Command Palette
Search for a command to run...
Der Script ist alles, was Sie brauchen: Ein agenter Rahmen für die Generierung von Langzeitdialog-zu-Kinofilm-Video
Der Script ist alles, was Sie brauchen: Ein agenter Rahmen für die Generierung von Langzeitdialog-zu-Kinofilm-Video
Zusammenfassung
Neuere Fortschritte in der Videogenerierung haben Modelle hervorgebracht, die beeindruckende visuelle Inhalte aus einfachen Textprompten synthetisieren können. Dennoch erweisen sich diese Modelle als unzulänglich, wenn es darum geht, langformige, kohärente Erzählungen aus hochleveligen Konzepten wie Dialogen zu generieren, was eine „semantische Lücke“ zwischen einer kreativen Idee und ihrer filmischen Umsetzung offenbart. Um diese Lücke zu schließen, stellen wir einen neuartigen, end-to-end agierenden Rahmen für die Dialog-zu-Kinofilm-Video-Generierung vor. Zentraler Bestandteil unseres Ansatzes ist der ScripterAgent, ein Modell, das darauf trainiert ist, grobe Dialoge in detaillierte, ausführbare kinematografische Skripte zu übersetzen. Dazu haben wir ScriptBench, eine neue großskalige Benchmark mit reichhaltigem multimodalem Kontext, erstellt, die mittels eines expertengeleiteten Annotationsschemas annotiert wurde. Das generierte Skript dient anschließend als Leitfaden für den DirectorAgent, der state-of-the-art Video-Modelle mithilfe einer cross-scene kontinuierlichen Generierungsstrategie koordiniert, um Kohärenz über längere Erzählhorizonte hinweg zu gewährleisten. Unsere umfassende Evaluation, die einen künstlichen Intelligenz-gestützten CriticAgent und eine neue Metrik für Visual-Script-Alignment (VSA) einsetzt, zeigt, dass unser Rahmen die Treue zum Skript und die zeitliche Genauigkeit signifikant gegenüber allen getesteten Video-Modellen verbessert. Darüber hinaus offenbart unsere Analyse ein entscheidendes Spannungsverhältnis in aktuellen SOTA-Modellen zwischen visuellem Spektakel und strenger Skriptkonformität, was wertvolle Einblicke für die Zukunft der automatisierten Filmproduktion liefert.
One-sentence Summary
Researchers from Tencent Hunyuan and Xidian University propose ScriptAgent, an agentic framework that bridges the semantic gap in dialogue-to-video generation via ScripterAgent (trained on ScriptBench), DirectorAgent for temporal coherence, and CriticAgent for evaluation—enhancing fidelity across SOTA models while revealing key trade-offs in automated cinematic storytelling.
Key Contributions
- We introduce an end-to-end agentic framework that bridges the semantic gap between sparse dialogue and cinematic video by decomposing the task into script generation (ScripterAgent), video orchestration (DirectorAgent), and evaluation (CriticAgent), enabling coherent long-form narrative synthesis.
- We construct ScriptBench, a large-scale multimodal benchmark annotated via an expert-guided pipeline, and train ScripterAgent using a two-stage SFT and GRPO method to produce executable cinematic scripts that resolve dialogue ambiguities and encode domain-specific filmmaking knowledge.
- Our evaluation across SOTA video models reveals a trade-off between visual quality and script adherence, and we demonstrate consistent improvements in script faithfulness and temporal coherence using our novel Visual-Script Alignment metric, with gains up to +0.4 in faithfulness and +7 in VSA.
Introduction
The authors leverage recent advances in video generation to tackle the challenge of producing long-form, coherent cinematic content from sparse dialogue—a task where current models fail due to a semantic gap between high-level narrative and executable visual planning. Prior systems struggle with temporal coherence, lack automated cinematographic reasoning, and require heavy manual input, limiting their use in narrative storytelling. Their main contribution is an end-to-end agentic framework comprising ScripterAgent (which converts dialogue into detailed cinematic scripts using a novel two-stage training method), DirectorAgent (which orchestrates video models with a cross-scene continuous generation strategy for long-horizon coherence), and CriticAgent (for evaluation). They also introduce ScriptBench, a large-scale multimodal benchmark, and a new metric, Visual-Script Alignment, to quantify temporal fidelity—showing their approach improves script faithfulness and coherence across leading video models while revealing a key trade-off between visual quality and narrative adherence.
Dataset
-
The authors use a custom-built dataset called ScriptBench, comprising 1,750 high-fidelity cinematic script instances derived from raw multimodal inputs (video + audio) of cinematic cutscenes, selected for rich dialogue, professional cinematography, and visual consistency.
-
Each instance corresponds to a video clip averaging 15.4 seconds, enabling multi-shot sequences while staying within generative model limits. The dataset is split into 1,700 training and 50 test instances, with the test set designed to challenge models to infer full cinematic elements from dialogue alone—mirroring real-world directorial workflows.
-
Scripts are generated via a three-stage LLM-powered pipeline (using Gemini 2.5 Pro) tightly constrained by expert templates and validation rules:
- Context Reconstruction and Dialogue Fusion — integrates audio and text to infer character, setting, emotion, and intent.
- Shot-Level Semantic Planning — segments scenes into self-contained, ≤10-second shots guided by narrative, technical, and continuity constraints.
- Multi-Round Adaptive Error Correction — iteratively validates scripts via four modules: Dialogue Completeness, Character Appearance Consistency, Scene Coherence, and Positional/Physical Rationality.
-
Post-generation, 60% of instances underwent expert audit, revealing subtle errors (e.g., character teleportation, prop inconsistencies), which fed back into refined prompts and verification logic. Final scripts are structured, internally consistent, and grounded in long-horizon narrative and physical continuity.
Method
The authors leverage a three-agent framework to address the challenge of long-horizon dialogue-to-cinematic video generation, with the ScripterAgent serving as the foundational component responsible for transforming raw dialogue into a structured, shot-level cinematic script. This process begins with a two-stage training paradigm. In the first stage, supervised fine-tuning (SFT), the model is trained to learn the structural syntax of cinematic scripts by mapping multi-turn dialogue inputs to target scripts in a structured JSON format. The base model, Qwen-Omni-7B, is fine-tuned to maximize the conditional log-likelihood of the ground-truth script, ensuring the output is structurally correct and content-complete. This SFT stage establishes a solid foundation for narrative coherence.
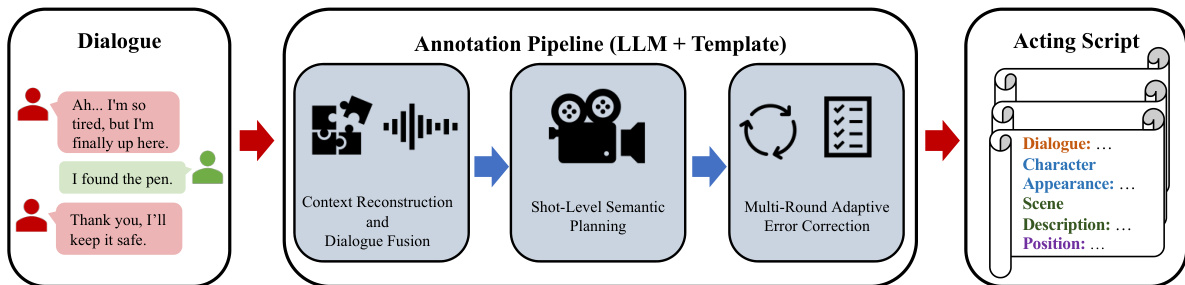
As shown in the figure below, the ScripterAgent takes a dialogue as input and produces a detailed acting script, which includes structured fields such as dialogue, character appearance, scene description, and position. This script serves as a blueprint for the subsequent video generation process.

The second stage employs reinforcement learning (RL) to align the model's outputs with professional directorial aesthetics, moving beyond structural correctness to capture subjective qualities like shot composition, pacing, and emotional impact. The authors use Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to train the ScripterAgent, which is well-suited for creative tasks with a subjective, one-to-many nature of valid outputs. A key innovation is the hybrid reward function, Rtotal, which balances objective correctness with subjective quality. This function is a weighted sum of a rule-based structural reward, Rstructure, which evaluates technical correctness through automated checks, and a human preference reward, Rhuman, which captures cinematic aesthetics by modeling expert human judgment using a BERT-based regression model trained on annotated samples. During optimization, the policy is updated by maximizing the advantage-weighted log-likelihood, constrained by a KL-divergence penalty to prevent large deviations from the SFT initialization.
The DirectorAgent addresses the challenge of translating the generated script into a continuous video sequence, overcoming the limited temporal capacity of state-of-the-art video generation models. Its primary function is to ensure both semantic coherence and visual consistency across multiple generated segments. The core of the DirectorAgent is a Cross-Scene Continuous Generation Strategy that combines intelligent, shot-aware segmentation with a frame-anchoring mechanism. Intelligent shot-based segmentation partitions the script into scenes that align with natural cinematographic boundaries, adhering to principles such as shot integrity, duration adaptation, semantic coherence, and technical feasibility. To ensure seamless visual transitions between scenes, the DirectorAgent employs a First-Last Frame Connection Mechanism. As illustrated in the figure below, the final frame of a generated scene is used as a visual anchor or conditioning image for the generation of the subsequent scene's first frame. This frame-anchoring strategy preserves visual consistency in character appearance, attire, and scene layout across multiple generation cycles, creating a seamless visual relay.
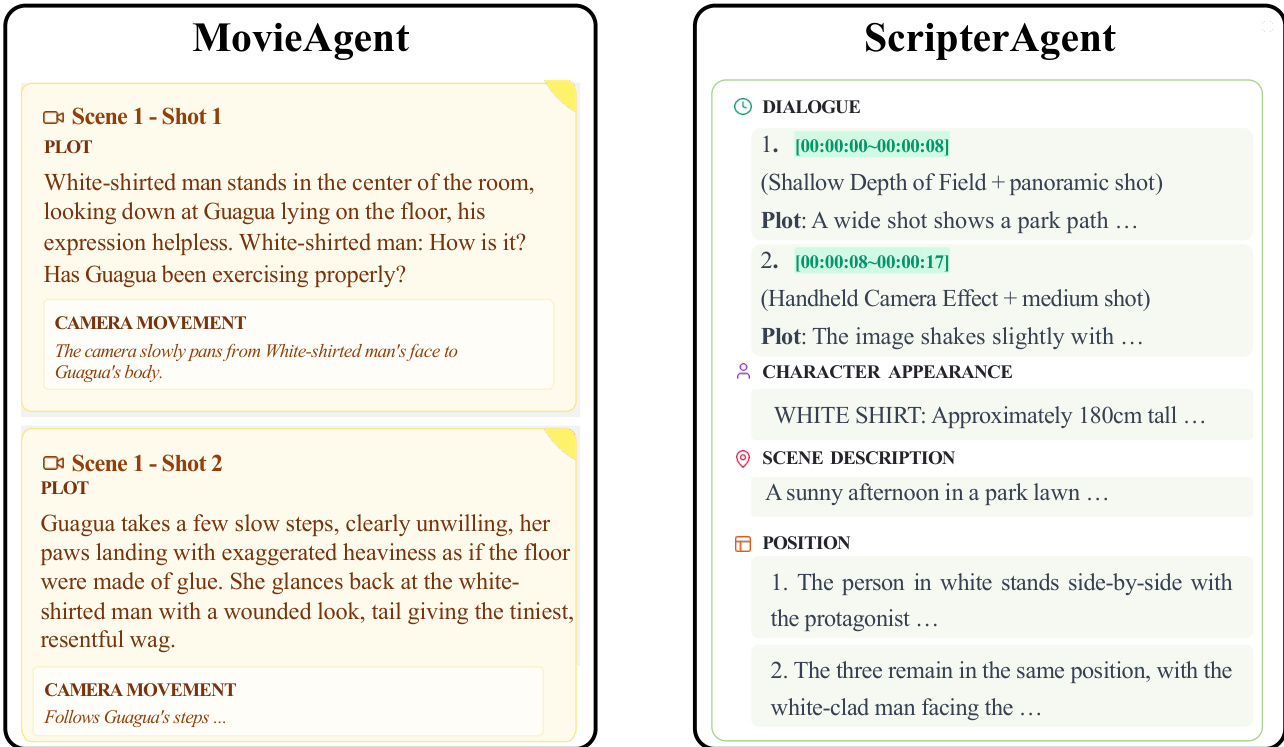
This approach effectively extends the coherence window of any underlying video model by transforming a long-horizon generation problem into a sequence of locally solvable, continuity-preserving subproblems. While this strategy significantly reduces identity drift and layout inconsistencies, challenges such as imperfect lip synchronization and residual misalignment of fine-grained actions remain.
Experiment
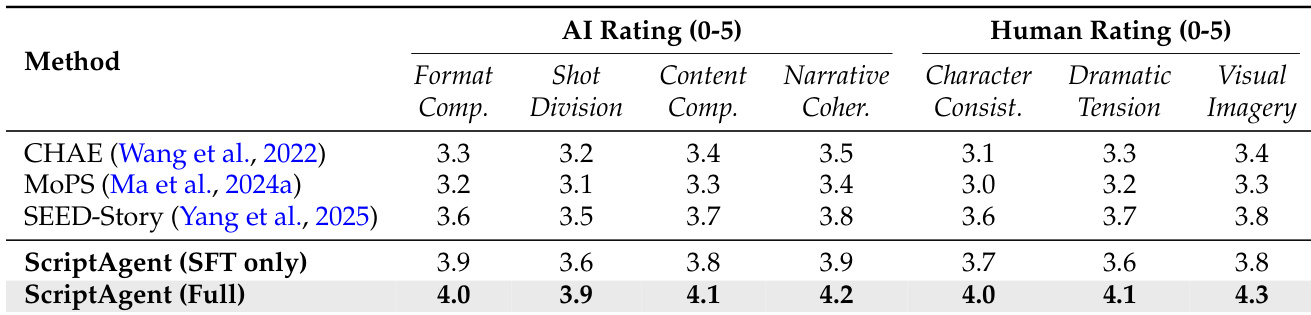
- Script generation evaluated via CriticAgent (gemini-2.5-pro) and human directors: ScripterAgent outperforms baselines (MoPS, CHAE, SEED-Story) on ScriptBench, achieving +0.4 in structural metrics and 4.3/5 in Visual Imagery vs. 3.8 for MovieAgent; RL fine-tuning boosts Dramatic Tension from 3.6 to 4.1.
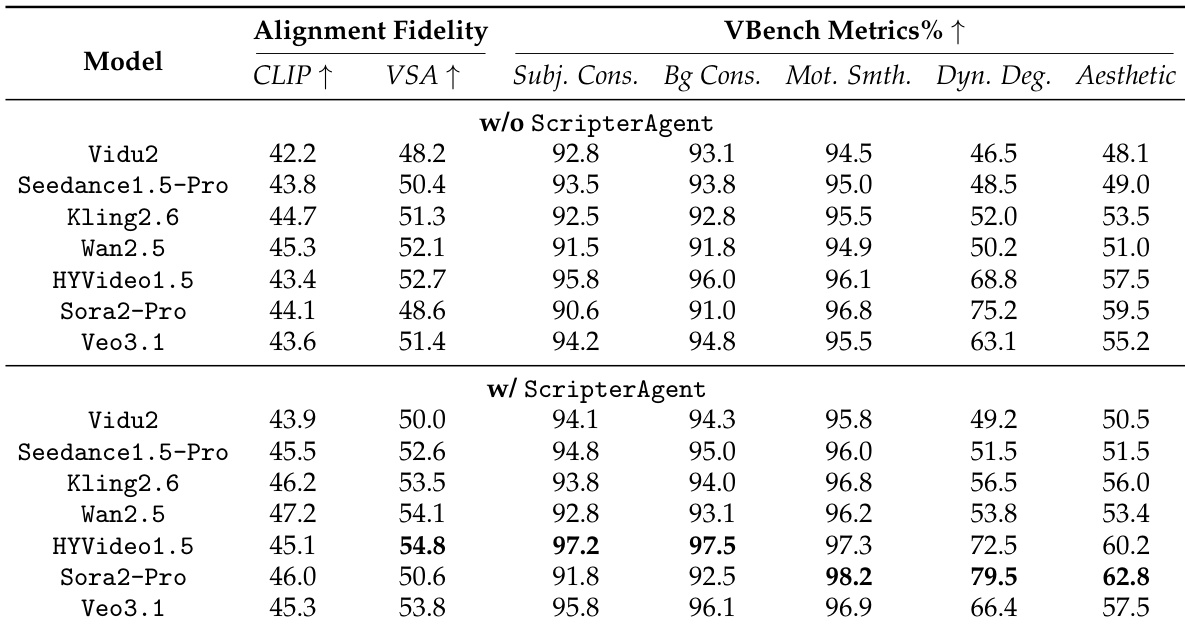
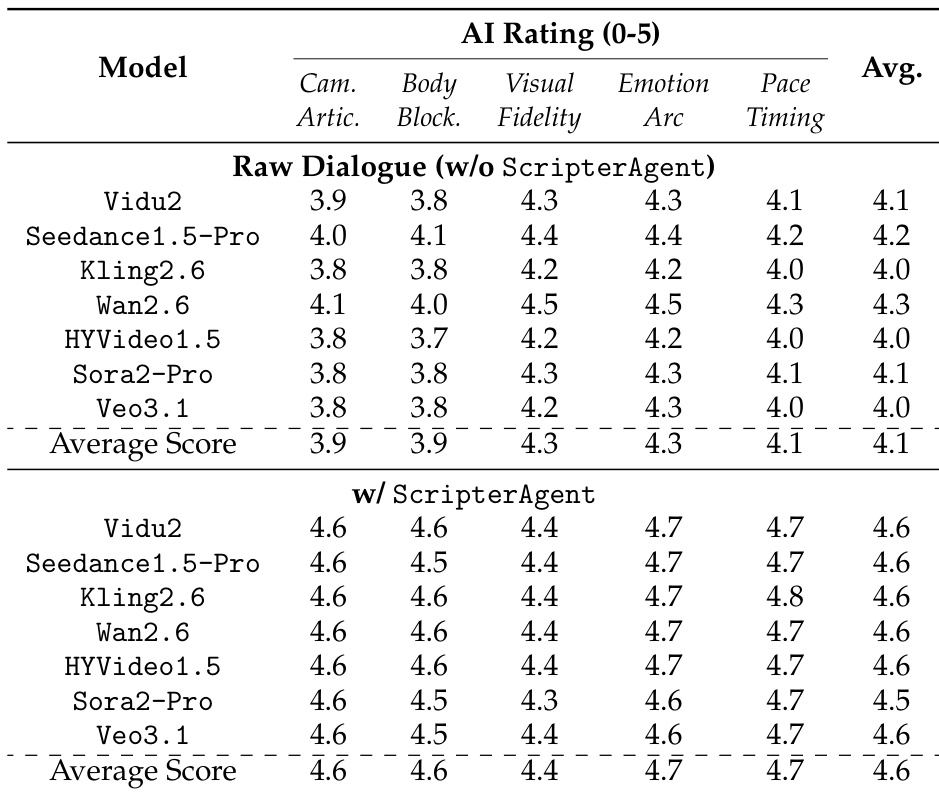
- Video generation assessed via CriticAgent, human raters, and novel VSA metric: Conditioning on ScripterAgent scripts lifts mean AI rating from 4.2 to 4.5 and human rating from 3.7 to 4.2; HYVideo1.5 leads in Script Faithfulness (4.6), Sora2-Pro in Visual Appeal (4.8).
- VSA metric confirms temporal-semantic alignment: HYVideo1.5 scores 54.8, Sora2-Pro improves from 48.6 to 50.6; CLIP scores rise avg +1.7, though fidelity sometimes trades off with aesthetics.
- Ablation shows Full Agent (script + segmentation + frame-anchoring) dominates: improves Narrative Pacing & Timing and Cinematic Camera Articulation; ScripterAgent alone boosts Visual Descriptive Fidelity and Body Blocking.
- Trade-off observed: Sora2-Pro excels in visual spectacle (Dynamic Degree 79.5, Physical Law 4.5), HYVideo1.5 in narrative integrity (Subject Consistency 97.2, Background Consistency 97.5).
The authors use a comprehensive evaluation framework to assess video generation models conditioned on scripts produced by ScripterAgent. Results show that conditioning on ScripterAgent outputs significantly improves both AI and human ratings across all models, with average scores increasing from 3.7 to 4.2 for human ratings and from 4.2 to 4.5 for AI ratings. The improvements are most pronounced in Script Faithfulness and Narrative Coherence, indicating that structured scripts enhance temporal-semantic alignment and storytelling quality.
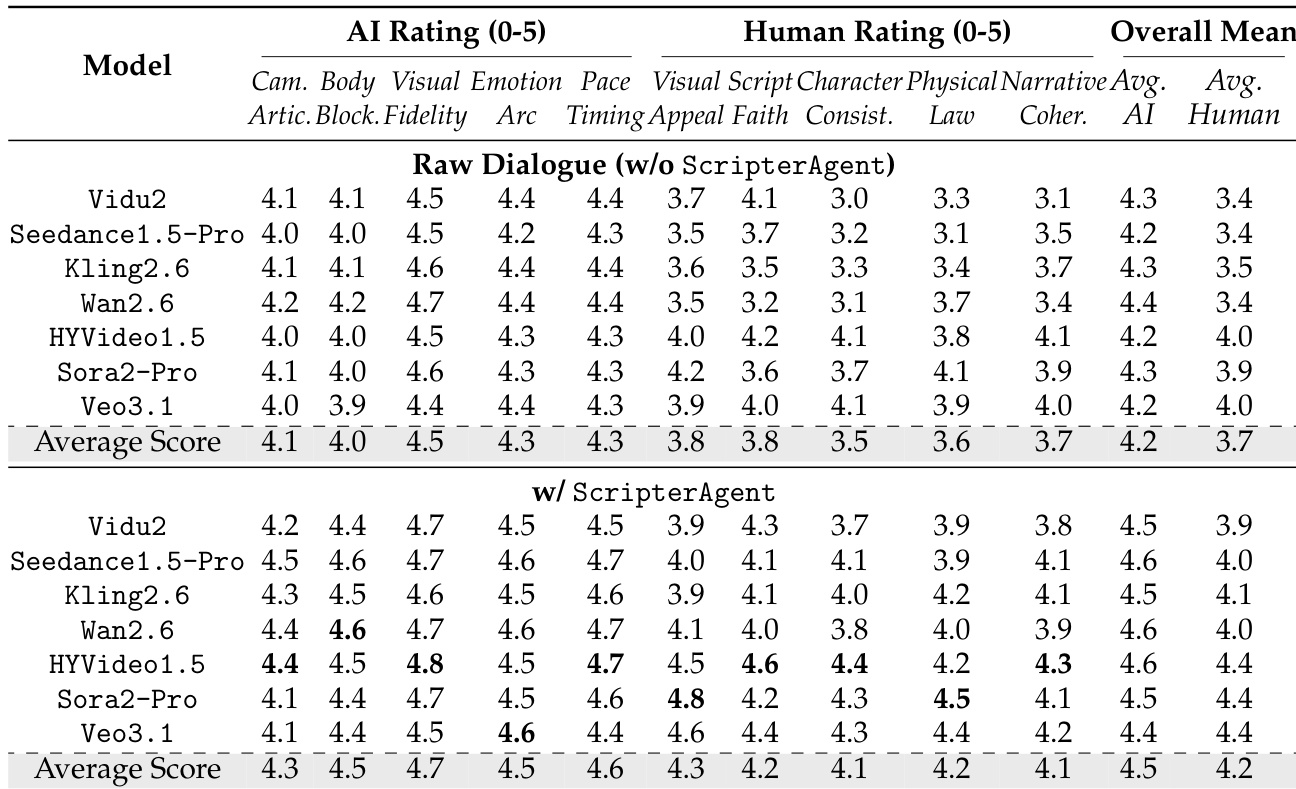
Results show that conditioning video generation models on scripts produced by ScripterAgent significantly improves both alignment fidelity and visual quality. The full pipeline achieves higher scores across all metrics, with notable gains in Visual-Script Alignment (VSA) and subject consistency, demonstrating that structured scripts enhance temporal and semantic alignment with the source dialogue.
The authors use a multi-stage framework to evaluate video generation quality, comparing the impact of structured scripts and segmentation on model performance. Results show that the full agent pipeline consistently outperforms baselines across all models and evaluators, with the highest gains in narrative coherence, visual fidelity, and emotional expression.
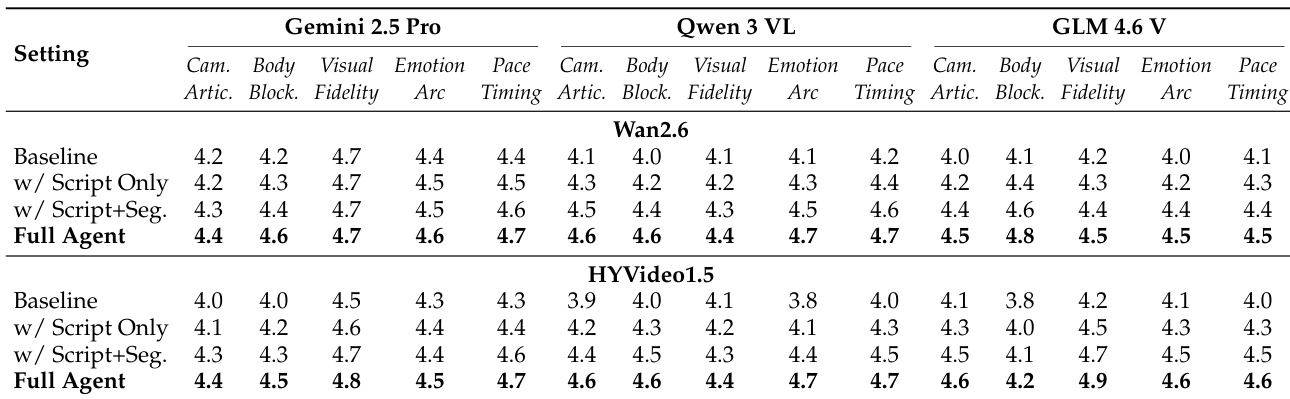
The authors use ScripterAgent to condition video generation models on structured scripts, resulting in significant improvements across all evaluated dimensions. Results show that the average AI rating increases from 4.1 to 4.6, with notable gains in Cinematic Camera Articulation, Kinetic Body Language, and Narrative Pacing, demonstrating that structured scripts enhance both technical execution and narrative coherence in generated videos.
The authors use an evaluation framework to assess script generation methods, comparing ScriptAgent against baselines like CHAE, MoPS, and SEED-Story. Results show that ScriptAgent (Full) outperforms all baselines across both AI and human evaluation metrics, achieving the highest scores in Format Compliance, Content Completeness, Narrative Coherence, Character Consistency, Dramatic Tension, and Visual Imagery.