Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Selected for AAAI 2025! To Solve the Problem of Soft Boundary and co-occurrence in Medical Image Segmentation, China University of Geosciences and Others Proposed the Image Segmentation Model ConDSeg
Medical image segmentation is a critical and complex step in the field of medical image processing. It mainly extracts the parts with special meanings from the medical image, thereby providing support for clinical diagnosis, rehabilitation treatment, and disease tracking. In recent years, with the support of computers and artificial intelligence, deep learning-based segmentation has gradually become the mainstream method of medical image segmentation, and its related achievements have also flourished.
Among the selected results announced at the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI 2025), the top international artificial intelligence conference, some papers once again showed the fruitful progress in automated medical image segmentation.One of the results, "ConDSeg: A General Medical Image Segmentation Framework via Contrast-Driven Feature Enhancement", jointly released by a team from China University of Geosciences and Baidu, attracted widespread attention.
In order to solve the two major problems of "soft boundaries" and co-occurrence in the field of medical image segmentation, researchers proposed a general framework called ConDSeg for contrast-driven medical image segmentation. This framework innovatively introduced the consistency reinforcement (CR) training strategy, semantic information decoupling (Semantic Information Decoupling, SID) module, contrast-driven feature aggregation (Contrast-Driven Feature Aggregation, CDFA) module and size-aware decoder (Size-Aware Decoder, SA-Decoder), etc., to further improve the accuracy of medical image segmentation models.
Paper address:
https://arxiv.org/abs/2412.08345
The open source project "awesome-ai4s" brings together more than 200 AI4S paper interpretations and provides massive data sets and tools:
https://github.com/hyperai/awesome-ai4s
Medical image segmentation accuracy faces two major challenges
In the past decade, the rise of artificial intelligence has helped the rapid development of automated medical image segmentation, freeing doctors and researchers from tedious tasks. However, given the complexity and professionalism of medical images, there is still a long way to go to achieve fully automated image segmentation, and accuracy is a challenge that cannot be ignored, because once accuracy is lost, automation is out of the question.
From the current perspective,The "soft boundaries" and co-occurrence phenomena in medical images are the key problems that hinder the improvement of medical image segmentation accuracy.
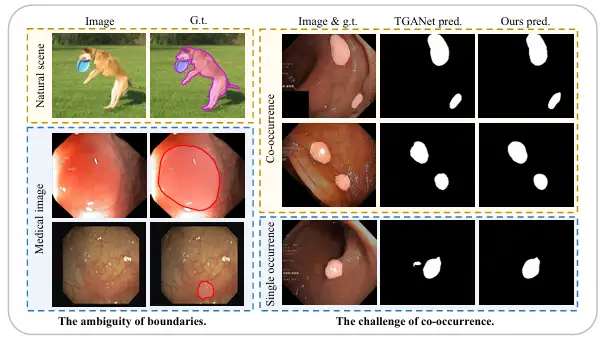
First, compared with natural images with clear boundaries between foreground and background, medical images often have a fuzzy "soft boundary" between the foreground (such as polyps, glands, lesions, etc.) and background. The main reason for this is that there is a transition zone between pathological tissue and surrounding normal tissue, making it difficult to define the boundary. In addition, in most cases, the poor lighting effects and low contrast of medical images will further blur the boundary between pathological tissue and normal tissue, which makes it more difficult to distinguish the boundary.
Secondly, unlike objects that appear randomly in natural scenes, organs and tissues in medical images are highly fixed and regular, so there is also a widespread co-occurrence phenomenon, that is, different image features, tissues or lesions appear in medical images at the same time. For example, in endoscopic polyp images, small polyps often appear at the same time as polyps of similar size, which makes it very easy for the model to learn certain co-occurrence features that are not related to polyps, but when pathological tissue appears alone, the model often cannot make accurate predictions.
In order to solve the above challenges, more and more research methods have focused on this in recent years. For example, the team of Associate Professor Yue Guanghui from the School of Biomedical Engineering, School of Medicine, Shenzhen University, released a boundary constraint network BCNet that can be used for accurate polyp segmentation. It mentions a bilateral boundary extraction module that can capture boundaries by combining shallow context features, high-level position features, and additional polyp boundary supervision. This achievement was published in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics under the title "Boundary constraint network with cross layer feature integration for polyp segmentation".
Paper address:
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9772424
Another example is the team led by Professor Dinggang Shen, the founding dean of the School of Biomedical Engineering at ShanghaiTech University, who proposed a cross-level feature aggregation network, CFA-Net, for polyp segmentation. It generates boundary-aware features by designing a boundary prediction network and merges these features into the segmentation network using a hierarchical strategy. The result was published in Pattern Recognition under the title "Cross-level Feature Aggregation Network for Polyp Segmentation".
Paper address:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031320323002558
However, although these methods have improved the model's attention to boundaries by explicitly introducing boundary-related supervision, they have not fundamentally enhanced the model's ability to spontaneously reduce uncertainty in fuzzy areas. Therefore, in harsh environments, the robustness of these methods is still weak and there are still limitations in improving the performance of the model. At the same time, the inability to accurately distinguish between foreground and background, as well as between different entities in the image, is still a problem faced by most models.
Different from previous methods,In a study conducted by a team from China University of Geosciences and Baidu, researchers proposed a general framework called ConDSeg for contrast-driven medical image segmentation.The specific innovations are as follows:
* In response to the robustness test in harsh environments, researchers proposed a consistency reinforcement (CR) pre-training strategy to enhance the robustness of the encoder, thereby extracting high-quality features. At the same time, the semantic information decoupling (SID) module can decouple feature maps into foreground, background, and uncertain areas, and learn to reduce uncertainty during training through a specially designed loss function.
* The proposed Contrast-Driven Feature Aggregation (CDFA) module guides the fusion and enhancement of multiple layers of features through the contrast features extracted by SID. The Size-Aware Decoder (SA-Decoder) aims to better distinguish different entities in the image and make separate predictions for entities of different sizes to overcome the interference of common features.
ConDSeg's four major innovations enable improved medical image segmentation accuracy
Overall,The ConDSeg proposed in this study is a general medical image segmentation framework with a two-stage architecture.As shown in the following figure:
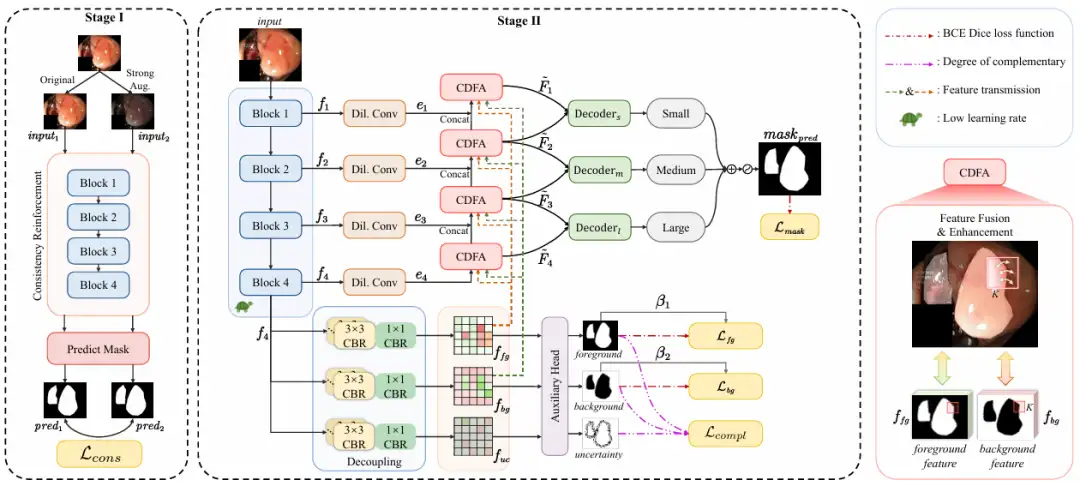
In the first stage,The goal of the research is to maximize the feature extraction capability and robustness of the encoder in low-light and low-contrast scenes.
The researchers introduced the CR pre-training strategy to conduct preliminary training on the encoder, separated the encoder from the entire network, and designed a simple prediction head (Predict Mask). By inputting the original image (Original) and the enhanced image (Strong Aug.) into the encoder, the consistency between the predicted masks is maximized, the robustness of the encoder under different lighting and contrast challenges is enhanced, and its ability to extract high-quality features in harsh environments is improved. The enhancement methods include randomly changing brightness, contrast, saturation, hue, and randomly converting to grayscale images and adding Gaussian blur.
It is also worth mentioning that the consistency loss Lcons proposed by the research team is designed based on pixel-level classification accuracy, using simple binarization operations and binary cross-entropy (BCE) loss calculation to directly compare the pixel-level differences between predicted masks. This method is simpler to calculate and avoids numerical instability, making it more suitable for large-scale data.
In the second stage,The whole network is fine-tuned, and the learning rate of the encoder is set at a low level. It is divided into 4 steps:
* Feature extraction, the ResNet-50 encoder extracts feature maps f₁ to f₄ with different semantic information at different levels.
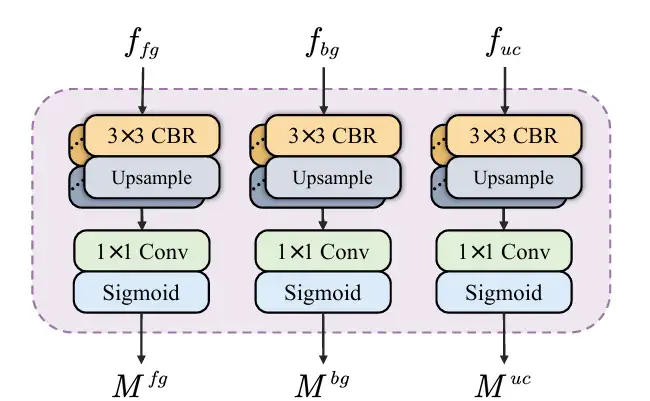
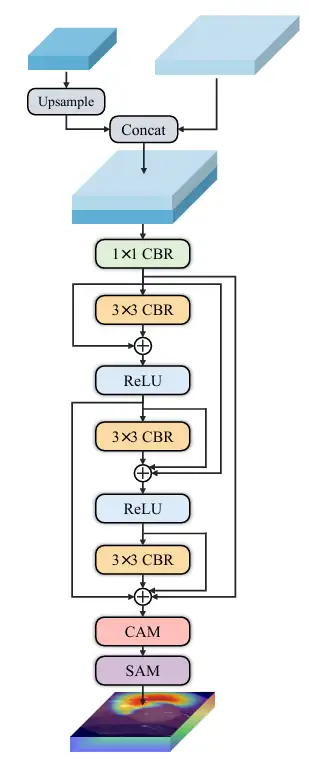
* Semantic information decoupling, input the feature map f₄ carrying deep semantic information into SID, and decouple it into a feature map containing foreground, background and uncertain area information. SID starts with 3 parallel branches, each branch consists of multiple CBR modules. After inputting the feature map f₄ into the 3 branches, 3 feature maps with different semantic information are obtained, which are enriched with foreground, background and uncertain area features respectively. Then an auxiliary head predicts the 3 feature maps and generates masks for the foreground, background and uncertain area. Through the constraints of the loss function, SID learns to reduce uncertainty and improve the mask accuracy between foreground and background. As shown in the figure below:
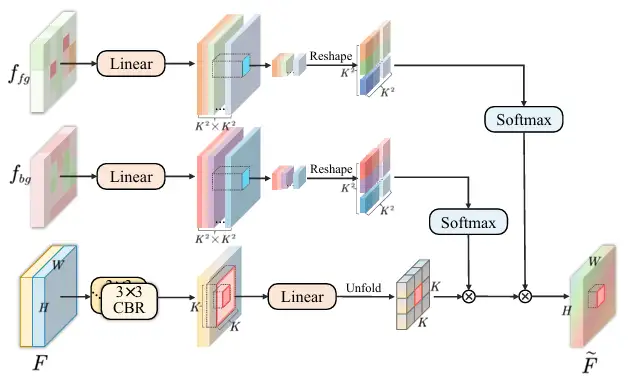
* Feature aggregation, sending feature maps f₁ to f₄ into the CDFA module, and gradually fusing multi-level feature maps guided by the decoupled feature maps to enhance the representation of foreground and background features. CDFA not only uses the contrast features of the foreground and background decoupled by SID to guide multi-level feature fusion, but also helps the model better distinguish between the entities to be segmented and the complex background environment. As shown in the figure below:
* Multi-scale prediction, the researchers built decoders of three sizes: small, medium, and large. Decoder ₛ, decoder ₘ, and decoder ₗ receive the output from CDFA at a specific level, and then locate multiple entities in the image according to size. The output of each decoder is fused to produce the final mask, so the model can accurately segment large entities and accurately locate small entities, which prevents the co-occurrence phenomenon from being learned incorrectly and solves the scale singularity problem of the decoder. As shown in the figure below:
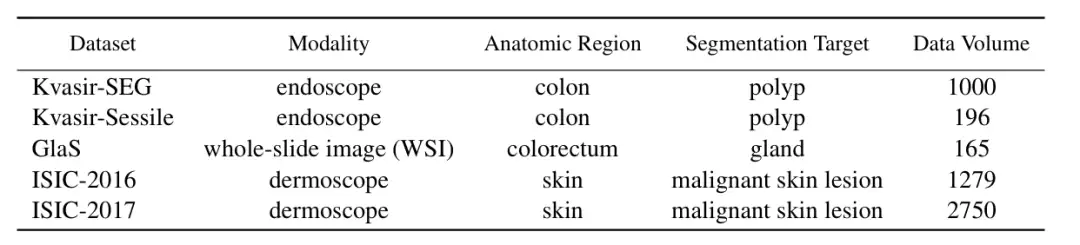
In order to verify the performance of ConDSeg in the field of medical image segmentation,The researchers selected five public datasets (Kvasir-SEG, Kvasir-Sessile, GlaS, ISIC-2016, ISIC-2017, as shown in the figure below) to test three medical image tasks (endoscopy, whole slide images, and dermatoscopy). The researchers resized the images to 256 × 256 pixels and set the batch size to 4. The Adam optimizer was used for optimization.
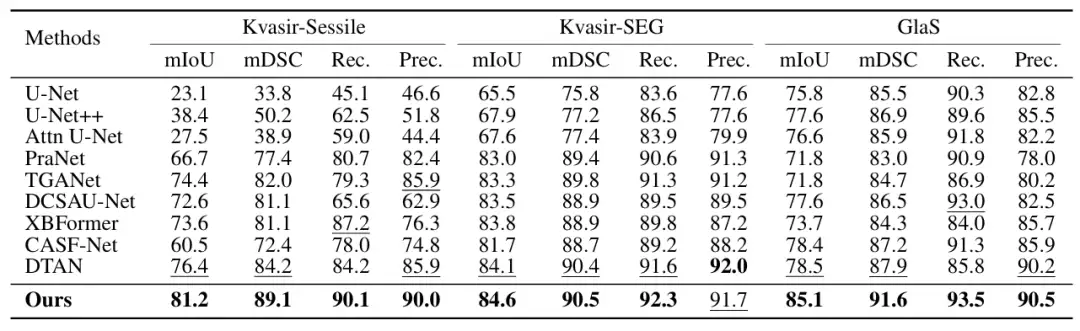
The main comparison objects include the most advanced methods such as U-Net, U-Net++, Attn U-Net, CENet, CPFNet, PraNet, FATNet, TGANet, DCSAUNet, XBoundFormer, CASF-Net, EIU-Net and DTAN.The results show that the proposed method achieves the best segmentation performance on all five datasets.As shown in the following figure:
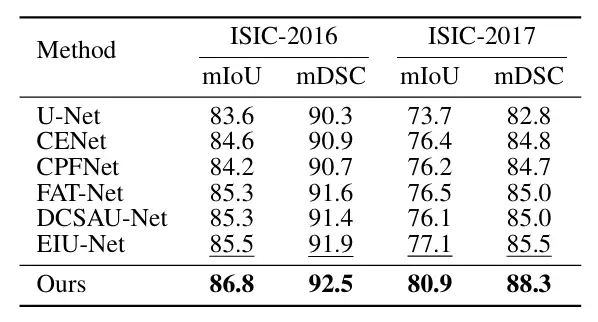
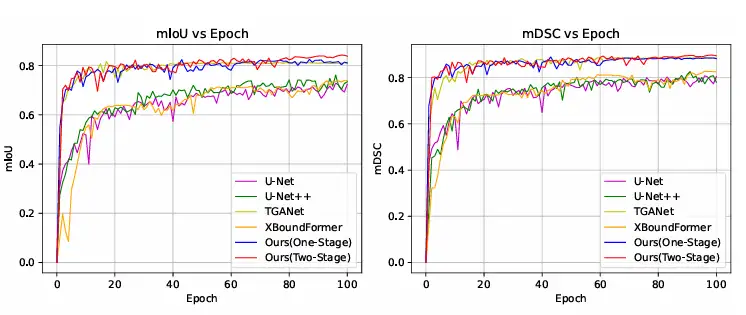
In addition, the researchers also compared the training convergence curve with other methods on the Kvasir-SEG dataset, and the results showed that ConDSeg can reach an advanced level even with only one stage of training, and when using the complete ConDSeg framework, this method achieved the fastest convergence speed and best performance, as shown in the figure below.
Medical image segmentation has become a hot topic for capital and technology
Medical image segmentation plays an important role in both clinical medicine and medical research. Specially trained AI systems have transformed traditional medical image segmentation methods with their high efficiency and intelligence, making it an indispensable auxiliary tool for medical staff and scientific researchers. The development and achievements of medical image segmentation are driven by both capital and technology.
In terms of capital, the intersection of AI and biomedicine has become a hot topic in the investment community in recent years, and this year, AI-driven medical imaging has taken the lead in getting off to a good start. On January 28, Spanish medical imaging company Quibim announced that it had completed a US$50 million (approximately RMB 360 million) Series A financing. It is worth mentioning that Quibim's core technology is artificial intelligence analysis based on medical imaging data, and its QP-Liver is an automated segmentation tool for MRI diagnosis of diffuse liver disease.
In terms of technology, the combination of AI and medical image segmentation has long been one of the research focuses of major laboratories. For example, the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (MIT CSAIL) team, in collaboration with researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, proposed a general model for interactive biomedical image segmentation, ScribblePrompt, which supports annotators to use different annotation methods such as graffiti, clicks, and bounding boxes to flexibly perform biomedical image segmentation tasks, even for untrained labels and image types.
The related results, titled "ScribblePrompt: Fast and Flexible Interactive Segmentation for Any Biomedical Image", were accepted by the top international academic conference ECCV 2024.
Paper address:
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.07381
In addition, based on SAM 2 released by Meta, the Oxford University team developed a medical image segmentation model called Medical SAM 2 (MedSAM-2), which treats medical images as videos. It not only performs well in 3D medical image segmentation tasks, but also unlocks a new single-prompt segmentation capability. Users only need to provide a prompt for a new specific object, and the segmentation of similar objects in subsequent images can be automatically completed by the model without further input.
In short, AI is no longer a technology that is shelved. The development of automated medical image segmentation has confirmed the potential of AI in the biomedical field, and also verified its commercial feasibility through one capital story after another. In the future, as the most important link in the field of medical imaging, medical image segmentation will benefit from AI and run on the highway of development, and capital will also be introduced into the broader biomedical market due to the success of medical image segmentation, realizing a perfect closed loop of technology, capital, and business.