Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Do You Think That Technology Alone Can Extend the Life of Notre Dame Cathedral? Naive!

The work of rebuilding historical buildings and cultural relics often takes several years. The use of artificial intelligence technologies such as 3D modeling, convolutional neural networks, and generative adversarial networks can provide guidance and reference suggestions for reconstruction and restoration work.
An unexpected fire plunged the whole of France into grief.
"The good things in the world are not solid, colorful clouds are easily dispersed and colored glass is fragile." The Notre Dame de Paris, a world treasure that took 180 years to build and is now more than 800 years old, was attacked by a fire on the evening of April 15, 2019, local time in France.

Notre Dame de Paris was not the only place destroyed by fire
This cultural relic building full of artistic atmosphere escaped the ravages of war and the erosion of time, but was destroyed by an accidental fire during renovation.

"Cultural relics only have one life, once lost they will never come back."
It is reported that after the firefighters rescued the two bell towers and the front building of Notre Dame, two-thirds of the roof was destroyed by the fire. In addition to the collapse of the iconic spire, the wooden roof frame no longer exists.However, the rose window, known as the "Flower of Heaven", miraculously survived.

This is not the first time that a fire has destroyed historic buildings and artifacts. Each restoration and reconstruction is a long journey.At least 10 yearsDuring this period, Notre Dame de Paris will no longer be open to the public.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence today, can technology help us restore these world treasures?
He used laser scanning to record the digital model
Fortunately, the late Andrew Tallon, professor of art at Vassar College, completed the laser scan of Notre Dame during his lifetime.
Tallon collected panoramic views, 3D information and detailed images of the building from multiple angles.He performed laser scans on the interior and detailed features of the cathedral, and used 3D archiving technology to accurately (1-2mm accuracy) and quickly (measure hundreds of thousands of points per second) obtain the spatial stereoscopic information of the building and construct a complete digital model.
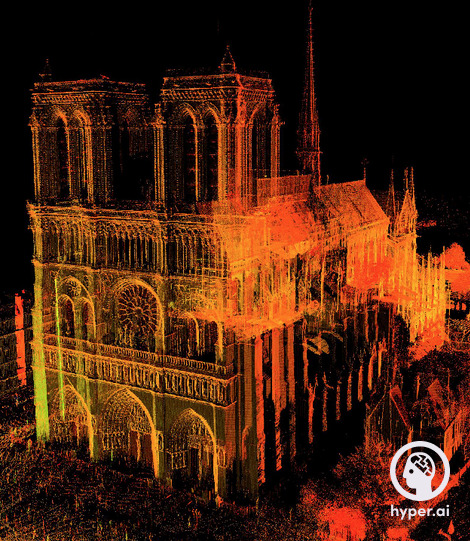

His work in 2014-2015 was meticulous and yielded some interesting findings: that the King’s Gallery had moved about a foot from the plumb bob, for example; that Notre Dame’s interior columns were not perfectly aligned, and so on.
Tallon passed away late last year.The digital information he left behind can provide a three-dimensional model for the restoration of Notre Dame de Paris, giving it a basis for reconstruction.
In the event of a sudden disaster, it is fortunate that the building has a 3D model, but what if no corresponding operation is performed?
Restoring the ruins from pictures
A company called Iconem built an AI model using Microsoft AI.Based on previous real-life photos of the building, the 3D image of the ruins before it was damaged can be restored.
To reconstruct the war-torn Ancient City of Palmyra (which was captured by the extremist terrorist organization ISIS in 2015 and subsequently destroyed), Iconem used photogrammetry technology to recreate a realistic digital model of the ancient city using more than 50,000 real-life photos of the ancient city.
Although the final repairs were not completed directly, this would have been a critical step if the building was to be physically restored.
So far, Iconem has used AI technology to build data models of many damaged relics, including the Meroe Pyramids in northern Sudan, the Libyan Amphitheater, and the ancient castle of Alamut in Iran.
Intel uses machine learning to help repair the Great Wall
Intel also uses AI technology to help with the repair work of the Jiankou Great Wall.
Faced with natural disasters and man-made damage, Jiankou Great Wall is in urgent need of repair. However, its steep terrain has added a certain degree of difficulty to the repair work.
Intel China Research Institute, Intel Data Center Group, and Wuhan University State Key Laboratory of Surveying, Mapping and Remote Sensing are working together to support the Jiankou Great Wall restoration project by combining drones with AI algorithms.

It is reported that the repair process is mainly divided into three steps:
1. Collect high-precision images
In the Jiankou Great Wall protection project, Intel's latest Falcon 8+ drone was used to take aerial photos and precise images of the entire Great Wall and its parts;
2. 3D modeling and artificial intelligence identification of damaged parts
With the help of the latest servers, high-resolution image data can be quickly analyzed and processed to produce a complete high-precision 3D model of the Great Wall.Artificial intelligence algorithms are used to identify parts that need to be repaired on the 3D model, providing measurement data of damage such as cracks and landslides to guide physical repairs.
3. Artificial Intelligence Digital Restoration of 3D Models
Based on 3D model damage identification,Using the latest 3D model adversarial generative network and regression convolutional network, the damaged parts of the city wall are digitally repaired.And provide guidance and reference suggestions for the actual repair and maintenance of the Great Wall.
Of course, the final repair work still has to be done by workers or machines operated by workers.
Technology brings progress in vision and experience
Although technology gives us hope, we have to admit that AI can only provide suggestions and references for restoration, and cannot completely restore Notre Dame de Paris.
Last year, a fire in a Brazilian museum reduced a large number of treasured cultural relics to ashes, but its full reconstruction will not begin until 2021. It faces obstacles from various aspects, including funding and technology.
The compromise isUse digital virtual methods to reproduce images.For example, Tencent cooperated with Brazilian museums to collect a large number of photos about Brazilian museums through Internet users, using image recognition and big data.Build a digital virtual museum.

Researchers at DeepMind also proposed a technology last year to convert images into 3D scenes.They used the Generative Query Network (GQN) combined with VR technology to recreate scenes in old photos.
Schematic diagram of the principle of GQN, paper title:
《Neural scene representation and rendering》
This allows people to have an immersive experience, such as "going back to the past" and experiencing the cradle they slept in as a child, or even "attending" their parents' wedding.
Technology can only help, but it can never completely restore
Looking back at the existing technologies and means, although there are many ways to achieve digital restoration, we must acknowledge the fact that the unique Notre Dame de Paris has left us forever while the fire was burning and the smoke was billowing, and a complete physical reconstruction is an impossible task.
We all know that digital models can only provide references or present virtual images, and those unique buildings and works of art can only remain in the hearts of those who have seen their beauty.
In fact, many textsRestorer of thingsThe work still needs to be done manually.The documentary "I Repair Cultural Relics in the Forbidden City" tells us the story of how generations of restoration masters use the spirit of craftsmanship to turn decay into magic. The Dunhuang murals were also restored after six years of work by restorers.

therefore,We advocate technology not because it is omnipotent, but because it is not yet high enough to rise to the moral level.Perhaps current technology cannot restore an art palace to us, but at least the advancement of technology can enable us to remain rational and hopeful when facing such events.