Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Jan-nano Technical Report
Jan-nano Technical Report
Alan Dao Dinh Bach Vu
Abstract
Most language models face a fundamental tradeoff where powerful capabilities require substantial computational resources. We shatter this constraint with Jan-nano, a 4B parameter language model that redefines efficiency through radical specialization: instead of trying to know everything, it masters the art of finding anything instantly. Fine-tuned from Qwen3-4B using our novel multi-stage Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) system that completely eliminates reliance on next token prediction training (SFT), Jan-nano achieves 83.2% on SimpleQA benchmark with MCP integration while running on consumer hardware. With 128K context length, Jan-nano proves that intelligence isn't about scale, it's about strategy.
One-sentence Summary
The authors from Menlo Research propose Jan-nano, a 4B-parameter language model that achieves high performance on SimpleQA (83.2%) through a novel multi-stage RLVR training approach eliminating next-token prediction, enabling efficient, strategy-driven information retrieval on consumer hardware with 128K context.
Key Contributions
- Jan-nano addresses the longstanding trade-off between model performance and computational efficiency by introducing a 4B-parameter language model specialized for rapid, accurate information retrieval rather than memorizing knowledge, enabling high-capability reasoning on consumer-grade hardware.
- The model is trained via a novel multi-stage Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) framework that eliminates reliance on next-token prediction (SFT), instead using DAPO and a "force non-thinking" regularization to optimize for concise, correct tool usage and avoid overthinking.
- Evaluated on the SimpleQA benchmark with MCP integration, Jan-nano achieves 83.2% accuracy—demonstrating strong performance competitive with much larger models—while supporting a 128K context length and operating efficiently in a local RAG environment.
Introduction
The development of large language models has long faced a trade-off between high performance and computational efficiency, with state-of-the-art results typically requiring large models that are impractical for local deployment. Prior work in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has improved reasoning through external tools, but most efforts focus on large 7B+ parameter models, leaving smaller, efficient models underutilized for complex, tool-augmented tasks. The authors introduce Jan-nano, a 4B-parameter model designed specifically for efficient, tool-driven reasoning. Their key contribution is the RLVR training framework, a multi-stage reinforcement learning approach that replaces traditional supervised fine-tuning. By using DAPO for preference optimization and a "force non-thinking" regularization to penalize unnecessary steps, Jan-nano is optimized for direct, accurate tool invocation. Evaluated on SimpleQA with a local RAG setup, it achieves 83.2% accuracy—surpassing its baseline and rivaling much larger models—demonstrating that specialized, efficient architectures can match high performance in knowledge-intensive tasks when strategically designed.
Dataset
- The dataset is derived from MuSiQue-Ans [Trivedi et al., 2022], a multihop question answering dataset designed to support reasoning across multiple steps.
- It includes 10,325 samples, categorized by reasoning depth: 7,000 two-hop questions (67.8%), 2,150 three-hop questions (20.8%), and 1,175 four-hop questions (11.4%).
- The dataset was selected for its structured progression in difficulty and inclusion of supporting paragraphs that provide evidence for each answer.
- The authors use this dataset as part of their training data, incorporating it with other sources in a mixture that reflects varying reasoning complexity.
- No explicit cropping or metadata construction is described, but the data is processed to align with the model’s input format, preserving the original question-answer pairs and supporting evidence.
Method
The authors leverage a multi-stage reinforcement learning framework with verifiable rewards (RLVR) to train Jan-nano, a 4B parameter language model that achieves high performance through specialized tool usage rather than relying on traditional next token prediction training. The training begins from Qwen3-4B and proceeds through a controlled environment using the MuSiQue dataset, augmented by a local RAG server that simulates real search engine behavior. This setup enables the model to learn efficient information retrieval and synthesis strategies while maintaining autonomy.
The training process follows a three-stage progression. In the first stage, the model learns basic tool mechanics and interaction patterns with an 8K context length. During this phase, the reward function is designed to balance multiple objectives: correct answer generation, successful tool execution, adherence to response format, and compliance with XML structure. This stage establishes foundational behaviors for tool invocation and response formatting. As shown in the figure below, the model initiates a web search to gather relevant information, demonstrating early-stage tool usage.

In the second stage, the focus shifts to answer quality, with the model continuing to operate under an 8K context. The reward function is reconfigured to prioritize correctness, removing incentives for tool execution and format adherence. This encourages the model to refine its reasoning and synthesis capabilities, ensuring that generated responses are accurate and well-supported by retrieved information. The structured XML format remains in place, with tools invoked using <tool> tags, results returned in <result> tags, and final answers enclosed in <answer> tags. This consistent format facilitates reliable parsing and comparison during reinforcement learning.
The third stage extends the context length from 8K to 40K, enabling the model to handle more complex, multi-step queries that require deeper information integration. This stage emphasizes context extension and the ability to perform repeated tool usage, as illustrated in the figure, where the model conducts multiple fetch operations to gather comprehensive data before generating a synthesized response. The training methodology ensures that the model develops autonomous reasoning patterns with minimal system prompts, allowing it to effectively navigate and respond to complex user queries.
Experiment
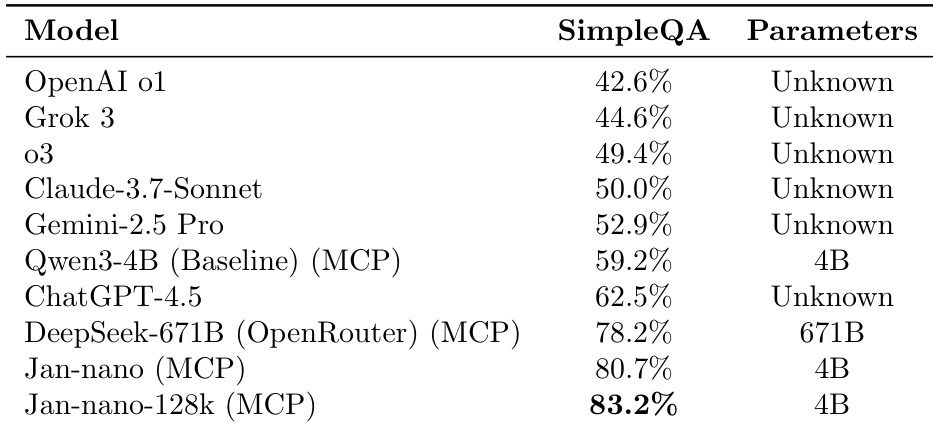
- Jan-nano achieves 83.2% accuracy on the SimpleQA benchmark with 4B parameters, a 24 percentage point improvement over Qwen3-4B with MCP (59.2%), demonstrating strong parameter efficiency; the 128K context variant shows a 2.5 percentage point gain, indicating benefits from extended context.
- Training with a 40K context window maintains high response quality while enabling longer input handling, with reward functions focused on correctness and XML structure.
- Larger models (8B) exhibit overthinking behaviors, applying unnecessary filters that eliminate relevant results and lead to hallucinations, whereas the 4B model’s direct search approach achieves higher accuracy and reliability.
- Disabling the thinking mechanism improves response speed significantly with only modest accuracy loss, leading to adoption of force non-thinking training for better user experience.
- Jan-nano performs better with LangGraph-based ReAct using MCP (80.7%) than with smolagents CodeAgent (76.2%), due to better alignment with JSON tool call templates used in training, highlighting the importance of format compatibility.
- MCP-based evaluation enables flexible, real-world agentic behavior assessment, supporting dynamic tool integration and authentic user experience replication, making it the preferred framework for evaluating autonomous reasoning.
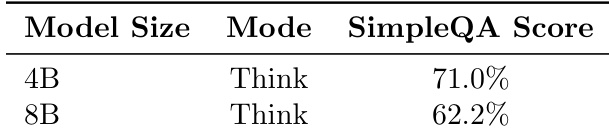
The authors evaluate the impact of model size and thinking mode on performance in the SimpleQA benchmark. Results show that the 4B model achieves a higher score of 71.0% compared to the 8B model's 62.2% when both operate in Think mode, indicating that larger models may suffer from overthinking behaviors that degrade performance.
The authors compare Jan-nano's performance across two agentic frameworks, finding that the LangGraph MCP configuration achieves higher accuracy (80.7%) than the smolagents CodeAgent setup (76.2%). This difference is attributed to better alignment with the model's training on JSON tool call templates, highlighting the importance of format compatibility in agentic system performance.

The authors use a SimpleQA benchmark to evaluate model performance with MCP integration, showing that Jan-nano achieves 83.2% accuracy with 4B parameters, a 24 percentage point improvement over the Qwen3-4B baseline. This result demonstrates competitive performance relative to larger models like DeepSeek-671B while maintaining high parameter efficiency.