Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Visuelle Generierung entfesselt menschenähnliches Schlussfolgern durch multimodale Weltmodelle
Visuelle Generierung entfesselt menschenähnliches Schlussfolgern durch multimodale Weltmodelle
Jialong Wu Xiaoying Zhang Hongyi Yuan Xiangcheng Zhang Tianhao Huang Changjing He Chaoyi Deng Renrui Zhang Youbin Wu Mingsheng Long
Zusammenfassung
Menschen konstruieren interne Weltmodelle und schließen durch die Manipulation von Konzepten innerhalb dieser Modelle. In jüngster Zeit haben Fortschritte im Bereich der Künstlichen Intelligenz, insbesondere die sogenannte Ketten-des-Gedankens (Chain-of-Thought, CoT)-Schlussfolgerung, eine Annäherung an diese menschlichen kognitiven Fähigkeiten ermöglicht, wobei angenommen wird, dass Weltmodelle in großen Sprachmodellen eingebettet sind. Aktuelle Systeme erreichen bereits Expertenleistung in formalen und abstrakten Bereichen wie Mathematik und Programmierung, wobei sie sich vor allem auf sprachbasierte Schlussfolgerungen stützen. Dennoch bleiben sie Menschen in Bereichen wie physischer und räumlicher Intelligenz erheblich unterlegen, da diese komplexere Darstellungen und vorheriges Wissen erfordern. Die Entwicklung einheitlicher multimodaler Modelle (Unified Multimodal Models, UMMs), die sowohl sprachliche als auch visuelle Generierung leisten können, hat daher großes Interesse an einer menschenähnlicheren Schlussfolgerung geweckt, die auf komplementären multimodalen Wegen beruht – ihre konkreten Vorteile bleiben jedoch bisher unklar. Aus der Perspektive der Weltmodellierung präsentiert dieser Artikel die erste systematische Studie dazu, wann und wie visuelle Generierung die Schlussfolgerung unterstützt. Unser zentrales Argument ist die Hypothese der visuellen Überlegenheit: Für bestimmte Aufgaben – insbesondere solche, die in der physischen Welt verankert sind – dient die visuelle Generierung natürlicher als Weltmodell, während reine sprachliche Weltmodelle an Grenzen stoßen, die durch Darstellungseinschränkungen oder unzureichendes vorheriges Wissen verursacht werden. Theoretisch formalisieren wir die interne Weltmodellierung als zentrale Komponente der CoT-Schlussfolgerung und analysieren Unterschiede zwischen verschiedenen Formen von Weltmodellen. Empirisch identifizieren wir Aufgaben, die eine abwechselnde visuell-sprachliche CoT-Schlussfolgerung erfordern, und entwickeln eine neue Evaluierungssuite namens VisWorld-Eval. Kontrollierte Experimente an einem führenden UMM zeigen, dass die abwechselnde CoT-Schlussfolgerung Aufgaben, die der visuellen Weltmodellierung zuträglich sind, deutlich übertrifft, jedoch keine klaren Vorteile bietet, wenn dies nicht der Fall ist. Zusammenfassend klärt diese Arbeit das Potenzial multimodaler Weltmodellierung für leistungsfähigere, menschenähnliche multimodale KI.
One-sentence Summary
Tsinghua University and ByteDance Seed researchers propose the visual superiority hypothesis, showing that interleaved visual-verbal chain-of-thought reasoning in unified multimodal models outperforms verbal-only approaches on physical-world tasks, validated via their new VisWorld-Eval benchmark.
Key Contributions
- The paper introduces the visual superiority hypothesis, arguing that for physical-world tasks, visual generation serves as a more natural world model than verbal reasoning alone, which faces representational and knowledge bottlenecks.
- It formalizes world modeling in CoT reasoning and introduces VisWorld-Eval, a new benchmark suite designed to evaluate interleaved visual-verbal reasoning on tasks requiring explicit visual simulation.
- Empirical results on state-of-the-art UMMs show interleaved CoT significantly outperforms verbal-only CoT on visual-favoring tasks, while offering no advantage on tasks not requiring visual modeling, clarifying the scope of multimodal reasoning benefits.
Introduction
The authors leverage unified multimodal models (UMMs) to explore how visual generation enhances reasoning by acting as explicit visual world models—complementing the verbal world models embedded in large language models. While current AI systems excel in abstract domains using verbal chain-of-thought reasoning, they struggle with physical and spatial tasks due to representational bottlenecks and insufficient visual prior knowledge. The authors introduce the “visual superiority hypothesis,” arguing that for tasks grounded in the physical world, visual generation provides richer, more grounded representations. Their main contribution is a principled theoretical framework linking world modeling to reasoning, plus the VisWorld-Eval benchmark—a controlled suite of tasks designed to isolate when visual generation helps. Empirical results show interleaved verbal-visual CoT significantly improves performance on tasks requiring spatial or physical simulation, but offers no gain on simpler symbolic tasks like Sokoban, validating their hypothesis.
Dataset
The authors use VisWorld-Eval, a curated suite of seven reasoning tasks designed to evaluate visual world modeling, organized into two categories: world simulation and world reconstruction.
-
Paper Folding (adapted from SpatialViz-Bench): Simulates unfolding paper after folds and hole punches. Grid sizes 3–8, 1–4 folds; holes in 5 shapes. Test set uses max difficulty (8x8 grid, 4 folds). CoTs generated via rule-based templates, refined by Gemini 2.5 Pro. Visual world modeling interleaves images of unfolding steps; verbal modeling uses grid matrices; implicit modeling skips state tracking.
-
Multi-hop Manipulation (based on CLEVR): Objects (cubes, spheres, cylinders) in Blender-rendered scenes undergo spatial operations (add/remove/change). Queries target final layout. Test prompts vary initial objects (3–6) and operations (1–5). CoTs simulate step-by-step execution, refined by Gemini 2.5 Pro.
-
Ball Tracking (adapted from RBench-V): Predicts ball trajectory after elastic wall reflections. Ball starts with green arrow direction; 4–8 randomized holes. Test cases require ≥1 wall bounce. CoTs generated by Seed 1.6, explaining frame-to-frame dynamics.
-
Sokoban: Grid puzzles (6–10x10) with one box and target. CoTs use search algorithm to find optimal path; only key steps rendered (approach, push, direction change). Augmented with randomized detours for reflection. CoTs from Seed 1.6. Visual modeling interleaves rendered steps; verbal removes images; implicit masks coordinates with [masked].
-
Maze: Fixed 5x5 grid puzzles. CoTs from rule-based templates, rewritten for naturalness. Visual modeling interleaves rendered path steps; verbal and implicit follow Sokoban protocol, masking positions as [masked].
-
Cube 3-view Projection (from SpatialViz-Bench): Infers unseen orthographic view from isometric + two orthographic views. Grids 3–5, two cube colors. Test set uses random grid sizes. CoTs construct queried view, mark occlusions with auxiliary color, count cubes—rewritten by Gemini 2.5 Pro. Visual modeling adds image of queried view; verbal uses character matrices for color encoding.
-
Real-world Spatial Reasoning (subset of MMSI-Bench): Uses real-world camera-object/region positional questions. Training CoTs generated via visual-CoT pipeline using SFT-trained BAGEL for novel view synthesis, then filtered and rewritten by Gemini 2.5 Pro.
All tasks use question-answering format with verifiable answers. Training data includes chain-of-thoughts (CoTs) generated via templates or models, refined for clarity. Visual world modeling interleaves intermediate state images; verbal modeling uses symbolic representations; implicit modeling removes or masks explicit state tracking. Training and test sample counts per task are summarized in Table 2.
Method
The authors formalize a world-model perspective on multimodal reasoning, conceptualizing the underlying environment as a multi-observable Markov decision process (MOMDP). This framework posits that a multimodal model operates by maintaining an internal representation of the world state, which is inferred from multiple, potentially incomplete, observations across different modalities. The core of this approach lies in two atomic capabilities: world reconstruction and world simulation. World reconstruction enables the model to infer the complete structure of the world from partial observations, allowing it to generate novel views of the same state. This is formalized as encoding a set of observations into an internal representation, s^=enc(oϕ1,…,oϕn), which can then be decoded to synthesize an unseen observation, o^ϕn+1=dec(s^,ϕn+1). In modern generative models, this capability is realized through end-to-end novel view generation, pθ(oϕn+1∣oϕ1,…,oϕn). The second capability, world simulation, allows the model to predict the future evolution of the world state. This is formalized as predicting the transition of the current state and action, s^′∼pred(s^,a), or more commonly in generative models, predicting future observations, pθ(ot+1∣o≤t,a≤t). The authors argue that deliberate reasoning, such as chain-of-thought, is a process of manipulating these internal world observations. This is formalized as a sequence of reasoning steps and observations, R=(r1,o1),(r2,o2),…,(rH,oH), where each step ri is a logical operation and oi is an observation generated by invoking one of the atomic world modeling capabilities. This formulation is modality-agnostic, allowing for verbal, visual, or implicit world modeling. 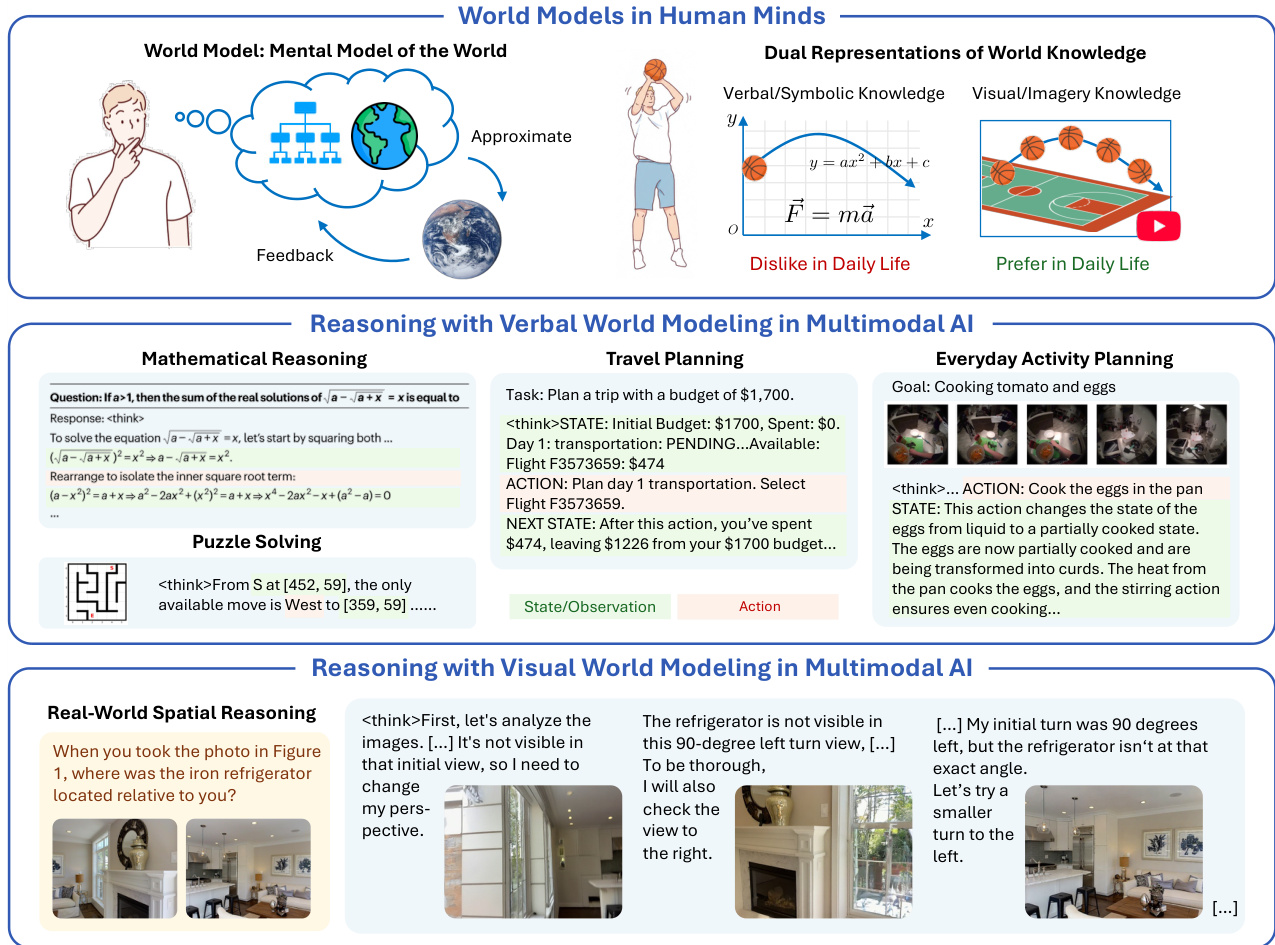
The model architecture is built upon a unified multimodal foundation, specifically the BAGEL model, which is designed to handle both verbal and visual generation. The training process is designed to optimize the model for generating interleaved verbal and visual reasoning steps. It begins with supervised fine-tuning (SFT) on task-specific datasets, where both the verbal reasoning steps and visual intermediate outputs are optimized. The loss function for visual world modeling combines cross-entropy for verbal generation with a flow-matching loss for visual generation, which is designed to learn the internal representations required for novel view synthesis. The training objective is to minimize the following loss: Lθ(Q,I,R,A)=−∑i=1H+1∑j=1∣ri∣logpθ(ri,j∣ri,<j,Ri)+∑i=1HEt,ϵ∥vθ(oit,t∣R~i)−(ϵ−oi)∥22. Following SFT, reinforcement learning from verifiable rewards (RLVR) is applied to further refine the model. During RL, the verbal generation component is optimized using GRPO, while the visual generation component is regularized via the KL-divergence with respect to the SFT-trained reference model to prevent degradation. The overall training framework is designed to enable the model to perform complex multimodal reasoning by explicitly generating and manipulating visual and verbal observations. 
Experiment
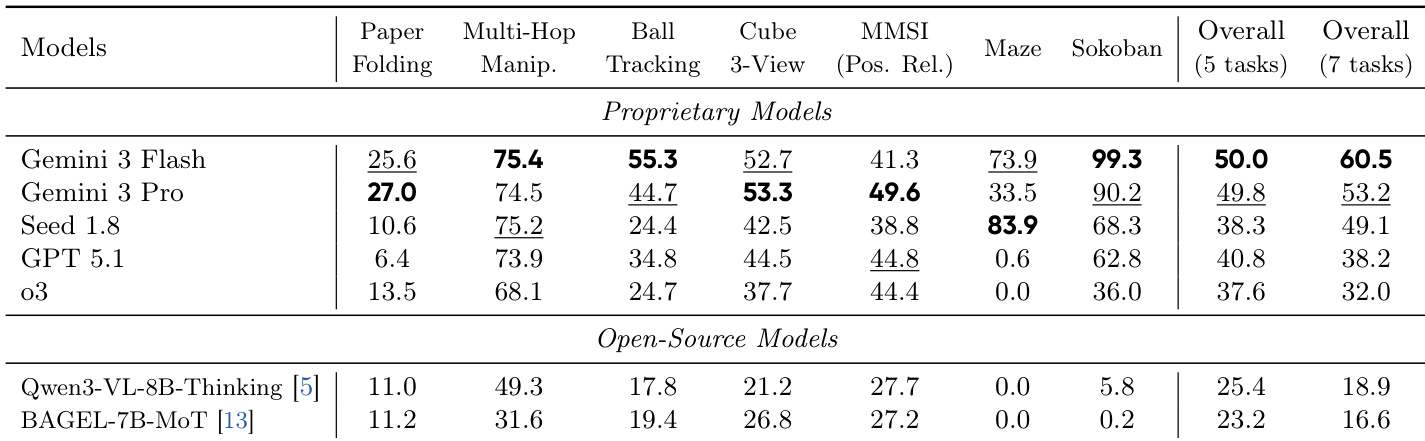
- Evaluated visual world modeling via VisWorld-Eval, a 7-task suite spanning synthetic and real-world domains; advanced VLMs (Gemini 3 Flash/Pro) outperform others but remain suboptimal on complex tasks like paper folding and spatial reasoning.
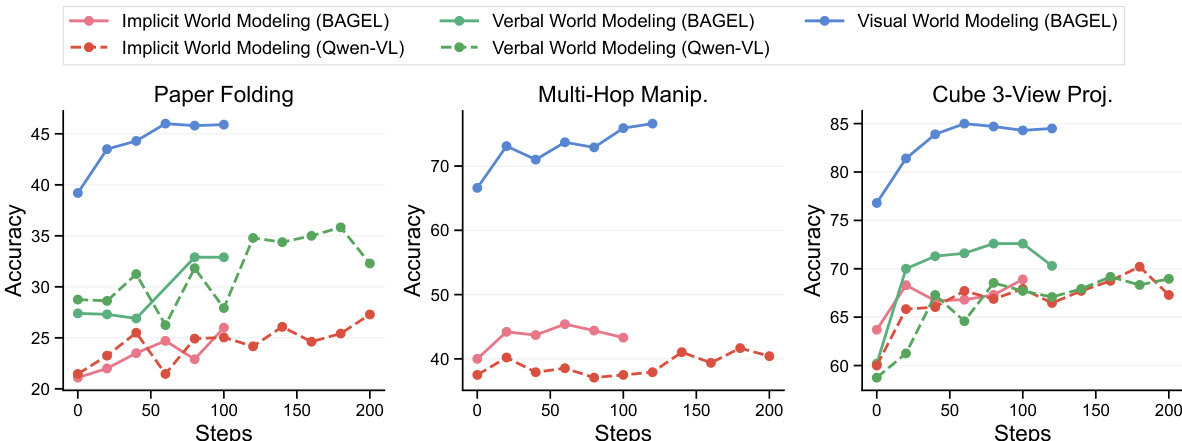
- Visual world modeling significantly boosts performance on world simulation tasks (paper folding, ball tracking, multi-hop manipulation) via richer spatial grounding; achieves 4x sample efficiency gain over verbal modeling in paper folding.
- Enhances world reconstruction tasks (cube 3-view, real-world spatial reasoning) by leveraging visual priors; maintains ~10% accuracy advantage even on out-of-distribution cube stacks (size 6) and achieves >50% fidelity in view synthesis vs. near-zero for verbal modeling.
- Offers no benefit on grid-world tasks (maze, Sokoban); implicit world modeling suffices, with internal model representations emerging post-pretraining and further refined via SFT without explicit coordinate supervision.
- UMMs outperform VLM baselines (Qwen2.5-VL) even when VLMs are fine-tuned on identical verbal CoT data, confirming visual modeling’s inherent advantage, not compromised verbal reasoning.
- RLVR improves all CoT formulations but does not close the performance gap; visual world modeling gains persist, suggesting its superiority is structural, not training-limited.
- Qualitative analysis reveals hallucinations in verbal reasoning (especially symmetry tasks) and generation artifacts in visual modeling, with spatial understanding still limited across viewpoints—expected to improve with stronger base models and curated data.
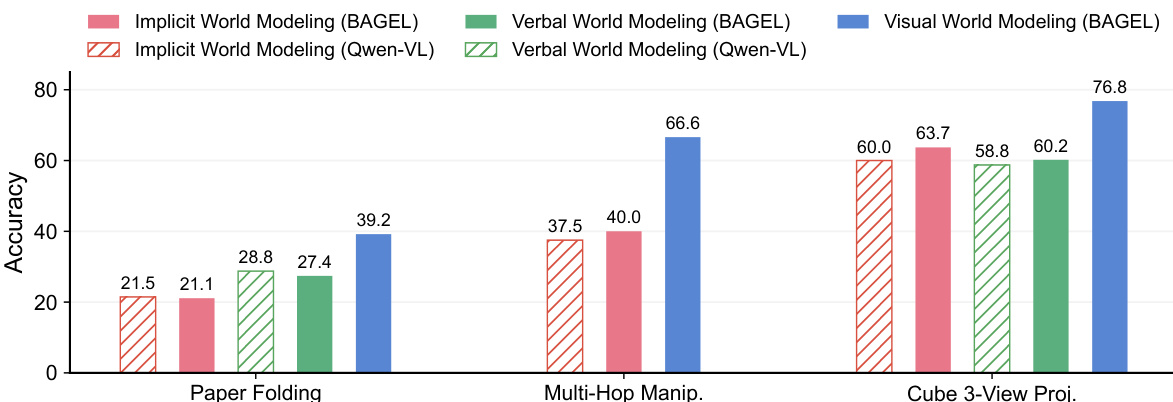
The authors use a bar chart to compare the performance of different models and reasoning methods on three tasks: Paper Folding, Multi-Hop Manipulation, and Cube 3-View Projection. Results show that visual world modeling consistently outperforms verbal and implicit world modeling across all tasks, with the largest gains observed in Multi-Hop Manipulation and Cube 3-View Projection. In Paper Folding, visual world modeling achieves the highest accuracy, while implicit and verbal world modeling show similar, lower performance.
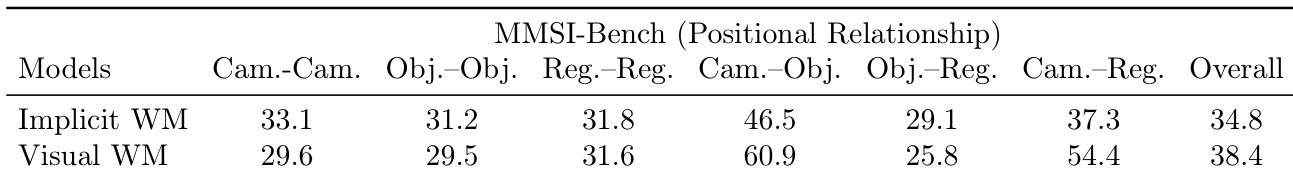
The authors compare implicit and visual world modeling on MMSI-Bench positional relationship tasks, showing that visual world modeling achieves higher accuracy on Cam.-Obj. and Cam.-Reg. subtasks, while implicit world modeling performs better on Obj.-Obj. and Obj.-Reg. The overall performance of visual world modeling is higher, indicating its effectiveness in spatial reasoning.
The authors use supervised fine-tuning with specific hyperparameters, including a learning rate of 1×10−5, a batch size of 128, and a GRPO mini batch size of 32, to train their models. The KL loss coefficient for visual generation is set to 0.1, while the coefficient for verbal generation is 0.0, indicating a focus on visual generation during training.

The authors use the VisWorld-Eval suite to evaluate advanced VLMs, reporting zero-shot performance across seven tasks. Results show that Gemini 3 Flash and Gemini 3 Pro significantly outperform other models, particularly on complex tasks like paper folding and ball tracking, though overall performance remains suboptimal.
The authors use supervised fine-tuning to evaluate the impact of different chain-of-thought formulations on multimodal reasoning tasks. Results show that visual world modeling significantly outperforms verbal and implicit world modeling on paper folding and multi-hop manipulation, where spatial reasoning requires precise geometric understanding. In contrast, for cube 3-view projection, visual world modeling achieves higher accuracy and better world-model fidelity compared to verbal approaches, though performance plateaus and hallucinations remain an issue.