Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
LLMCache: Layer-Wise Caching Strategies for Accelerated Reuse in Transformer Inference
LLMCache: Layer-Wise Caching Strategies for Accelerated Reuse in Transformer Inference
Harsh Vardhan Bansal
Abstract
Transformer-based language models have achieved remarkable performance across a wide range of tasks, yet their high inference latency poses a significant challenge for real-timeand large-scale deployment. While existing caching mechanisms,such as token-level key-value caches, offer speedups in autore-gressive decoding, they are limited in scope and applicability. In this paper, we present LLMCache, a novel layer-wise caching framework that accelerates transformer inference by reusing intermediate activations based on semantic similarity of input sequences. Unlike prior work, LLMCache is model-agnostic,operates across both encoder and decoder architectures, and supports caching at arbitrary transformer layers. We introduce a lightweight fingerprinting mechanism for matching seman-tically similar inputs and propose adaptive eviction strategies to manage cache staleness. Experiments on BERT and GPT-2 across SQuAD, WikiText-103, and OpenBookQA show up to 3.1 X speedup in inference time with <0.5% accuracy degradation. Our results highlight LLMCache as a practical and general-purpose solution for optimizing transformer inference in real-world applications
One-sentence Summary
Harsh Vardhan Bansal from Amazon Web Services proposes LLMCache, a model-agnostic layer-wise caching framework that accelerates transformer inference by reusing intermediate activations through semantic similarity matching. Unlike token-level key-value caches, it operates across both encoder and decoder architectures with adaptive eviction strategies, achieving up to 3.1× speedup with minimal accuracy degradation in real-world applications like chat systems and document processing pipelines.
Key Contributions
- Transformer inference faces high latency due to redundant computations on semantically similar inputs, as existing token-level caches like key-value caching are restricted to decoder-only architectures and cannot exploit cross-input activation reuse in encoder or encoder-decoder models.
- LLMCache introduces a model-agnostic layer-wise caching framework that reuses intermediate activations by matching input fingerprints based on semantic similarity, operating across arbitrary transformer layers with adaptive eviction strategies to manage cache staleness without model retraining.
- Experiments on BERT and GPT-2 across SQuAD, WikiText-103, and OpenBookQA demonstrate up to 3.1× inference speedup with less than 0.5% accuracy degradation, validating its effectiveness for real-world applications like conversational agents and document pipelines.
Introduction
Transformer inference latency remains a critical barrier for real-time deployment of large language models, especially in applications like conversational AI and document processing where inputs often share semantic or structural similarities. Prior optimization techniques such as quantization, pruning, or key-value caching suffer from key limitations: quantization and pruning require retraining or sacrifice accuracy, while standard key-value caching only accelerates autoregressive decoding in decoder-only models and cannot reuse intermediate activations across encoder or encoder-decoder architectures. The authors leverage layer-wise caching of intermediate activations to address this gap, introducing LLMCache—a model-agnostic framework that fingerprints input semantics to identify and reuse stable representations across arbitrary transformer layers. Their approach supports both encoder and decoder models, uses adaptive eviction to manage cache staleness, and achieves up to 3.1× inference speedups with minimal accuracy loss on tasks like question answering and language modeling.
Method
The authors leverage a modular, layer-wise caching framework to accelerate transformer inference by reusing intermediate activations across semantically similar inputs. The system operates without modifying the underlying model architecture and is compatible with both encoder and decoder models. At its core, LLMCache introduces a semantic fingerprinting mechanism that enables adaptive matching, allowing reuse even under partial input drift.
The system architecture comprises five key components: an Input Fingerprint Generator, Layer-wise Cache Banks, a Cache Matching and Lookup Engine, a Layer Execution Manager, and a Cache Refresh and Replacement Controller. Refer to the framework diagram for a high-level view of how these components interact across transformer layers.
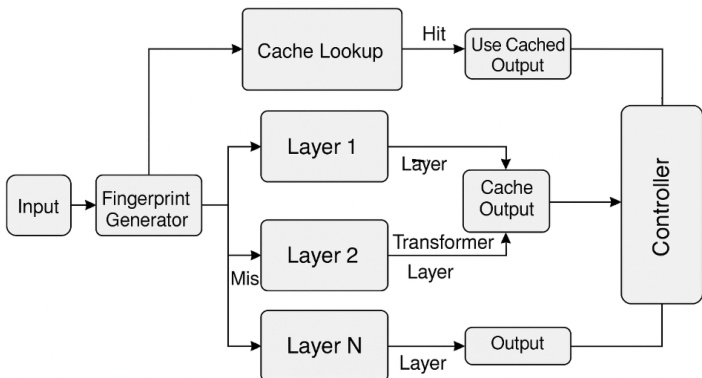
The inference workflow begins with the Input Fingerprint Generator, which computes a fixed-length semantic fingerprint fX for the input sequence X={x1,x2,…,xn}. This fingerprint is derived from aggregated token embeddings, optionally augmented with attention statistics, and compressed via SimHash or PCA to ensure efficient comparison. Fingerprints serve as keys for cache lookup and are compared using cosine similarity or Jaccard index, depending on the hashing scheme.
Each transformer layer l maintains an independent cache bank Cl storing tuples (f,hl), where f is a fingerprint and hl is the corresponding hidden state output. During inference, the Cache Matching and Lookup Engine checks Cl for a fingerprint f′ such that sim(fX,f′)≥τ, where τ is a tunable similarity threshold. If a match is found, the cached activation hl is reused; otherwise, the layer is computed normally and the result is stored in the cache.
The Layer Execution Manager acts as a dynamic decision gate, seamlessly integrating with the transformer’s forward pass by selecting between cached reuse and full computation at each layer. This is implemented via PyTorch module hooks or subclass overrides, preserving compatibility with existing model implementations.
As shown in the figure below, the inference flow proceeds layer by layer, with each layer independently deciding whether to reuse or recompute based on cache lookup results. This layer-wise granularity avoids the overhead of token-level key-value caching and enables fine-grained control over reuse behavior.
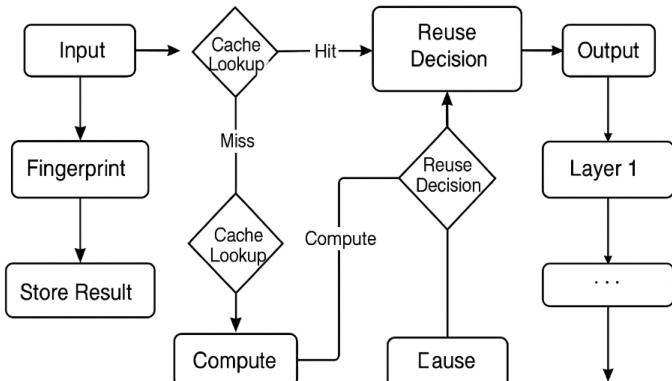
To maintain cache efficiency and prevent memory bloat, the Cache Refresh and Replacement Controller employs eviction policies such as Least Recently Used (LRU), staleness-aware decay, and divergence monitoring. Divergence is measured by tracking output drift for a given fingerprint across inference calls, triggering revalidation when performance degrades. Temporal decay factors further ensure that outdated entries are flushed over time.
The overall inference process is formalized as:
hl={Cl[fX]fl(hl−1)if sim(fX,f′)>τotherwisewhere Cl is the cache for layer l, f′ are existing fingerprint keys, and τ governs the trade-off between reuse rate and semantic fidelity. The system allows tuning of τ, cache size, and layer selection to balance speed and accuracy per application.
Experiment
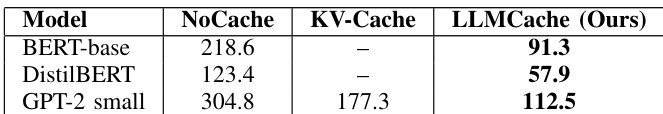
- Achieved 2.4× latency reduction on BERT-base and up to 3.1× overall versus NoCache across WikiText-103, SQuAD v2, and OpenBookQA, outperforming KV-Cache on GPT-2
- Recorded up to 92% cache hit rates in lower/mid transformer layers on GPT-2 WikiText-103, with upper layers showing higher sensitivity to semantic variation
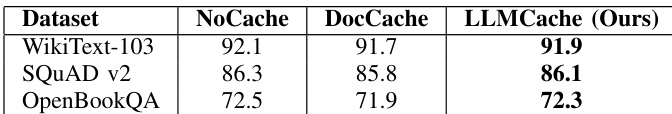
- Maintained task accuracy within 0.5% drop across all benchmarks, demonstrating superior robustness versus DocCache due to finer-grained layer control
- Enabled flexible memory-hit rate tradeoffs with logarithmic overhead growth, bounded by efficient fingerprinting in BERT-base experiments
- Identified optimal similarity threshold (τ) between 0.82 and 0.88 via ablation, balancing reuse frequency and output fidelity
The authors use LLMCache to accelerate transformer inference by reusing intermediate representations, achieving significant latency reductions across BERT-base, DistilBERT, and GPT-2-small. Results show LLMCache cuts inference time by up to 2.4× compared to no caching and outperforms KV-Cache on GPT-2, indicating finer-grained reuse yields greater speedups. All models maintain high efficiency with minimal accuracy loss, validating the method’s practicality for real-time applications.
Results show that LLMCache maintains task accuracy within 0.5% of the baseline across all evaluated datasets, outperforming DocCache in preserving fidelity while enabling inference acceleration. The authors use this to validate the semantic stability of their layer-wise caching approach.