where D is the estimated depth map. This defocus map guides the diffusion process in BokehNet, which also employs a DiT architecture with iterative denoising to render spatially variant blur that mimics real optical behavior. The aperture shape is optionally injected as a binary mask to modulate the bokeh kernel, enabling creative effects such as heart-shaped bokeh.
The training regime is semi-supervised, combining synthetic paired data with unpaired real bokeh images. Synthetic data provides geometric consistency through ground-truth defocus maps derived from depth and user-specified focus parameters. Real unpaired data, annotated with EXIF metadata, enables the model to learn authentic lens characteristics that simulators cannot replicate. The authors construct defocus maps for real images using estimated depth and user-defined focus planes, allowing the model to generalize beyond synthetic renderings. This hybrid approach ensures both physical plausibility and visual realism in the generated bokeh.
Experiment
- Defocus deblurring: DeblurNet outperforms all baselines on reference metrics, surpassing ground truth on certain NR-IQA measures; achieves faithful text recovery and structure-consistent results on challenging scenes.
- Bokeh synthesis: On LF-BOKEH dataset, BokehNet achieves highest fidelity and perceptual scores, validated via per-image SSIM-optimized bokeh levels; semi-supervised training on real bokeh data eliminates artifacts like over-smoothing and inconsistent defocus seen in baselines.
- Refocusing: On LF-REFOCUS dataset, the DeblurNet+BokehNet pipeline outperforms all two-stage baseline combinations across fidelity and perceptual metrics, enabling accurate focal-plane placement and photorealistic bokeh synthesis.
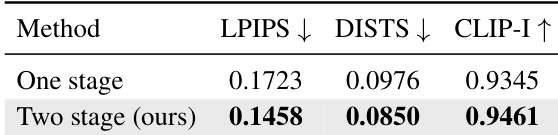
- Ablation studies: Two-stage refocusing surpasses one-stage variants by 0.82 PSNR on LF-REFOCUS; adding real unpaired bokeh data to BokehNet training improves SSIM by 0.03 and LPIPS by 0.05 on LF-BOKEH.
- Additional validations: Enables text-guided deblurring for correcting hallucinations and synthesizes user-specified aperture shapes; preserves original content better than VLM-based refocusing methods like Gemini-3 Nano Banana Pro.
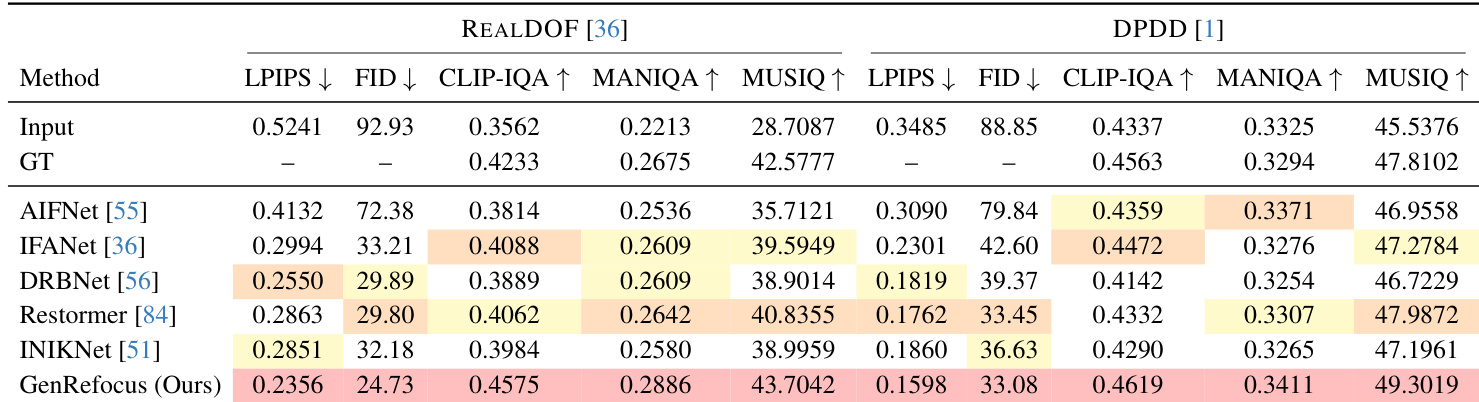
The authors evaluate GenRefocus against several baselines on REALDOF and DPDD datasets, showing it achieves the lowest LPIPS and FID scores and the highest CLIP-IQA, MANIQA, and MUSIQ scores, indicating superior perceptual quality and fidelity. Results demonstrate consistent outperformance across both datasets, with GenRefocus delivering the most realistic deblurred outputs as measured by multiple reference and no-reference metrics. The method’s two-stage design and semi-supervised training contribute to its advantage over single-stage and purely synthetic-trained approaches.
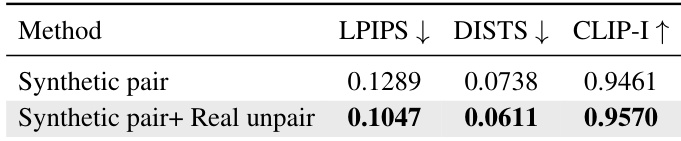
The authors evaluate BokehNet training with and without real unpaired bokeh images, showing that adding real data improves performance across all metrics: LPIPS and DISTS decrease while CLIP-I increases. Results confirm that semi-supervised training with real-world examples enables more authentic optical behavior than synthetic-only training.
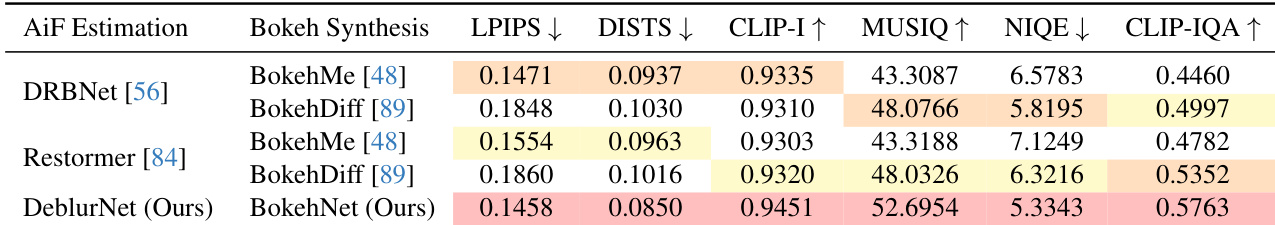
The authors compare their DeblurNet+BokehNet pipeline against combinations of existing all-in-focus estimators and bokeh synthesizers on the refocusing benchmark. Results show their method achieves the best scores across all metrics, including lower LPIPS and DISTS, and higher CLIP-I, MUSIQ, NIQE, and CLIP-IQA, indicating superior fidelity and perceptual quality. This improvement stems from joint optimization and semi-supervised training, enabling more accurate focus placement and physically consistent bokeh synthesis.
The authors compare one-stage and two-stage refocusing pipelines on the LF-REFOCUS benchmark, showing that their two-stage approach achieves superior performance across all metrics. Results indicate that the two-stage design enables better depth control and independent semi-supervised learning per stage, leading to more accurate refocusing and realistic bokeh synthesis.
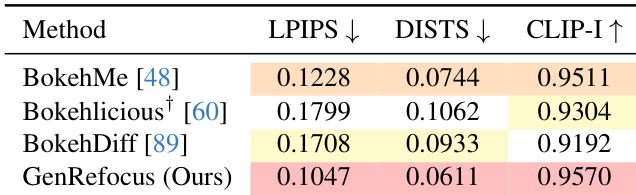
The authors evaluate bokeh synthesis methods on perceptual metrics using the LF-BOKEH benchmark, where GenRefocus outperforms all baselines. Results show GenRefocus achieves the lowest LPIPS and DISTS scores and the highest CLIP-I score, indicating superior perceptual fidelity and semantic alignment with ground truth. This improvement is attributed to semi-supervised training on real bokeh images, which enables more authentic blur rendering than simulator-based approaches.